Abstract
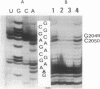
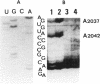
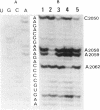
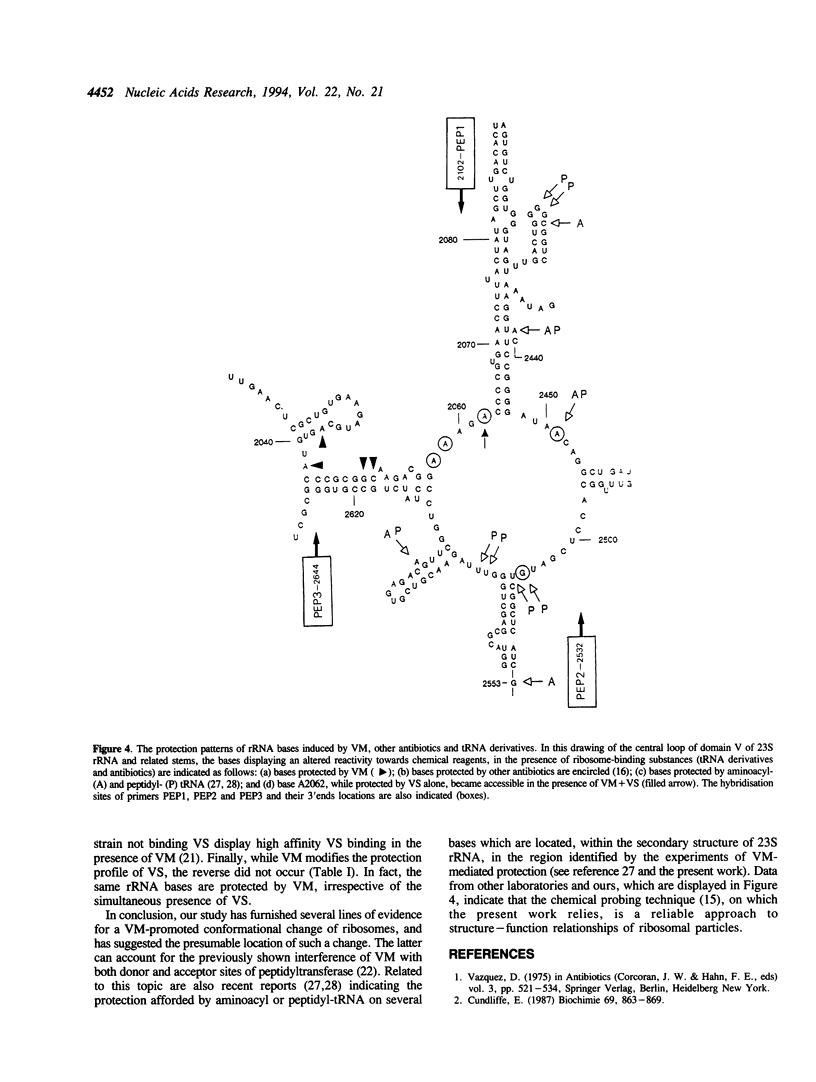
Previous findings suggest the location of the central loop of domain V of 23S rRNA within the peptidyltransferase domain of ribosomes. This enzymatic activity is inhibited by some antibiotics, including type A (virginiamycin M or VM) and type B (virginiamycin S or VS) synergimycins, antibiotics endowed with a synergistic action in vivo. In the present work, the ability of VM and VS to modify the accessibility of 23S rRNA bases within ribosomes to chemical reagents has been explored. VM afforded a protection of rRNA bases A2037, A2042, G2049 and C2050. Moreover, when ribosomes were incubated with the two virginiamycin components, the base A2062, which was protected by VS alone, became accessible to dimethyl sulphate (DMS). Modified reactivity to chemical reagents of different rRNA bases located either in the central loop of domain V or in its proximity furnishes experimental evidence for conformational ribosome alterations induced by VM binding.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arévalo M. A., Tejedor F., Polo F., Ballesta J. P. Protein components of the erythromycin binding site in bacterial ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):58–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinali G., Moureau P., Cocito C. G. The action of virginiamycin M on the acceptor, donor, and catalytic sites of peptidyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9563–9568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinali G., Nyssen E., Di Giambattista M., Cocito C. Inhibition of polypeptide synthesis in cell-free systems by virginiamycin S and erythromycin. Evidence for a common mode of action of type B synergimycins and 14-membered macrolides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jan 25;949(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90056-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C. Antibiotics of the virginiamycin family, inhibitors which contain synergistic components. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Jun;43(2):145–192. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.2.145-192.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras A., Vázquez D. Synergistic interaction of the streptogramins with the ribosome. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Apr 15;74(3):549–551. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11423.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cundliffe E. On the nature of antibiotic binding sites in ribosomes. Biochimie. 1987 Aug;69(8):863–869. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Giambattista M., Chinali G., Cocito C. The molecular basis of the inhibitory activities of type A and type B synergimycins and related antibiotics on ribosomes. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Oct;24(4):485–507. doi: 10.1093/jac/24.4.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Giambattista M., Engelborghs Y., Nyssen E., Cocito C. Kinetics of binding of macrolides, lincosamides, and synergimycins to ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8591–8597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Giambattista M., Ide G., Engelborghs Y., Cocito C. Analysis of fluorescence quenching of ribosome-bound virginiamycin S. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6334–6339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Giambattista M., Nyssen E., Pecher A., Cocito C. Affinity labeling of the virginiamycin S binding site on bacterial ribosome. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 2;29(39):9203–9211. doi: 10.1021/bi00491a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douthwaite S., Prince J. B., Noller H. F. Evidence for functional interaction between domains II and V of 23S ribosomal RNA from an erythromycin-resistant mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8330–8334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Chloramphenicol, erythromycin, carbomycin and vernamycin B protect overlapping sites in the peptidyl transferase region of 23S ribosomal RNA. Biochimie. 1987 Aug;69(8):879–884. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Interaction of tRNA with 23S rRNA in the ribosomal A, P, and E sites. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):585–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90128-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Sites of interaction of the CCA end of peptidyl-tRNA with 23S rRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3725–3728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moureau P., Engelborghs Y., Di Giambattista M., Cocito C. Fluorescence stopped flow analysis of the interaction of virginiamycin components and erythromycin with bacterial ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14233–14238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. Ribosomal RNA and translation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:191–227. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.001203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyssen E., Di Giambattista M., Cocito C. Analysis of the reversible binding of virginiamycin M to ribosome and particle functions after removal of the antibiotic. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Sep 21;1009(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parfait R., de Béthune M. P., Cocito C. A spectrofluorimetric study of the interaction between virginiamycin S and bacterial ribosomes. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Oct 25;166(1):45–51. doi: 10.1007/BF00379728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze H., Nierhaus K. H. Minimal set of ribosomal components for reconstitution of the peptidyltransferase activity. EMBO J. 1982;1(5):609–613. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01216.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigmund C. D., Ettayebi M., Borden A., Morgan E. A. Antibiotic resistance mutations in ribosomal RNA genes of Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1988;164:673–690. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)64077-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Moazed D., Noller H. F. Structural analysis of RNA using chemical and enzymatic probing monitored by primer extension. Methods Enzymol. 1988;164:481–489. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)64064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannuffel P., Di Giambattista M., Cocito C. The role of rRNA bases in the interaction of peptidyltransferase inhibitors with bacterial ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16114–16120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannuffel P., Di Giambattista M., Morgan E. A., Cocito C. Identification of a single base change in ribosomal RNA leading to erythromycin resistance. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8377–8382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walleczek J., Schüler D., Stöffler-Meilicke M., Brimacombe R., Stöffler G. A model for the spatial arrangement of the proteins in the large subunit of the Escherichia coli ribosome. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3571–3576. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03234.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]