Abstract
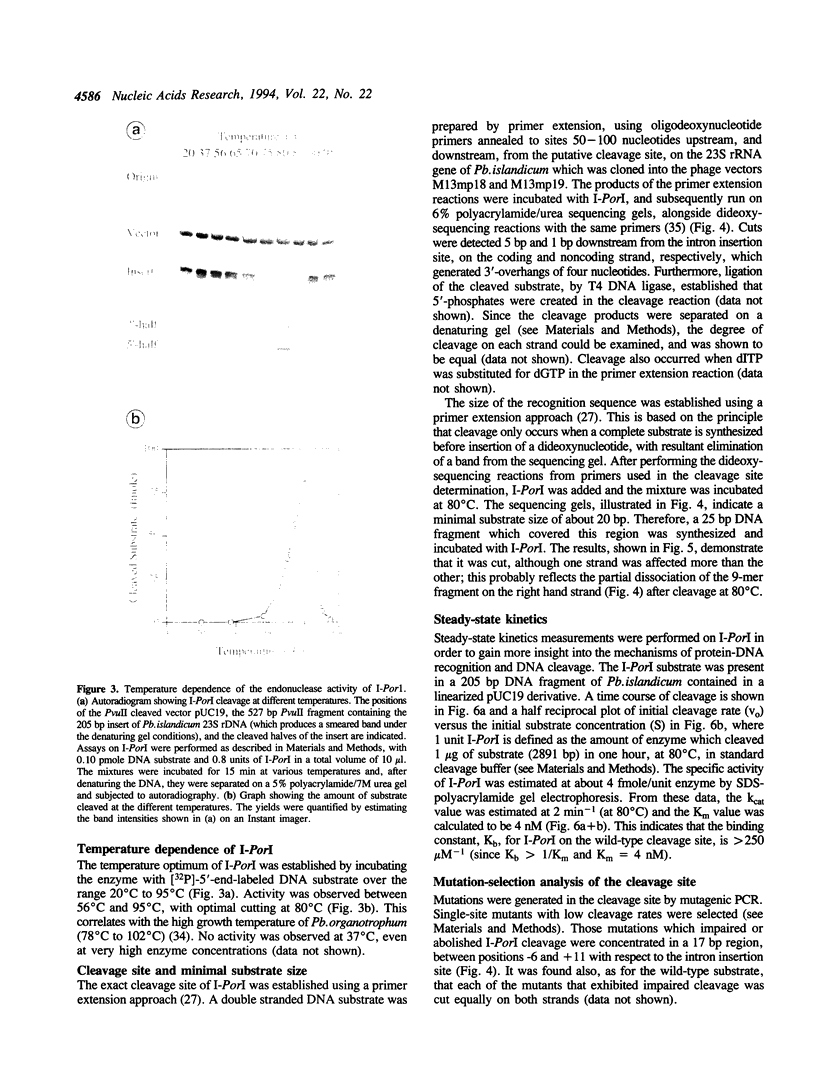
The protein encoded by intron 1 of the single 23S rRNA gene of the archaeal hyperthermophile Pyrobaculum organotrophum was isolated and shown to constitute a homing-type DNA endonuclease, I-PorI. It cleaves the intron- 23S rDNA of the closely related organism Pyrobaculum islandicum near the site of intron insertion in Pb.organotrophum. In contrast, no endonuclease activity was detected for the protein product of intron 2 of the same gene of Pb.organotrophum which, like I-PorI, carries the LAGLI-DADG motif, common to group I intron-encoded homing enzymes. I-PorI cleaves optimally at 80 degrees C, with kcat and Km values of about 2 min-1 and 4 nM, respectively, and generates four nucleotide 3'-overhangs and 5'-phosphates. It can cleave a 25 base pair DNA fragment encompassing the intron insertion site. A mutation-selection study established the base pair specificity of the endonuclease within a 17 bp region, from positions -6 to +11 with respect to the intron-insertion site. Four of the essential base pairs encode the sequence involved in the intron-exon interaction in the pre-rRNA that is required for recognition by the RNA splicing enzymes. Properties of the enzyme are compared and contrasted with those of eucaryotic homing endonucleases.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anziano P. Q., Hanson D. K., Mahler H. R., Perlman P. S. Functional domains in introns: trans-acting and cis-acting regions of intron 4 of the cob gene. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):925–932. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90297-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell-Pedersen D., Quirk S., Clyman J., Belfort M. Intron mobility in phage T4 is dependent upon a distinctive class of endonucleases and independent of DNA sequences encoding the intron core: mechanistic and evolutionary implications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3763–3770. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burggraf S., Larsen N., Woese C. R., Stetter K. O. An intron within the 16S ribosomal RNA gene of the archaeon Pyrobaculum aerophilum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2547–2550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadwell R. C., Joyce G. F. Randomization of genes by PCR mutagenesis. PCR Methods Appl. 1992 Aug;2(1):28–33. doi: 10.1101/gr.2.1.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu F. K., Maley G., Pedersen-Lane J., Wang A. M., Maley F. Characterization of the restriction site of a prokaryotic intron-encoded endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3574–3578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colleaux L., D'Auriol L., Galibert F., Dujon B. Recognition and cleavage site of the intron-encoded omega transposase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6022–6026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgaard J. Z., Garrett R. A., Belfort M. A site-specific endonuclease encoded by a typical archaeal intron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5414–5417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgaard J. Z., Garrett R. A. Protein-coding introns from the 23S rRNA-encoding gene form stable circles in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrobaculum organotrophum. Gene. 1992 Nov 2;121(1):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90167-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis E. O., Jenner P. J., Brooks P. C., Colston M. J., Sedgwick S. G. Protein splicing in the maturation of M. tuberculosis recA protein: a mechanism for tolerating a novel class of intervening sequence. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):201–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90349-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De La Salle H., Jacq C., Slonimski P. P. Critical sequences within mitochondrial introns: pleiotropic mRNA maturase and cis-dominant signals of the box intron controlling reductase and oxidase. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dujon B., Belfort M., Butow R. A., Jacq C., Lemieux C., Perlman P. S., Vogt V. M. Mobile introns: definition of terms and recommended nomenclature. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90035-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dujon B. Group I introns as mobile genetic elements: facts and mechanistic speculations--a review. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):91–114. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90034-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddy S. R., Gold L. The phage T4 nrdB intron: a deletion mutant of a version found in the wild. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):1032–1041. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.1032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimble F. S., Thorner J. Homing of a DNA endonuclease gene by meiotic gene conversion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 1992 May 28;357(6376):301–306. doi: 10.1038/357301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensgens L. A., Bonen L., de Haan M., van der Horst G., Grivell L. A. Two intron sequences in yeast mitochondrial COX1 gene: homology among URF-containing introns and strain-dependent variation in flanking exons. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):379–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90457-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane P. M., Yamashiro C. T., Wolczyk D. F., Neff N., Goebl M., Stevens T. H. Protein splicing converts the yeast TFP1 gene product to the 69-kD subunit of the vacuolar H(+)-adenosine triphosphatase. Science. 1990 Nov 2;250(4981):651–657. doi: 10.1126/science.2146742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjems J., Garrett R. A. Novel splicing mechanism for the ribosomal RNA intron in the archaebacterium Desulfurococcus mobilis. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):693–703. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjems J., Garrett R. A. Ribosomal RNA introns in archaea and evidence for RNA conformational changes associated with splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):439–443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjems J., Jensen J., Olesen T., Garrett R. A. Comparison of transfer RNA and ribosomal RNA intron splicing in the extreme thermophile and archaebacterium Desulfurococcus mobilis. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Jan;35(1):210–214. doi: 10.1139/m89-033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambowitz A. M., Belfort M. Introns as mobile genetic elements. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:587–622. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.003103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazowska J., Jacq C., Slonimski P. P. Sequence of introns and flanking exons in wild-type and box3 mutants of cytochrome b reveals an interlaced splicing protein coded by an intron. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90344-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffers H., Egebjerg J., Andersen A., Christensen T., Garrett R. A. Domain VI of Escherichia coli 23 S ribosomal RNA. Structure, assembly and function. J Mol Biol. 1988 Dec 5;204(3):507–522. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90351-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall P., Lemieux C. The I-CeuI endonuclease recognizes a sequence of 19 base pairs and preferentially cleaves the coding strand of the Chlamydomonas moewusii chloroplast large subunit rRNA gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 11;20(23):6401–6407. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.23.6401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perler F. B., Comb D. G., Jack W. E., Moran L. S., Qiang B., Kucera R. B., Benner J., Slatko B. E., Nwankwo D. O., Hempstead S. K. Intervening sequences in an Archaea DNA polymerase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5577–5581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin A., Buckle M., Dujon B. Asymmetrical recognition and activity of the I-SceI endonuclease on its site and on intron-exon junctions. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2939–2947. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05956.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargueil B., Hatat D., Delahodde A., Jacq C. In vivo and in vitro analyses of an intron-encoded DNA endonuclease from yeast mitochondria. Recognition site by site-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5659–5665. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. D., Daniels C. J. A tRNA(Trp) intron endonuclease from Halobacterium volcanii. Unique substrate recognition properties. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):17951–17959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. D., Daniels C. J. Recognition of exon-intron boundaries by the Halobacterium volcanii tRNA intron endonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18104–18111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzlau J. M., Saldanha R. J., Butow R. A., Perlman P. S. A latent intron-encoded maturase is also an endonuclease needed for intron mobility. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):421–430. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90245-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernette C., Saldanha R., Smith D., Ming D., Perlman P. S., Butow R. A. Complex recognition site for the group I intron-encoded endonuclease I-SceII. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):716–723. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]