Abstract
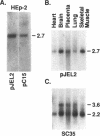
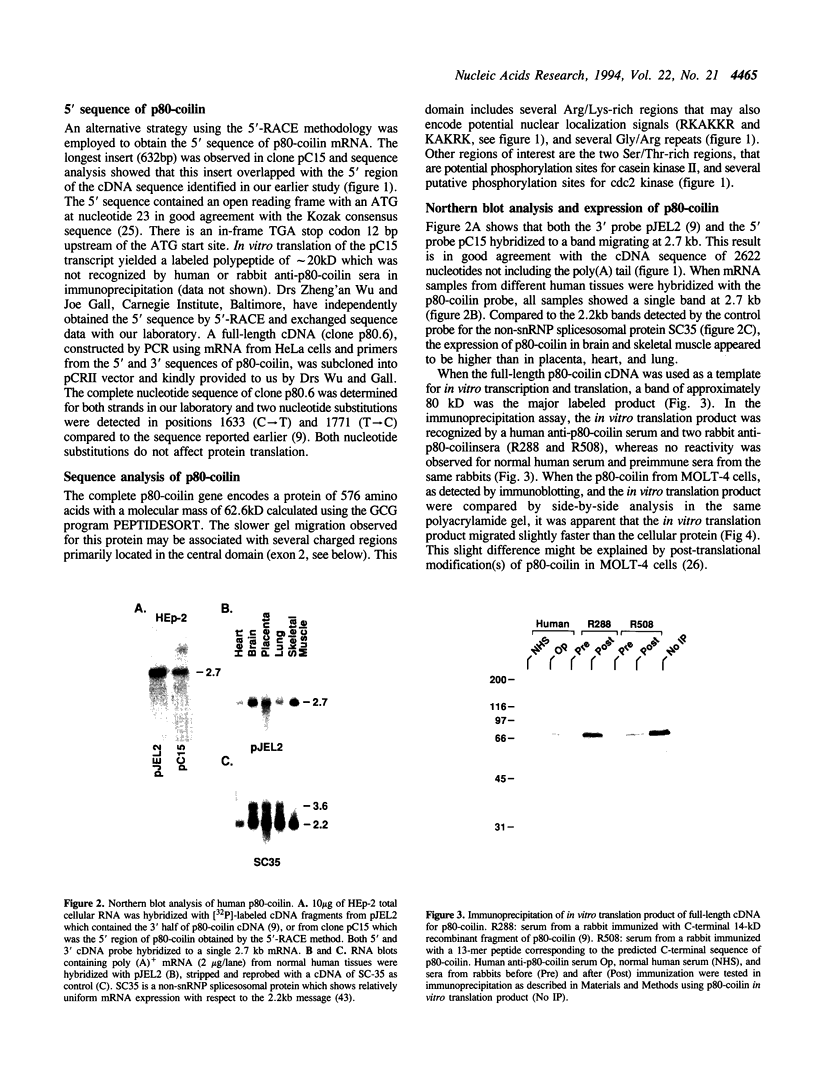
Coiled bodies (CBs) are non-capsular nuclear bodies with a diameter of 0.3-1 micron and appear to be composed of coiled fibrils. Human autoantibodies to CBs recognize an 80-kD nuclear protein highly enriched in CBs, and this protein has been named p80-coilin. CBs are known to assemble and disassemble during the cell cycle, with the highest number of CBs occurring at mid to late G1 where p80-coilin is assembled into several small nuclear body-like structures. In S and G2 phases, CBs become larger and their number decreases and often they are undetectable during mitosis. Using a human autoantibody as a probe for expression cloning, we initially isolated a partial cDNA encoding p80-coilin. In this report, the 5' end of the complete cDNA for p80-coilin was obtained using the 5'-RACE (rapid amplification of cDNA ends) methodology. The size of the reconstructed full-length cDNA corresponds to the 2.7-kb mRNA detected in Northern blot analysis. The complete p80-coilin protein consists of 576 amino acids with a predicted molecular mass of 62,608. A putative p80-coilin pseudogene was also detected during the rescreening of p80-coilin cDNA. To confirm the validity of the cDNA sequence, three overlapping genomic DNA clones representing the human p80-coilin gene were selected for further analysis. The complete gene for p80-coilin contains 7 exons spanning approximately 25kb. Sequence analysis of exons 1 and 2 in genomic DNA clones confirmed the accuracy of the 5' cDNA sequence derived from the 5'-RACE procedure. Furthermore, the human p80-coilin gene was localized to chromosome 17q22-23 by fluorescence in situ hybridization.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrade L. E., Chan E. K., Raska I., Peebles C. L., Roos G., Tan E. M. Human autoantibody to a novel protein of the nuclear coiled body: immunological characterization and cDNA cloning of p80-coilin. J Exp Med. 1991 Jun 1;173(6):1407–1419. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.6.1407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade L. E., Tan E. M., Chan E. K. Immunocytochemical analysis of the coiled body in the cell cycle and during cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1947–1951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascoli C. A., Maul G. G. Identification of a novel nuclear domain. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(5):785–795. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.5.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard S. G., Ward D. C. Fluorescence in situ hybridization using digital imaging microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1993 Dec;41(12):1755–1759. doi: 10.1177/41.12.8245423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasch K., Ochs R. L. Nuclear bodies (NBs): a newly "rediscovered" organelle. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Oct;202(2):211–223. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90068-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmo-Fonseca M., Ferreira J., Lamond A. I. Assembly of snRNP-containing coiled bodies is regulated in interphase and mitosis--evidence that the coiled body is a kinetic nuclear structure. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(4):841–852. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.4.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter K. C., Taneja K. L., Lawrence J. B. Discrete nuclear domains of poly(A) RNA and their relationship to the functional organization of the nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(5):1191–1202. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.5.1191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan E. K., Hamel J. C., Buyon J. P., Tan E. M. Molecular definition and sequence motifs of the 52-kD component of human SS-A/Ro autoantigen. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):68–76. doi: 10.1172/JCI115003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyck J. A., Maul G. G., Miller W. H., Jr, Chen J. D., Kakizuka A., Evans R. M. A novel macromolecular structure is a target of the promyelocyte-retinoic acid receptor oncoprotein. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):333–343. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90340-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliceiri G. L., Ryerse J. S. Detection of intranuclear clusters of Sm antigens with monoclonal anti-Sm antibodies by immunoelectron microscopy. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Nov;121(2):449–451. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041210226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakan S., Leser G., Martin T. E. Ultrastructural distribution of nuclear ribonucleoproteins as visualized by immunocytochemistry on thin sections. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):358–363. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Maniatis T. Isolation of a complementary DNA that encodes the mammalian splicing factor SC35. Science. 1992 Apr 24;256(5056):535–538. doi: 10.1126/science.1373910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G. Spliceosomes and snurposomes. Science. 1991 Jun 14;252(5012):1499–1500. doi: 10.1126/science.1828621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardin J. H., Spicer S. S., Greene W. B. The paranucleolar structure, accessory body of Cajal, sex chromatin, and related structures in nuclei of rat trigeminal neurons: a cytochemical and ultrastructural study. Anat Rec. 1969 Aug;164(4):403–431. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091640403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S., Spector D. L. U1 and U2 small nuclear RNAs are present in nuclear speckles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):305–308. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafarga M., Andres M. A., Berciano M. T., Maquiera E. Organization of nucleoli and nuclear bodies in osmotically stimulated supraoptic neurons of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1991 Jun 15;308(3):329–339. doi: 10.1002/cne.903080302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafarga M., Hervás J. P., Santa-Cruz M. C., Villegas J., Crespo D. The "accessory body" of Cajal in the neuronal nucleus. A light and electron microscopic approach. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1983;166(1):19–30. doi: 10.1007/BF00317942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamond A. I., Carmo-Fonseca M. The coiled body. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;3(6):198–204. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90214-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Tang C. J., Call K., Hermanson G., Evans G. A., Housman D., Ward D. C. High-resolution mapping of human chromosome 11 by in situ hybridization with cosmid clones. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):64–69. doi: 10.1126/science.2294592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Zinnecker M., Hamaoka T., Katz D. H. New procedures for preparation and isolation of conjugates of proteins and a synthetic copolymer of D-amino acids and immunochemical characterization of such conjugates. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):690–693. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malatesta M., Zancanaro C., Martin T. E., Chan E. K., Amalric F., Lührmann R., Vogel P., Fakan S. Is the coiled body involved in nucleolar functions? Exp Cell Res. 1994 Apr;211(2):415–419. doi: 10.1006/excr.1994.1106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matera A. G., Ward D. C. Nucleoplasmic organization of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins in cultured human cells. J Cell Biol. 1993 May;121(4):715–727. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.4.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monneron A., Bernhard W. Fine structural organization of the interphase nucleus in some mammalian cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 May;27(3):266–288. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)80017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs R. L., Stein T. W., Jr, Tan E. M. Coiled bodies in the nucleolus of breast cancer cells. J Cell Sci. 1994 Feb;107(Pt 2):385–399. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.2.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raska I., Andrade L. E., Ochs R. L., Chan E. K., Chang C. M., Roos G., Tan E. M. Immunological and ultrastructural studies of the nuclear coiled body with autoimmune antibodies. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Jul;195(1):27–37. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90496-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raska I., Ochs R. L., Andrade L. E., Chan E. K., Burlingame R., Peebles C., Gruol D., Tan E. M. Association between the nucleolus and the coiled body. J Struct Biol. 1990 Jul-Sep;104(1-3):120–127. doi: 10.1016/1047-8477(90)90066-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders W. S., Cooke C. A., Earnshaw W. C. Compartmentalization within the nucleus: discovery of a novel subnuclear region. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(4):919–931. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L., Lark G., Huang S. Differences in snRNP localization between transformed and nontransformed cells. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 May;3(5):555–569. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.5.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L. Macromolecular domains within the cell nucleus. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:265–315. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuma R. S., Stolk J. A., Roth M. B. Identification and characterization of a sphere organelle protein. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(4):767–773. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.4.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vagner-Capodano A. M., Mauchamp J., Stahl A., Lissitzky S. Nucleolar budding and formation of nuclear bodies in cultured thyroid cells stimulated by thyrotropin, dibutyryl cyclic AMP, and prostaglandin E2. J Ultrastruct Res. 1980 Jan;70(1):37–51. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(80)90020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varesco L., Caligo M. A., Simi P., Black D. M., Nardini V., Casarino L., Rocchi M., Ferrara G., Solomon E., Bevilacqua G. The NM23 gene maps to human chromosome band 17q22 and shows a restriction fragment length polymorphism with BglII. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1992 Jan;4(1):84–88. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870040113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis K., Rambaud S., Lavau C., Jansen J., Carvalho T., Carmo-Fonseca M., Lamond A., Dejean A. Retinoic acid regulates aberrant nuclear localization of PML-RAR alpha in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):345–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. H., Gall J. G. U7 small nuclear RNA in C snurposomes of the Xenopus germinal vesicle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6257–6259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Z. A., Murphy C., Callan H. G., Gall J. G. Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins in the amphibian germinal vesicle: loops, spheres, and snurposomes. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(3):465–483. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.3.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano T., Sander C. A., Andrade R. E., Gauwerky C. E., Croce C. M., Longo D. L., Jaffe E. S., Raffeld M. Molecular analysis of the BCL-3 locus at chromosome 17q22 in B-cell neoplasms. Blood. 1993 Sep 15;82(6):1813–1819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]