Abstract
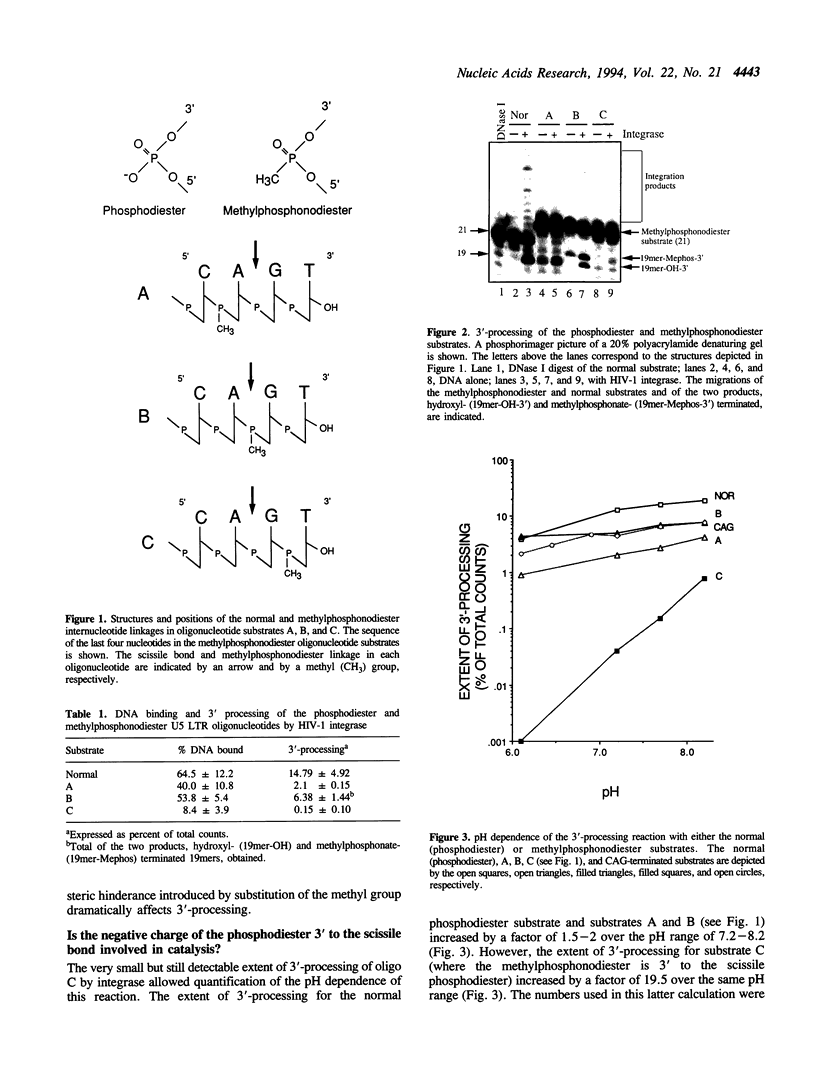
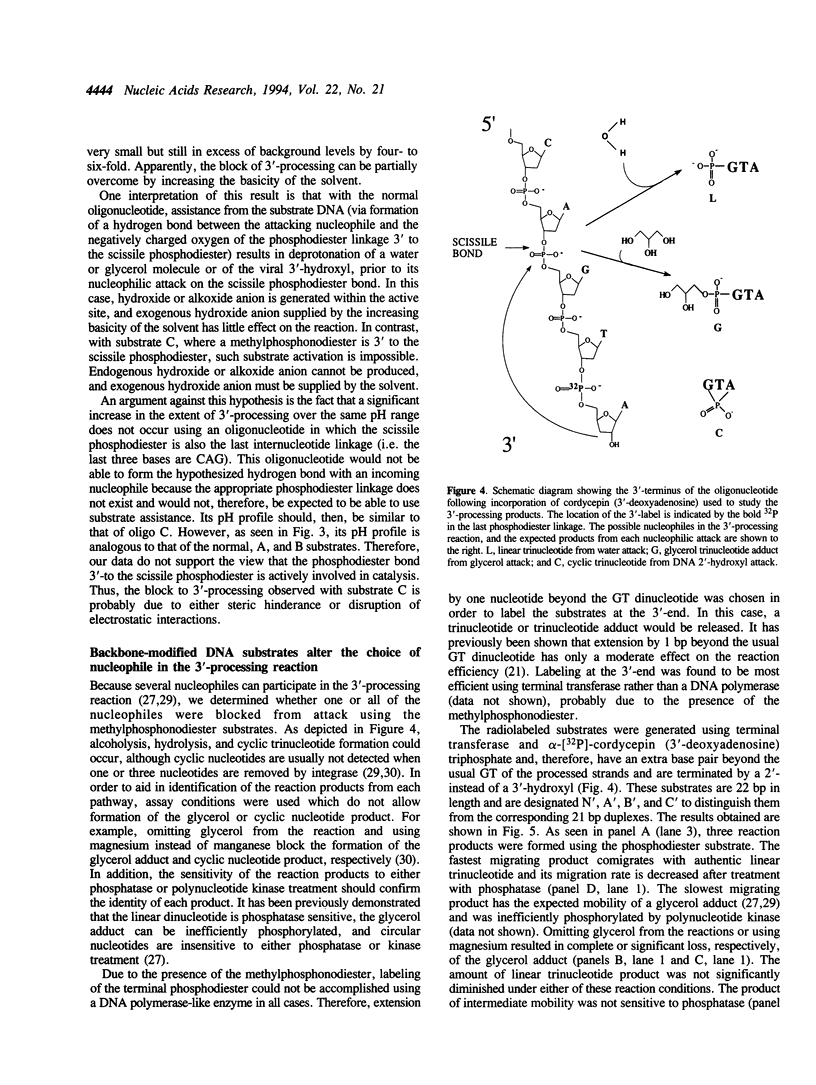
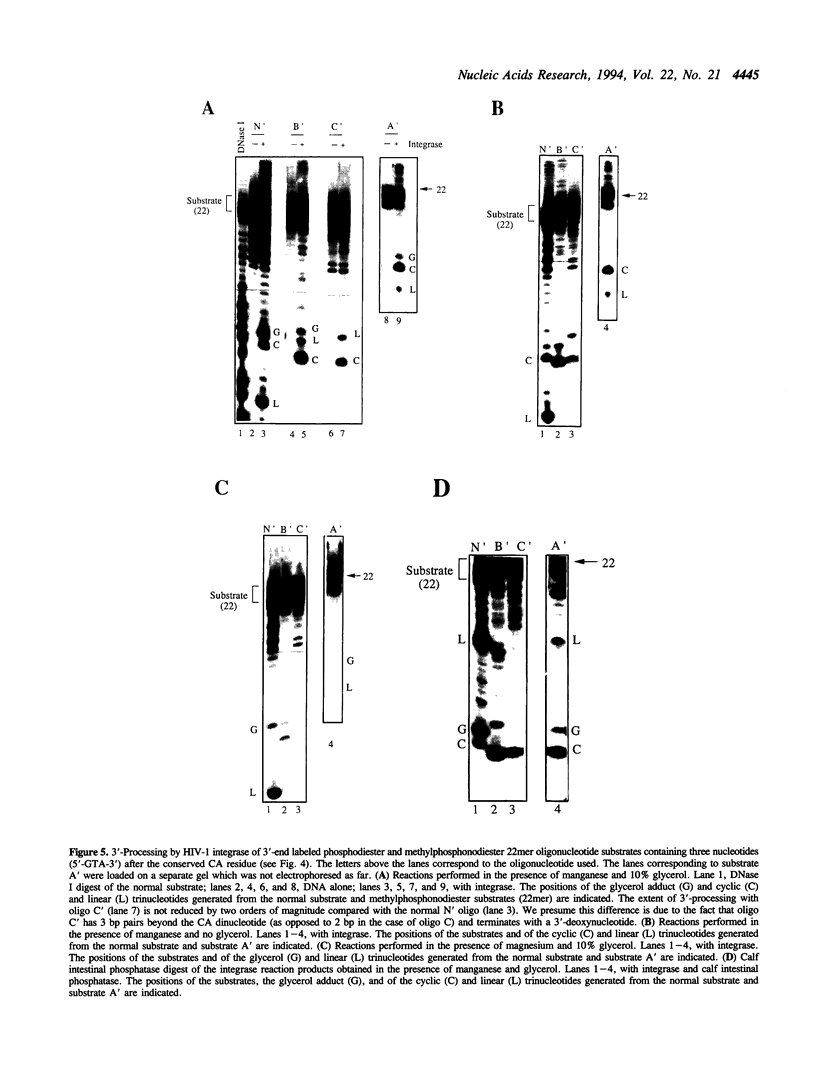
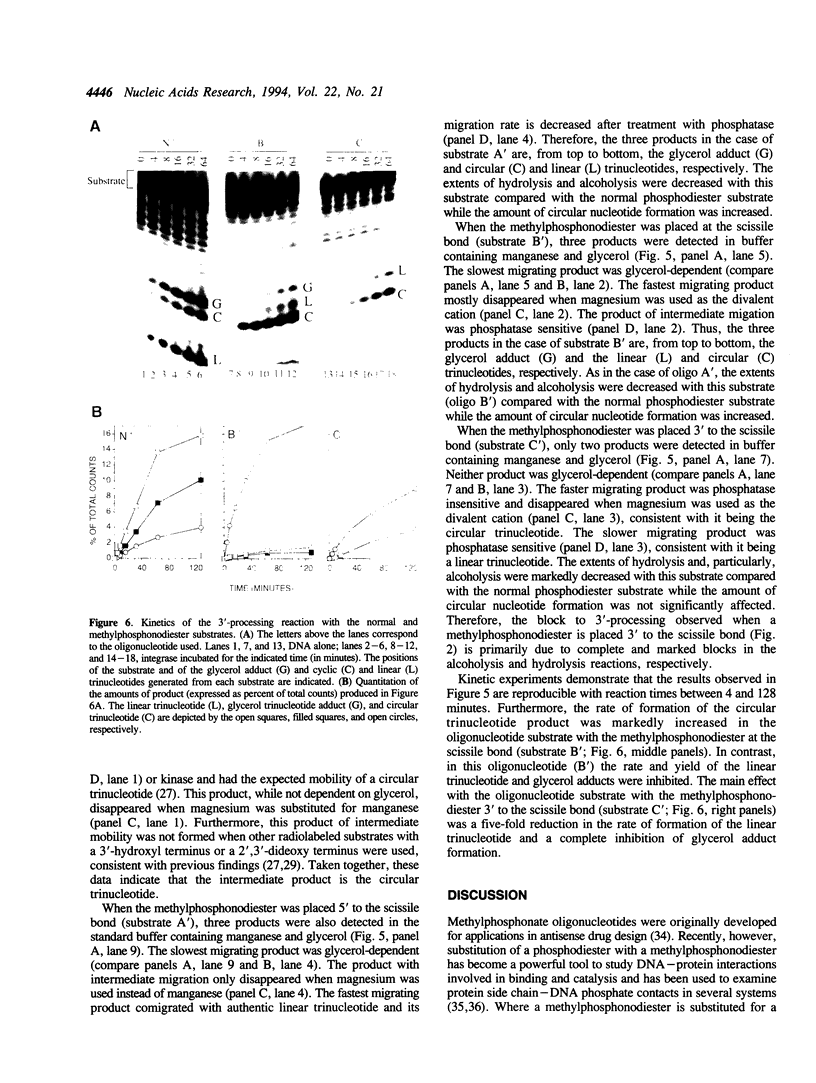
We present evidence suggesting that the 3'-processing activity of HIV-1 integrase is dramatically affected by electrostatic and/or steric perturbations 3' to the conserved CA dinucleotide. When the phosphodiester bond 3' to the scissile phosphodiester is replaced by a methylphosphonodiester linkage, 3'-processing decreases by two orders of magnitude. This block of cleavage can be somewhat overcome by increasing the pH of the reaction. Labeling of the substrates at the 3'-end revealed blockage of water and glycerol, but stimulation of the viral DNA 3'-hydroxyl, acting as the nucleophile with the methylphosphonodiester substrate. Interestingly, a circular trinucleotide was formed using the phosphodiester and methylphosphonodiester substrates when the terminal nucleotide was 3'-deoxyadenosine but not 2'-deoxyadenosine. Mutagenesis of the enzyme active site has previously been shown to alter the choice of nucleophile in the 3'-processing reaction. Taken together, the results in this study suggest that 'mutagenesis' of the DNA backbone can also alter the choice of nucleophile.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Botfield M. C., Weiss M. A. Bipartite DNA recognition by the human Oct-2 POU domain: POUs-specific phosphate contacts are analogous to those of bacteriophage lambda repressor. Biochemistry. 1994 Mar 8;33(9):2349–2355. doi: 10.1021/bi00175a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Bowerman B., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Correct integration of retroviral DNA in vitro. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. D., Craigie R. Activities of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) integration protein in vitro: specific cleavage and integration of HIV DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1339–1343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. D., Craigie R. Integration of human immunodeficiency virus DNA: adduct interference analysis of required DNA sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3458–3462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. D., Fujiwara T., Craigie R. Retroviral DNA integration directed by HIV integration protein in vitro. Science. 1990 Sep 28;249(4976):1555–1558. doi: 10.1126/science.2171144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow S. A., Brown P. O. Substrate features important for recognition and catalysis by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase identified by using novel DNA substrates. J Virol. 1994 Jun;68(6):3896–3907. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.6.3896-3907.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow S. A., Vincent K. A., Ellison V., Brown P. O. Reversal of integration and DNA splicing mediated by integrase of human immunodeficiency virus. Science. 1992 Feb 7;255(5045):723–726. doi: 10.1126/science.1738845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R., Fujiwara T., Bushman F. The IN protein of Moloney murine leukemia virus processes the viral DNA ends and accomplishes their integration in vitro. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):829–837. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90126-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower L. A., Varmus H. E. A mutant murine leukemia virus with a single missense codon in pol is defective in a function affecting integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6461–6465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donzella G. A., Jonsson C. B., Roth M. J. Influence of substrate structure on disintegration activity of Moloney murine leukemia virus integrase. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):7077–7087. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7077-7087.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman A., Mizuuchi K., Craigie R. HIV-1 DNA integration: mechanism of viral DNA cleavage and DNA strand transfer. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1211–1221. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90297-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson D. M., Kollman P. A. Application of free-energy decomposition to determine the relative stability of R and S oligodeoxyribonucleotide methylphosphonates. Antisense Res Dev. 1991 Fall;1(3):243–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Mizuuchi K. Retroviral DNA integration: structure of an integration intermediate. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamy F., Asseline U., Grasby J., Iwai S., Pritchard C., Slim G., Butler P. J., Karn J., Gait M. J. Hydrogen-bonding contacts in the major groove are required for human immunodeficiency virus type-1 tat protein recognition of TAR RNA. J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 5;230(1):111–123. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hippenmeyer P. J., Grandgenett D. P. Requirement of the avian retrovirus pp32 DNA binding protein domain for replication. Virology. 1984 Sep;137(2):358–370. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeltsch A., Alves J., Wolfes H., Maass G., Pingoud A. Substrate-assisted catalysis in the cleavage of DNA by the EcoRI and EcoRV restriction enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8499–8503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R. A., Merkel G., Kulkosky J., Leis J., Skalka A. M. The avian retroviral IN protein is both necessary and sufficient for integrative recombination in vitro. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90290-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R. A., Skalka A. M. The retroviral enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:133–173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.001025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman M., Katz R. A., Skalka A. M., Leis J. The avian retroviral integration protein cleaves the terminal sequences of linear viral DNA at the in vivo sites of integration. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5319–5327. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5319-5327.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman M., Sudol M. In vitro activities of purified visna virus integrase. J Virol. 1994 Jun;68(6):3558–3569. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.6.3558-3569.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulkosky J., Skalka A. M. HIV DNA integration: observations and interferences. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(9):839–851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P. S., Ts'o P. O. A new approach to chemotherapy based on molecular biology and nucleic acid chemistry: Matagen (masking tape for gene expression). Anticancer Drug Des. 1987 Oct;2(2):117–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K. Polynucleotidyl transfer reactions in transpositional DNA recombination. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21273–21276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami A., Blake K. R., Miller P. S. Characterization of sequence-specific oligodeoxyribonucleoside methylphosphonates and their interaction with rabbit globin mRNA. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 16;24(15):4041–4046. doi: 10.1021/bi00336a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller B., Jones K. S., Merkel G. W., Skalka A. M. Rapid solution assays for retroviral integration reactions and their use in kinetic analyses of wild-type and mutant Rous sarcoma virus integrases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11633–11637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panganiban A. T., Temin H. M. The retrovirus pol gene encodes a product required for DNA integration: identification of a retrovirus int locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7885–7889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. J., Schwartzberg P. L., Goff S. P. Structure of the termini of DNA intermediates in the integration of retroviral DNA: dependence on IN function and terminal DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90401-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzberg P., Colicelli J., Goff S. P. Construction and analysis of deletion mutations in the pol gene of Moloney murine leukemia virus: a new viral function required for productive infection. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1043–1052. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90439-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. A., Dickson M. L., Fyfe J. A. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integration protein: DNA sequence requirements for cleaving and joining reactions. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3593–3601. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3593-3601.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. A., Fyfe J. A. Human immunodeficiency virus integration protein expressed in Escherichia coli possesses selective DNA cleaving activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5119–5123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swarnalatha Y., Yathindra N. Stereochemical effects of methylphosphonate in B- and Z-DNA helices: variation in hydrophobicity and effective widths of grooves. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1993 Jun;10(6):1023–1045. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1993.10508694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent K. A., York-Higgins D., Quiroga M., Brown P. O. Host sequences flanking the HIV provirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6045–6047. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink C., Groenink M., Elgersma Y., Fouchier R. A., Tersmette M., Plasterk R. H. Analysis of the junctions between human immunodeficiency virus type 1 proviral DNA and human DNA. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5626–5627. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5626-5627.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink C., Plasterk R. H. The human immunodeficiency virus integrase protein. Trends Genet. 1993 Dec;9(12):433–438. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90107-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink C., Yeheskiely E., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Plasterk R. H. Site-specific hydrolysis and alcoholysis of human immunodeficiency virus DNA termini mediated by the viral integrase protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 25;19(24):6691–6698. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.24.6691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink C., van Gent D. C., Elgersma Y., Plasterk R. H. Human immunodeficiency virus integrase protein requires a subterminal position of its viral DNA recognition sequence for efficient cleavage. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4636–4644. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4636-4644.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink C., van der Linden K. H., Plasterk R. H. Activities of the feline immunodeficiency virus integrase protein produced in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):1468–1474. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.1468-1474.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vora A. C., Fitzgerald M. L., Grandgenett D. P. Removal of 3'-OH-terminal nucleotides from blunt-ended long terminal repeat termini by the avian retrovirus integration protein. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5656–5659. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5656-5659.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gent D. C., Oude Groeneger A. A., Plasterk R. H. Identification of amino acids in HIV-2 integrase involved in site-specific hydrolysis and alcoholysis of viral DNA termini. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 25;21(15):3373–3377. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.15.3373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]