Abstract
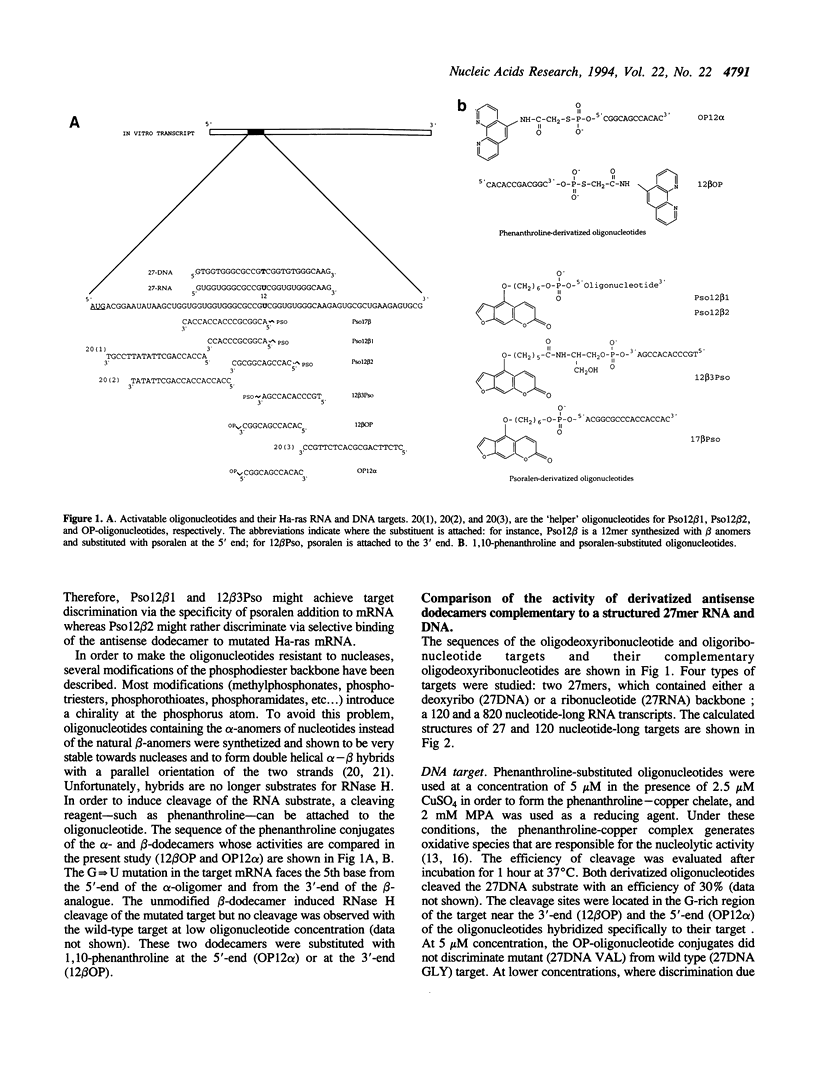
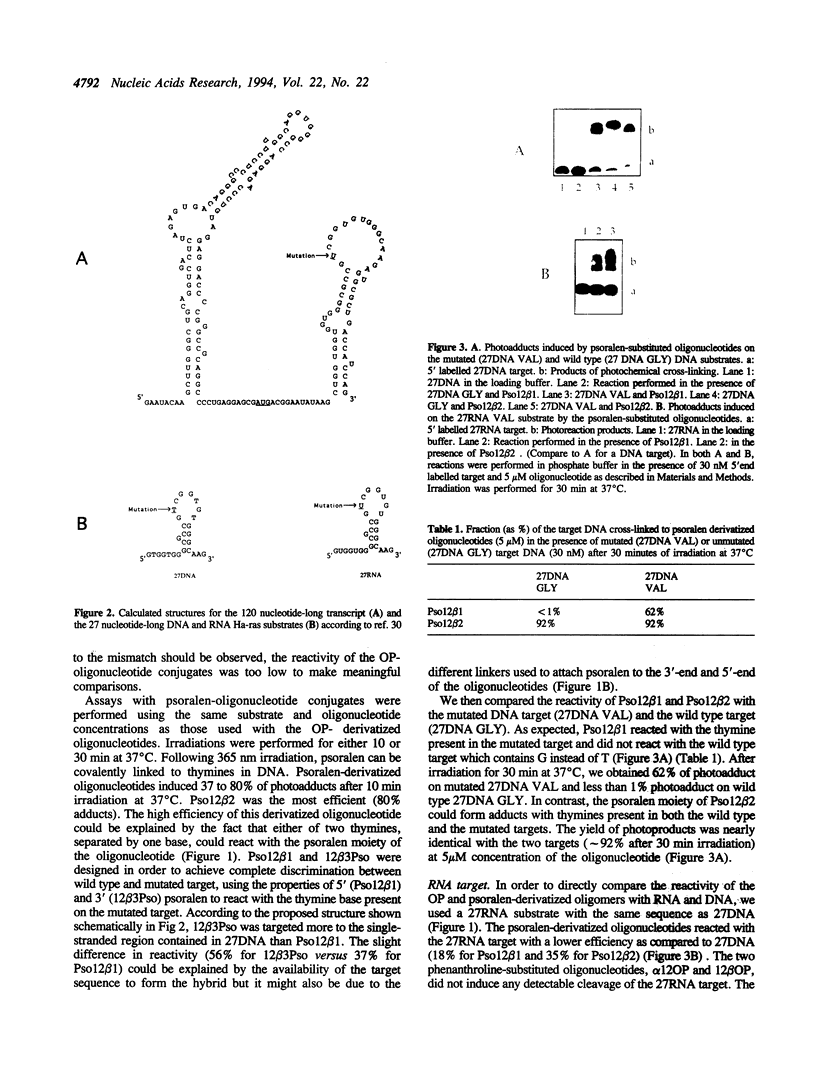
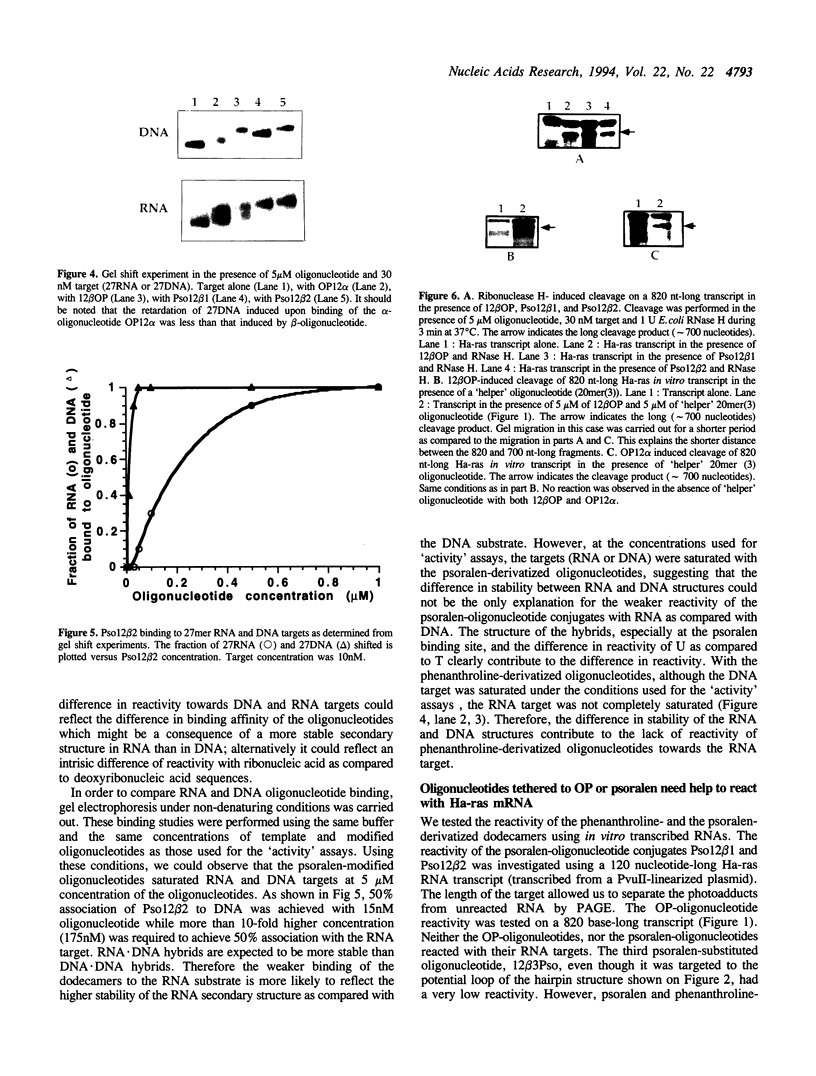
Dodecadeoxyribonucleotides derivatized with 1,10-phenanthroline or psoralen were targeted to the point mutation (G<-->U) in codon 12 of the Ha-ras mRNA. DNA and RNA fragments, 27 nucleotides in length, and containing the complementary sequence of the 12mers, were used to compare the reactivity of the activatable dodecamers (cleavage of the target by the phenanthroline-12mer conjugates; photo-induced cross-linking of psoralen-12mer conjugates to the target). The reactivity of the RNA with the dodecamers was weaker than that of the DNA target. With psoralen-substituted oligonucleotides, it was possible to obtain complete discrimination between the mutated target (which contained a psoralen-reactive T(U) in the 12th codon) and the normal target (which contained G at the same position). When longer Ha-ras RNA fragments were used as targets (120 and 820 nucleotides), very little reactivity was observed. Part of the reactivity could be recovered by using 'helper' oligonucleotides that hybridized to adjacent sites on the substrate. A 'helper' chain length greater than 13 was required to improve the reactivity of dodecamers. However, the dodecanucleotides induced RNase H cleavage of the target RNA in the absence of 'helper' oligonucleotide. Therefore, in the absence of the RNase H enzyme, long oligonucleotides are needed to compete with the secondary structures of the mRNA. In contrast, formation of a ternary complex oligonucleotide-mRNA-RNase H led to RNAT cleavage with shorter oligonucleotides.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang E. H., Miller P. S., Cushman C., Devadas K., Pirollo K. F., Ts'o P. O., Yu Z. P. Antisense inhibition of ras p21 expression that is sensitive to a point mutation. Biochemistry. 1991 Aug 27;30(34):8283–8286. doi: 10.1021/bi00098a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. H., Mazumder A., Constant J. F., Sigman D. S. Nuclease activity of 1,10-phenanthroline-copper. New conjugates with low molecular weight targeting ligands. Bioconjug Chem. 1993 Jan-Feb;4(1):69–77. doi: 10.1021/bc00019a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. H., Sigman D. S. Nuclease activity of 1,10-phenanthroline-copper: sequence-specific targeting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7147–7151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessen P., Fondrat C., Valencien C., Mugnier C. BISANCE: a French service for access to biomolecular sequence databases. Comput Appl Biosci. 1990 Oct;6(4):355–356. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/6.4.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein F. Nucleoside phosphorothioates. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:367–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- François J. C., Saison-Behmoaras T., Barbier C., Chassignol M., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Sequence-specific recognition and cleavage of duplex DNA via triple-helix formation by oligonucleotides covalently linked to a phenanthroline-copper chelate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9702–9706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- François J. C., Saison-Behmoaras T., Chassignol M., Thuong N. T., Sun J. S., Hélène C. Periodic cleavage of poly(dA) by oligothymidylates covalently linked to the 1,10-phenanthroline-copper complex. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 5;27(7):2272–2276. doi: 10.1021/bi00407a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayase Y., Inoue H., Ohtsuka E. Secondary structure in formylmethionine tRNA influences the site-directed cleavage of ribonuclease H using chimeric 2'-O-methyl oligodeoxyribonucleotides. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 18;29(37):8793–8797. doi: 10.1021/bi00489a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hélène C., Toulmé J. J. Specific regulation of gene expression by antisense, sense and antigene nucleic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 21;1049(2):99–125. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90031-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs S. T., Shen C. K., Hearst J. E., Rapoport H. Synthesis and characterization of new psoralen derivatives with superior photoreactivity with DNA and RNA. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 22;16(6):1058–1064. doi: 10.1021/bi00625a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob A., Duval-Valentin G., Ingrand D., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Inhibition of viral growth by an alpha-oligonucleotide directed to the splice junction of herpes simplex virus type-1 immediate-early pre-mRNA species 22 and 47. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Aug 15;216(1):19–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kean J. M., Miller P. S. Effect of target structure on cross-linking by psoralen-derivatized oligonucleoside methylphosphonates. Biochemistry. 1994 Aug 9;33(31):9178–9186. doi: 10.1021/bi00197a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kean J. M., Murakami A., Blake K. R., Cushman C. D., Miller P. S. Photochemical cross-linking of psoralen-derivatized oligonucleoside methylphosphonates to rabbit globin messenger RNA. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 27;27(26):9113–9121. doi: 10.1021/bi00426a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulka M., Smith C. C., Aurelian L., Fishelevich R., Meade K., Miller P., Ts'o P. O. Site specificity of the inhibitory effects of oligo(nucleoside methylphosphonate)s complementary to the acceptor splice junction of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early mRNA 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6868–6872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonetti J. P., Rayner B., Lemaitre M., Gagnor C., Milhaud P. G., Imbach J. L., Lebleu B. Antiviral activity of conjugates between poly(L-lysine) and synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):323–332. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90159-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher L. J., 3rd, Dolnick B. J. Specific hybridization arrest of dihydrofolate reductase mRNA in vitro using anti-sense RNA or anti-sense oligonucleotides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Feb 15;253(1):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90654-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P. S., McParland K. B., Jayaraman K., Ts'o P. O. Biochemical and biological effects of nonionic nucleic acid methylphosphonates. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 31;20(7):1874–1880. doi: 10.1021/bi00510a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morvan F., Rayner B., Imbach J. L. Alpha-oligonucleotides: a unique class of modified chimeric nucleic acids. Anticancer Drug Des. 1991 Dec;6(6):521–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlakis G. N., Lockard R. E., Vamvakopoulos N., Rieser L., RajBhandary U. L., Vournakis J. N. Secondary structure of mouse and rabbit alpha- and beta-globin mRNAs: differential accessibility of alpha and beta initiator AUG codons towards nucleases. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):91–102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90391-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porumb H., Bertrand J. R., Paoletti J., Vasseur J. J., Rayner B., Imbach J. L., Malvy C. 9-Aminoellipticine-derivatized alpha- and beta-oligodeoxyribonucleotides targeted to the cap of beta-globin mRNA: hybridization to natural and engineered mRNA, inhibition of translation, and improved effect of tandem chains. Antisense Res Dev. 1992 Winter;2(4):279–292. doi: 10.1089/ard.1992.2.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds M. A., Beck T. A., Hogrefe R. I., McCaffrey A., Arnold L. J., Jr, Vaghefi M. M. A non-nucleotide-based linking method for the preparation of psoralen-derivatized methylphosphonate oligonucleotides. Bioconjug Chem. 1992 Sep-Oct;3(5):366–374. doi: 10.1021/bc00017a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saison-Behmoaras T., Tocqué B., Rey I., Chassignol M., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Short modified antisense oligonucleotides directed against Ha-ras point mutation induce selective cleavage of the mRNA and inhibit T24 cells proliferation. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1111–1118. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08051.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sproat B. S., Lamond A. I., Beijer B., Neuner P., Ryder U. Highly efficient chemical synthesis of 2'-O-methyloligoribonucleotides and tetrabiotinylated derivatives; novel probes that are resistant to degradation by RNA or DNA specific nucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3373–3386. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J. S., Asseline U., Rouzaud D., Montenay-Garestier T., Nguyen T. T., Hélène C. Oligo-[alpha]-deoxynucleotides covalently linked to an intercalating agent. Double helices with parallel strands are formed with complementary oligo-[beta]-deoxynucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):6149–6158. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.6149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teare J., Wollenzien P. Specificity of site directed psoralen addition to RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3359–3372. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zon G., Geiser T. G. Phosphorothioate oligonucleotides: chemistry, purification, analysis, scale-up and future directions. Anticancer Drug Des. 1991 Dec;6(6):539–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]