Abstract
The crystal structure of the title compound, C6H16N+·C19H18O2PS2 −, consists of the dithiophosphonate anions and the triethylammonium cations, which are linked by N—H⋯S hydrogen bonds and weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. In the anion, the benzene ring is oriented with respect to the naphthalene ring system at a dihedral angle of 24.92 (5)°. In the crystal, weak C—H⋯π interactions also occur.
Related literature
For dithiophosphorus compounds and their complexes, see: Heiduc et al. (2006 ▶); Karakuş et al. (2007 ▶); Gataulina et al. (2008 ▶). For the roles of dithiophosphorus compounds in agricultural, industrial and medicinal products such as additives to lubricant oils, solvent extraction reagents for metals, floatation agents for minerals, pesticides and insecticides, see: Thomas et al. (2001 ▶); Gray et al. (2003 ▶). For the synthetic routes reported for dithiophosphorus-type ligands, see: Alberti et al. (2007 ▶). For the preparation of ferrocenyl and aryldithiophosphonates and their complexes with a range of transition metals, see: Gray et al. (2004 ▶). For bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶).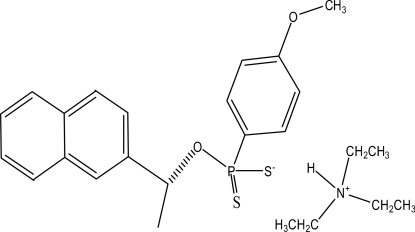
Experimental
Crystal data
C6H16N+·C19H18O2PS2 −
M r = 475.62
Orthorhombic,

a = 9.3782 (3) Å
b = 12.3467 (5) Å
c = 21.9651 (8) Å
V = 2543.33 (16) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.29 mm−1
T = 294 K
0.52 × 0.36 × 0.32 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.862, T max = 0.912
43596 measured reflections
6343 independent reflections
5946 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.030
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.036
wR(F 2) = 0.094
S = 1.06
6343 reflections
289 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.78 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.26 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 2752 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: −0.01 (6)
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811015820/xu5201sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811015820/xu5201Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811015820/xu5201Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the C1–C6 and C10–C13/C18/C19 rings, respectively.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯S2i | 0.84 (3) | 2.52 (3) | 3.2911 (17) | 154 (2) |
| C20—H20A⋯O1 | 0.97 | 2.56 | 3.505 (2) | 166 |
| C7—H7B⋯Cg2ii | 0.96 | 2.90 | 3.658 (3) | 137 |
| C24—H24B⋯Cg1iii | 0.97 | 2.79 | 3.750 (2) | 171 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to Anadolu University and the Medicinal Plants and Medicine Research Centre of Anadolu University, Eskişehir, Turkey, for the use of the diffractometer. This work was supported financially by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (grant No. 107T817).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Dithiophosphorus compounds and their complexes have been widely investigated in last decades (Heiduc et al., 2006; Karakuş et al., 2007; Gataulina et al., 2008). They have been utilized in agricultural, industrial and medicinal products such as additive to lubricant oils, solvent extraction reagents for metals, floatation agents for minerals, pectidites and insecticides (Thomas et al., 2001; Gray et al., 2003). For example, tin diphenyldithiophosphinato complexes show an antiproliferation activity towards certain leukaemia cells (Gray et al., 2003). In general, dithiophosphorus type ligands are not commercially available, but a few synthetic routes were reported in the literature (Alberti et al., 2007). When compared to the other dithiophosphorus derivatives, there is very limited research on dithiophosphonates in the last century, due to the difficulties in sythesizing these compounds. Recently, ferrocenyl and aryldithiophosphonates and their complexes with a range of transition metals were prepared by Woolins et al. (Gray et al., 2003; Gray et al., 2004). The present study was undertaken to ascertain the crystal structure of the title compound to contribute to this relatively less developed area.
The title compound consists of a dithiophosphonate bridged napthylethyl and methoxyphenyl groups and a triethylammonium moiety linked by a C-H···O hydrogen bond (Table 1 and Fig. 1), where the bond lengths are close to standard values (Allen et al., 1987).
An examination of the deviations from the least-squares planes through individual rings shows that rings A (C1—C6), B (C10—C13/C18/C19) and C (C13—C18) are planar. The naphthalene group, containing the rings B and C are also nearly planar [with a maximum deviation of -0.022 (2) Å for atom C13] with a dihedral angle of B/C = 1.67 (7)°. Ring A is oriented with respect to the planar naphthalene group at a dihedral angle of 24.92 (5)°.
In the crystal, C—H···O and N-H···S hydrogen bonds link the molecules into chains along [100] (Table 1 and Fig. 2). There also exist two weak C-H···π interactions (Table 1).
Experimental
For the preparation of the title compound, (I), 2,4-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,3,2,4-dithiadiphosphetane-2,4-disulfide (0.51 g, 1.23 mmol) and (S)-(-)-1-(2-naphthyl)ethanol (0.43 g, 2.46 mmol) were suspended in toluene (20 ml). The mixture was refluxed until all solids had dissolved. The yellow solution was cooled to room temperature, filtered and treated with excess triethyl amine. The product was precipitated at 291 K from hexane/toluene (1:4) as colorless crystals. They were isolated by filtration, washed with n-pentane and dried in air (yield; 0.85 g, 72.64%, m.p. 359-360 K).
Refinement
H1 atom is located in a difference Fourier synthesis and refined isotropically. The C-bound H-atoms were positioned geometrically with C—H = 0.93, 0.98, 0.97 and 0.96 Å, for aromatic, methine, methylene and methyl H-atoms, respectively, and constrained to ride on their parent atoms, with Uiso(H) = k × Ueq(C), where k = 1.5 for methyl H-atoms and k = 1.2 for all other H-atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title molecule with the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. C—H···O hydrogen bond is shown as dashed line.
Fig. 2.
A view of the crystal packing of the title compound. The C-H···O and N-H···S hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines [H-atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been omitted for clarity].
Crystal data
| C6H16N+·C19H18O2PS2− | F(000) = 1016 |
| Mr = 475.62 | Dx = 1.242 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 9895 reflections |
| a = 9.3782 (3) Å | θ = 2.7–28.4° |
| b = 12.3467 (5) Å | µ = 0.29 mm−1 |
| c = 21.9651 (8) Å | T = 294 K |
| V = 2543.33 (16) Å3 | Block, colorless |
| Z = 4 | 0.52 × 0.36 × 0.32 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer | 6343 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 5946 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.030 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 28.4°, θmin = 1.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005) | h = −11→12 |
| Tmin = 0.862, Tmax = 0.912 | k = −15→16 |
| 43596 measured reflections | l = −29→29 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.036 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.094 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0477P)2 + 1.2869P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.06 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 6343 reflections | Δρmax = 0.78 e Å−3 |
| 289 parameters | Δρmin = −0.26 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 2752 Friedel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Flack parameter: −0.01 (6) |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.60412 (5) | 0.18821 (4) | 0.04905 (2) | 0.02652 (11) | |
| S2 | 0.57588 (5) | 0.14708 (4) | 0.19936 (2) | 0.02634 (11) | |
| P1 | 0.48082 (5) | 0.18524 (4) | 0.12180 (2) | 0.01859 (10) | |
| O1 | 0.34594 (14) | 0.10520 (11) | 0.11076 (6) | 0.0211 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.14963 (18) | 0.59555 (13) | 0.14733 (7) | 0.0327 (3) | |
| N1 | −0.09897 (17) | 0.20257 (14) | 0.15241 (7) | 0.0233 (3) | |
| H1 | −0.187 (3) | 0.190 (2) | 0.1517 (11) | 0.029 (6)* | |
| C1 | 0.38210 (18) | 0.31092 (15) | 0.12904 (8) | 0.0192 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.3729 (2) | 0.36634 (17) | 0.18402 (8) | 0.0235 (4) | |
| H2 | 0.4193 | 0.3392 | 0.2182 | 0.028* | |
| C3 | 0.2957 (2) | 0.46103 (17) | 0.18858 (9) | 0.0264 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.2904 | 0.4972 | 0.2257 | 0.032* | |
| C4 | 0.2256 (2) | 0.50278 (16) | 0.13774 (9) | 0.0235 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.2361 (2) | 0.44975 (16) | 0.08213 (9) | 0.0229 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.1911 | 0.4777 | 0.0478 | 0.027* | |
| C6 | 0.3143 (2) | 0.35486 (17) | 0.07823 (8) | 0.0222 (4) | |
| H6 | 0.3217 | 0.3197 | 0.0409 | 0.027* | |
| C7 | 0.0639 (3) | 0.6348 (2) | 0.09831 (11) | 0.0393 (5) | |
| H7A | 0.0105 | 0.6967 | 0.1117 | 0.059* | |
| H7B | −0.0007 | 0.5790 | 0.0854 | 0.059* | |
| H7C | 0.1241 | 0.6551 | 0.0649 | 0.059* | |
| C8 | 0.3722 (2) | −0.00862 (16) | 0.09988 (10) | 0.0261 (4) | |
| H8 | 0.4752 | −0.0209 | 0.0970 | 0.031* | |
| C9 | 0.3140 (3) | −0.07059 (18) | 0.15388 (11) | 0.0331 (5) | |
| H9A | 0.3298 | −0.1467 | 0.1480 | 0.050* | |
| H9B | 0.2136 | −0.0571 | 0.1576 | 0.050* | |
| H9C | 0.3617 | −0.0473 | 0.1903 | 0.050* | |
| C10 | 0.3016 (2) | −0.03846 (18) | 0.03867 (10) | 0.0291 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.2350 (2) | 0.04142 (18) | 0.00213 (10) | 0.0295 (4) | |
| H11 | 0.2360 | 0.1134 | 0.0146 | 0.035* | |
| C12 | 0.1688 (2) | 0.01411 (19) | −0.05147 (11) | 0.0322 (4) | |
| H12 | 0.1235 | 0.0672 | −0.0744 | 0.039* | |
| C13 | 0.1694 (2) | −0.09410 (19) | −0.07195 (10) | 0.0308 (4) | |
| C14 | 0.1044 (2) | −0.1237 (2) | −0.12876 (11) | 0.0358 (5) | |
| H14 | 0.0577 | −0.0718 | −0.1521 | 0.043* | |
| C15 | 0.1116 (3) | −0.2262 (2) | −0.14773 (11) | 0.0381 (5) | |
| H15 | 0.0704 | −0.2448 | −0.1848 | 0.046* | |
| C16 | 0.1806 (3) | −0.3082 (2) | −0.11267 (11) | 0.0406 (5) | |
| H16 | 0.1840 | −0.3790 | −0.1270 | 0.049* | |
| C17 | 0.2415 (3) | −0.28267 (19) | −0.05816 (11) | 0.0363 (5) | |
| H17 | 0.2852 | −0.3362 | −0.0350 | 0.044* | |
| C18 | 0.2382 (2) | −0.17606 (17) | −0.03732 (9) | 0.0264 (4) | |
| C19 | 0.3031 (2) | −0.14337 (19) | 0.01921 (10) | 0.0301 (4) | |
| H19 | 0.3475 | −0.1955 | 0.0432 | 0.036* | |
| C20 | −0.0239 (2) | 0.14297 (19) | 0.10174 (10) | 0.0304 (4) | |
| H20A | 0.0780 | 0.1436 | 0.1093 | 0.037* | |
| H20B | −0.0410 | 0.1803 | 0.0636 | 0.037* | |
| C21 | −0.0742 (3) | 0.0270 (2) | 0.09624 (13) | 0.0425 (6) | |
| H21A | −0.0452 | −0.0130 | 0.1316 | 0.064* | |
| H21B | −0.0330 | −0.0053 | 0.0606 | 0.064* | |
| H21C | −0.1763 | 0.0256 | 0.0930 | 0.064* | |
| C22 | −0.0597 (2) | 0.16311 (18) | 0.21476 (9) | 0.0292 (4) | |
| H22B | −0.0739 | 0.0854 | 0.2164 | 0.035* | |
| H22A | −0.1235 | 0.1960 | 0.2442 | 0.035* | |
| C23 | 0.0930 (2) | 0.1883 (2) | 0.23275 (10) | 0.0356 (5) | |
| H23A | 0.1128 | 0.1572 | 0.2719 | 0.053* | |
| H23B | 0.1060 | 0.2653 | 0.2346 | 0.053* | |
| H23C | 0.1569 | 0.1582 | 0.2031 | 0.053* | |
| C24 | −0.0782 (2) | 0.32156 (17) | 0.14353 (10) | 0.0305 (4) | |
| H24A | −0.1139 | 0.3416 | 0.1036 | 0.037* | |
| H24B | 0.0230 | 0.3375 | 0.1445 | 0.037* | |
| C25 | −0.1526 (3) | 0.3895 (2) | 0.19115 (12) | 0.0438 (6) | |
| H25A | −0.1499 | 0.4643 | 0.1792 | 0.066* | |
| H25B | −0.1051 | 0.3810 | 0.2296 | 0.066* | |
| H25C | −0.2500 | 0.3665 | 0.1949 | 0.066* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0237 (2) | 0.0337 (2) | 0.0222 (2) | 0.0015 (2) | 0.00873 (17) | 0.0038 (2) |
| S2 | 0.0195 (2) | 0.0391 (3) | 0.0204 (2) | 0.00257 (18) | −0.00307 (17) | 0.0067 (2) |
| P1 | 0.01450 (18) | 0.0253 (2) | 0.01599 (19) | −0.00017 (17) | 0.00075 (15) | 0.00270 (18) |
| O1 | 0.0184 (6) | 0.0224 (6) | 0.0225 (6) | −0.0001 (5) | 0.0014 (5) | −0.0009 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0394 (8) | 0.0292 (8) | 0.0294 (8) | 0.0085 (6) | −0.0055 (6) | −0.0048 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0169 (7) | 0.0286 (9) | 0.0245 (8) | −0.0022 (6) | 0.0012 (6) | 0.0043 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0180 (7) | 0.0228 (8) | 0.0167 (8) | −0.0016 (7) | −0.0001 (6) | 0.0010 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0263 (9) | 0.0282 (10) | 0.0161 (8) | −0.0030 (7) | −0.0046 (6) | 0.0013 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0322 (10) | 0.0281 (10) | 0.0190 (9) | −0.0016 (8) | −0.0033 (7) | −0.0057 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0233 (9) | 0.0222 (9) | 0.0248 (10) | −0.0021 (7) | −0.0008 (7) | −0.0013 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0236 (9) | 0.0276 (10) | 0.0176 (9) | 0.0016 (7) | −0.0029 (7) | 0.0024 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0227 (8) | 0.0288 (9) | 0.0150 (8) | 0.0007 (7) | 0.0002 (6) | −0.0009 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0469 (14) | 0.0349 (12) | 0.0360 (12) | 0.0139 (11) | −0.0034 (10) | 0.0013 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0228 (9) | 0.0237 (9) | 0.0317 (10) | 0.0011 (7) | 0.0058 (8) | −0.0022 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0378 (12) | 0.0277 (11) | 0.0338 (11) | 0.0008 (9) | 0.0010 (9) | 0.0060 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0249 (9) | 0.0300 (10) | 0.0325 (11) | −0.0059 (8) | 0.0099 (8) | −0.0050 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0312 (10) | 0.0282 (10) | 0.0292 (11) | 0.0023 (8) | 0.0028 (8) | −0.0004 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0323 (10) | 0.0318 (11) | 0.0324 (11) | 0.0051 (9) | 0.0000 (9) | 0.0051 (9) |
| C13 | 0.0269 (10) | 0.0309 (11) | 0.0346 (11) | 0.0006 (8) | 0.0049 (8) | 0.0011 (9) |
| C14 | 0.0275 (10) | 0.0462 (13) | 0.0336 (11) | −0.0018 (9) | −0.0005 (9) | −0.0022 (10) |
| C15 | 0.0341 (11) | 0.0497 (14) | 0.0304 (11) | −0.0024 (10) | −0.0062 (9) | −0.0061 (10) |
| C16 | 0.0425 (13) | 0.0359 (12) | 0.0432 (13) | −0.0048 (11) | −0.0009 (10) | −0.0022 (11) |
| C17 | 0.0392 (12) | 0.0289 (11) | 0.0409 (13) | 0.0010 (9) | −0.0019 (10) | −0.0011 (9) |
| C18 | 0.0200 (8) | 0.0276 (10) | 0.0316 (10) | −0.0024 (7) | 0.0021 (7) | 0.0047 (8) |
| C19 | 0.0261 (10) | 0.0301 (10) | 0.0341 (11) | 0.0026 (8) | −0.0016 (8) | 0.0056 (9) |
| C20 | 0.0208 (9) | 0.0390 (11) | 0.0315 (10) | −0.0016 (8) | 0.0026 (7) | −0.0054 (9) |
| C21 | 0.0301 (11) | 0.0376 (13) | 0.0597 (16) | 0.0023 (10) | −0.0012 (11) | −0.0117 (11) |
| C22 | 0.0237 (9) | 0.0366 (12) | 0.0271 (9) | −0.0038 (8) | −0.0005 (7) | 0.0099 (8) |
| C23 | 0.0259 (10) | 0.0507 (13) | 0.0302 (10) | −0.0059 (10) | −0.0052 (8) | 0.0083 (10) |
| C24 | 0.0340 (10) | 0.0279 (10) | 0.0295 (9) | −0.0025 (9) | 0.0022 (8) | 0.0040 (8) |
| C25 | 0.0553 (15) | 0.0315 (12) | 0.0445 (14) | 0.0017 (11) | 0.0031 (12) | −0.0052 (11) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| S1—P1 | 1.9726 (6) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| S2—P1 | 1.9798 (6) | C12—C13 | 1.410 (3) |
| P1—O1 | 1.6234 (14) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| P1—C1 | 1.8140 (19) | C13—C14 | 1.436 (3) |
| O1—C8 | 1.447 (2) | C13—C18 | 1.421 (3) |
| O2—C4 | 1.365 (2) | C14—C15 | 1.335 (4) |
| O2—C7 | 1.429 (3) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C20 | 1.509 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.427 (4) |
| N1—C22 | 1.500 (2) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C24 | 1.495 (3) | C16—C17 | 1.364 (3) |
| N1—H1 | 0.84 (3) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.391 (3) | C17—C18 | 1.394 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.379 (3) | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C18—C19 | 1.441 (3) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C19—H19 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C3 | 1.395 (3) | C20—H20A | 0.9700 |
| C4—C5 | 1.390 (3) | C20—H20B | 0.9700 |
| C5—C6 | 1.385 (3) | C21—C20 | 1.513 (3) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C21—H21A | 0.9600 |
| C6—C1 | 1.395 (2) | C21—H21B | 0.9600 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C21—H21C | 0.9600 |
| C7—H7A | 0.9600 | C22—C23 | 1.518 (3) |
| C7—H7B | 0.9600 | C22—H22A | 0.9700 |
| C7—H7C | 0.9600 | C22—H22B | 0.9700 |
| C8—C9 | 1.513 (3) | C23—H23A | 0.9600 |
| C8—C10 | 1.543 (3) | C23—H23B | 0.9600 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9800 | C23—H23C | 0.9600 |
| C9—H9A | 0.9600 | C24—H24A | 0.9700 |
| C9—H9B | 0.9600 | C24—H24B | 0.9700 |
| C9—H9C | 0.9600 | C25—C24 | 1.512 (3) |
| C10—C11 | 1.417 (3) | C25—H25A | 0.9600 |
| C10—C19 | 1.364 (3) | C25—H25B | 0.9600 |
| C11—C12 | 1.373 (3) | C25—H25C | 0.9600 |
| S1—P1—S2 | 115.95 (3) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.8 |
| O1—P1—S1 | 110.31 (5) | C12—C13—C14 | 121.1 (2) |
| O1—P1—S2 | 109.54 (5) | C12—C13—C18 | 120.4 (2) |
| O1—P1—C1 | 97.83 (8) | C18—C13—C14 | 118.5 (2) |
| C1—P1—S1 | 110.75 (6) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.3 |
| C1—P1—S2 | 110.97 (6) | C15—C14—C13 | 119.4 (2) |
| C8—O1—P1 | 118.90 (12) | C15—C14—H14 | 120.3 |
| C4—O2—C7 | 117.52 (17) | C14—C15—C16 | 121.8 (2) |
| C20—N1—H1 | 110.5 (18) | C14—C15—H15 | 119.1 |
| C22—N1—C20 | 113.63 (17) | C16—C15—H15 | 119.1 |
| C22—N1—H1 | 101.4 (17) | C15—C16—H16 | 120.0 |
| C24—N1—C20 | 108.81 (16) | C17—C16—C15 | 120.0 (2) |
| C24—N1—C22 | 113.99 (16) | C17—C16—H16 | 120.0 |
| C24—N1—H1 | 108.2 (18) | C16—C17—C18 | 119.8 (2) |
| C2—C1—P1 | 121.93 (14) | C16—C17—H17 | 120.1 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 118.37 (17) | C18—C17—H17 | 120.1 |
| C6—C1—P1 | 119.70 (14) | C13—C18—C19 | 117.0 (2) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.6 | C17—C18—C13 | 120.5 (2) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.87 (17) | C17—C18—C19 | 122.5 (2) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.6 | C10—C19—C18 | 122.1 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.19 (18) | C10—C19—H19 | 118.9 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.9 | C18—C19—H19 | 118.9 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.9 | N1—C20—C21 | 112.04 (19) |
| O2—C4—C3 | 115.63 (17) | N1—C20—H20A | 109.2 |
| O2—C4—C5 | 124.61 (18) | N1—C20—H20B | 109.2 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 119.75 (18) | C21—C20—H20A | 109.2 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.3 | C21—C20—H20B | 109.2 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 119.39 (17) | H20A—C20—H20B | 107.9 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.3 | C20—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 119.3 | C20—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 121.41 (17) | C20—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.3 | H21B—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| O2—C7—H7A | 109.5 | H21B—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| O2—C7—H7B | 109.5 | H21C—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| O2—C7—H7C | 109.5 | N1—C22—C23 | 113.76 (17) |
| H7A—C7—H7B | 109.5 | N1—C22—H22B | 108.8 |
| H7A—C7—H7C | 109.5 | N1—C22—H22A | 108.8 |
| H7B—C7—H7C | 109.5 | C23—C22—H22A | 108.8 |
| O1—C8—C9 | 107.47 (16) | C23—C22—H22B | 108.8 |
| O1—C8—C10 | 107.62 (16) | H22B—C22—H22A | 107.7 |
| O1—C8—H8 | 109.2 | C22—C23—H23A | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C10 | 114.04 (18) | C22—C23—H23B | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 109.2 | C22—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| C10—C8—H8 | 109.2 | H23A—C23—H23B | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—H9A | 109.5 | H23A—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—H9B | 109.5 | H23B—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—H9C | 109.5 | N1—C24—C25 | 113.29 (18) |
| H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 | N1—C24—H24A | 108.9 |
| H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 | N1—C24—H24B | 108.9 |
| H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 | C25—C24—H24A | 108.9 |
| C11—C10—C8 | 121.10 (18) | C25—C24—H24B | 108.9 |
| C19—C10—C8 | 119.7 (2) | H24A—C24—H24B | 107.7 |
| C19—C10—C11 | 119.2 (2) | C24—C25—H25A | 109.5 |
| C10—C11—H11 | 119.5 | C24—C25—H25B | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—C10 | 120.9 (2) | C24—C25—H25C | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—H11 | 119.5 | H25A—C25—H25B | 109.5 |
| C11—C12—C13 | 120.3 (2) | H25A—C25—H25C | 109.5 |
| C11—C12—H12 | 119.8 | H25B—C25—H25C | 109.5 |
| S1—P1—O1—C8 | 62.17 (14) | C5—C6—C1—P1 | 179.00 (15) |
| S2—P1—O1—C8 | −66.62 (14) | C5—C6—C1—C2 | −1.7 (3) |
| C1—P1—O1—C8 | 177.78 (14) | O1—C8—C10—C11 | 3.9 (2) |
| S1—P1—C1—C2 | −133.20 (14) | O1—C8—C10—C19 | −176.08 (17) |
| S1—P1—C1—C6 | 46.06 (16) | C9—C8—C10—C11 | 123.0 (2) |
| S2—P1—C1—C2 | −2.94 (17) | C9—C8—C10—C19 | −57.0 (3) |
| S2—P1—C1—C6 | 176.32 (13) | C8—C10—C11—C12 | −178.18 (19) |
| O1—P1—C1—C2 | 111.53 (16) | C19—C10—C11—C12 | 1.8 (3) |
| O1—P1—C1—C6 | −69.20 (16) | C8—C10—C19—C18 | 179.61 (18) |
| P1—O1—C8—C9 | 113.03 (16) | C11—C10—C19—C18 | −0.4 (3) |
| P1—O1—C8—C10 | −123.74 (14) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −1.7 (3) |
| C7—O2—C4—C3 | −173.5 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −178.2 (2) |
| C7—O2—C4—C5 | 6.5 (3) | C11—C12—C13—C18 | 0.1 (3) |
| C22—N1—C20—C21 | 68.7 (2) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 177.6 (2) |
| C24—N1—C20—C21 | −163.15 (19) | C18—C13—C14—C15 | −0.7 (3) |
| C20—N1—C22—C23 | 68.3 (2) | C12—C13—C18—C17 | −178.6 (2) |
| C24—N1—C22—C23 | −57.1 (2) | C12—C13—C18—C19 | 1.2 (3) |
| C20—N1—C24—C25 | 178.55 (19) | C14—C13—C18—C17 | −0.3 (3) |
| C22—N1—C24—C25 | −53.5 (2) | C14—C13—C18—C19 | 179.57 (19) |
| P1—C1—C2—C3 | −179.18 (16) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.9 (4) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 1.6 (3) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | 0.0 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.1 (3) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | −1.0 (4) |
| O2—C4—C3—C2 | 178.63 (18) | C16—C17—C18—C13 | 1.2 (3) |
| C5—C4—C3—C2 | −1.3 (3) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | −178.7 (2) |
| O2—C4—C5—C6 | −178.79 (19) | C13—C18—C19—C10 | −1.1 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 1.1 (3) | C17—C18—C19—C10 | 178.7 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.4 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the C1–C6 and C10–C13/C18/C19 rings, respectively. |
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···S2i | 0.84 (3) | 2.52 (3) | 3.2911 (17) | 154 (2) |
| C20—H20A···O1 | 0.97 | 2.56 | 3.505 (2) | 166 |
| C7—H7B···Cg2ii | 0.96 | 2.90 | 3.6578 (28) | 137 |
| C24—H24B···Cg1iii | 0.97 | 2.79 | 3.7496 (24) | 171 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1, y, z; (ii) −x−1, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (iii) x+1, y, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: XU5201).
References
- Alberti, E., Ardizzoia, G. A., Brenna, S., Castelli, F., Gali, S. & Maspero, A. (2007). Polyhedron, 26, 958–966.
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Bruker (2005). SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2007). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 837–838.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Gataulina, A. R., Safin, D. A., Gimadiev, T. R. & Pinus, M. V. (2008). Transition Met. Chem. 33, 921–924.
- Gray, I. P., Milton, H. L., Slawin, A. M. Z. & Woolins, J. D. (2003). Dalton Trans. pp. 3450–3457.
- Gray, I. P., Milton, H. L., Slawin, A. M. Z. & Woolins, J. D. (2004). Dalton Trans. pp. 2477–2486. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Heiduc, I., Mezei, G., Micu-Semeniuc, R., Edelman, F. T. & Fisher, A. (2006). Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 632, 295–300.
- Karakuş, M., Aydoğdu, Y., Çelik, O., Kuzucu, V., İde, S. & Hey-Hawkins, E. (2007). Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 633, 405–410.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C. M., Neels, A., Stoekli-Evans, H. & Süss-Fink, G. (2001). J. Organomet. Chem. 633, 85–90.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811015820/xu5201sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811015820/xu5201Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811015820/xu5201Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




