Abstract
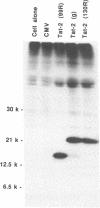
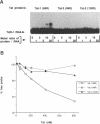
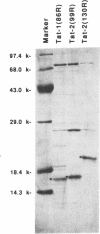
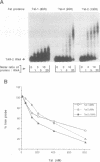
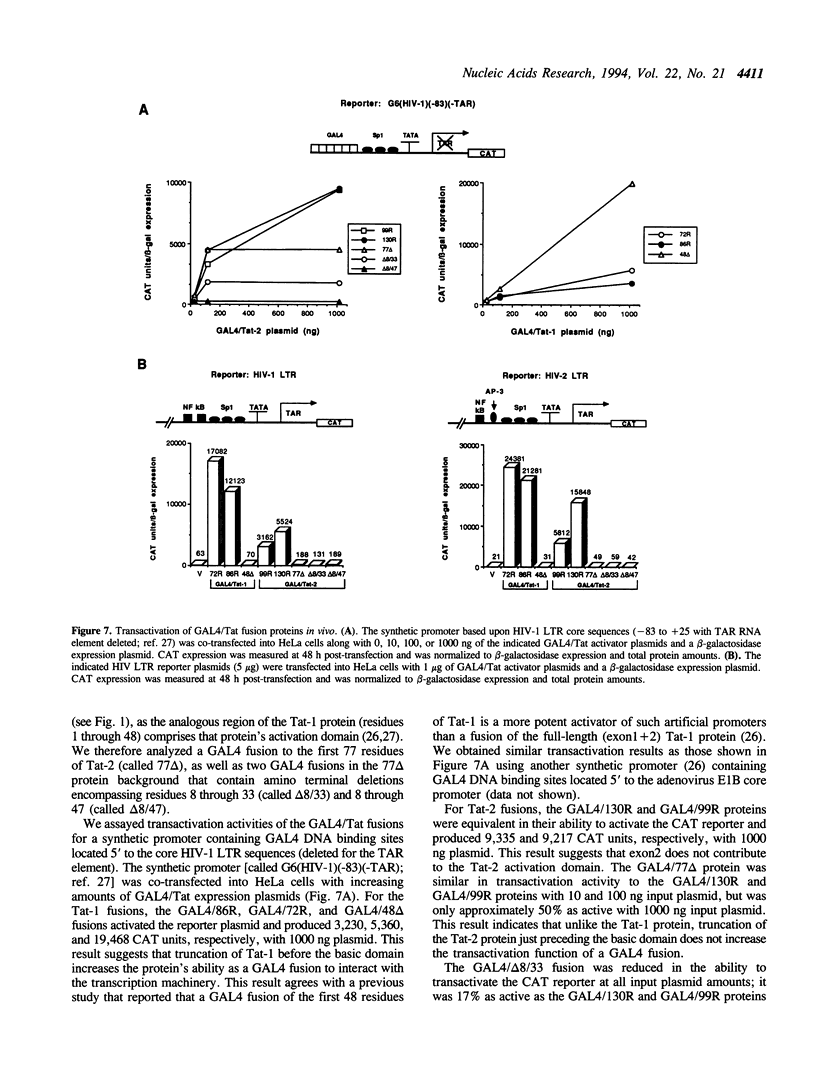
Human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2 (HIV-1 and HIV-2) express related Tat proteins that are encoded in two exons. Tat proteins bind directly to the TAR RNA element contained in the 5' ends of viral transcripts and thereby stimulate transcription through an as yet unidentified mechanism. We have investigated the functional significance of exon2 of the HIV-2 Tat protein by examining properties of proteins consisting of exon1 alone or exon1 + 2. In transactivation assays in vivo, exon2 modestly increased HIV-2 Tat stimulation of transcription from the HIV-2 long terminal repeat (LTR) but had no effect on transcription from the HIV-1 LTR. In HeLa cells, exon2 increased transactivation of the HIV-2 LTR by approximately three-fold, while in COS and Jurkat cells this value was less than two-fold. In binding assays in vitro, exon2 increased the binding affinity of the HIV-2 Tat protein to HIV-2 TAR RNA. Results with GAL4 fusion proteins and a synthetic promoter containing GAL4 DNA binding sites indicated that exon2 does not contribute to the HIV-2 Tat activation domain. These observations suggest that exon2 of HIV-2 Tat contributes to transactivation of the HIV-2 LTR by increasing the binding affinity to HIV-2 TAR RNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arya S. K., Gallo R. C. Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 long terminal repeat: analysis of regulatory elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9753–9757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Gatignol A., Silver J., Jeang K. T. Efficient trans-activation by the HIV-2 Tat protein requires a duplicated TAR RNA structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1839–1846. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnan B. J., Biancalana S., Hudson D., Frankel A. D. Analysis of arginine-rich peptides from the HIV Tat protein reveals unusual features of RNA-protein recognition. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):201–210. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll R., Martarano L., Derse D. Identification of lentivirus tat functional domains through generation of equine infectious anemia virus/human immunodeficiency virus type 1 tat gene chimeras. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3460–3467. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3460-3467.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. N., Jeang K. T. The basic RNA-binding domain of HIV-2 Tat contributes to preferential trans-activation of a TAR2-containing LTR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 25;20(20):5465–5472. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.20.5465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley M. G., LaFemina R. L., Callahan P. L., Condra J. H., Sardana V. V., Graham D. J., Nguyen T. M., LeGrow K., Gotlib L., Schlabach A. J. Sequence-specific interaction of Tat protein and Tat peptides with the transactivation-responsive sequence element of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8985–8989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Does HIV-1 Tat induce a change in viral initiation rights? Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90126-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Trans-activation of human immunodeficiency virus occurs via a bimodal mechanism. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90696-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Ernberg I., Gait M. J., Green S. M., Heaphy S., Karn J., Lowe A. D., Singh M., Skinner M. A. HIV-1 tat protein stimulates transcription by binding to a U-rich bulge in the stem of the TAR RNA structure. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):4145–4153. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07637.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echetebu C. O., Rhim H., Herrmann C. H., Rice A. P. Construction and characterization of a potent HIV-2 Tat transdominant mutant protein. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1994 Jul;7(7):655–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echetebu C. O., Rice A. P. Mutational analysis of the amino and carboxy termini of the HIV-2 Tat protein. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1993 Jun;6(6):550–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elangovan B., Subramanian T., Chinnadurai G. Functional comparison of the basic domains of the Tat proteins of human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2 in trans activation. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2031–2036. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2031-2036.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerman M., Guyader M., Montagnier L., Baltimore D., Muesing M. A. The specificity of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2 transactivator is different from that of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3755–3760. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02710.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg M. B., Baltimore D., Frankel A. D. The role of Tat in the human immunodeficiency virus life cycle indicates a primary effect on transcriptional elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenrick R., Malim M. H., Hauber J., Le S. Y., Maizel J., Cullen B. R. Functional analysis of the Tat trans activator of human immunodeficiency virus type 2. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5006–5012. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5006-5012.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. D., Bredt D. S., Pabo C. O. Tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus forms a metal-linked dimer. Science. 1988 Apr 1;240(4848):70–73. doi: 10.1126/science.2832944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gait M. J., Karn J. RNA recognition by the human immunodeficiency virus Tat and Rev proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Jul;18(7):255–259. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90176-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C. The AIDS virus. Sci Am. 1987 Jan;256(1):46–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. A., Harrich D., Pearson L., Mitsuyasu R., Gaynor R. B. Functional domains required for tat-induced transcriptional activation of the HIV-1 long terminal repeat. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3143–3147. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03181.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauber J., Malim M. H., Cullen B. R. Mutational analysis of the conserved basic domain of human immunodeficiency virus tat protein. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1181–1187. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1181-1187.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann C. H., Rice A. P. Specific interaction of the human immunodeficiency virus Tat proteins with a cellular protein kinase. Virology. 1993 Dec;197(2):601–608. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howcroft T. K., Strebel K., Martin M. A., Singer D. S. Repression of MHC class I gene promoter activity by two-exon Tat of HIV. Science. 1993 May 28;260(5112):1320–1322. doi: 10.1126/science.8493575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeang K. T., Berkhout B., Dropulic B. Effects of integration and replication on transcription of the HIV-1 long terminal repeat. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):24940–24949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A. Tat and the HIV-1 promoter. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;5(3):461–468. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90012-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamine J., Subramanian T., Chinnadurai G. Sp1-dependent activation of a synthetic promoter by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8510–8514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao S. Y., Calman A. F., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Anti-termination of transcription within the long terminal repeat of HIV-1 by tat gene product. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):489–493. doi: 10.1038/330489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong L. I., Lee S. W., Kappes J. C., Parkin J. S., Decker D., Hoxie J. A., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M. West African HIV-2-related human retrovirus with attenuated cytopathicity. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1525–1529. doi: 10.1126/science.3375832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuppuswamy M., Subramanian T., Srinivasan A., Chinnadurai G. Multiple functional domains of Tat, the trans-activator of HIV-1, defined by mutational analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3551–3561. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laspia M. F., Rice A. P., Mathews M. B. HIV-1 Tat protein increases transcriptional initiation and stabilizes elongation. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90290-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor G. R., Caskey C. T. Construction of plasmids that express E. coli beta-galactosidase in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 25;17(6):2365–2365. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.6.2365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madore S. J., Cullen B. R. Genetic analysis of the cofactor requirement for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat function. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):3703–3711. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.3703-3711.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak R. A., Sharp P. A. HIV-1 Tat protein promotes formation of more-processive elongation complexes. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4189–4196. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfützner A., Dietrich U., von Eichel U., von Briesen H., Brede H. D., Maniar J. K., Rübsamen-Waigmann H. HIV-1 and HIV-2 infections in a high-risk population in Bombay, India: evidence for the spread of HIV-2 and presence of a divergent HIV-1 subtype. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1992 Oct;5(10):972–977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport J., Lee S. J., Khalili K., Wong-Staal F. The acidic amino-terminal region of the HIV-1 Tat protein constitutes an essential activating domain. New Biol. 1989 Oct;1(1):101–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhim H., Chan F., Echetebu C. O., Rice A. P. Rapid purification of monomer HIV-2 Tat protein expressed in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif. 1993 Feb;4(1):24–31. doi: 10.1006/prep.1993.1004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhim H., Rice A. P. Functional significance of the dinucleotide bulge in stem-loop1 and stem-loop2 of HIV-2 TAR RNA. Virology. 1994 Jul;202(1):202–211. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhim H., Rice A. P. TAR RNA binding properties and relative transactivation activities of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and 2 Tat proteins. J Virol. 1993 Feb;67(2):1110–1121. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.2.1110-1121.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice A. P., Carlotti F. Mutational analysis of the conserved cysteine-rich region of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat protein. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1864–1868. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1864-1868.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice A. P., Carlotti F. Structural analysis of wild-type and mutant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat proteins. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6018–6026. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6018-6026.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S., Delling U., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A., Sonenberg N. A bulge structure in HIV-1 TAR RNA is required for Tat binding and Tat-mediated trans-activation. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1365–1373. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S., Perkins A., Purcell R., Joung K., Sia R., Burghoff R., Haseltine W. A., Rosen C. A. Structural and functional characterization of human immunodeficiency virus tat protein. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.1-8.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ptashne M. A vector for expressing GAL4(1-147) fusions in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7539–7539. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby M. J., Bain E. S., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Structure, sequence, and position of the stem-loop in tar determine transcriptional elongation by tat through the HIV-1 long terminal repeat. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):547–558. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby M. J., Peterlin B. M. Trans-activation by HIV-1 Tat via a heterologous RNA binding protein. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):769–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90121-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Patarca R., Rosen C., Wong-Staal F., Haseltine W. Location of the trans-activating region on the genome of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III. Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):74–77. doi: 10.1126/science.2990041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southgate C. D., Green M. R. The HIV-1 Tat protein activates transcription from an upstream DNA-binding site: implications for Tat function. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2496–2507. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southgate C., Zapp M. L., Green M. R. Activation of transcription by HIV-1 Tat protein tethered to nascent RNA through another protein. Nature. 1990 Jun 14;345(6276):640–642. doi: 10.1038/345640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiley L. S., Brown P. H., Cullen B. R. Does the human immunodeficiency virus Tat trans-activator contain a discrete activation domain? Virology. 1990 Oct;178(2):560–567. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90354-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong-Starksen S. E., Baur A., Lu X. B., Peck E., Peterlin B. M. Second exon of Tat of HIV-2 is required for optimal trans-activation of HIV-1 and HIV-2 LTRs. Virology. 1993 Aug;195(2):826–830. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaishnav Y. N., Wong-Staal F. The biochemistry of AIDS. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:577–630. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]