Abstract
The title compound, [Cu(C10H24N4)(H2O)2][CH3(CH2)10CO2]2·2H2O, consists of one cationic copper(II) complex, two dodecanoate anions and two water solvent molecules. The CuII atom is located on an inversion center and is chelated by the four aza N atoms of the neutral 1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane (cyclam) ligand and by two water molecules in axial positions, giving an octahedral coordination geometry, distorted as a consequence of the Jahn–Teller effect. The uncoordinated water molecules link the complex cations and the dodecanoate counter-ions through O—H⋯O hydrogen bonding, forming a layer structure parallel to (001). Intermolecular N—H⋯O interactions also occur.
Related literature
For the complexation of cyclam with transition metals, see: Ahmad Tajidi et al. (2010a
▶,b
▶,c
▶,d
▶); Lindoy et al. (2003 ▶); Holanda et al. (2007 ▶); Sreedaran et al. (2008 ▶); Zgolli et al. (2010 ▶).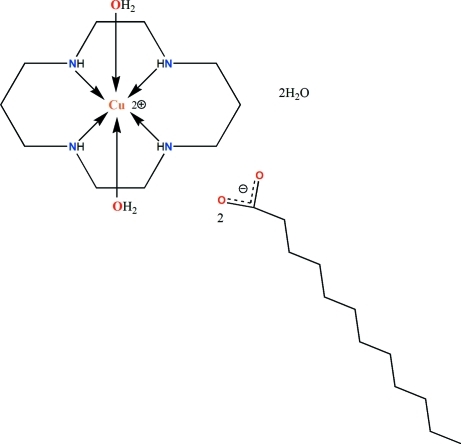
Experimental
Crystal data
[Cu(C10H24N4)(H2O)2](C12H23O2)2·2H2O
M r = 734.54
Triclinic,
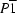
a = 6.9972 (4) Å
b = 8.8164 (5) Å
c = 17.1495 (10) Å
α = 96.218 (3)°
β = 99.137 (3)°
γ = 98.329 (3)°
V = 1024.13 (10) Å3
Z = 1
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.58 mm−1
T = 150 K
0.41 × 0.41 × 0.08 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 1997 ▶) T min = 0.796, T max = 0.955
7085 measured reflections
4623 independent reflections
4138 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.045
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.047
wR(F 2) = 0.129
S = 1.07
4623 reflections
215 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.54 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.52 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 1997 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 1997 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEPIII (Burnett & Johnson, 1996 ▶), ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811012773/dn2672sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811012773/dn2672Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1W—H1WB⋯O2 | 0.90 | 1.91 | 2.774 (2) | 160 |
| O1W—H1WA⋯O2i | 0.90 | 1.81 | 2.694 (2) | 168 |
| O2W—H2WB⋯O1W | 0.90 | 1.93 | 2.8037 (19) | 164 |
| O2W—H2WA⋯O1ii | 0.90 | 1.89 | 2.777 (2) | 168 |
| N2—H2⋯O1i | 0.93 | 2.25 | 3.030 (2) | 141 |
| N1—H1⋯O1Wiii | 0.93 | 2.12 | 2.982 (2) | 153 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 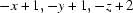 ; (ii)
; (ii) 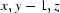 ; (iii)
; (iii) 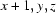 .
.
Acknowledgments
This project was financed by the University of Malaya (grant No. A-50101-DA000-B21519). The authors thank Mr Harry Adams for his support and cooperation.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Copper(II) cyclam complexes are potential functional materials in the field of molecular electronic, photonics and spintronics whose properties may be tuned by steric and electronic effects. The present complex represents our attempt to synthesize a functional material that possesses metallomesogenic properties for such applications. Several cyclam complexes with copper(II) (Ahmad Tajidi et al., 2010a,b,c,d) and other transition metals (Lindoy et al., 2003; Holanda et al., 2007; Sreedaran et al., 2008; Zgolli et al., 2010) have been reported.
In the complex, the CuII atom, located on an inversion center, is coordinated to the 1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane through the four aza-N atoms forming the basal plane of a distorted octahedra whose apices are occupy by two water molecules. Two solvate water molecules link anion and cations through O-H···O hydrogen bondings (Fig. 1, Table 1). The relatively long Cu-O(water) distance, 2.455 (1)Å, is a consequence of the Jahn-Teller effect resulting in the distorted octahedron coordination geometry.
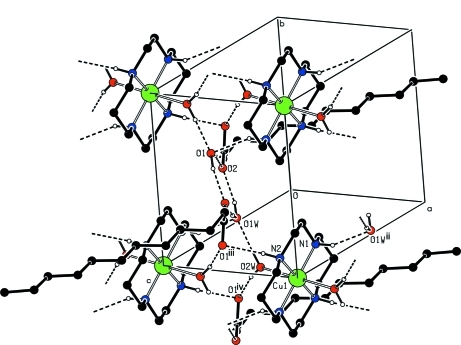
O-H···O and N-H···O Hydrogen bonds involving the coordinated and non coordinated water molecules, the carboxylate O atoms as well as the N atoms of the cyclam build up a two dimensionnal network forming a layer parallel to the (0 0 1) plane (Table 1, Fig. 2).
Experimental
An ethanolic solution of cyclam (2.50 mmol, 50 ml) was added to a warm ethanolic solution of dimeric copper(II) dodecanoate (1.25 mmol, 100 ml), forming a clear purple solution. The solution was then gently heated for 2 h. Purple plates formed upon cooling to room temperature. The yield was 60%.
Refinement
All H atoms attached to C atoms and N atom were fixed geometrically and treated as riding on their parent atoms with C—H = 0.98 Å (methyl) or 0.99 Å (methylene) and N—H = 0.93 Å with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C or N) or Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(Cmethyl). H atoms of water molecule were located in difference Fourier maps and included in the subsequent refinement using restraints (O-H= 0.89 (1)Å and H···H= 1.42 (2)Å) with Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(O). In the last cycles of refinement they were treated as riding on their parent O atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
View of the title compound with the atom labeling scheme. Ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level. H atoms are represented as small spheres of arbitrary radii. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. [Symmetry code: (i) -x+2, -y, -z+2]
Fig. 2.
Partial packing view showing the formation of layer through O-H···O and N-H···O hydrogen bonds. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bondings have been omitted for clarity. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. [Symmetry codes: (ii) -x+1, -y+1, -z+2; (iii) x, y-1, z; (iv) x+1, y, z]
Crystal data
| [Cu(C10H24N4)(H2O)2](C12H23O2)2·2H2O | Z = 1 |
| Mr = 734.54 | F(000) = 403 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.191 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 6.9972 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 2586 reflections |
| b = 8.8164 (5) Å | θ = 2.8–27.6° |
| c = 17.1495 (10) Å | µ = 0.58 mm−1 |
| α = 96.218 (3)° | T = 150 K |
| β = 99.137 (3)° | Plate, violet |
| γ = 98.329 (3)° | 0.41 × 0.41 × 0.08 mm |
| V = 1024.13 (10) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer | 4623 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 4138 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.045 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 27.6°, θmin = 2.8° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2008) | h = −9→8 |
| Tmin = 0.796, Tmax = 0.955 | k = −11→11 |
| 7085 measured reflections | l = 0→22 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.047 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.129 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.07 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0591P)2 + 0.109P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4623 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 215 parameters | Δρmax = 0.54 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.52 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cu1 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.01254 (12) | |
| O2W | 0.6641 (2) | 0.00995 (16) | 0.93529 (9) | 0.0230 (3) | |
| H2WA | 0.5631 | −0.0637 | 0.9110 | 0.034* | |
| H2WB | 0.6086 | 0.0954 | 0.9319 | 0.034* | |
| N1 | 1.1080 (2) | 0.18383 (18) | 0.95170 (10) | 0.0151 (3) | |
| H1 | 1.2439 | 0.1913 | 0.9617 | 0.018* | |
| N2 | 0.9722 (2) | 0.15474 (18) | 1.09264 (9) | 0.0159 (3) | |
| H2 | 0.8416 | 0.1686 | 1.0853 | 0.019* | |
| C1 | 1.1016 (3) | 0.0404 (3) | 0.81813 (12) | 0.0234 (5) | |
| H1A | 1.0855 | 0.0541 | 0.7610 | 0.028* | |
| H1B | 1.2416 | 0.0352 | 0.8367 | 0.028* | |
| C2 | 1.0491 (3) | 0.1814 (2) | 0.86470 (12) | 0.0210 (4) | |
| H2A | 1.1157 | 0.2767 | 0.8484 | 0.025* | |
| H2B | 0.9057 | 0.1799 | 0.8518 | 0.025* | |
| C3 | 1.0621 (3) | 0.3232 (2) | 0.99684 (13) | 0.0203 (4) | |
| H3A | 0.9248 | 0.3356 | 0.9778 | 0.024* | |
| H3B | 1.1501 | 0.4166 | 0.9888 | 0.024* | |
| C4 | 1.0903 (3) | 0.3035 (2) | 1.08367 (13) | 0.0207 (4) | |
| H4A | 1.2308 | 0.3037 | 1.1043 | 0.025* | |
| H4B | 1.0478 | 0.3902 | 1.1145 | 0.025* | |
| C5 | 1.0207 (3) | 0.1110 (3) | 1.17381 (12) | 0.0221 (4) | |
| H5A | 0.9975 | 0.1934 | 1.2135 | 0.027* | |
| H5B | 1.1615 | 0.1019 | 1.1851 | 0.027* | |
| O1 | 0.3901 (2) | 0.76965 (15) | 0.84556 (8) | 0.0201 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.3977 (3) | 0.54859 (17) | 0.89662 (9) | 0.0277 (4) | |
| C6 | 1.5268 (4) | 0.8928 (3) | 0.31756 (16) | 0.0379 (6) | |
| H6A | 1.6020 | 0.9753 | 0.3585 | 0.057* | |
| H6B | 1.5357 | 0.9224 | 0.2646 | 0.057* | |
| H6C | 1.5804 | 0.7970 | 0.3229 | 0.057* | |
| C7 | 1.3129 (3) | 0.8673 (3) | 0.32783 (13) | 0.0302 (5) | |
| H7A | 1.2590 | 0.9636 | 0.3204 | 0.036* | |
| H7B | 1.2380 | 0.7852 | 0.2856 | 0.036* | |
| C8 | 1.2814 (3) | 0.8219 (3) | 0.40846 (12) | 0.0216 (4) | |
| H8A | 1.3601 | 0.9020 | 0.4509 | 0.026* | |
| H8B | 1.3301 | 0.7233 | 0.4151 | 0.026* | |
| C9 | 1.0669 (3) | 0.8029 (3) | 0.41888 (12) | 0.0217 (4) | |
| H9A | 1.0194 | 0.9024 | 0.4136 | 0.026* | |
| H9B | 0.9879 | 0.7250 | 0.3755 | 0.026* | |
| C10 | 1.0328 (3) | 0.7534 (3) | 0.49849 (12) | 0.0227 (4) | |
| H10A | 1.1154 | 0.8293 | 0.5420 | 0.027* | |
| H10B | 1.0755 | 0.6520 | 0.5030 | 0.027* | |
| C11 | 0.8192 (3) | 0.7402 (3) | 0.50970 (12) | 0.0223 (4) | |
| H11A | 0.7362 | 0.6671 | 0.4652 | 0.027* | |
| H11B | 0.7779 | 0.8426 | 0.5069 | 0.027* | |
| C12 | 0.7825 (3) | 0.6855 (3) | 0.58845 (13) | 0.0241 (5) | |
| H12A | 0.8202 | 0.5819 | 0.5907 | 0.029* | |
| H12B | 0.8676 | 0.7572 | 0.6330 | 0.029* | |
| C13 | 0.5699 (3) | 0.6768 (3) | 0.59969 (12) | 0.0225 (4) | |
| H13A | 0.4846 | 0.6099 | 0.5534 | 0.027* | |
| H13B | 0.5348 | 0.7817 | 0.6002 | 0.027* | |
| C14 | 0.5274 (3) | 0.6143 (2) | 0.67581 (12) | 0.0214 (4) | |
| H14A | 0.6137 | 0.6802 | 0.7222 | 0.026* | |
| H14B | 0.5598 | 0.5086 | 0.6750 | 0.026* | |
| C15 | 0.3140 (3) | 0.6090 (2) | 0.68655 (12) | 0.0202 (4) | |
| H15A | 0.2270 | 0.5519 | 0.6379 | 0.024* | |
| H15B | 0.2853 | 0.7160 | 0.6928 | 0.024* | |
| C16 | 0.2673 (3) | 0.5319 (2) | 0.75860 (11) | 0.0192 (4) | |
| H16A | 0.3117 | 0.4302 | 0.7555 | 0.023* | |
| H16B | 0.1231 | 0.5128 | 0.7554 | 0.023* | |
| C17 | 0.3612 (3) | 0.6252 (2) | 0.83941 (11) | 0.0154 (4) | |
| O1W | 0.5329 (2) | 0.29510 (16) | 0.95510 (9) | 0.0208 (3) | |
| H1WA | 0.5554 | 0.3337 | 1.0070 | 0.031* | |
| H1WB | 0.4965 | 0.3679 | 0.9255 | 0.031* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cu1 | 0.01428 (19) | 0.01012 (17) | 0.01465 (18) | 0.00220 (12) | 0.00653 (13) | 0.00193 (12) |
| O2W | 0.0123 (7) | 0.0189 (7) | 0.0358 (9) | 0.0048 (6) | 0.0002 (6) | −0.0017 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0121 (8) | 0.0136 (8) | 0.0210 (8) | 0.0032 (6) | 0.0051 (6) | 0.0044 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0122 (8) | 0.0170 (8) | 0.0185 (8) | 0.0028 (6) | 0.0044 (6) | −0.0010 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0183 (11) | 0.0389 (12) | 0.0173 (10) | 0.0080 (9) | 0.0088 (8) | 0.0097 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0174 (10) | 0.0254 (10) | 0.0231 (10) | 0.0038 (8) | 0.0059 (8) | 0.0122 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0161 (10) | 0.0101 (8) | 0.0367 (12) | 0.0022 (7) | 0.0100 (9) | 0.0036 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0175 (10) | 0.0136 (9) | 0.0298 (11) | −0.0002 (8) | 0.0080 (8) | −0.0042 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0207 (11) | 0.0306 (11) | 0.0149 (9) | 0.0069 (9) | 0.0037 (8) | −0.0024 (8) |
| O1 | 0.0231 (8) | 0.0157 (7) | 0.0213 (7) | 0.0048 (6) | 0.0033 (6) | 0.0001 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0426 (10) | 0.0209 (8) | 0.0188 (7) | 0.0039 (7) | 0.0029 (7) | 0.0052 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0286 (14) | 0.0546 (17) | 0.0364 (14) | 0.0053 (12) | 0.0196 (11) | 0.0141 (12) |
| C7 | 0.0229 (12) | 0.0478 (14) | 0.0213 (11) | 0.0013 (10) | 0.0098 (9) | 0.0090 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0182 (11) | 0.0290 (11) | 0.0185 (10) | 0.0018 (8) | 0.0077 (8) | 0.0037 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0189 (11) | 0.0281 (11) | 0.0170 (10) | −0.0017 (8) | 0.0059 (8) | 0.0020 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0204 (11) | 0.0292 (11) | 0.0196 (10) | 0.0018 (9) | 0.0086 (8) | 0.0030 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0203 (11) | 0.0272 (11) | 0.0191 (10) | −0.0008 (8) | 0.0089 (8) | 0.0000 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0216 (11) | 0.0313 (12) | 0.0215 (11) | 0.0041 (9) | 0.0100 (9) | 0.0044 (9) |
| C13 | 0.0225 (11) | 0.0275 (11) | 0.0190 (10) | 0.0017 (9) | 0.0104 (8) | 0.0025 (8) |
| C14 | 0.0201 (11) | 0.0271 (11) | 0.0182 (10) | 0.0040 (8) | 0.0072 (8) | 0.0028 (8) |
| C15 | 0.0214 (11) | 0.0253 (10) | 0.0137 (9) | 0.0019 (8) | 0.0065 (8) | −0.0002 (8) |
| C16 | 0.0220 (11) | 0.0189 (10) | 0.0160 (9) | −0.0008 (8) | 0.0063 (8) | 0.0006 (7) |
| C17 | 0.0127 (9) | 0.0180 (9) | 0.0178 (9) | 0.0046 (7) | 0.0076 (7) | 0.0019 (7) |
| O1W | 0.0201 (8) | 0.0195 (7) | 0.0234 (7) | 0.0054 (6) | 0.0033 (6) | 0.0025 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cu1—N1i | 2.0048 (16) | C7—C8 | 1.521 (3) |
| Cu1—N1 | 2.0048 (16) | C7—H7A | 0.9900 |
| Cu1—N2i | 2.0319 (15) | C7—H7B | 0.9900 |
| Cu1—N2 | 2.0319 (15) | C8—C9 | 1.527 (3) |
| O2W—H2WA | 0.8998 | C8—H8A | 0.9900 |
| O2W—H2WB | 0.8994 | C8—H8B | 0.9900 |
| N1—C2 | 1.481 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.521 (3) |
| N1—C3 | 1.483 (2) | C9—H9A | 0.9900 |
| N1—H1 | 0.9300 | C9—H9B | 0.9900 |
| N2—C4 | 1.482 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.527 (3) |
| N2—C5 | 1.485 (2) | C10—H10A | 0.9900 |
| N2—H2 | 0.9300 | C10—H10B | 0.9900 |
| C1—C5i | 1.510 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.529 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.526 (3) | C11—H11A | 0.9900 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9900 | C11—H11B | 0.9900 |
| C1—H1B | 0.9900 | C12—C13 | 1.523 (3) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9900 | C12—H12A | 0.9900 |
| C2—H2B | 0.9900 | C12—H12B | 0.9900 |
| C3—C4 | 1.503 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.526 (3) |
| C3—H3A | 0.9900 | C13—H13A | 0.9900 |
| C3—H3B | 0.9900 | C13—H13B | 0.9900 |
| C4—H4A | 0.9900 | C14—C15 | 1.528 (3) |
| C4—H4B | 0.9900 | C14—H14A | 0.9900 |
| C5—C1i | 1.510 (3) | C14—H14B | 0.9900 |
| C5—H5A | 0.9900 | C15—C16 | 1.530 (3) |
| C5—H5B | 0.9900 | C15—H15A | 0.9900 |
| O1—C17 | 1.250 (2) | C15—H15B | 0.9900 |
| O2—C17 | 1.264 (2) | C16—C17 | 1.529 (3) |
| C6—C7 | 1.522 (3) | C16—H16A | 0.9900 |
| C6—H6A | 0.9800 | C16—H16B | 0.9900 |
| C6—H6B | 0.9800 | O1W—H1WA | 0.8986 |
| C6—H6C | 0.9800 | O1W—H1WB | 0.9006 |
| N1i—Cu1—N1 | 180.0 | H7A—C7—H7B | 107.6 |
| N1i—Cu1—N2i | 86.18 (7) | C7—C8—C9 | 113.37 (18) |
| N1—Cu1—N2i | 93.82 (7) | C7—C8—H8A | 108.9 |
| N1i—Cu1—N2 | 93.82 (7) | C9—C8—H8A | 108.9 |
| N1—Cu1—N2 | 86.18 (7) | C7—C8—H8B | 108.9 |
| N2i—Cu1—N2 | 180.000 (1) | C9—C8—H8B | 108.9 |
| H2WA—O2W—H2WB | 100.8 | H8A—C8—H8B | 107.7 |
| C2—N1—C3 | 111.39 (15) | C10—C9—C8 | 113.87 (17) |
| C2—N1—Cu1 | 117.57 (13) | C10—C9—H9A | 108.8 |
| C3—N1—Cu1 | 107.35 (12) | C8—C9—H9A | 108.8 |
| C2—N1—H1 | 106.6 | C10—C9—H9B | 108.8 |
| C3—N1—H1 | 106.6 | C8—C9—H9B | 108.8 |
| Cu1—N1—H1 | 106.6 | H9A—C9—H9B | 107.7 |
| C4—N2—C5 | 112.33 (16) | C9—C10—C11 | 113.57 (17) |
| C4—N2—Cu1 | 106.22 (12) | C9—C10—H10A | 108.9 |
| C5—N2—Cu1 | 116.78 (12) | C11—C10—H10A | 108.9 |
| C4—N2—H2 | 107.0 | C9—C10—H10B | 108.9 |
| C5—N2—H2 | 107.0 | C11—C10—H10B | 108.9 |
| Cu1—N2—H2 | 107.0 | H10A—C10—H10B | 107.7 |
| C5i—C1—C2 | 114.02 (17) | C10—C11—C12 | 113.90 (18) |
| C5i—C1—H1A | 108.7 | C10—C11—H11A | 108.8 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 108.7 | C12—C11—H11A | 108.8 |
| C5i—C1—H1B | 108.7 | C10—C11—H11B | 108.8 |
| C2—C1—H1B | 108.7 | C12—C11—H11B | 108.8 |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 107.6 | H11A—C11—H11B | 107.7 |
| N1—C2—C1 | 111.41 (15) | C13—C12—C11 | 113.29 (18) |
| N1—C2—H2A | 109.3 | C13—C12—H12A | 108.9 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 109.3 | C11—C12—H12A | 108.9 |
| N1—C2—H2B | 109.3 | C13—C12—H12B | 108.9 |
| C1—C2—H2B | 109.3 | C11—C12—H12B | 108.9 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 108.0 | H12A—C12—H12B | 107.7 |
| N1—C3—C4 | 108.34 (15) | C12—C13—C14 | 114.26 (18) |
| N1—C3—H3A | 110.0 | C12—C13—H13A | 108.7 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 110.0 | C14—C13—H13A | 108.7 |
| N1—C3—H3B | 110.0 | C12—C13—H13B | 108.7 |
| C4—C3—H3B | 110.0 | C14—C13—H13B | 108.7 |
| H3A—C3—H3B | 108.4 | H13A—C13—H13B | 107.6 |
| N2—C4—C3 | 108.71 (16) | C13—C14—C15 | 113.37 (17) |
| N2—C4—H4A | 109.9 | C13—C14—H14A | 108.9 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 109.9 | C15—C14—H14A | 108.9 |
| N2—C4—H4B | 109.9 | C13—C14—H14B | 108.9 |
| C3—C4—H4B | 109.9 | C15—C14—H14B | 108.9 |
| H4A—C4—H4B | 108.3 | H14A—C14—H14B | 107.7 |
| N2—C5—C1i | 111.54 (17) | C14—C15—C16 | 113.17 (17) |
| N2—C5—H5A | 109.3 | C14—C15—H15A | 108.9 |
| C1i—C5—H5A | 109.3 | C16—C15—H15A | 108.9 |
| N2—C5—H5B | 109.3 | C14—C15—H15B | 108.9 |
| C1i—C5—H5B | 109.3 | C16—C15—H15B | 108.9 |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 108.0 | H15A—C15—H15B | 107.8 |
| C7—C6—H6A | 109.5 | C15—C16—C17 | 114.68 (17) |
| C7—C6—H6B | 109.5 | C15—C16—H16A | 108.6 |
| H6A—C6—H6B | 109.5 | C17—C16—H16A | 108.6 |
| C7—C6—H6C | 109.5 | C15—C16—H16B | 108.6 |
| H6A—C6—H6C | 109.5 | C17—C16—H16B | 108.6 |
| H6B—C6—H6C | 109.5 | H16A—C16—H16B | 107.6 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 114.1 (2) | O1—C17—O2 | 124.53 (19) |
| C8—C7—H7A | 108.7 | O1—C17—C16 | 118.96 (17) |
| C6—C7—H7A | 108.7 | O2—C17—C16 | 116.46 (17) |
| C8—C7—H7B | 108.7 | H1WA—O1W—H1WB | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7B | 108.7 | ||
| C3—N1—C2—C1 | 178.39 (16) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 178.49 (19) |
| Cu1—N1—C2—C1 | −57.1 (2) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 177.93 (18) |
| C5i—C1—C2—N1 | 70.0 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 178.14 (18) |
| C2—N1—C3—C4 | 169.59 (16) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 178.57 (17) |
| Cu1—N1—C3—C4 | 39.57 (18) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 176.93 (18) |
| C5—N2—C4—C3 | 168.83 (15) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 179.07 (18) |
| Cu1—N2—C4—C3 | 40.02 (17) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 174.42 (17) |
| N1—C3—C4—N2 | −53.9 (2) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | 70.0 (2) |
| C4—N2—C5—C1i | 179.78 (15) | C15—C16—C17—O1 | 30.9 (3) |
| Cu1—N2—C5—C1i | −57.2 (2) | C15—C16—C17—O2 | −151.66 (19) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | 177.8 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, −y, −z+2.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1W—H1WB···O2 | 0.90 | 1.91 | 2.774 (2) | 160. |
| O1W—H1WA···O2ii | 0.90 | 1.81 | 2.694 (2) | 168. |
| O2W—H2WB···O1W | 0.90 | 1.93 | 2.8037 (19) | 164. |
| O2W—H2WA···O1iii | 0.90 | 1.89 | 2.777 (2) | 168. |
| N2—H2···O1ii | 0.93 | 2.25 | 3.030 (2) | 141. |
| N1—H1···O1Wiv | 0.93 | 2.12 | 2.982 (2) | 153. |
Symmetry codes: (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+2; (iii) x, y−1, z; (iv) x+1, y, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: DN2672).
References
- Ahmad Tajidi, N. S., Abdullah, N., Arifin, Z., Tan, K. W. & Ng, S. W. (2010a). Acta Cryst. E66, m887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ahmad Tajidi, N. S., Abdullah, N., Arifin, Z., Tan, K. W. & Ng, S. W. (2010b). Acta Cryst. E66, m888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ahmad Tajidi, N. S., Abdullah, N., Arifin, Z., Tan, K. W. & Ng, S. W. (2010c). Acta Cryst. E66, m889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ahmad Tajidi, N. S., Abdullah, N., Arifin, Z., Tan, K. W. & Ng, S. W. (2010d). Acta Cryst. E66, m890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bruker (1997). SMART, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Burnett, M. N. & Johnson, C. K. (1996). ORTEPIII Report ORNL-6895. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Tennessee, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Holanda, A. K. M., da Silva, F. O. N., Carvalho, I. M. M., Batista, A. A., Ellena, J., Castellano, E. E., Moreira, I. S. & Lopes, L. G. F. (2007). Polyhedron, 26, 4653–4658.
- Lindoy, L. F., Mahinay, M. S., Skelton, B. W. & White, A. H. (2003). J. Coord. Chem 56, 1203–1213.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst A64, 112-122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sreedaran, S., Bharathi, K. S., Rahiman, A. K., Rajesh, K., Nirmala, G. & Narayanan, V. (2008). J. Coord. Chem. 22, 3594–3609.
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
- Zaouali Zgolli, D., Boughzala, H. & Driss, A. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, m265–m266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811012773/dn2672sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811012773/dn2672Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report