Abstract
The title thiourea derivative, C14H18N4O5S, features two substantial twists between its component fragments: the dihedral angle between the SN2C (thiourea) and ONC2 (amide) residues is 48.89 (7)° and that between the benzene ring and the amide residue is 30.27 (7)°. In the crystal, molecules are linked by bifurcated N—H⋯(O,S) hydrogen bonds, generating [001] supramolecular chains.
Related literature
For the biological activity of thiourea derivatives, see: Venkatachalam et al., (2004 ▶); Saeed et al. (2011 ▶). For related thiourea structures, see: Gunasekaran et al. (2010 ▶); Saeed et al. (2010 ▶); Dzulkifli et al. (2011 ▶).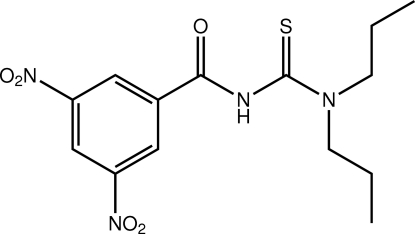
Experimental
Crystal data
C14H18N4O5S
M r = 354.38
Monoclinic,

a = 7.9406 (4) Å
b = 21.2839 (10) Å
c = 9.5967 (4) Å
β = 94.379 (4)°
V = 1617.17 (13) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.23 mm−1
T = 295 K
0.30 × 0.20 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Agilent SuperNova Dual diffractometer with an Atlas detector
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2010 ▶) T min = 0.933, T max = 0.977
8055 measured reflections
3614 independent reflections
2878 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.027
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.055
wR(F 2) = 0.154
S = 1.02
3614 reflections
221 parameters
1 restraint
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 1.04 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.46 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Agilent, 2010 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and DIAMOND (Brandenburg, 2006 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811013638/hb5845sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811013638/hb5845Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2⋯O1i | 0.87 (1) | 2.53 (2) | 3.264 (3) | 142 (2) |
| N2—H2⋯S1i | 0.87 (1) | 2.69 (2) | 3.436 (2) | 144 (2) |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad, Pakistan, for the allocation of research and analytical laboratory facilities. The authors also thank the University of Malaya for supporting this study.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The biological potential of thiourea derivatives (Venkatachalam et al., 2004; Saeed et al., 2011) motivates structural studies of these compounds (Gunasekaran et al. 2010; Saeed et al. 2010; Dzulkifli et al., 2011). Herein, the crystal and molecular structure of the title thiourea derivative, (I), is described.
The molecular structure of (I), Fig. 1, shows a significant twist around the central atoms as seen in the value of the dihedral angle formed between the least-squares planes through the S1,N1,N2,C7 (thiourea) and O1,N2,C8,C9 (amide) atoms of 48.89 (7) °. Further, the benzene ring is twisted out of the plane of the carbonyl residue as indicated by the O1—C8—C9—C10 torsion angle of 147.1 (2) °. With respect to the S1,N1,N2,C7 plane, the n-propyl groups lie to either side. Whereas the O2-nitro group is co-planar with the benzene ring to which it is bonded, the O2—N3—C11—C10 torsion angle = -4.2 (3) °, the O4-nitro group is slightly twisted out of the plane as seen in the value of the O4—N4—C13—C12 torsion angle of -9.3 (3) °.
The crystal packing is dominated by N—H···O,S hydrogen bonds as the N1—H H atoms is bifurcated, Table 1. These result in the formation of six-membered {···H···OCNCS} synthons and linear supramolecular chains along the c direction, Fig. 2.
Experimental
A solution of 3,5-dinitrobenzoyl chloride (0.01 mol) in anhydrous acetone (75 ml) and 3% tetrabutylammonium bromide (TBAB) as a phase-transfer catalyst (PTC) in anhydrous acetone was added drop-wise to a suspension of dry potassium thiocyanate (0.01 mol) in acetone (50 ml) and the reaction mixture was refluxed for 50 min. After cooling to room temperature, a solution of dipropyl amine (0.01 mol) in anhydrous acetone (25 ml) was added drop-wise and the resulting mixture refluxed for 3 h. Hydrochloric acid (0.1 N, 300 ml) was added and the solution was filtered. The solid product was washed with water and purified by re-crystallization from ethyl acetate to yield light-yellow prisms of (I). Yield: 1.29 g (82%); M.pt. 407–408 K. IR (KBr, cm-1): 3173 ν(NH), 1690 ν(C═O), 1536 ν(benzene ring), 1180 ν(C═S). Anal. Calcd. for C14H18N4O5S: C, 47.45; H, 5.12; N, 15.81; S, 9.05%. Found: C, 47.53; H, 5.17; N, 15.75; S, 9.03%.
Refinement
Carbon-bound H-atoms were placed in calculated positions [C—H 0.93–0.97 Å, Uiso(H) 1.2–1.5Ueq(C)] and were included in the refinement in the riding model approximation. The amino H-atoms were located in a difference Fourier map, and were refined with a distance restraint of N—H 0.88±0.01 Å; the Uiso values were refined. The maximum and minimum residual electron density peaks of 1.04 and 0.46 e Å-3, respectively, were located 1.05 Å and 0.33 Å from the C2 and H2a atoms, respectively.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I) showing displacement ellipsoids at the 35% probability level.
Fig. 2.
Supramolecular chain aligned along the c axis in (I) mediated by N—H···O, S hydrogen bonding shown as blue and orange dashed lines, respectively.
Crystal data
| C14H18N4O5S | F(000) = 744 |
| Mr = 354.38 | Dx = 1.456 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 3443 reflections |
| a = 7.9406 (4) Å | θ = 2.3–29.3° |
| b = 21.2839 (10) Å | µ = 0.23 mm−1 |
| c = 9.5967 (4) Å | T = 295 K |
| β = 94.379 (4)° | Prism, light yellow |
| V = 1617.17 (13) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.20 × 0.10 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Agilent SuperNova Dual diffractometer with an Atlas detector | 3614 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: SuperNova (Mo) X-ray Source | 2878 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror | Rint = 0.027 |
| Detector resolution: 10.4041 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 2.3° |
| ω scans | h = −10→10 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2010) | k = −27→26 |
| Tmin = 0.933, Tmax = 0.977 | l = −12→10 |
| 8055 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.055 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.154 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.02 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0697P)2 + 1.1729P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3614 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 221 parameters | Δρmax = 1.04 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Δρmin = −0.46 e Å−3 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.37257 (8) | 0.21276 (3) | 0.24866 (6) | 0.0405 (2) | |
| O1 | 0.7561 (2) | 0.24758 (9) | 0.29218 (19) | 0.0505 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.5844 (3) | 0.44242 (11) | 0.7375 (2) | 0.0621 (6) | |
| O3 | 0.8149 (3) | 0.49393 (11) | 0.7748 (3) | 0.0761 (7) | |
| O4 | 1.2906 (3) | 0.44304 (11) | 0.5156 (3) | 0.0711 (7) | |
| O5 | 1.3052 (3) | 0.35161 (11) | 0.4221 (2) | 0.0623 (6) | |
| N1 | 0.4129 (2) | 0.15013 (9) | 0.4887 (2) | 0.0334 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.5882 (3) | 0.23606 (9) | 0.4730 (2) | 0.0343 (4) | |
| H2 | 0.581 (3) | 0.2455 (12) | 0.5607 (13) | 0.044 (7)* | |
| N3 | 0.7311 (3) | 0.45149 (10) | 0.7190 (2) | 0.0451 (5) | |
| N4 | 1.2306 (3) | 0.39224 (11) | 0.4807 (2) | 0.0440 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.2706 (3) | 0.10939 (12) | 0.4387 (3) | 0.0433 (6) | |
| H1A | 0.2787 | 0.0701 | 0.4899 | 0.052* | |
| H1B | 0.2802 | 0.0999 | 0.3408 | 0.052* | |
| C2 | 0.0973 (4) | 0.1384 (2) | 0.4550 (4) | 0.0746 (10) | |
| H2A | 0.0819 | 0.1733 | 0.3903 | 0.089* | |
| H2B | 0.0117 | 0.1073 | 0.4280 | 0.089* | |
| C3 | 0.0687 (5) | 0.1608 (2) | 0.5930 (5) | 0.0882 (13) | |
| H3A | −0.0414 | 0.1795 | 0.5919 | 0.132* | |
| H3B | 0.1528 | 0.1915 | 0.6217 | 0.132* | |
| H3C | 0.0757 | 0.1262 | 0.6574 | 0.132* | |
| C4 | 0.5096 (3) | 0.12842 (12) | 0.6168 (2) | 0.0396 (6) | |
| H4A | 0.4329 | 0.1098 | 0.6791 | 0.047* | |
| H4B | 0.5640 | 0.1641 | 0.6642 | 0.047* | |
| C5 | 0.6417 (4) | 0.08077 (13) | 0.5847 (3) | 0.0510 (7) | |
| H5A | 0.7223 | 0.1002 | 0.5270 | 0.061* | |
| H5B | 0.5880 | 0.0464 | 0.5318 | 0.061* | |
| C6 | 0.7351 (4) | 0.05486 (15) | 0.7163 (4) | 0.0659 (9) | |
| H6A | 0.8211 | 0.0262 | 0.6912 | 0.099* | |
| H6B | 0.6569 | 0.0332 | 0.7708 | 0.099* | |
| H6C | 0.7862 | 0.0888 | 0.7701 | 0.099* | |
| C7 | 0.4603 (3) | 0.19711 (10) | 0.4084 (2) | 0.0313 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.7150 (3) | 0.26338 (11) | 0.4063 (2) | 0.0339 (5) | |
| C9 | 0.8066 (3) | 0.31654 (10) | 0.4830 (2) | 0.0320 (5) | |
| C10 | 0.7262 (3) | 0.35735 (11) | 0.5703 (2) | 0.0337 (5) | |
| H10 | 0.6152 | 0.3502 | 0.5908 | 0.040* | |
| C11 | 0.8147 (3) | 0.40847 (11) | 0.6256 (2) | 0.0350 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.9793 (3) | 0.42129 (11) | 0.5982 (2) | 0.0367 (5) | |
| H12 | 1.0361 | 0.4564 | 0.6352 | 0.044* | |
| C13 | 1.0552 (3) | 0.37937 (11) | 0.5132 (2) | 0.0353 (5) | |
| C14 | 0.9729 (3) | 0.32754 (11) | 0.4549 (2) | 0.0338 (5) | |
| H14 | 1.0280 | 0.3004 | 0.3976 | 0.041* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0449 (4) | 0.0445 (4) | 0.0315 (3) | −0.0042 (3) | −0.0021 (2) | 0.0030 (2) |
| O1 | 0.0508 (11) | 0.0646 (12) | 0.0378 (10) | −0.0172 (9) | 0.0146 (8) | −0.0188 (9) |
| O2 | 0.0525 (12) | 0.0665 (14) | 0.0695 (14) | 0.0005 (10) | 0.0182 (10) | −0.0207 (11) |
| O3 | 0.0734 (15) | 0.0652 (14) | 0.0909 (17) | −0.0130 (12) | 0.0146 (13) | −0.0475 (13) |
| O4 | 0.0519 (12) | 0.0681 (15) | 0.0941 (18) | −0.0262 (11) | 0.0118 (12) | −0.0156 (13) |
| O5 | 0.0438 (11) | 0.0814 (15) | 0.0636 (13) | −0.0046 (10) | 0.0156 (10) | −0.0176 (12) |
| N1 | 0.0346 (10) | 0.0325 (10) | 0.0331 (10) | −0.0015 (8) | 0.0025 (8) | −0.0001 (8) |
| N2 | 0.0410 (11) | 0.0364 (10) | 0.0259 (9) | −0.0079 (8) | 0.0048 (8) | −0.0052 (8) |
| N3 | 0.0514 (14) | 0.0432 (12) | 0.0409 (12) | 0.0023 (10) | 0.0037 (10) | −0.0077 (10) |
| N4 | 0.0355 (11) | 0.0570 (14) | 0.0393 (11) | −0.0067 (10) | 0.0005 (9) | 0.0007 (10) |
| C1 | 0.0423 (14) | 0.0389 (13) | 0.0486 (14) | −0.0094 (11) | 0.0036 (11) | −0.0017 (11) |
| C2 | 0.0510 (18) | 0.097 (3) | 0.076 (2) | −0.0187 (18) | 0.0090 (16) | −0.015 (2) |
| C3 | 0.059 (2) | 0.102 (3) | 0.107 (3) | −0.015 (2) | 0.022 (2) | −0.040 (3) |
| C4 | 0.0476 (14) | 0.0394 (13) | 0.0317 (12) | −0.0022 (11) | 0.0031 (10) | 0.0047 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0528 (16) | 0.0482 (15) | 0.0500 (16) | 0.0068 (13) | −0.0093 (13) | −0.0058 (12) |
| C6 | 0.072 (2) | 0.0484 (17) | 0.072 (2) | 0.0038 (15) | −0.0257 (17) | 0.0032 (15) |
| C7 | 0.0323 (11) | 0.0305 (11) | 0.0315 (11) | 0.0008 (9) | 0.0055 (9) | −0.0042 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0363 (12) | 0.0348 (12) | 0.0308 (11) | −0.0036 (9) | 0.0035 (9) | −0.0035 (9) |
| C9 | 0.0362 (12) | 0.0337 (11) | 0.0259 (10) | −0.0029 (9) | 0.0015 (9) | 0.0012 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0353 (12) | 0.0372 (12) | 0.0285 (11) | −0.0025 (10) | 0.0019 (9) | 0.0023 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0398 (13) | 0.0344 (12) | 0.0304 (11) | 0.0023 (10) | 0.0006 (9) | −0.0022 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0424 (13) | 0.0351 (12) | 0.0318 (11) | −0.0063 (10) | −0.0024 (10) | −0.0029 (9) |
| C13 | 0.0341 (12) | 0.0416 (13) | 0.0299 (11) | −0.0042 (10) | 0.0002 (9) | 0.0037 (9) |
| C14 | 0.0364 (12) | 0.0363 (12) | 0.0290 (11) | 0.0003 (10) | 0.0040 (9) | −0.0005 (9) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| S1—C7 | 1.668 (2) | C3—H3B | 0.9600 |
| O1—C8 | 1.214 (3) | C3—H3C | 0.9600 |
| O2—N3 | 1.207 (3) | C4—C5 | 1.508 (4) |
| O3—N3 | 1.221 (3) | C4—H4A | 0.9700 |
| O4—N4 | 1.218 (3) | C4—H4B | 0.9700 |
| O5—N4 | 1.211 (3) | C5—C6 | 1.519 (4) |
| N1—C7 | 1.334 (3) | C5—H5A | 0.9700 |
| N1—C4 | 1.473 (3) | C5—H5B | 0.9700 |
| N1—C1 | 1.475 (3) | C6—H6A | 0.9600 |
| N2—C8 | 1.364 (3) | C6—H6B | 0.9600 |
| N2—C7 | 1.417 (3) | C6—H6C | 0.9600 |
| N2—H2 | 0.871 (10) | C8—C9 | 1.507 (3) |
| N3—C11 | 1.474 (3) | C9—C14 | 1.388 (3) |
| N4—C13 | 1.476 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.394 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.527 (4) | C10—C11 | 1.379 (3) |
| C1—H1A | 0.9700 | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C1—H1B | 0.9700 | C11—C12 | 1.380 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.441 (5) | C12—C13 | 1.378 (3) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9700 | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2B | 0.9700 | C13—C14 | 1.379 (3) |
| C3—H3A | 0.9600 | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C7—N1—C4 | 124.44 (19) | C4—C5—C6 | 112.2 (2) |
| C7—N1—C1 | 119.7 (2) | C4—C5—H5A | 109.2 |
| C4—N1—C1 | 115.12 (19) | C6—C5—H5A | 109.2 |
| C8—N2—C7 | 125.03 (19) | C4—C5—H5B | 109.2 |
| C8—N2—H2 | 117.3 (18) | C6—C5—H5B | 109.2 |
| C7—N2—H2 | 117.5 (18) | H5A—C5—H5B | 107.9 |
| O2—N3—O3 | 123.6 (2) | C5—C6—H6A | 109.5 |
| O2—N3—C11 | 118.3 (2) | C5—C6—H6B | 109.5 |
| O3—N3—C11 | 118.1 (2) | H6A—C6—H6B | 109.5 |
| O5—N4—O4 | 124.5 (2) | C5—C6—H6C | 109.5 |
| O5—N4—C13 | 117.9 (2) | H6A—C6—H6C | 109.5 |
| O4—N4—C13 | 117.5 (2) | H6B—C6—H6C | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 113.7 (2) | N1—C7—N2 | 114.2 (2) |
| N1—C1—H1A | 108.8 | N1—C7—S1 | 124.35 (18) |
| C2—C1—H1A | 108.8 | N2—C7—S1 | 121.38 (17) |
| N1—C1—H1B | 108.8 | O1—C8—N2 | 124.3 (2) |
| C2—C1—H1B | 108.8 | O1—C8—C9 | 119.7 (2) |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 107.7 | N2—C8—C9 | 115.93 (19) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 115.8 (3) | C14—C9—C10 | 119.9 (2) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 108.3 | C14—C9—C8 | 117.6 (2) |
| C1—C2—H2A | 108.3 | C10—C9—C8 | 122.3 (2) |
| C3—C2—H2B | 108.3 | C11—C10—C9 | 118.6 (2) |
| C1—C2—H2B | 108.3 | C11—C10—H10 | 120.7 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 107.4 | C9—C10—H10 | 120.7 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 109.5 | C10—C11—C12 | 123.0 (2) |
| C2—C3—H3B | 109.5 | C10—C11—N3 | 118.9 (2) |
| H3A—C3—H3B | 109.5 | C12—C11—N3 | 118.1 (2) |
| C2—C3—H3C | 109.5 | C13—C12—C11 | 116.6 (2) |
| H3A—C3—H3C | 109.5 | C13—C12—H12 | 121.7 |
| H3B—C3—H3C | 109.5 | C11—C12—H12 | 121.7 |
| N1—C4—C5 | 111.5 (2) | C12—C13—C14 | 122.9 (2) |
| N1—C4—H4A | 109.3 | C12—C13—N4 | 117.9 (2) |
| C5—C4—H4A | 109.3 | C14—C13—N4 | 119.2 (2) |
| N1—C4—H4B | 109.3 | C13—C14—C9 | 119.0 (2) |
| C5—C4—H4B | 109.3 | C13—C14—H14 | 120.5 |
| H4A—C4—H4B | 108.0 | C9—C14—H14 | 120.5 |
| C7—N1—C1—C2 | −79.3 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −173.6 (2) |
| C4—N1—C1—C2 | 110.2 (3) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 0.2 (3) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −52.9 (4) | C9—C10—C11—N3 | −179.4 (2) |
| C7—N1—C4—C5 | −86.1 (3) | O2—N3—C11—C10 | −4.2 (3) |
| C1—N1—C4—C5 | 83.9 (3) | O3—N3—C11—C10 | 174.9 (2) |
| N1—C4—C5—C6 | −176.4 (2) | O2—N3—C11—C12 | 176.2 (2) |
| C4—N1—C7—N2 | −15.8 (3) | O3—N3—C11—C12 | −4.8 (4) |
| C1—N1—C7—N2 | 174.7 (2) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −1.2 (3) |
| C4—N1—C7—S1 | 167.53 (18) | N3—C11—C12—C13 | 178.5 (2) |
| C1—N1—C7—S1 | −2.0 (3) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 1.2 (3) |
| C8—N2—C7—N1 | 144.3 (2) | C11—C12—C13—N4 | 179.3 (2) |
| C8—N2—C7—S1 | −38.9 (3) | O5—N4—C13—C12 | 170.3 (2) |
| C7—N2—C8—O1 | −16.5 (4) | O4—N4—C13—C12 | −9.3 (3) |
| C7—N2—C8—C9 | 163.4 (2) | O5—N4—C13—C14 | −11.5 (3) |
| O1—C8—C9—C14 | −27.4 (3) | O4—N4—C13—C14 | 168.9 (2) |
| N2—C8—C9—C14 | 152.7 (2) | C12—C13—C14—C9 | −0.3 (3) |
| O1—C8—C9—C10 | 147.1 (2) | N4—C13—C14—C9 | −178.4 (2) |
| N2—C8—C9—C10 | −32.8 (3) | C10—C9—C14—C13 | −0.7 (3) |
| C14—C9—C10—C11 | 0.7 (3) | C8—C9—C14—C13 | 173.9 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2···O1i | 0.87 (1) | 2.53 (2) | 3.264 (3) | 142 (2) |
| N2—H2···S1i | 0.87 (1) | 2.69 (2) | 3.436 (2) | 144 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HB5845).
References
- Agilent (2010). CrysAlis PRO Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, Oxfordshire, England.
- Brandenburg, K. (2006). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Dzulkifli, N. N., Farina, Y., Yamin, B. M., Baba, I. & Tiekink, E. R. T. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Gunasekaran, N., Karvembu, R., Ng, S. W. & Tiekink, E. R. T. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o2601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Saeed, S., Rashid, N., Jones, P. G. & Tahir, A. (2011). J. Heterocycl. Chem. 48, 74–84.
- Saeed, S., Rashid, N. & Wong, W.-T. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Venkatachalam, T. K., Mao, C. & Uckun, F. M. (2004). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 12, 4275–4284. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811013638/hb5845sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811013638/hb5845Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




