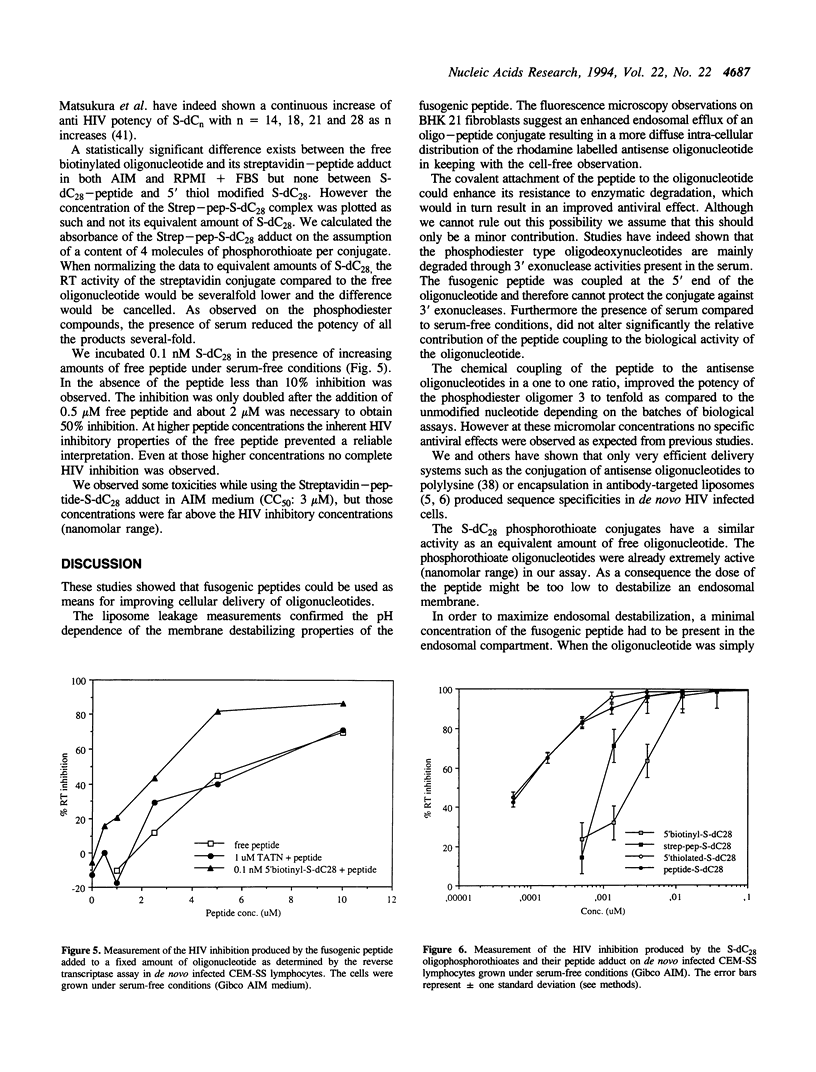
Abstract
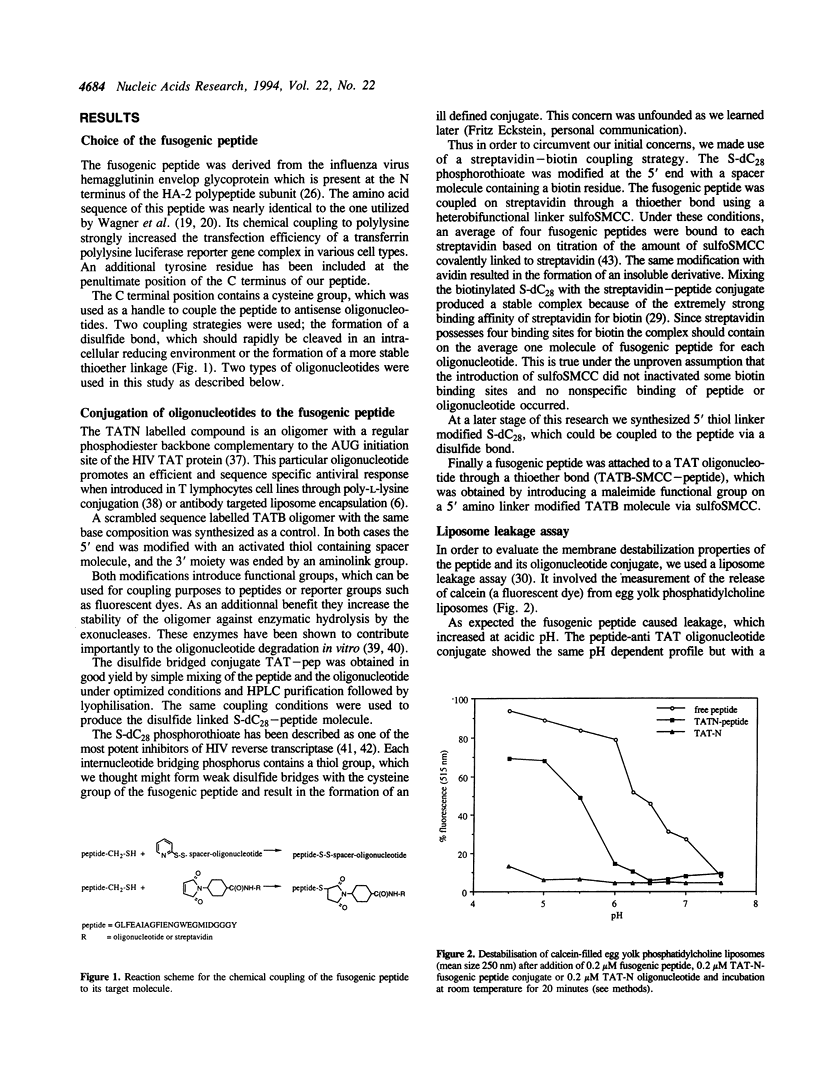
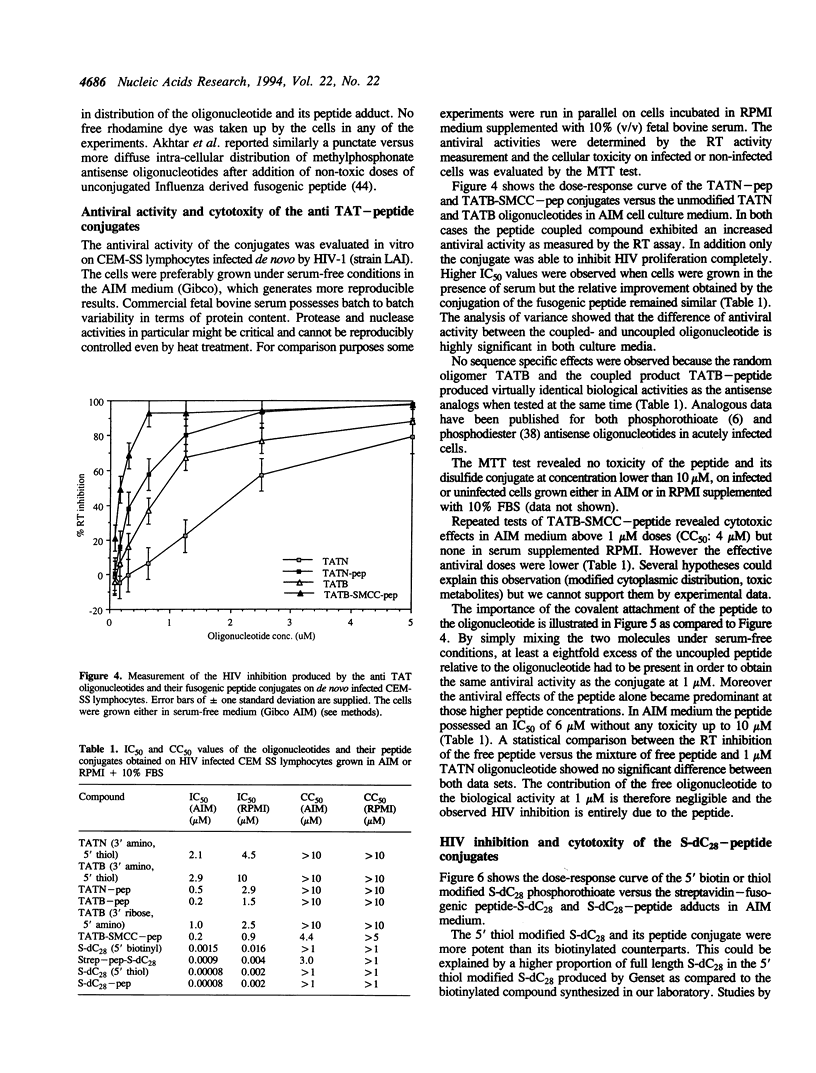
Recently several groups reported a dramatic improvement of reporter gene transfection efficiency using a fusogenic peptide, derived from the Influenza hemagglutinin envelop protein. This peptide changes conformation at acidic pH and destabilizes the endosomal membranes thus resulting in an increased cytoplasmic gene delivery. We describe the use of a similar fusogenic peptide in order to improve the antiviral potency of antisense oligodeoxynucleotides (anti TAT) and oligophosphorothioates (S-dC28) on de novo HIV infected CEM-SS lymphocytes in serum-free medium. We observed as 5 to 10 fold improvement of the anti HIV activities of the phosphodiester antisense oligonucleotides after chemical coupling to the peptide in a one to one ratio by a disulfide or thioether bond. No toxicities were observed at the effective doses (0.1-1 microM). No sequence specificity was obtained and the fusogenic peptide possessed some antiviral activities on its own (IC50: 6 microM). A S-dC28-peptide disulfide linked conjugate and a streptavidin-peptide-biotinylated S-dC28 adduct showed similar activities as the free S-dC28 oligonucleotide (IC50: 0.1-1 nM). As expected, all the compounds were less potent in the presence of serum but the relative contribution of peptide coupling was maintained.
Full text
PDF


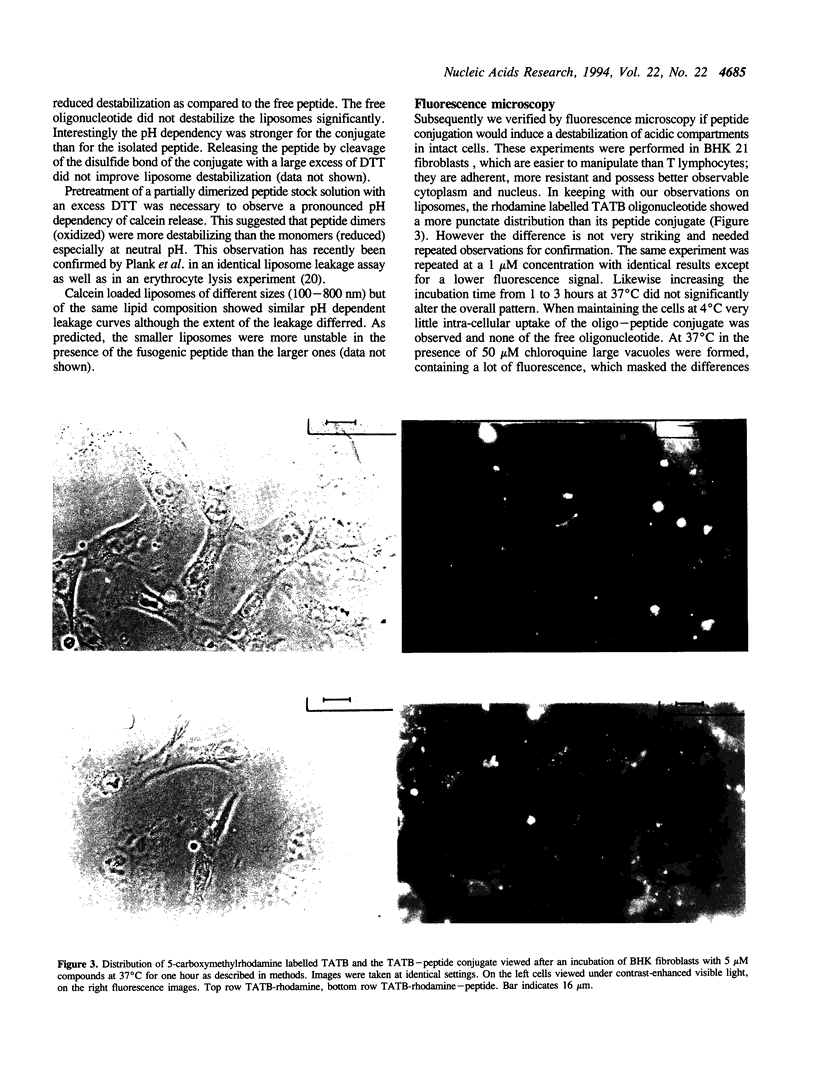

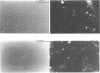
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akhtar S., Basu S., Wickstrom E., Juliano R. L. Interactions of antisense DNA oligonucleotide analogs with phospholipid membranes (liposomes). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5551–5559. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondeson J., Wijkander J., Sundler R. Proton-induced membrane fusion. Role of phospholipid composition and protein-mediated intermembrane contact. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Oct 17;777(1):21–27. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90492-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boutorine A. S., Kostina E. V. Reversible covalent attachment of cholesterol to oligodeoxyribonucleotides for studies of the mechanisms of their penetration into eucaryotic cells. Biochimie. 1993;75(1-2):35–41. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(93)90022-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullough P. A., Hughson F. M., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of influenza haemagglutinin at the pH of membrane fusion. Nature. 1994 Sep 1;371(6492):37–43. doi: 10.1038/371037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capaccioli S., Di Pasquale G., Mini E., Mazzei T., Quattrone A. Cationic lipids improve antisense oligonucleotide uptake and prevent degradation in cultured cells and in human serum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Dec 15;197(2):818–825. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarenc J. P., Degols G., Leonetti J. P., Milhaud P., Lebleu B. Delivery of antisense oligonucleotides by poly(L-lysine) conjugation and liposome encapsulation. Anticancer Drug Des. 1993 Feb;8(1):81–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compagnon B., Milhaud P., Bienvenüe A., Philippot J. R. Targeting of poly(rI)-poly(rC) by fusogenic (F protein) immunoliposomes. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Jun;200(2):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90180-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotten M., Wagner E., Zatloukal K., Phillips S., Curiel D. T., Birnstiel M. L. High-efficiency receptor-mediated delivery of small and large (48 kilobase gene constructs using the endosome-disruption activity of defective or chemically inactivated adenovirus particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6094–6098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cristiano R. J., Smith L. C., Woo S. L. Hepatic gene therapy: adenovirus enhancement of receptor-mediated gene delivery and expression in primary hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2122–2126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curiel D. T., Agarwal S., Wagner E., Cotten M. Adenovirus enhancement of transferrin-polylysine-mediated gene delivery. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8850–8854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degols G., Leonetti J. P., Benkirane M., Devaux C., Lebleu B. Poly(L-lysine)-conjugated oligonucleotides promote sequence-specific inhibition of acute HIV-1 infection. Antisense Res Dev. 1992 Winter;2(4):293–301. doi: 10.1089/ard.1992.2.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Düzgüneş N., Shavnin S. A. Membrane destabilization by N-terminal peptides of viral envelope proteins. J Membr Biol. 1992 May;128(1):71–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00231872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodchild J., Agrawal S., Civeira M. P., Sarin P. S., Sun D., Zamecnik P. C. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus replication by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5507–5511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosselin G., Schinazi R. F., Sommadossi J. P., Mathé C., Bergogne M. C., Aubertin A. M., Kirn A., Imbach J. L. Anti-human immunodeficiency virus activities of the beta-L enantiomer of 2',3'-dideoxycytidine and its 5-fluoro derivative in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994 Jun;38(6):1292–1297. doi: 10.1128/aac.38.6.1292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haensler J., Szoka F. C., Jr Polyamidoamine cascade polymers mediate efficient transfection of cells in culture. Bioconjug Chem. 1993 Sep-Oct;4(5):372–379. doi: 10.1021/bc00023a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamata H., Yagisawa H., Takahashi S., Hirata H. Amphiphilic peptides enhance the efficiency of liposome-mediated DNA transfection. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Feb 11;22(3):536–537. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.3.536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonetti J. P., Degols G., Lebleu B. Biological activity of oligonucleotide-poly(L-lysine) conjugates: mechanism of cell uptake. Bioconjug Chem. 1990 Mar-Apr;1(2):149–153. doi: 10.1021/bc00002a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonetti J. P., Machy P., Degols G., Lebleu B., Leserman L. Antibody-targeted liposomes containing oligodeoxyribonucleotides complementary to viral RNA selectively inhibit viral replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2448–2451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsukura M., Shinozuka K., Zon G., Mitsuya H., Reitz M., Cohen J. S., Broder S. Phosphorothioate analogs of oligodeoxynucleotides: inhibitors of replication and cytopathic effects of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7706–7710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsukura M., Zon G., Shinozuka K., Stein C. A., Mitsuya H., Cohen J. S., Broder S. Synthesis of phosphorothioate analogues of oligodeoxyribonucleotides and their antiviral activity against human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):343–347. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90161-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midoux P., Mendes C., Legrand A., Raimond J., Mayer R., Monsigny M., Roche A. C. Specific gene transfer mediated by lactosylated poly-L-lysine into hepatoma cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 25;21(4):871–878. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.4.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moog C., Wick A., Le Ber P., Kirn A., Aubertin A. M. Bicyclic imidazo derivatives, a new class of highly selective inhibitors for the human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Antiviral Res. 1994 Aug;24(4):275–288. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(94)90075-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita R., Gibbons G. H., Ellison K. E., Nakajima M., Zhang L., Kaneda Y., Ogihara T., Dzau V. J. Single intraluminal delivery of antisense cdc2 kinase and proliferating-cell nuclear antigen oligonucleotides results in chronic inhibition of neointimal hyperplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8474–8478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata M., Sugahara Y., Takahashi S., Ohnishi S. pH-dependent membrane fusion activity of a synthetic twenty amino acid peptide with the same sequence as that of the hydrophobic segment of influenza virus hemagglutinin. J Biochem. 1987 Oct;102(4):957–962. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata M., Takahashi S., Kagiwada S., Suzuki A., Ohnishi S. pH-dependent membrane fusion and vesiculation of phospholipid large unilamellar vesicles induced by amphiphilic anionic and cationic peptides. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 25;31(7):1986–1992. doi: 10.1021/bi00122a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plank C., Oberhauser B., Mechtler K., Koch C., Wagner E. The influence of endosome-disruptive peptides on gene transfer using synthetic virus-like gene transfer systems. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 29;269(17):12918–12924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajaonarivony M., Vauthier C., Couarraze G., Puisieux F., Couvreur P. Development of a new drug carrier made from alginate. J Pharm Sci. 1993 Sep;82(9):912–917. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600820909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickwood D., Ford T., Graham J. Nycodenz: a new nonionic iodinated gradient medium. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jun;123(1):23–31. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90618-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E., Plank C., Zatloukal K., Cotten M., Birnstiel M. L. Influenza virus hemagglutinin HA-2 N-terminal fusogenic peptides augment gene transfer by transferrin-polylysine-DNA complexes: toward a synthetic virus-like gene-transfer vehicle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):7934–7938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.7934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E., Zatloukal K., Cotten M., Kirlappos H., Mechtler K., Curiel D. T., Birnstiel M. L. Coupling of adenovirus to transferrin-polylysine/DNA complexes greatly enhances receptor-mediated gene delivery and expression of transfected genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6099–6103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickstrom E. Oligodeoxynucleotide stability in subcellular extracts and culture media. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1986 Sep;13(2):97–102. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(86)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelphati O., Zon G., Leserman L. Inhibition of HIV-1 replication in cultured cells with antisense oligonucleotides encapsulated in immunoliposomes. Antisense Res Dev. 1993 Winter;3(4):323–338. doi: 10.1089/ard.1993.3.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu N., Liggitt D., Liu Y., Debs R. Systemic gene expression after intravenous DNA delivery into adult mice. Science. 1993 Jul 9;261(5118):209–211. doi: 10.1126/science.7687073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]