Abstract
The commercially available title compound, C25H23N3O2, has been known since 1993 [Nesper et al. (1993 ▶). Helv. Chim. Acta, 76, 2239–2249], but has not been structurally characterized until now. In the free ligand, the N atoms of both oxazoline rings point in opposite directions. The phenyl rings make dihedral angles of 30.56 (5) and 84.57 (3)° with the pyridine ring and 72.85 (3)° with each other.
Related literature
For the synthesis, see: Nesper et al. (1993 ▶; 1996 ▶); Schaus & Jacobsen (2000 ▶); Towers et al. (2003 ▶); Meng et al. (2005 ▶); Hui et al. (2006 ▶). For crystal structures showing the same ligand coordinated to Pd(BF4)2 or AgBF4, see: Nesper et al. (1996 ▶); Provent et al. (1997 ▶). For applications in asymmetric catalysis, see: Desimoni et al. (2003 ▶); Tse et al. (2006 ▶). 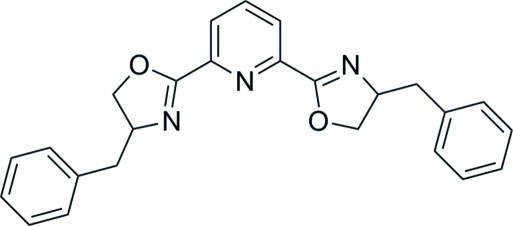
Experimental
Crystal data
C25H23N3O2
M r = 397.46
Orthorhombic,

a = 7.0184 (2) Å
b = 13.2654 (3) Å
c = 21.5542 (8) Å
V = 2006.74 (10) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 150 K
0.50 × 0.45 × 0.25 mm
Data collection
Stoe IPDS II diffractometer
38412 measured reflections
5433 independent reflections
4254 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.045
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.029
wR(F 2) = 0.053
S = 0.86
5433 reflections
271 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.13 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3
Data collection: X-AREA (Stoe & Cie, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: X-AREA; data reduction: X-AREA; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: XP in SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811014061/om2419sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811014061/om2419Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The synthesis of chiral tridentate N,N,N-pyridine-2,6-bisoxazolines (pybox ligands) constitute a useful toolbox for the application in asymmetric catalysis (Desimoni et al., 2003). The title compound was used as part of our ongoing studies (Tse et al., 2006).
In contrast to the complexed ligand (Nesper et al., 1996; Provent et al., 1997) where all N atoms are pointed to the metal to permit coordination, in the free ligand the N atoms of both oxazoline rings point in the opposite direction (Fig. 1). The dihedral angle between the planes defined by C13 - C18 and C20 - C25 is 72.85 (3)°. The phenyl rings (C13 - C18 and C20 - C25) are twisted out of the N1, C4 - C8 plane by an angle of 30.56 (5)° and 84.57 (3)°, respectively. The absolute configuration has been assigned to correspond with that of the known chiral centres of the starting material.
Experimental
The synthesis of the commercially available title compound was described by Nesper et al., 1993; Nesper et al., 1996; Schaus & Jacobsen, 2000; Towers et al., 2003; Meng et al., 2005 and Hui et al., 2006. The title compound was purchased from STREM and crystals were grown from a dichloromethane/hexane mixture. The solution was slowly evaporated to dryness for two days and colourless crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were isolated.
Refinement
H atoms were placed in idealized positions with d(C—H) = 0.99 (CH2) and 0.95–1.00 Å (CH) and refined using a riding model with Uiso(H) fixed at 1.2 Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound showing the atom-labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Crystal data
| C25H23N3O2 | F(000) = 840 |
| Mr = 397.46 | Dx = 1.316 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 7372 reflections |
| a = 7.0184 (2) Å | θ = 1.8–29.6° |
| b = 13.2654 (3) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 21.5542 (8) Å | T = 150 K |
| V = 2006.74 (10) Å3 | Prism, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.50 × 0.45 × 0.25 mm |
Data collection
| Stoe IPDS II diffractometer | 4254 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.045 |
| graphite | θmax = 29.2°, θmin = 1.8° |
| ω scans | h = −9→9 |
| 38412 measured reflections | k = −18→18 |
| 5433 independent reflections | l = −29→29 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.029 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.053 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 0.86 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0277P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 5433 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 271 parameters | Δρmax = 0.13 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.08221 (18) | 0.78242 (8) | 0.86378 (6) | 0.0391 (3) | |
| H1A | 0.0477 | 0.8470 | 0.8436 | 0.047* | |
| H1B | 0.1124 | 0.7953 | 0.9079 | 0.047* | |
| C2 | −0.07905 (16) | 0.70557 (7) | 0.85760 (5) | 0.0307 (2) | |
| H2 | −0.1664 | 0.7274 | 0.8235 | 0.037* | |
| C3 | 0.18890 (16) | 0.63775 (7) | 0.82495 (5) | 0.0271 (2) | |
| C4 | 0.33449 (15) | 0.56927 (7) | 0.79877 (5) | 0.0271 (2) | |
| C5 | 0.30631 (16) | 0.46567 (7) | 0.80236 (5) | 0.0320 (2) | |
| H5 | 0.1993 | 0.4390 | 0.8238 | 0.038* | |
| C6 | 0.43561 (16) | 0.40269 (8) | 0.77450 (5) | 0.0330 (3) | |
| H6 | 0.4199 | 0.3316 | 0.7762 | 0.040* | |
| C7 | 0.58872 (16) | 0.44469 (7) | 0.74402 (5) | 0.0302 (2) | |
| H7 | 0.6801 | 0.4029 | 0.7241 | 0.036* | |
| C8 | 0.60768 (16) | 0.54896 (7) | 0.74277 (5) | 0.0261 (2) | |
| C9 | 0.76549 (16) | 0.59535 (7) | 0.70744 (4) | 0.0274 (2) | |
| C10 | 1.02808 (19) | 0.58556 (8) | 0.64867 (6) | 0.0410 (3) | |
| H10A | 1.0471 | 0.5688 | 0.6044 | 0.049* | |
| H10B | 1.1483 | 0.5731 | 0.6715 | 0.049* | |
| C11 | 0.96205 (16) | 0.69563 (8) | 0.65652 (5) | 0.0307 (2) | |
| H11 | 0.9089 | 0.7199 | 0.6161 | 0.037* | |
| C12 | 1.11831 (16) | 0.76752 (8) | 0.67706 (5) | 0.0308 (2) | |
| H12A | 1.0595 | 0.8305 | 0.6927 | 0.037* | |
| H12B | 1.1903 | 0.7366 | 0.7116 | 0.037* | |
| C13 | 1.25418 (16) | 0.79284 (7) | 0.62524 (5) | 0.0287 (2) | |
| C14 | 1.23770 (17) | 0.88259 (8) | 0.59240 (5) | 0.0341 (2) | |
| H14 | 1.1407 | 0.9293 | 0.6032 | 0.041* | |
| C15 | 1.36016 (18) | 0.90471 (10) | 0.54433 (6) | 0.0422 (3) | |
| H15 | 1.3472 | 0.9665 | 0.5225 | 0.051* | |
| C16 | 1.50168 (19) | 0.83760 (9) | 0.52768 (6) | 0.0415 (3) | |
| H16 | 1.5855 | 0.8528 | 0.4944 | 0.050* | |
| C17 | 1.52003 (17) | 0.74822 (9) | 0.55991 (6) | 0.0403 (3) | |
| H17 | 1.6169 | 0.7016 | 0.5488 | 0.048* | |
| C18 | 1.39795 (17) | 0.72647 (8) | 0.60832 (5) | 0.0352 (3) | |
| H18 | 1.4126 | 0.6650 | 0.6304 | 0.042* | |
| C19 | −0.19380 (17) | 0.69334 (8) | 0.91699 (5) | 0.0338 (2) | |
| H19A | −0.3029 | 0.6477 | 0.9093 | 0.041* | |
| H19B | −0.1127 | 0.6623 | 0.9494 | 0.041* | |
| C20 | −0.26647 (15) | 0.79374 (7) | 0.93971 (5) | 0.0284 (2) | |
| C21 | −0.19421 (16) | 0.83776 (8) | 0.99302 (5) | 0.0331 (3) | |
| H21 | −0.0999 | 0.8031 | 1.0164 | 0.040* | |
| C22 | −0.25669 (18) | 0.93129 (8) | 1.01295 (5) | 0.0369 (3) | |
| H22 | −0.2051 | 0.9603 | 1.0496 | 0.044* | |
| C23 | −0.39392 (18) | 0.98226 (8) | 0.97955 (6) | 0.0385 (3) | |
| H23 | −0.4370 | 1.0466 | 0.9930 | 0.046* | |
| C24 | −0.46803 (17) | 0.93922 (9) | 0.92658 (6) | 0.0380 (3) | |
| H24 | −0.5632 | 0.9739 | 0.9037 | 0.046* | |
| C25 | −0.40519 (17) | 0.84613 (8) | 0.90655 (5) | 0.0329 (2) | |
| H25 | −0.4570 | 0.8175 | 0.8698 | 0.040* | |
| N1 | 0.48293 (13) | 0.61177 (6) | 0.76977 (4) | 0.02706 (19) | |
| N2 | 0.02005 (14) | 0.61231 (6) | 0.83845 (4) | 0.0311 (2) | |
| N3 | 0.80484 (13) | 0.68788 (6) | 0.70200 (4) | 0.0307 (2) | |
| O1 | 0.24182 (12) | 0.73528 (5) | 0.83241 (3) | 0.03401 (18) | |
| O2 | 0.87275 (12) | 0.52786 (5) | 0.67492 (4) | 0.0402 (2) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0401 (7) | 0.0291 (5) | 0.0482 (7) | −0.0040 (5) | 0.0204 (6) | −0.0039 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0318 (6) | 0.0266 (5) | 0.0337 (6) | −0.0005 (4) | 0.0013 (5) | 0.0007 (4) |
| C3 | 0.0318 (6) | 0.0241 (5) | 0.0255 (5) | −0.0043 (4) | 0.0004 (5) | 0.0029 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0289 (6) | 0.0273 (5) | 0.0251 (5) | −0.0027 (4) | −0.0007 (4) | 0.0015 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0320 (6) | 0.0283 (5) | 0.0357 (6) | −0.0042 (5) | 0.0018 (5) | 0.0048 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0398 (7) | 0.0218 (5) | 0.0375 (6) | −0.0016 (5) | −0.0023 (5) | 0.0023 (4) |
| C7 | 0.0332 (6) | 0.0264 (5) | 0.0310 (6) | 0.0034 (4) | 0.0003 (5) | −0.0002 (4) |
| C8 | 0.0289 (6) | 0.0249 (5) | 0.0245 (5) | −0.0005 (4) | −0.0013 (4) | 0.0006 (4) |
| C9 | 0.0293 (6) | 0.0266 (5) | 0.0262 (5) | 0.0016 (5) | 0.0004 (5) | −0.0035 (4) |
| C10 | 0.0403 (7) | 0.0347 (6) | 0.0480 (7) | −0.0067 (5) | 0.0162 (6) | −0.0078 (5) |
| C11 | 0.0302 (6) | 0.0337 (5) | 0.0282 (5) | −0.0001 (5) | 0.0037 (5) | 0.0020 (4) |
| C12 | 0.0330 (6) | 0.0295 (5) | 0.0299 (5) | 0.0017 (5) | 0.0008 (5) | 0.0009 (4) |
| C13 | 0.0255 (6) | 0.0297 (5) | 0.0310 (5) | −0.0031 (4) | −0.0036 (5) | −0.0033 (4) |
| C14 | 0.0294 (6) | 0.0325 (5) | 0.0404 (6) | −0.0010 (5) | −0.0008 (5) | 0.0025 (4) |
| C15 | 0.0402 (7) | 0.0439 (7) | 0.0424 (7) | −0.0079 (6) | −0.0013 (6) | 0.0104 (5) |
| C16 | 0.0349 (7) | 0.0544 (7) | 0.0351 (6) | −0.0136 (6) | 0.0054 (6) | −0.0025 (5) |
| C17 | 0.0264 (6) | 0.0450 (7) | 0.0494 (7) | −0.0017 (5) | 0.0039 (6) | −0.0128 (5) |
| C18 | 0.0297 (6) | 0.0315 (6) | 0.0444 (7) | −0.0004 (5) | −0.0007 (5) | −0.0013 (5) |
| C19 | 0.0294 (6) | 0.0292 (5) | 0.0429 (6) | −0.0006 (5) | 0.0083 (5) | 0.0054 (5) |
| C20 | 0.0228 (5) | 0.0304 (5) | 0.0320 (5) | −0.0024 (5) | 0.0068 (5) | 0.0071 (4) |
| C21 | 0.0263 (6) | 0.0406 (6) | 0.0323 (6) | 0.0000 (5) | 0.0018 (5) | 0.0084 (4) |
| C22 | 0.0376 (7) | 0.0416 (6) | 0.0314 (5) | −0.0076 (5) | 0.0043 (5) | −0.0013 (5) |
| C23 | 0.0416 (7) | 0.0297 (6) | 0.0443 (7) | 0.0022 (5) | 0.0132 (6) | 0.0028 (5) |
| C24 | 0.0311 (6) | 0.0396 (6) | 0.0433 (7) | 0.0069 (5) | 0.0001 (5) | 0.0101 (5) |
| C25 | 0.0289 (6) | 0.0364 (6) | 0.0335 (6) | −0.0028 (5) | −0.0015 (5) | 0.0031 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0295 (5) | 0.0247 (4) | 0.0270 (4) | −0.0009 (4) | 0.0019 (4) | −0.0001 (3) |
| N2 | 0.0297 (5) | 0.0268 (4) | 0.0370 (5) | −0.0031 (4) | 0.0034 (4) | −0.0014 (4) |
| N3 | 0.0300 (5) | 0.0277 (4) | 0.0345 (5) | 0.0021 (4) | 0.0052 (4) | 0.0030 (4) |
| O1 | 0.0351 (4) | 0.0253 (3) | 0.0416 (4) | −0.0049 (3) | 0.0136 (4) | −0.0037 (3) |
| O2 | 0.0407 (5) | 0.0283 (4) | 0.0515 (5) | −0.0052 (4) | 0.0187 (4) | −0.0111 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—O1 | 1.4503 (14) | C12—C13 | 1.5065 (15) |
| C1—C2 | 1.5290 (17) | C12—H12A | 0.9900 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9900 | C12—H12B | 0.9900 |
| C1—H1B | 0.9900 | C13—C18 | 1.3879 (15) |
| C2—N2 | 1.4781 (14) | C13—C14 | 1.3899 (14) |
| C2—C19 | 1.5211 (15) | C14—C15 | 1.3778 (16) |
| C2—H2 | 1.0000 | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C3—N2 | 1.2660 (14) | C15—C16 | 1.3813 (18) |
| C3—O1 | 1.3556 (11) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C4 | 1.4790 (14) | C16—C17 | 1.3801 (17) |
| C4—N1 | 1.3394 (13) | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| C4—C5 | 1.3905 (14) | C17—C18 | 1.3808 (16) |
| C5—C6 | 1.3719 (15) | C17—H17 | 0.9500 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C18—H18 | 0.9500 |
| C6—C7 | 1.3773 (15) | C19—C20 | 1.5078 (14) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C19—H19A | 0.9900 |
| C7—C8 | 1.3898 (13) | C19—H19B | 0.9900 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9500 | C20—C21 | 1.3852 (15) |
| C8—N1 | 1.3415 (13) | C20—C25 | 1.3934 (15) |
| C8—C9 | 1.4784 (15) | C21—C22 | 1.3843 (16) |
| C9—N3 | 1.2636 (13) | C21—H21 | 0.9500 |
| C9—O2 | 1.3636 (12) | C22—C23 | 1.3796 (17) |
| C10—O2 | 1.4472 (14) | C22—H22 | 0.9500 |
| C10—C11 | 1.5413 (15) | C23—C24 | 1.3784 (17) |
| C10—H10A | 0.9900 | C23—H23 | 0.9500 |
| C10—H10B | 0.9900 | C24—C25 | 1.3806 (15) |
| C11—N3 | 1.4796 (14) | C24—H24 | 0.9500 |
| C11—C12 | 1.5193 (16) | C25—H25 | 0.9500 |
| C11—H11 | 1.0000 | ||
| O1—C1—C2 | 104.10 (8) | C11—C12—H12B | 109.1 |
| O1—C1—H1A | 110.9 | H12A—C12—H12B | 107.9 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 110.9 | C18—C13—C14 | 118.04 (10) |
| O1—C1—H1B | 110.9 | C18—C13—C12 | 120.90 (9) |
| C2—C1—H1B | 110.9 | C14—C13—C12 | 121.05 (10) |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 109.0 | C15—C14—C13 | 120.90 (11) |
| N2—C2—C19 | 113.26 (8) | C15—C14—H14 | 119.6 |
| N2—C2—C1 | 103.54 (9) | C13—C14—H14 | 119.6 |
| C19—C2—C1 | 112.94 (9) | C14—C15—C16 | 120.44 (11) |
| N2—C2—H2 | 109.0 | C14—C15—H15 | 119.8 |
| C19—C2—H2 | 109.0 | C16—C15—H15 | 119.8 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 109.0 | C17—C16—C15 | 119.34 (11) |
| N2—C3—O1 | 118.92 (10) | C17—C16—H16 | 120.3 |
| N2—C3—C4 | 124.80 (9) | C15—C16—H16 | 120.3 |
| O1—C3—C4 | 116.24 (9) | C16—C17—C18 | 120.13 (11) |
| N1—C4—C5 | 123.55 (10) | C16—C17—H17 | 119.9 |
| N1—C4—C3 | 117.18 (8) | C18—C17—H17 | 119.9 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 119.17 (10) | C17—C18—C13 | 121.14 (10) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 118.91 (10) | C17—C18—H18 | 119.4 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.5 | C13—C18—H18 | 119.4 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.5 | C20—C19—C2 | 110.99 (8) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 118.60 (9) | C20—C19—H19A | 109.4 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.7 | C2—C19—H19A | 109.4 |
| C7—C6—H6 | 120.7 | C20—C19—H19B | 109.4 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 119.11 (10) | C2—C19—H19B | 109.4 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 120.4 | H19A—C19—H19B | 108.0 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 120.4 | C21—C20—C25 | 118.10 (10) |
| N1—C8—C7 | 123.18 (10) | C21—C20—C19 | 121.19 (10) |
| N1—C8—C9 | 116.99 (8) | C25—C20—C19 | 120.69 (10) |
| C7—C8—C9 | 119.74 (9) | C22—C21—C20 | 121.29 (11) |
| N3—C9—O2 | 118.00 (9) | C22—C21—H21 | 119.4 |
| N3—C9—C8 | 128.02 (9) | C20—C21—H21 | 119.4 |
| O2—C9—C8 | 113.89 (8) | C23—C22—C21 | 119.90 (11) |
| O2—C10—C11 | 103.39 (9) | C23—C22—H22 | 120.1 |
| O2—C10—H10A | 111.1 | C21—C22—H22 | 120.1 |
| C11—C10—H10A | 111.1 | C24—C23—C22 | 119.52 (11) |
| O2—C10—H10B | 111.1 | C24—C23—H23 | 120.2 |
| C11—C10—H10B | 111.1 | C22—C23—H23 | 120.2 |
| H10A—C10—H10B | 109.0 | C23—C24—C25 | 120.59 (11) |
| N3—C11—C12 | 112.88 (9) | C23—C24—H24 | 119.7 |
| N3—C11—C10 | 103.36 (8) | C25—C24—H24 | 119.7 |
| C12—C11—C10 | 114.18 (10) | C24—C25—C20 | 120.60 (11) |
| N3—C11—H11 | 108.7 | C24—C25—H25 | 119.7 |
| C12—C11—H11 | 108.7 | C20—C25—H25 | 119.7 |
| C10—C11—H11 | 108.7 | C4—N1—C8 | 116.66 (8) |
| C13—C12—C11 | 112.38 (9) | C3—N2—C2 | 106.35 (8) |
| C13—C12—H12A | 109.1 | C9—N3—C11 | 106.97 (8) |
| C11—C12—H12A | 109.1 | C3—O1—C1 | 104.79 (8) |
| C13—C12—H12B | 109.1 | C9—O2—C10 | 105.64 (8) |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: OM2419).
References
- Desimoni, G., Faiti, G. & Quadrelli, P. (2003). Chem. Rev. 103, 3119–3154. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Hui, X.-P., Huang, J.-I., Chiou, S.-J. & Gau, H.-M. (2006). J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 53, 421–427.
- Meng, J.-C., Fokin, V. V. & Finn, M. G. (2005). Tetrahedron Lett. 46, 4543–4546.
- Nesper, R., Pregosin, P. S., Püntener, K. & Wörle, M. (1993). Helv. Chim. Acta, 76, 2239–2249.
- Nesper, R., Pregosin, P., Püntener, K., Wörle, M. & Albinati, A. (1996). J Organomet. Chem. 507, 85–101.
- Provent, C., Hewage, S., Brand, G., Bernardinelli, G., Charbonnière, L. J. & Williams, A. F. (1997). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 36, 1287–1289.
- Schaus, S. E. & Jacobsen, E. N. (2000). Org. Lett. 2, 1001–1004. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Stoe & Cie (2005). X-AREA Stoe & Cie, Darmstadt, Germany.
- Towers, M. D. K. N., Woodgate, P. D. & Brimble, M. A. (2003). ARKIVOC, pp. 43–55.
- Tse, M. K., Bhor, S., Klawonn, M., Anilkumar, G., Jiao, H., Döbler, C., Spannenberg, A., Mägerlein, W., Hugl, H. & Beller, M. (2006). Chem. Eur. J. 12, 1855–1874. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811014061/om2419sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811014061/om2419Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



