Abstract
In the title compound, 2C8H9BrO2·H2O, the O—C—C—C torsion angles for the hydroxyethyl group and the Br—C—C—O torsion angles involving bromo and phenol groups are 61.7 (11) and 0.7 (12)°, respectively, in one independent molecule and 61.5 (11) and 0.2 (11)°, respectively, in the other. In the crystal, molecules are linked through O—H⋯O and O—H⋯Br hydrogen bonds, forming a polymeric chain.
Related literature
For synthesis of the title compound and background information, see: Bovicelli et al. (2007 ▶). For a related structure, see: Mewett et al. (2009 ▶).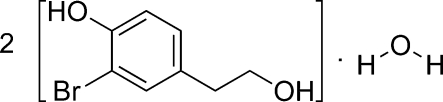
Experimental
Crystal data
2C8H9BrO2·H2O
M r = 452.14
Monoclinic,

a = 5.9790 (12) Å
b = 18.396 (4) Å
c = 16.801 (3) Å
β = 98.83 (3)°
V = 1826.0 (6) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 4.46 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.20 × 0.10 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Enraf–Nonius CAD-4 diffractometer
Absorption correction: ψ scan (ψ-scans; North et al., 1968 ▶) T min = 0.469, T max = 0.664
3585 measured reflections
1827 independent reflections
1302 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.045
3 standard reflections every 200 reflections intensity decay: 1%
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.045
wR(F 2) = 0.095
S = 1.01
1827 reflections
208 parameters
2 restraints
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.32 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.45 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 746 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: 0.00 (2)
Data collection: CAD-4 EXPRESS (Enraf–Nonius, 1989 ▶); cell refinement: CAD-4 EXPRESS; data reduction: XCAD4 (Harms & Wocadlo, 1995 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681101066X/pv2391sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681101066X/pv2391Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OW—HWA⋯Br1 | 0.89 | 2.86 | 3.537 (8) | 134 |
| OW—HWA⋯O2 | 0.89 | 2.00 | 2.820 (10) | 151 |
| O1—H1A⋯O4 | 0.82 | 1.84 | 2.633 (9) | 163 |
| OW—HWB⋯O1i | 0.88 | 2.07 | 2.745 (10) | 133 |
| O2—H2A⋯Br1 | 0.85 | 2.56 | 3.026 (6) | 115 |
| O2—H2A⋯OW | 0.85 | 2.18 | 2.820 (9) | 131 |
| O3—H3A⋯O2ii | 0.82 | 1.80 | 2.592 (9) | 162 |
| O4—H4B⋯Br2 | 0.85 | 2.57 | 3.039 (7) | 116 |
| O4—H4B⋯OWiii | 0.85 | 2.21 | 2.804 (10) | 127 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
This research work was supported financially by the Department of Science and Technology of Jiangsu Province (BE200830457) and the ‘863′ project (2007 A A02Z211) of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The title compound is used as the key intermediate in the synthesis of hydroxytyrosol (Bovicelli et al., 2007). As a part of our studies on the synthesis of hydroxytyrosol we report herein the crystal structure of the title compound.
In the molecules of the title compound, (Fig. 1), the bond lengths and angles agree very well with the corresponding bond lengths and angles reporeted in a structure containing the title compound as its fragment (Mewett et al., 2009).
In the crystal structure, O—H···O and O—H···Br type hydrogen bonding interactions (Table 1) link the molecules into ribbons extended along the a-axis (Fig. 2). The two molecules of the title compound in the asymmetric unit are identical. The torsion angles O1/C1/C2/C3 and C1/C2/C3/C8 are 61.7 (12) and -100.6 (11)°, respectively, in one molecule. The corresponding torion angles in the other molecule are 61.5 (11) and -101.5 (11)° (for O3/C9/C10/C11 and C9/C10/C11/C12, respectively).
Experimental
To a solution of 4-hydroxyphenethyl alcohol (217.4 mmol, 30 g) and NaBr (217.4 mmol, 22.17 g) in acetone (600 ml), a solution of oxone (200 g) in water (1 L) was added dropwise at 263 K within 3 h. The progress of the reaction was monitored by thin-layer chromatography (TLC, hexane/ethyl acetate 6:4), and when the reaction was over (complete consumption of the substrate), AcOEt (500 ml) was added to the mixture. The organic layer was separated, and the aqueous phase was extracted with two 300 mL portions of AcOEt. The combined organic solutions were washed with water (300 ml), dried over anhydrous Na2SO4 (100 g), and evaporated. The monobrominated product, obtained in almost quantitative yield (47.1 g), appeared to be spectroscopically pure, white solid (Bovicelli et al., 2007). Crystals of (I) suitable for X-ray diffraction were obtained by slow evaporation of an ethanol solution.
Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically with C—H = 0.93, 0.98 and 0.97 Å for aromatic, methine and methylene H atoms, respectively, and constrained to ride on their parent atoms, with Uiso(H) = 1.2 (or 1.5 for methyl groups) times Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title molecule, with the atom numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at 30% probability levels.
Fig. 2.
A practical packing diagram of the title compound. Hydron bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| 2C8H9BrO2·H2O | F(000) = 904 |
| Mr = 452.14 | Dx = 1.645 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, Cc | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: C -2yc | Cell parameters from 25 reflections |
| a = 5.9790 (12) Å | θ = 9–13° |
| b = 18.396 (4) Å | µ = 4.46 mm−1 |
| c = 16.801 (3) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 98.83 (3)° | Block, colorless |
| V = 1826.0 (6) Å3 | 0.20 × 0.10 × 0.10 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Enraf–Nonius CAD-4 diffractometer | 1302 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.045 |
| graphite | θmax = 25.3°, θmin = 2.2° |
| ω/2θ scans | h = 0→7 |
| Absorption correction: ψ scan (ψ-scans; North et al., 1968) | k = −22→22 |
| Tmin = 0.469, Tmax = 0.664 | l = −20→19 |
| 3585 measured reflections | 3 standard reflections every 200 reflections |
| 1827 independent reflections | intensity decay: 1% |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.045 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.095 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.050P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.01 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 1827 reflections | Δρmax = 0.32 e Å−3 |
| 208 parameters | Δρmin = −0.45 e Å−3 |
| 2 restraints | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 746 Friedel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Flack parameter: 0.00 (2) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br2 | 0.98869 (14) | 0.25839 (6) | 0.74826 (7) | 0.0700 (4) | |
| O3 | 0.7384 (12) | 0.5738 (3) | 0.6248 (4) | 0.0621 (18) | |
| H3A | 0.8398 | 0.5653 | 0.5983 | 0.093* | |
| O4 | 0.5409 (11) | 0.2412 (3) | 0.6368 (4) | 0.0566 (17) | |
| H4B | 0.6442 | 0.2103 | 0.6523 | 0.068* | |
| C9 | 0.827 (2) | 0.5705 (6) | 0.7086 (6) | 0.060 (3) | |
| H9A | 0.8513 | 0.6194 | 0.7299 | 0.072* | |
| H9B | 0.9718 | 0.5455 | 0.7161 | 0.072* | |
| C10 | 0.6614 (18) | 0.5301 (5) | 0.7535 (6) | 0.061 (3) | |
| H10A | 0.7193 | 0.5299 | 0.8107 | 0.073* | |
| H10B | 0.5173 | 0.5554 | 0.7458 | 0.073* | |
| C11 | 0.6262 (19) | 0.4526 (5) | 0.7238 (6) | 0.053 (3) | |
| C12 | 0.4362 (16) | 0.4334 (5) | 0.6716 (5) | 0.048 (2) | |
| H12A | 0.3248 | 0.4680 | 0.6560 | 0.058* | |
| C13 | 0.4082 (16) | 0.3643 (5) | 0.6423 (5) | 0.051 (2) | |
| H13A | 0.2781 | 0.3530 | 0.6066 | 0.062* | |
| C14 | 0.5678 (14) | 0.3105 (5) | 0.6643 (5) | 0.044 (2) | |
| C15 | 0.7609 (14) | 0.3305 (5) | 0.7164 (5) | 0.042 (2) | |
| C16 | 0.7941 (16) | 0.3996 (5) | 0.7461 (6) | 0.052 (2) | |
| H16A | 0.9260 | 0.4113 | 0.7807 | 0.062* | |
| OW | 0.3419 (11) | 0.6470 (4) | 0.5757 (5) | 0.074 (2) | |
| HWA | 0.2649 | 0.6129 | 0.5450 | 0.089* | |
| HWB | 0.3857 | 0.6750 | 0.5383 | 0.089* | |
| Br1 | 0.34194 (14) | 0.53555 (5) | 0.40416 (7) | 0.0640 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.1966 (11) | 0.2167 (3) | 0.5222 (4) | 0.064 (2) | |
| H1A | 0.3182 | 0.2261 | 0.5501 | 0.096* | |
| C1 | 0.2190 (18) | 0.2218 (6) | 0.4413 (6) | 0.054 (3) | |
| H1B | 0.2241 | 0.1734 | 0.4187 | 0.065* | |
| H1C | 0.3597 | 0.2463 | 0.4361 | 0.065* | |
| O2 | −0.0093 (10) | 0.5504 (3) | 0.5150 (4) | 0.0542 (17) | |
| H2A | 0.0843 | 0.5814 | 0.5021 | 0.065* | |
| C2 | 0.0224 (18) | 0.2636 (5) | 0.3950 (6) | 0.058 (3) | |
| H2B | 0.0376 | 0.2644 | 0.3383 | 0.069* | |
| H2C | −0.1178 | 0.2388 | 0.4002 | 0.069* | |
| C3 | 0.0112 (17) | 0.3401 (5) | 0.4246 (5) | 0.049 (2) | |
| C4 | 0.1511 (15) | 0.3940 (5) | 0.4051 (5) | 0.044 (2) | |
| H4A | 0.2537 | 0.3834 | 0.3703 | 0.053* | |
| C5 | 0.1449 (15) | 0.4620 (5) | 0.4346 (5) | 0.045 (2) | |
| C6 | −0.0025 (16) | 0.4810 (5) | 0.4867 (5) | 0.044 (2) | |
| C7 | −0.1492 (16) | 0.4280 (5) | 0.5058 (5) | 0.051 (2) | |
| H7A | −0.2543 | 0.4396 | 0.5393 | 0.061* | |
| C8 | −0.1427 (15) | 0.3594 (5) | 0.4767 (6) | 0.050 (2) | |
| H8A | −0.2415 | 0.3246 | 0.4914 | 0.060* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br2 | 0.0482 (5) | 0.0791 (8) | 0.0764 (7) | 0.0122 (6) | −0.0106 (5) | 0.0016 (7) |
| O3 | 0.073 (5) | 0.066 (4) | 0.054 (4) | 0.009 (4) | 0.032 (4) | 0.004 (3) |
| O4 | 0.045 (4) | 0.050 (4) | 0.072 (4) | 0.009 (4) | −0.002 (3) | −0.008 (4) |
| C9 | 0.070 (7) | 0.047 (6) | 0.066 (7) | −0.003 (5) | 0.018 (6) | −0.007 (5) |
| C10 | 0.064 (7) | 0.064 (7) | 0.058 (6) | −0.005 (6) | 0.019 (5) | −0.007 (5) |
| C11 | 0.065 (7) | 0.058 (6) | 0.039 (6) | −0.006 (6) | 0.017 (5) | 0.010 (5) |
| C12 | 0.038 (5) | 0.060 (6) | 0.046 (5) | 0.001 (5) | 0.002 (4) | −0.004 (5) |
| C13 | 0.033 (5) | 0.062 (7) | 0.057 (6) | 0.002 (5) | 0.001 (4) | −0.008 (5) |
| C14 | 0.035 (5) | 0.056 (6) | 0.040 (5) | −0.008 (4) | 0.001 (4) | 0.000 (4) |
| C15 | 0.032 (5) | 0.051 (6) | 0.043 (5) | 0.002 (4) | 0.004 (4) | 0.009 (4) |
| C16 | 0.043 (6) | 0.066 (7) | 0.046 (6) | −0.009 (5) | 0.005 (4) | −0.001 (5) |
| OW | 0.059 (5) | 0.071 (4) | 0.095 (5) | −0.010 (4) | 0.020 (4) | −0.024 (4) |
| Br1 | 0.0591 (6) | 0.0682 (6) | 0.0715 (7) | −0.0019 (6) | 0.0322 (5) | 0.0040 (6) |
| O1 | 0.054 (4) | 0.067 (4) | 0.062 (4) | −0.012 (4) | −0.020 (4) | 0.005 (3) |
| C1 | 0.054 (7) | 0.049 (6) | 0.058 (7) | 0.015 (5) | 0.004 (5) | 0.003 (5) |
| O2 | 0.043 (4) | 0.050 (4) | 0.074 (4) | −0.005 (3) | 0.022 (3) | −0.002 (3) |
| C2 | 0.059 (7) | 0.069 (7) | 0.045 (6) | 0.007 (6) | 0.006 (5) | −0.009 (5) |
| C3 | 0.051 (6) | 0.048 (6) | 0.044 (6) | 0.005 (5) | −0.008 (5) | −0.001 (5) |
| C4 | 0.041 (5) | 0.053 (6) | 0.039 (5) | −0.001 (5) | 0.005 (4) | −0.001 (5) |
| C5 | 0.044 (5) | 0.051 (5) | 0.042 (5) | −0.004 (4) | 0.009 (4) | 0.006 (5) |
| C6 | 0.039 (5) | 0.051 (7) | 0.042 (5) | 0.003 (5) | 0.009 (4) | −0.002 (5) |
| C7 | 0.038 (5) | 0.067 (7) | 0.050 (5) | 0.012 (5) | 0.013 (4) | 0.003 (5) |
| C8 | 0.037 (5) | 0.053 (6) | 0.059 (6) | 0.001 (5) | 0.007 (5) | 0.001 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Br2—C15 | 1.918 (8) | OW—HWB | 0.8827 |
| O3—C9 | 1.428 (11) | Br1—C5 | 1.915 (9) |
| O3—H3A | 0.8200 | O1—C1 | 1.391 (12) |
| O4—C14 | 1.357 (11) | O1—H1A | 0.8200 |
| O4—H4B | 0.8500 | C1—C2 | 1.515 (14) |
| C9—C10 | 1.529 (14) | C1—H1B | 0.9700 |
| C9—H9A | 0.9700 | C1—H1C | 0.9700 |
| C9—H9B | 0.9700 | O2—C6 | 1.365 (10) |
| C10—C11 | 1.515 (13) | O2—H2A | 0.8500 |
| C10—H10A | 0.9700 | C2—C3 | 1.497 (12) |
| C10—H10B | 0.9700 | C2—H2B | 0.9700 |
| C11—C12 | 1.370 (14) | C2—H2C | 0.9700 |
| C11—C16 | 1.409 (14) | C3—C4 | 1.370 (12) |
| C12—C13 | 1.364 (12) | C3—C8 | 1.410 (13) |
| C12—H12A | 0.9300 | C4—C5 | 1.348 (11) |
| C13—C14 | 1.385 (12) | C4—H4A | 0.9300 |
| C13—H13A | 0.9300 | C5—C6 | 1.380 (12) |
| C14—C15 | 1.388 (11) | C6—C7 | 1.382 (12) |
| C15—C16 | 1.368 (12) | C7—C8 | 1.355 (12) |
| C16—H16A | 0.9300 | C7—H7A | 0.9300 |
| OW—HWA | 0.8938 | C8—H8A | 0.9300 |
| C9—O3—H3A | 109.5 | C1—O1—H1A | 109.5 |
| C14—O4—H4B | 118.7 | O1—C1—C2 | 110.7 (8) |
| O3—C9—C10 | 109.7 (8) | O1—C1—H1B | 109.5 |
| O3—C9—H9A | 109.7 | C2—C1—H1B | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—H9A | 109.7 | O1—C1—H1C | 109.5 |
| O3—C9—H9B | 109.7 | C2—C1—H1C | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—H9B | 109.7 | H1B—C1—H1C | 108.1 |
| H9A—C9—H9B | 108.2 | C6—O2—H2A | 118.8 |
| C11—C10—C9 | 111.3 (8) | C3—C2—C1 | 112.2 (8) |
| C11—C10—H10A | 109.4 | C3—C2—H2B | 109.2 |
| C9—C10—H10A | 109.4 | C1—C2—H2B | 109.2 |
| C11—C10—H10B | 109.4 | C3—C2—H2C | 109.2 |
| C9—C10—H10B | 109.4 | C1—C2—H2C | 109.2 |
| H10A—C10—H10B | 108.0 | H2B—C2—H2C | 107.9 |
| C12—C11—C16 | 118.6 (9) | C4—C3—C8 | 116.5 (8) |
| C12—C11—C10 | 120.8 (10) | C4—C3—C2 | 122.7 (9) |
| C16—C11—C10 | 120.5 (10) | C8—C3—C2 | 120.7 (9) |
| C13—C12—C11 | 121.0 (10) | C5—C4—C3 | 122.1 (9) |
| C13—C12—H12A | 119.5 | C5—C4—H4A | 119.0 |
| C11—C12—H12A | 119.5 | C3—C4—H4A | 119.0 |
| C12—C13—C14 | 121.9 (9) | C4—C5—C6 | 121.8 (8) |
| C12—C13—H13A | 119.1 | C4—C5—Br1 | 120.2 (6) |
| C14—C13—H13A | 119.1 | C6—C5—Br1 | 118.0 (7) |
| O4—C14—C13 | 122.7 (8) | O2—C6—C5 | 121.0 (8) |
| O4—C14—C15 | 120.5 (8) | O2—C6—C7 | 121.7 (8) |
| C13—C14—C15 | 116.8 (9) | C5—C6—C7 | 117.2 (8) |
| C16—C15—C14 | 122.5 (8) | C8—C7—C6 | 121.3 (9) |
| C16—C15—Br2 | 118.9 (7) | C8—C7—H7A | 119.4 |
| C14—C15—Br2 | 118.6 (7) | C6—C7—H7A | 119.4 |
| C15—C16—C11 | 119.2 (9) | C7—C8—C3 | 121.1 (9) |
| C15—C16—H16A | 120.4 | C7—C8—H8A | 119.5 |
| C11—C16—H16A | 120.4 | C3—C8—H8A | 119.5 |
| HWA—OW—HWB | 100.5 | ||
| O3—C9—C10—C11 | 61.5 (11) | O1—C1—C2—C3 | 61.7 (11) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | −101.5 (11) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | 77.6 (11) |
| C9—C10—C11—C16 | 75.1 (12) | C1—C2—C3—C8 | −100.6 (11) |
| C16—C11—C12—C13 | 0.7 (14) | C8—C3—C4—C5 | 0.8 (14) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | 177.4 (9) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | −177.4 (8) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.6 (15) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.3 (14) |
| C12—C13—C14—O4 | 178.9 (9) | C3—C4—C5—Br1 | −179.2 (7) |
| C12—C13—C14—C15 | −1.3 (13) | C4—C5—C6—O2 | −178.8 (8) |
| O4—C14—C15—C16 | −179.4 (8) | Br1—C5—C6—O2 | 0.7 (12) |
| C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.8 (13) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | −1.8 (13) |
| O4—C14—C15—Br2 | 0.2 (11) | Br1—C5—C6—C7 | 177.7 (7) |
| C13—C14—C15—Br2 | −179.6 (6) | O2—C6—C7—C8 | 179.3 (8) |
| C14—C15—C16—C11 | 0.5 (14) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | 2.3 (14) |
| Br2—C15—C16—C11 | −179.2 (7) | C6—C7—C8—C3 | −1.2 (14) |
| C12—C11—C16—C15 | −1.2 (14) | C4—C3—C8—C7 | −0.3 (14) |
| C10—C11—C16—C15 | −177.9 (8) | C2—C3—C8—C7 | 177.9 (9) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| OW—HWA···Br1 | 0.89 | 2.86 | 3.537 (8) | 134 |
| OW—HWA···O2 | 0.89 | 2.00 | 2.820 (10) | 151 |
| O1—H1A···O4 | 0.82 | 1.84 | 2.633 (9) | 163 |
| OW—HWB···O1i | 0.88 | 2.07 | 2.745 (10) | 133 |
| O2—H2A···Br1 | 0.85 | 2.56 | 3.026 (6) | 115 |
| O2—H2A···OW | 0.85 | 2.18 | 2.820 (9) | 131 |
| O3—H3A···O2ii | 0.82 | 1.80 | 2.592 (9) | 162 |
| O4—H4B···Br2 | 0.85 | 2.57 | 3.039 (7) | 116 |
| O4—H4B···OWiii | 0.85 | 2.21 | 2.804 (10) | 127 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1/2, y+1/2, z; (ii) x+1, y, z; (iii) x+1/2, y−1/2, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: PV2391).
References
- Bovicelli, P., Antonioletti, R., Mancini, S., Causio, S., Borioni, G., Ammendola, S. & Barontini, M. (2007). Synth. Commun. 37, 4245–4252.
- Enraf–Nonius (1989). CAD-4 EXPRESS. Enraf–Nonius, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Harms, K. & Wocadlo, S. (1995). XCAD4 University of Marburg, Germany.
- Mewett, K. N., Fernandez, S. P., Pasricha, A. K., Pong, A., Devenish, S. O., Hibbs, D. E., Chebib, M., Johnston, G. A. & Hanrahan, J. R. (2009). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17, 7156–7173. [DOI] [PubMed]
- North, A. C. T., Phillips, D. C. & Mathews, F. S. (1968). Acta Cryst. A24, 351–359.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681101066X/pv2391sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681101066X/pv2391Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




