Abstract
Aims
Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) is a cell surface protein with oncogenic features that is expressed on healthy human epithelia and corresponding malignant tumours. EpCAM expression frequently correlates with more aggressive tumour behaviour and new EpCAM-specific therapeutic agents have recently been approved for clinical use in patients with cancer. However, no consensus exists on how and when to evaluate EpCAM expression in patients with cancer.
Material and methods
EpCAM expression was assessed by a well-established immunohistochemical staining protocol in 2291 primary tumour tissues and in 108 metastases using the EpCAM-specific antibody clone VU1D9. A total immunostaining score was calculated as the product of a proportion score and an intensity score. Four expression subgroups (no, weak, moderate and intense) were defined. As described previously, the term ‘EpCAM overexpression’ was reserved for tissues showing a total immunostaining score >4.
Results
EpCAM was highly expressed in most tumours of gastrointestinal origin and in some carcinomas of the genitourinary tract. However, hepatocellular carcinomas, clear cell renal cell cancer, urothelial cancer and squamous cell cancers were frequently EpCAM negative. EpCAM expression in breast cancer depended on the histological subtype; lobular histology usually showed no or weak expression. Most metastases were EpCAM positive and they frequently reflected the expression phenotype of the primary tumour.
Conclusion
EpCAM expression was detected on adenocarcinomas of various primary sites. If EpCAM-specific antibodies are intended to be used in patients with cancer, we recommend prior immunohistochemical evaluation of EpCAM expression, particularly in patients with renal cell cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, urothelial carcinoma, breast cancer and squamous cell carcinomas.
Keywords: Antibodies, immunohistochemistry
Introduction
Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM; syn. GA733-2, TACSTD1, KSA, EGP40, CD326, 17-1A, HEA125, MK-1, EGP-2, EGP-34, ESA, KS1/4) is a tumour-associated antigen that is expressed in normal epithelia, with the exception of squamous epithelia, epidermal keratinocytes, gastric parietal cells, myoepithelial cells, thymic cortical epithelium and hepatocytes.1
Tumour tissues, such as primary and metastatic breast cancer, frequently overexpress EpCAM.2 Gastl and colleagues observed EpCAM overexpression in 35.6% of patients with invasive breast cancer, and this was associated with poor disease-free and overall survival.3 Moreover, our group has shown that survival decreases significantly with increasing amounts of EpCAM expression.4 EpCAM can be used as prognostic marker in node-positive and node-negative breast cancer.5 Furthermore, frequent and high-level EpCAM expression has been found in adenocarcinomas of the colon, stomach, pancreas and prostate.6 Most soft-tissue tumours and all lymphomas are EpCAM negative. EpCAM overexpression has been associated with a dismal prognosis in other tumour entities, such as gallbladder cancer,7 ovarian cancer8 and pancreatic cancer.9
Overexpression of EpCAM has been found to be associated with enhanced transcription and translation of the proto-oncogene c-myc.10 Recently, the proteolytic cleavage of the intracellular domain of EpCAM (EpICD) has been shown to confer a mitogenic signal.11 12 Furthermore, DNA methylation appears to be a potential mechanism for regulation of EpCAM expression.13
The observation of antigen overexpression on carcinomas and its correlation with decreased survival have promoted the EpCAM antigen to a ‘druggable’ target for cancer treatment. Several EpCAM-targeting immunotherapeutic approaches are currently being tested in clinical trials.11 The first monoclonal antibody applied for human cancer therapy of gastrointestinal tumours was the EpCAM-directed monoclonal antibody 17-1A.14 Many years later in 2009, the first anti-EpCAM antibody, named catumaxomab,15 was approved by the European Commission for the treatment of malignant ascites in cancer patients with EpCAM-positive tumours. Catumaxomab showed a clear clinical benefit in patients with malignant ascites secondary to epithelial cancers, with an acceptable safety profile.16 Overall survival showed a positive trend for the catumaxomab group, and in a prospectively planned analysis it was significantly prolonged in patients with gastric cancer. Adecatumumab (MT201) is a fully human monoclonal anti-EpCAM antibody that mediates complement-dependent and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. In patients with metastatic breast cancer, this antibody showed dose-dependent and target-dependent clinical activity and the occurrence of new metastases was reduced.17 A new bispecific T-cell engager (BiTE) anti-EpCAM/CD3 antibody has been shown to have significant antitumour activity in breast cancer and lung cancer mouse models. The human surrogate MT110 is currently in preclinical development.18
So far, no consensus exists on which tumours and methods should be used for testing EpCAM expression. To help clinicians in their decision to select patients for treatment with EpCAM-specific antibodies, EpCAM expression was evaluated in the most frequent tumour entities and metastases to determine the grade of expression and its stability.
Material and methods
Tumour samples
Primary tumour samples from 2291 patients with cancer, and metastases from 108 patients with different tumour entities, were assessed for EpCAM expression. Tumour tissues and staining were in part obtained from previously published series. Slides were obtained from either classical paraffin blocks or tissue microarrays. Tissues were divided into five groups: gastrointestinal cancers, genitourinary cancer, upper digestive tract and respiratory tract cancers, breast cancer and metastases.
Paraffin blocks from two breast cancer cell line spheroids (MCF-7 cells: EpCAM positive; Hs578T cells: EpCAM negative) were used as negative and positive controls. Paraffin blocks of the two cell lines were prepared, and slides were cut for each immunohistochemical run.
Slide preparation, deparaffinisation and rehydration
Sections (4 μm thick) from paraffin blocks were cut and mounted onto adhesive-coated glass slides. Slides were placed in a xylene bath and incubated for 5 min. The xylene in the baths was changed, and the procedure was repeated twice. Slides were then placed in absolute ethanol for 3 min, and this was repeated once. Slides were then placed in 95% ethanol for 3 min, and this was repeated once. Slides were finally placed in distilled water for a minimum of 30 s.
Proteolytic digestion
Slides were placed in pronase (Dako Pronase, code no. S2013; Dako, Glostrup, Denmark) and incubated for 20 min at 37°C. Slides were then placed in Tris-buffered saline (Dako TBS; code no. S3001 or S1968).
Staining procedure using an automated system
Slides were placed into the Dako Autostainer Universal Staining System and a specific programme for EpCAM immunostaining consisted of the following steps: (1) endogenous peroxidase blocking by treating slides with 3% hydrogen peroxide and incubating for 5 min; (2) incubation with the primary antibody (NCL-ESA, clone VU1D9, concentration 1:100; Novocastra, Newcastle, UK) for 60 min; (3) incubation with the peroxidase-labelled secondary antibody (Dako EnVision+, code no. K4000) for 30 min; (4) incubation with the substrate-chromogen 3,3′-diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride (Dako Liquid DAB+, code no. K3467) for 8 min; (5) upon completion of the run, slides were removed from the staining machine and rinsed in Dako TBS; (6) slides were placed in a bath of aqueous haematoxylin (code no. S3309) for 45 s; (7) slides were then gently rinsed in a distilled water bath; (8) slides were dehydrated through the following solutions: 95% ethanol over 3 min with one bath change, 100% ethanol over 3 min with two bath changes, and xylene over 5 min with two bath changes; (9) coverslips were then applied to specimens using routine pathological procedures.
Immunohistochemical evaluation and statistical analysis
Antigen expression was defined as specific when a staining signal was present on the tumour cell membrane. Similar to the Allred score in the evaluation of oestrogen receptor positivity,19 EpCAM expression was evaluated by calculating a total immunostaining score (TIS) as the product of a proportion score (PS) and an intensity score (IS). The PS describes the estimated fraction of positively stained tumour cells (0, none; 1, <10%; 2, 10–50%; 3, 51–80%; 4, >80%). The IS represents the estimated staining intensity as compared with control cell lines (0, no staining; 1, weak; 2, moderate; 3, strong). The TIS (TIS=PS × IS) ranges from 0 to 12 with only nine possible values (that is, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9 and 12). EpCAM ‘overexpression’ has been defined previously as a TIS >4.3 Furthermore we defined four subgroups: no expression, TIS 0; weak expression, TIS 1–4; moderate expression, TIS 6 and 8; intense expression, TIS 9 and 12. For correlation of EpCAM expression in primary tumours and corresponding metastases, a regression analyses using the SPSS software program for Windows (SPSS, Chicago, Illinois, USA) was performed.
Results
EpCAM expression in gastrointestinal cancers
Colorectal cancer showed the highest EpCAM expression overall (table 1). From 104 adenocarcinoma tissue samples, 82% (n=85) showed intense expression (TIS 9 and 12) and 12% (n=12) showed moderate expression (TIS 6 and 8), accounting for an overexpression rate of 94% (TIS >4; n=97); only 6% (n=7) showed weak expression (TIS 1–4).
Table 1.
EpCAM expression in primary adenocarcinoma of the gastrointestinal tract
| Tumour type (no. of samples) | No EpCAM overexpression* | EpCAM overexpression* | ||||||
| No expression (TIS 0) | Weak expression (TIS 1–4) | Moderate expression (TIS 6, 8) | Intense expression (TIS 9, 12) | |||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| Colon cancer (104) | 0 | 0 | 7 | 6 | 12 | 12 | 85 | 82 |
| Ampullary cancer (34) | 0 | 0 | 5 | 15 | 14 | 41 | 15 | 44 |
| Gastric cancer (73) | 3 | 4 | 16 | 22 | 14 | 19 | 40 | 55 |
| Oesophageal cancer (43) | 5 | 12 | 10 | 23 | 11 | 26 | 17 | 39 |
| Gallbladder cancer (128) | 9 | 7 | 34 | 27 | 53 | 41 | 32 | 25 |
| Pancreatic cancer (203) | 2 | 1 | 71 | 35 | 56 | 26 | 74 | 37 |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma (47) | 40 | 86 | 3 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 4 |
EpCAM expression was determined by immunohistochemistry.
EpCAM overexpression defined by Gastl et al3.
EpCAM, epithelial cell adhesion molecule; TIS, total immunostaining score.
Ampullary cancer and gastric cancer showed overexpression rates (TIS >4) of 85% (n=29) and 74% (n=54), respectively. Oesophageal cancer showed an intense EpCAM expression in 39% (TIS 9 and 12; n=17) and a moderate expression (TIS 6 and 8) in 26% (n=11) of tumour samples (overexpression 65%; TIS >4; n=28). EpCAM negativity (TIS 0) was observed in 12% (n=5) and weak expression (TIS 1–4) in 23% (n=10) of the tumour samples. Of 128 gallbladder samples, 7% were negative (TIS 0; n=9); EpCAM overexpression rate (TIS >4) was 66% (n=85), and 27% (n=34) showed only weak expression (TIS 1–4). Hepatocellular carcinomas were predominantly EpCAM negative. In fact, 86% (n=40) of tumour samples were negative; intense, moderate and weak expression was found in 6%, 4% and 4% of cases, respectively.
EpCAM expression in breast cancer
In patients with breast cancer (table 2) EpCAM overexpression (TIS >4) was observed in 46% (n=87) of 188 samples with invasive ductal carcinoma. By subgroup analysis, 19% (n=35) lacked EpCAM expression (TIS 0), 35% (n=66) showed weak expression (TIS 1–4), 20% (n=37) stained moderately (TIS 6 and 8), and 26% (n=50) exhibited intense EpCAM expression (TIS 9 and 12).
Table 2.
EpCAM expression in primary breast cancer
| Tumour type (no. of samples) | No EpCAM overexpression* | EpCAM overexpression* | ||||||
| No expression (TIS 0) | Weak expression (TIS 1–4) | Moderate expression (TIS 6, 8) | Intense expression (TIS 9, 12) | |||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| Invasive ductal breast cancer (188) | 35 | 19 | 66 | 35 | 37 | 20 | 50 | 26 |
| Invasive lobular breast cancer (82) | 34 | 41 | 36 | 44 | 9 | 11 | 3 | 4 |
| Other breast cancer histologies (107) | 18 | 17 | 42 | 39 | 26 | 24 | 21 | 20 |
EpCAM expression was determined by immunohistochemistry.
EpCAM overexpression defined by Gastl et al3.
EpCAM, epithelial cell adhesion molecule; TIS, total immunostaining score.
In contrast, invasive lobular breast cancer showed lower EpCAM expression scores. In these tumours, EpCAM overexpression (TIS >4) was found in 15% (n=12) of 82 samples. By subgroup analysis, 41% (n=34) were EpCAM negative (TIS 0), 44% (n=36) showed weak expression (TIS 1–4), 11% (n=9) stained moderately (TIS 6 and 8), and 4% (n=3) exhibited intense EpCAM expression (TIS 9 and 12).
EpCAM expression in genitourinary cancers
Ovarian, endometrial and prostate cancers were observed to be high EpCAM expressers, showing overexpression rates (TIS >4) of 73% (n=236), 88% (n=62) and 89% (n=96), respectively. Moreover, weak EpCAM expression (TIS 1–4) was observed in 19% (n=63), 6% (n=4) and 10% (n=11) of these tumours, respectively. Of note, the expression of EpCAM in patients with ovarian cancer depended on histology (table 3). In fact, mucinous ovarian cancer had a lower EpCAM overexpression rate (TIS >4; 55%, n=32) as compared with serous, endometrioid or other histologies (TIS >4, 76%, n=204). Furthermore, in patients with renal cancer, EpCAM expression depended strongly on the histological subtype. Clear cell renal cell cancers were predominantly EpCAM negative (TIS 0). In fact, 79% (n=38) of these tumours were found to lack EpCAM expression. Only 12% (n=6) were found to display EpCAM overexpression (TIS >4). Non-clear-cell renal cell cancer lacked EpCAM expression (TIS 0) in 31% (n=23) of cases. Weak (TIS 1–4) and overexpression (TIS >4) were observed in 14% (n=10) and 56% (n=41) of these tumours, respectively.
Table 3.
EpCAM expression in genitourinary tract cancers
| Tumour type (no. of samples) | No EpCAM overexpression* | EpCAM overexpression* | ||||||
| No expression (TIS 0) | Weak expression (TIS 1–4) | Moderate expression (TIS 6, 8) | Intense expression (TIS 9, 12) | |||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| Ovarian cancer (326) | 27 | 8 | 63 | 19 | 100 | 31 | 136 | 42 |
| Serous, endometrioid and other histologies (268) | 21 | 8 | 43 | 16 | 87 | 32 | 117 | 44 |
| Mucinous histology (58) | 6 | 10 | 20 | 35 | 13 | 22 | 19 | 33 |
| Renal cancer (122) | 61 | 50 | 14 | 12 | 15 | 12 | 32 | 26 |
| Clear cell histology (48) | 38 | 79 | 4 | 9 | 5 | 10 | 1 | 2 |
| Non-clear-cell histology (74) | 23 | 31 | 10 | 14 | 10 | 14 | 31 | 41 |
| Urothelial cancer (91) | 51 | 56 | 15 | 17 | 21 | 23 | 4 | 4 |
| Endometrial cancer (70) | 4 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 16 | 23 | 46 | 65 |
| Prostate cancer (108) | 1 | 1 | 11 | 10 | 35 | 32 | 61 | 57 |
| SCC of the cervix, vagina and vulva (92) | 54 | 59 | 14 | 15 | 13 | 14 | 11 | 12 |
EpCAM expression was determined by immunohistochemistry.
EpCAM overexpression defined by Gastl et al3.
EpCAM, epithelial cell adhesion molecule; SCC, squamous cell cancer; TIS, total immunostaining score.
Fifty-nine per cent (n=54) of squamous cell cancers of the cervix, vagina and vulva were predominantly EpCAM negative (TIS 0). EpCAM overexpression (TIS >4) and weak expression (TIS 1–4) were observed in 26% (n=24) and 15% (n=14), respectively. Finally, we observed EpCAM negativity (TIS 0) in 56% (n=51) of urothelial carcinomas, and an EpCAM overexpression rate (TIS >4) of 27% (n=25).
EpCAM expression in upper digestive, respiratory tract and (neuro)endocrine cancers
We observed no significant differences between non-small-cell and small cell lung cancer (table 4). Both types were observed to be high expressers, showing overexpression rates (TIS >4) of 74% (n=107) and 75% (n=45), respectively. EpCAM expression lacked (TIS 0) in only 7% (n=11) and 20% (n=12), respectively. Moreover, there was no significant difference in EpCAM expression between different histological subtypes of non-small-cell lung cancer. High expression rates were shown by (neuro)endocrine tumours. The overexpression rate (TIS >4) of well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumours was 88% (n=47). The overexpression rate (TIS >4) of differentiated thyroid cancer was 87% (n=77). As observed for squamous cell cancers from other origins, squamous cell cancers of the oral cavity showed EpCAM negativity in 40% (n=51) (TIS 0) or weak expression in 38% (n=48) (TIS 1–4).
Table 4.
EpCAM expression in upper digestive, respiratory tract and (neuro)endocrine cancers
| Tumour type (no. of samples) | No EpCAM overexpression* | EpCAM overexpression* | ||||||
| No expression (TIS 0) | Weak expression (TIS 1–4) | Moderate expression (TIS 6, 8) | Intense expression (TIS 9, 12) | |||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| Oral cavity cancer, SCC (126) | 51 | 40 | 48 | 38 | 11 | 9 | 16 | 13 |
| Non-small-cell lung cancer (146) | 11 | 7 | 28 | 19 | 36 | 25 | 71 | 49 |
| Small cell lung cancer and other PDNET (60) | 12 | 20 | 3 | 5 | 18 | 30 | 27 | 45 |
| WDNET (53) | 2 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 2 | 4 | 45 | 84 |
| Differentiated thyroid cancer (88) | 2 | 3 | 9 | 10 | 25 | 28 | 52 | 59 |
EpCAM expression was determined by immunohistochemistry.
EpCAM overexpression defined by Gastl et al3.
EpCAM, epithelial cell adhesion molecule; PDNET, poorly differentiated neuroendocrine tumour; SCC, squamous cell cancer; TIS, total immunostaining score; WDNET, well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumour.
EpCAM expression in metastases
In total, from 108 metastases that were stained for evaluation of EpCAM expression, only 4% (n=4) lacked EpCAM expression (TIS 0; table 5). The expression phenotype of the metastases usually reflects the expression of the primary tumour (figure 1A–D). In fact, in lymph node metastases from patients with colorectal cancer, 89% (n=43) of samples were observed to have EpCAM overexpression (TIS >4) and 10% (n=5) showed weak EpCAM expression (TIS 1–4). In line with these observations, 83% (n=15) of colorectal cancer liver metastases were EpCAM overexpressing (TIS >4) and 17% (n=3) showed a weak EpCAM expression (TIS 1–4). Peritoneal metastases from different tumour origins were usually EpCAM positive. EpCAM overexpression (TIS >4) and weak expression (TIS 1–4) were found in 64% (n=14) and 32% (n=7) of tumour samples, respectively. Only 4% (n=1) lacked EpCAM expression (TIS 0).
Table 5.
EpCAM expression in metastases of different tumour origin
| Tumour type (no. of samples) | No EpCAM overexpression* | EpCAM overexpression* | ||||||
| No expression (TIS 0) | Weak expression (TIS 1–4) | Moderate expression (TIS 6, 8) | Intense expression (TIS 9, 12) | |||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| Liver metastases from colorectal cancer (18) | 0 | 0 | 3 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 83 |
| CNS metastases from breast cancer (15) | 1 | 7 | 5 | 33 | 4 | 27 | 5 | 33 |
| Peritoneal metastases from colon, ovary, pancreatobiliary and gastric cancer (22) | 1 | 4 | 7 | 32 | 10 | 45 | 4 | 19 |
| Lymph node metastases from breast cancer (5) | 2 | 40 | 1 | 20 | 1 | 20 | 1 | 20 |
| Lymph node metastases from colon cancer (48) | 0 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 4 | 8 | 39 | 81 |
EpCAM expression was determined by immunohistochemistry.
EpCAM overexpression defined by Gastl et al3.
CNS, central nervous system; EpCAM, epithelial cell adhesion molecule; TIS, total immunostaining score.
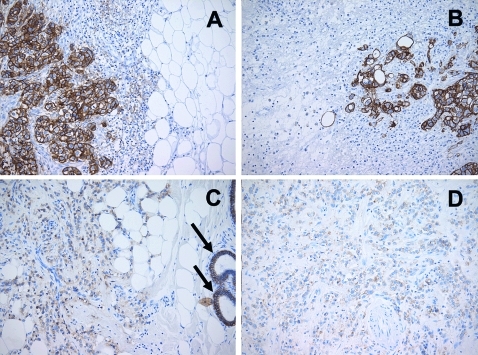
Figure 1.
Comparison between immunohistochemical epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) expression in primary breast cancer and metastases. (A) Invasive ductal carcinoma with strong EpCAM expression (total immunostaining score (TIS) 12). (B) Brain metastases from the same patient showing strong EpCAM expression (TIS 12). (C) Invasive lobular carcinoma with weak EpCAM expression (TIS 3); arrows: normal breast ducts showing EpCAM expression. (D) Peritoneal metastases from the same patient showing weak EpCAM expression (TIS 3).
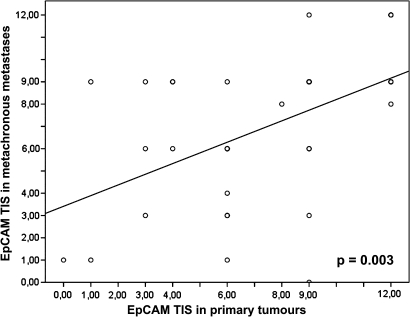
We observed a correlation between the EpCAM expression scores (TIS) of primary tumours and those of synchronous metastases (p<0.001; figure 2). Moreover, a correlation of EpCAM expression in primary tumours and metachronous metastases was seen (p=0.003, figure 3). The degree of concordance between EpCAM overexpression in primary tumour and metastases was highest in patients with ovarian cancer (n=8). In fact, 100% (n=8) showed concordance in EpCAM overexpression or non-overexpression. In 71 available patients with primary colorectal cancer and metastases, the degree of concordance was 76% (n=54). Fourteen per cent (n=10) changed the EpCAM status from overexpression to non-overexpression, and 10% (n=7) changed the EpCAM status from non-overexpression to overexpression. Moreover, patients with breast cancer available for this analyses (n=20) showed a concordance of 65% (n=13). Fifteen per cent (n=3) changed EpCAM status from overexpression to non-overexpression and 20% (n=4) changed EpCAM status from non-overexpression to overexpression.
Figure 2.
Regression analysis of the correlation of epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) expression between primary tumours and synchronous metastases. TIS, total immunostaining score.
Figure 3.
Regression analysis of the correlation of epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) expression between primary tumours and metachronous metastases. TIS, total immunostaining score.
Discussion
During recent decades, immunohistochemistry (IHC) has become a useful adjunctive method in diagnostic histopathology. The development of novel cancer therapies has raised the demand for accurate measurement of target molecules as a means to select patients. IHC is easy to perform on a variety of tumour samples, and therefore it has rapidly become the predominant method for measuring therapeutic targets in clinical practice. However, comparative immunohistochemical analysis of antigens such as hormone receptors or Her-2/neu in different laboratories with the same detection system has led to discrepant data,20 21 and some tests have been abandoned (that is, epidermal growth factor receptor). There are a number of drawbacks with IHC, the most important of which are lack of assay standardisation (pre-test variability) and variance in the interpretation of the immunohistochemical staining (post-test variability). As such, the interpretation of antigen staining intensity is a matter of debate, and in some cases not recommended (that is, American Society of Clinical Oncology hormone receptor testing guidelines).22
Achieving reproducible thresholds applicable across laboratories is one of the most difficult challenges of modern IHC. Correct semiquantitative estimation of the antigen content requires the setting of cut-off levels between what is to be considered a positive or negative result. The cut-off between EpCAM-overexpressing and non-overexpressing samples was defined by our group taking into account a bimodal distribution of EpCAM expression scores (TIS) in 205 breast cancer patients3 and a statistical power-driven disease-free survival analyses similar to an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC-) analysis.23 A very similar percentage of EpCAM-expressing breast cancer samples defined by western blot analysis has been reported by an independent group.24 Taking together these observations and all validation studies that have followed,4 7 8 25 we suggest that this cut-off is probably the most useful threshold for clinical use. However, it remains to be determined whether EpCAM expression defined by IHC predicts therapy response in patients treated with EpCAM-specific targeting agents, and whether patients with weak or even negative EpCAM expression might also benefit from such treatment approaches. The first clinical trial assessing this issue showed a target-dependent clinical activity of the adecatumumab antibody in patients with metastastatic breast cancer.17 However, validation trials with large patient samples and adequate EpCAM-expression-based selection are warranted to clarify this question. In consideration of this fact, we decided to additionally illustrate four subgroups with different grades of EpCAM expression (that is, no, low, moderate or intense) to favour adequate prospective evaluation of the predictive value of EpCAM expression in clinical trials and observational studies.
Adenocarcinomas usually revealed high EpCAM expression scores. Exceptions were hepatocellular carcinomas, breast cancer and renal cell cancer. In some cases, the EpCAM expression profile might indicate a particular biological behaviour of the tumour. In fact, invasive lobular breast cancer frequently showed either no or weak EpCAM expression. Lobular carcinomas tend to metastasise later than invasive ductal carcinomas and spread to unusual locations such as the peritoneum (figure 1D), meninges and gastrointestinal tract.26 Since EpCAM appears to be important for detection of circulating tumour cells, the evaluation of EpCAM expression in primary breast cancer is becoming fundamental.27 Other malignant tumours that frequently lack EpCAM expression are urothelial carcinomas and squamous cell cancer. In these cases, the expression of malignant cells reflects the expression of their benign counterparts in healthy tissues.
Important information has been derived from the evaluation of EpCAM expression in metastases. We observed that EpCAM expression in synchronous and metachronous metastases correlated with that of the primary tumour. Thus, evaluation of EpCAM expression in patients treated with EpCAM-specific antibodies might be performed on archived tumour samples obtained at the time of primary diagnosis or alternatively on metastases. However, since we observed that concordance of EpCAM status between primary tumour and metastases is not always assured, EpCAM IHC should be preferentially performed on metastatic lesions, if available. Taking the results together, we suggest performing EpCAM IHC particularly in patients with breast cancer, renal cell cancer, squamous cell carcinomas, hepatocellular carcinoma and urothelial cancer when treatment with EpCAM-specific antibodies is planned.
Take-home messages.
The antibody catumaxomab has been approved for intraperitoneal use in cancer patients with epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM)-positive tumours.
EpCAM is expressed in certain human cancers and its expression in metastases frequently reflects that of primary tumours.
If treatment with EpCAM-specific antibodies (that is, catumaxomab) is planned in patients with cancer, we suggest evaluation of EpCAM expression by immunohistochemistry on primary tumours or preferentially on metastases. This evaluation should be performed particularly in patients with breast cancer, renal cell cancer, squamous cell carcinomas, hepatocellular carcinomas and urothelial cancer.
Footnotes
Funding: This work was supported by the COMET Center ONCOTYROL and funded by the Federal Ministry for Transport Innovation and Technology (BMVIT) and the Federal Ministry of Economics and Labour/the Federal Ministry of Economy, Family and Youth (BMWA/BMWFJ), the Tiroler Zukunftsstiftung (TZS) and the State of Styria represented by the Styrian Business Promotion Agency (SFG). It was also supported by the Innsbruck Medical University, Fresenius Biotech GmbH, and TILAK Tiroler Landeskrankenanstalten GmbH (TILAK-Hospital Holding Company).
Competing interests: Gilbert Spizzo has served as consultant and advisory board member for Fresenius Biotech and received research funding for ONCOTYROL Project 3.5.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
References
- 1.Schmelzer E, Reid LM. EpCAM expression in normal, non-pathological tissues. Front Biosci 2008;13:3096–100 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Osta WA, Chen Y, Mikhitarian K, et al. EpCAM is overexpressed in breast cancer and is a potential target for breast cancer gene therapy. Cancer Res 2004;64:5818–24 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gastl G, Spizzo G, Obrist P, et al. Ep-CAM overexpression in breast cancer as a predictor of survival. Lancet 2000;356:1981–2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Spizzo G, Went P, Dirnhofer S, et al. High Ep-CAM expression is associated with poor prognosis in node-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2004;86:207–13 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Schmidt M, Hasenclever D, Schaeffer M, et al. Prognostic effect of epithelial cell adhesion molecule overexpression in untreated node-negative breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2008;14:5849–55 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Went PT, Lugli A, Meier S, et al. Frequent EpCam protein expression in human carcinomas. Hum Pathol 2004;35:122–8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Varga M, Obrist P, Schneeberger S, et al. Overexpression of epithelial cell adhesion molecule antigen in gallbladder carcinoma is an independent marker for poor survival. Clin Cancer Res 2004;10:3131–6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Spizzo G, Went P, Dirnhofer S, et al. Overexpression of epithelial cell adhesion molecule (Ep-CAM) is an independent prognostic marker for reduced survival of patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 2006;103:483–8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Fong D, Steurer M, Obrist P, et al. Ep-CAM expression in pancreatic and ampullary carcinomas: frequency and prognostic relevance. J Clin Pathol 2008;61:31–5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Munz M, Kieu C, Mack B, et al. The carcinoma-associated antigen EpCAM upregulates c-myc and induces cell proliferation. Oncogene 2004;23:5748–58 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Baeuerle PA, Gires O. EpCAM (CD326) finding its role in cancer. Br J Cancer 2007;96:4–2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Maetzel D, Denzel S, Mack B, et al. Nuclear signalling by tumour-associated antigen EpCAM. Nat Cell Biol 2009;11:1–71 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Spizzo G, Gastl G, Obrist P, et al. Methylation status of the Ep-CAM promoter region in human breast cancer cell lines and breast cancer tissue. Cancer Lett 2007;246:253–61 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sears HF, Atkinson B, Mattis J, et al. Phase-I clinical trial of monoclonal antibody in treatment of gastrointestinal tumours. Lancet 1982;1:762–5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chelius D, Ruf P, Gruber P, et al. Structural and functional characterization of the trifunctional antibody catumaxomab. MAbs 2010;2:309–19 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Heiss MM, Murawa P, Koralewski P, et al. The trifunctional antibody catumaxomab for the treatment of malignant ascites due to epithelial cancer: Results of a prospective randomized phase II/III trial. Int J Cancer 2010;127:2209–21 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Schmidt M, Scheulen ME, Dittrich C, et al. An open-label, randomized phase II study of adecatumumab, a fully human anti-EpCAM antibody, as monotherapy in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol 2010;21:275–82 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Brischwein K, Schlereth B, Guller B, et al. MT110: a novel bispecific single-chain antibody construct with high efficacy in eradicating established tumors. Mol Immunol 2006;43:1129–43 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Harvey JM, Clark GM, Osborne CK, et al. Estrogen receptor status by immunohistochemistry is superior to the ligand-binding assay for predicting response to adjuvant endocrine therapy in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 1999;17:1474–81 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rhodes A, Jasani B, Balaton AJ, et al. Study of interlaboratory reliability and reproducibility of estrogen and progesterone receptor assays in Europe. Documentation of poor reliability and identification of insufficient microwave antigen retrieval time as a major contributory element of unreliable assays. Am J Clin Pathol 2001;115:44–58 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Roche PC, Suman VJ, Jenkins RB, et al. Concordance between local and central laboratory HER2 testing in the breast intergroup trial N9831. J Natl Cancer Inst 2002;94:855–7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hammond ME, Hayes DF, Dowsett M, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/ College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 2010;28:2784–95 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Tzankov A, Zlobec I, Went P, et al. Prognostic immunophenotypic biomarker studies in diffuse large B cell lymphoma with special emphasis on rational determination of cut-off scores. Leuk Lymphoma 2010;51:199–212 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tandon AK, Clark GM, Chamness GC, et al. Association of the 323/A3 surface glycoprotein with tumor characteristics and behavior in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 1990;50:3317–21 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Laimer K, Fong D, Gastl G, et al. EpCAM expression in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity: frequency and relationship to clinicopathologic features. Oral Oncol 2008;44:72–7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ferlicot S, Vincent-Salomon A, Medioni J, et al. Wide metastatic spreading in infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast. Eur J Cancer 2004;40:336–41 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Punnoose EA, Atwal SK, Spoerke JM, et al. Molecular biomarker analyses using circulating tumor cells. PLoS One 2010;5:e12517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]