Abstract
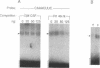
Ribonucleotide reductase is a highly regulated rate-limiting enzyme activity in DNA synthesis, responsible for reducing ribonucleotides to their deoxyribonucleotide forms. Using 3'-end labeled RNA and band-shift and UV cross-linking analyses, we have identified a cis-element, 5'-CAAACUUC-3', within the 3'-untranslated region of the mammalian ribonucleotide reductase R1 mRNA, which binds a cytoplasmic protein in BALB/c 3T3 mouse cells, to form a 57 kDa RNA-protein complex. Sequence-specific binding was observed, and binding was prevented by several different mutations within the cis-element. We suggest that this cis-trans interaction plays a role in R1 mRNA stability.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amara F. M., Chen F. Y., Wright J. A. A novel transforming growth factor-beta 1 responsive cytoplasmic trans-acting factor binds selectively to the 3'-untranslated region of mammalian ribonucleotide reductase R2 mRNA: role in message stability. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Oct 11;21(20):4803–4809. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.20.4803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amara F. M., Chen F. Y., Wright J. A. Phorbol ester modulation of a novel cytoplasmic protein binding activity at the 3'-untranslated region of mammalian ribonucleotide reductase R2 mRNA and role in message stability. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6709–6715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater J. A., Wisdom R., Verma I. M. Regulated mRNA stability. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:519–541. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.002511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce A. G., Uhlenbeck O. C. Reactions at the termini of tRNA with T4 RNA ligase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Oct;5(10):3665–3677. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.10.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter B. Z., Malter J. S. Regulation of mRNA stability and its relevance to disease. Lab Invest. 1991 Dec;65(6):610–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J. L., Di Jeso B., Rao K., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. Two genetic loci participate in the regulation by iron of the gene for the human transferrin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1787–1791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen F. Y., Amara F. M., Wright J. A. Mammalian ribonucleotide reductase R1 mRNA stability under normal and phorbol ester stimulating conditions: involvement of a cis-trans interaction at the 3' untranslated region. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3977–3986. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06075.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen F. Y., Amara F. M., Wright J. A. Regulation of mammalian ribonucleotide reductase R1 mRNA stability is mediated by a ribonucleotide reductase R1 mRNA 3'-untranslated region cis-trans interaction through a protein kinase C-controlled pathway. Biochem J. 1994 Aug 15;302(Pt 1):125–132. doi: 10.1042/bj3020125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurta R. A., Samuel S. K., Greenberg A. H., Wright J. A. Early induction of ribonucleotide reductase gene expression by transforming growth factor beta 1 in malignant H-ras transformed cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):24097–24100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurta R. A., Wright J. A. Alterations in the activity and regulation of mammalian ribonucleotide reductase by chlorambucil, a DNA damaging agent. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):7066–7071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Rouault T. A., Harford J. B. Regulating the fate of mRNA: the control of cellular iron metabolism. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90046-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzella J. M., Blackshear P. J. Specific protein binding to a conserved region of the ornithine decarboxylase mRNA 5'-untranslated region. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):7077–7082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rondon I. J., MacMillan L. A., Beckman B. S., Goldberg M. A., Schneider T., Bunn H. F., Malter J. S. Hypoxia up-regulates the activity of a novel erythropoietin mRNA binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16594–16598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B. Messenger RNA degradation in eukaryotes. Cell. 1993 Aug 13;74(3):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80043-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelander L., Berg P. Isolation and characterization of expressible cDNA clones encoding the M1 and M2 subunits of mouse ribonucleotide reductase. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3433–3442. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vakalopoulou E., Schaack J., Shenk T. A 32-kilodalton protein binds to AU-rich domains in the 3' untranslated regions of rapidly degraded mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3355–3364. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. A., Chan A. K., Choy B. K., Hurta R. A., McClarty G. A., Tagger A. Y. Regulation and drug resistance mechanisms of mammalian ribonucleotide reductase, and the significance to DNA synthesis. Biochem Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;68(12):1364–1371. doi: 10.1139/o90-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]