Abstract
The organic molecule in the title molecule, C14H12N6O5S·H2O, is roughly planar with a maximum deviation of 0.156 (2) Å. An intramolecular N—H⋯N hydrogen bond occurs. In the crystal, intermolecular N—H⋯O and O—H⋯O hydrogen-bonding interactions connect the molecules into a two-dimensional network that lies parallel to (101).
Related literature
For background to this study and our previous work on the structural chemistry of N,N′-disubstituted thiourea, see: Saeed et al. (2011 ▶).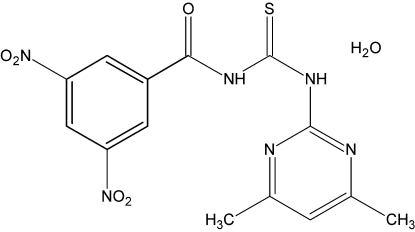
Experimental
Crystal data
C14H12N6O5S·H2O
M r = 394.37
Monoclinic,

a = 6.7892 (6) Å
b = 10.1823 (9) Å
c = 24.267 (2) Å
β = 92.901 (1)°
V = 1675.4 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.24 mm−1
T = 297 K
0.40 × 0.16 × 0.14 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART 1000 CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2004 ▶) T min = 0.909, T max = 0.967
9067 measured reflections
2942 independent reflections
2499 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.020
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.038
wR(F 2) = 0.105
S = 1.06
2942 reflections
263 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SIR92 (Altomare et al., 1994 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: Mercury (Macrae et al., 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811012323/pv2402sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811012323/pv2402Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N4—H4N⋯O6 | 0.88 (2) | 1.97 (2) | 2.849 (2) | 171.9 (19) |
| N3—H3N⋯N6 | 0.83 (2) | 2.00 (2) | 2.705 (2) | 141.8 (19) |
| O6—H6A⋯O3i | 0.82 (4) | 2.32 (4) | 3.119 (3) | 168 (4) |
| O6—H6B⋯O2ii | 0.73 (4) | 2.44 (4) | 3.143 (3) | 164 (4) |
| O6—H6B⋯O1ii | 0.73 (4) | 2.62 (4) | 3.248 (3) | 146 (4) |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad, Pakistan, for the allocation of research and analytical laboratory facilities.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The background to this study has been described in our previous work on the structural chemistry of N,N'-disubstituted thiourea (Saeed et al., 2011). In continuation of our studies, the crystal structure of the title compound, is presented in this paper.
In the title molecule (Fig. 1), the nitro groups N1/O1/O2 and N2/O3/O4 are oriented are 5.05 (11) and 9.40 (15)°, respectively, with rest to the mean-plane of the phenyl ring C1—C6. Moreover, the 4,6-dimethyl-pyrimidinyl ring plane, C9—C14/N5/N6, makes a dihedral angle of 1.31 (5)° with the the plane formed by the atoms C7/O5/N3/C8/S1/N4.
The structure is stabilized by intra-molecular N—H···O and N—H···N hydrogen bonding interactions. The inter-molecular hydrogen bonds O—H···O link the molecules into a two dimensinal network (Tab. 1 and Fig. 2).
Experimental
A solution of 3,5-dinitrobenzoyl chloride (0.01 mol) in anhydrous acetone (75 ml) and 3% tetrabutylammonium bromide as a phase-transfer catalyst in anhydrous acetone was added dropwise to a suspension of dry potassium thiocyanate (0.01 mol) in acetone (50 ml) and the reaction mixture was refluxed for 50 min. After cooling to room temperature, a solution of 2-amino-4,6-dimethylpyrimidine (0.01 mol) in anhydrous acetone (25 ml) was added dropwise and the resulting mixture refluxed for 3 h. Hydrochloric acid (0.1 N, 300 ml) was added, and the solution was filtered. The solid product was washed with water and purified by re-crystallization from ethanol.
Refinement
All of the C-bound H atoms were observable from difference Fourier map but were placed at geometrically idealized positions with C—H = 0.93 and 0.96Å for phenyl and methyl H-atoms, respectively. The C-bound H-atoms were refined using riding model with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C). Both the N– and O-bound H-atoms were located from difference Fourier map and refined isotropically.
Figures
Fig. 1.
An ORTEP plot of the title molecule drawn with 50% probability thermal ellipsoids showing the atom numbering scheme.
Fig. 2.
Packing diagram of the title compound viewed down the a axis.
Crystal data
| C14H12N6O5S·H2O | F(000) = 816 |
| Mr = 394.37 | Dx = 1.563 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 11914 reflections |
| a = 6.7892 (6) Å | θ = 2.0–25.0° |
| b = 10.1823 (9) Å | µ = 0.24 mm−1 |
| c = 24.267 (2) Å | T = 297 K |
| β = 92.901 (1)° | Prism, yellow |
| V = 1675.4 (3) Å3 | 0.40 × 0.16 × 0.14 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART 1000 CCD diffractometer | 2942 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2499 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.020 |
| ω scans | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 2.6° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2004) | h = −8→8 |
| Tmin = 0.909, Tmax = 0.967 | k = −11→12 |
| 9067 measured reflections | l = −23→28 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.038 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.105 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0466P)2 + 0.9069P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.06 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.003 |
| 2942 reflections | Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3 |
| 263 parameters | Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.0044 (6) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger.The structure was solved by direct methods (SHELXS97) and expanded using Fourier techniques. All non-H atoms were refined anisotropically.All of the C-bound H atoms are observable from difference Fourier map but are all placed at geometrical positions with C—H = 0.93 and 0.96Å for phenyl and methyl H-atoms. All C-bound H-atoms are refined using riding model with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(Carrier). Both the N– and O-bound H-atoms were located from difference Fourier map and refined isotropically.Highest peak is 0.20 at (0.0792, 0.5848, 0.1447) [0.83Å from Hl4C] Deepest hole is -0.23 at (0.0397, 0.8302, 0.0937) [0.74Å from Sl] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.64692 (10) | 0.68130 (5) | 0.59394 (2) | 0.05020 (19) | |
| O1 | 0.9131 (3) | 0.89155 (18) | 0.30790 (8) | 0.0777 (6) | |
| O2 | 1.0041 (4) | 0.7610 (2) | 0.24468 (8) | 0.0851 (7) | |
| O3 | 0.9757 (3) | 0.29505 (18) | 0.27197 (7) | 0.0759 (6) | |
| O4 | 0.8719 (4) | 0.21594 (17) | 0.34703 (7) | 0.0802 (6) | |
| O5 | 0.7636 (3) | 0.73999 (15) | 0.48300 (6) | 0.0608 (5) | |
| O6 | 0.5934 (4) | 0.4521 (2) | 0.70525 (8) | 0.0692 (6) | |
| H6A | 0.561 (5) | 0.395 (4) | 0.7269 (16) | 0.108 (14)* | |
| H6B | 0.569 (6) | 0.512 (4) | 0.7202 (16) | 0.108 (15)* | |
| N1 | 0.9439 (3) | 0.7823 (2) | 0.29029 (8) | 0.0563 (5) | |
| N2 | 0.9151 (3) | 0.30735 (18) | 0.31844 (8) | 0.0519 (5) | |
| N3 | 0.7393 (2) | 0.52460 (16) | 0.50834 (6) | 0.0338 (4) | |
| H3N | 0.753 (3) | 0.447 (2) | 0.4988 (8) | 0.035 (6)* | |
| N4 | 0.6648 (2) | 0.42786 (15) | 0.59103 (7) | 0.0354 (4) | |
| H4N | 0.632 (3) | 0.440 (2) | 0.6254 (10) | 0.037 (5)* | |
| N5 | 0.6445 (3) | 0.21615 (16) | 0.61919 (7) | 0.0405 (4) | |
| N6 | 0.7339 (2) | 0.26275 (15) | 0.52709 (6) | 0.0346 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.8532 (3) | 0.6919 (2) | 0.37878 (8) | 0.0395 (5) | |
| H1 | 0.8383 | 0.7775 | 0.3913 | 0.047* | |
| C2 | 0.9061 (3) | 0.6685 (2) | 0.32582 (8) | 0.0416 (5) | |
| C3 | 0.9278 (3) | 0.5444 (2) | 0.30505 (8) | 0.0437 (5) | |
| H3 | 0.9645 | 0.5305 | 0.2691 | 0.052* | |
| C4 | 0.8928 (3) | 0.4414 (2) | 0.33990 (8) | 0.0399 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.8407 (3) | 0.45841 (19) | 0.39404 (8) | 0.0363 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.8188 | 0.3865 | 0.4166 | 0.044* | |
| C6 | 0.8221 (3) | 0.58592 (19) | 0.41368 (8) | 0.0341 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.7720 (3) | 0.62534 (18) | 0.47127 (8) | 0.0362 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.6868 (3) | 0.54090 (18) | 0.56219 (8) | 0.0330 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.6830 (3) | 0.29543 (18) | 0.57718 (8) | 0.0331 (4) | |
| C10 | 0.6548 (3) | 0.0876 (2) | 0.60875 (8) | 0.0417 (5) | |
| C11 | 0.7017 (3) | 0.04196 (19) | 0.55717 (8) | 0.0429 (5) | |
| H11 | 0.7055 | −0.0477 | 0.5499 | 0.051* | |
| C12 | 0.7424 (3) | 0.13190 (19) | 0.51685 (8) | 0.0371 (4) | |
| C13 | 0.7985 (4) | 0.0930 (2) | 0.46069 (8) | 0.0496 (6) | |
| H13A | 0.9262 | 0.1281 | 0.4539 | 0.060* | |
| H13B | 0.7032 | 0.1269 | 0.4338 | 0.060* | |
| H13C | 0.8021 | −0.0010 | 0.4581 | 0.060* | |
| C14 | 0.6125 (4) | −0.0021 (2) | 0.65554 (9) | 0.0600 (7) | |
| H14A | 0.6208 | 0.0462 | 0.6895 | 0.072* | |
| H14B | 0.7073 | −0.0722 | 0.6573 | 0.072* | |
| H14C | 0.4824 | −0.0381 | 0.6498 | 0.072* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0823 (4) | 0.0302 (3) | 0.0389 (3) | 0.0073 (2) | 0.0114 (3) | −0.0046 (2) |
| O1 | 0.1246 (17) | 0.0442 (10) | 0.0658 (12) | −0.0034 (10) | 0.0201 (11) | 0.0142 (9) |
| O2 | 0.1375 (18) | 0.0706 (13) | 0.0507 (11) | −0.0010 (12) | 0.0386 (11) | 0.0165 (9) |
| O3 | 0.1253 (16) | 0.0596 (11) | 0.0457 (10) | 0.0000 (10) | 0.0324 (10) | −0.0116 (8) |
| O4 | 0.1496 (19) | 0.0412 (9) | 0.0524 (11) | −0.0108 (11) | 0.0316 (11) | −0.0044 (8) |
| O5 | 0.1047 (13) | 0.0309 (8) | 0.0490 (9) | −0.0032 (8) | 0.0266 (9) | −0.0014 (7) |
| O6 | 0.1083 (16) | 0.0545 (11) | 0.0466 (10) | 0.0065 (11) | 0.0221 (10) | −0.0072 (9) |
| N1 | 0.0725 (14) | 0.0516 (12) | 0.0452 (11) | −0.0031 (10) | 0.0085 (10) | 0.0142 (9) |
| N2 | 0.0741 (13) | 0.0450 (11) | 0.0374 (10) | −0.0029 (9) | 0.0101 (9) | −0.0037 (8) |
| N3 | 0.0430 (9) | 0.0269 (8) | 0.0320 (8) | 0.0018 (7) | 0.0057 (7) | −0.0014 (7) |
| N4 | 0.0495 (10) | 0.0294 (8) | 0.0278 (8) | 0.0022 (7) | 0.0070 (7) | −0.0019 (6) |
| N5 | 0.0561 (10) | 0.0331 (9) | 0.0327 (9) | −0.0012 (7) | 0.0063 (7) | 0.0004 (7) |
| N6 | 0.0429 (9) | 0.0296 (8) | 0.0315 (8) | 0.0024 (7) | 0.0038 (7) | −0.0008 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0421 (11) | 0.0363 (11) | 0.0403 (11) | −0.0004 (8) | 0.0036 (9) | 0.0033 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0458 (11) | 0.0443 (12) | 0.0349 (11) | −0.0030 (9) | 0.0042 (9) | 0.0102 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0495 (12) | 0.0506 (12) | 0.0316 (10) | −0.0043 (10) | 0.0071 (9) | 0.0013 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0459 (11) | 0.0409 (11) | 0.0330 (10) | −0.0012 (9) | 0.0036 (8) | −0.0025 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0390 (10) | 0.0375 (10) | 0.0325 (10) | −0.0035 (8) | 0.0033 (8) | 0.0020 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0337 (10) | 0.0364 (10) | 0.0323 (10) | −0.0009 (8) | 0.0025 (7) | 0.0020 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0409 (11) | 0.0305 (10) | 0.0374 (10) | −0.0013 (8) | 0.0041 (8) | −0.0001 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0351 (10) | 0.0317 (9) | 0.0321 (10) | 0.0014 (8) | 0.0013 (8) | −0.0011 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0369 (10) | 0.0304 (9) | 0.0320 (10) | 0.0008 (8) | 0.0023 (8) | 0.0002 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0557 (12) | 0.0342 (10) | 0.0353 (10) | −0.0034 (9) | 0.0044 (9) | 0.0017 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0602 (13) | 0.0287 (10) | 0.0403 (11) | 0.0009 (9) | 0.0073 (9) | −0.0020 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0438 (11) | 0.0326 (10) | 0.0350 (10) | 0.0028 (8) | 0.0031 (8) | −0.0024 (8) |
| C13 | 0.0744 (15) | 0.0351 (11) | 0.0403 (12) | 0.0044 (10) | 0.0132 (11) | −0.0043 (9) |
| C14 | 0.105 (2) | 0.0363 (12) | 0.0400 (12) | −0.0073 (12) | 0.0160 (12) | 0.0025 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| S1—C8 | 1.6528 (19) | C1—C6 | 1.395 (3) |
| O1—N1 | 1.213 (3) | C1—H1 | 0.9300 |
| O2—N1 | 1.218 (3) | C2—C3 | 1.372 (3) |
| O3—N2 | 1.226 (2) | C3—C4 | 1.375 (3) |
| O4—N2 | 1.206 (2) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| O5—C7 | 1.204 (2) | C4—C5 | 1.389 (3) |
| O6—H6A | 0.82 (4) | C5—C6 | 1.391 (3) |
| O6—H6B | 0.73 (4) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C2 | 1.475 (3) | C6—C7 | 1.509 (3) |
| N2—C4 | 1.472 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.387 (3) |
| N3—C8 | 1.382 (2) | C10—C14 | 1.496 (3) |
| N3—C7 | 1.390 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.379 (3) |
| N3—H3N | 0.83 (2) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| N4—C8 | 1.359 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.487 (3) |
| N4—C9 | 1.397 (2) | C13—H13A | 0.9600 |
| N4—H4N | 0.88 (2) | C13—H13B | 0.9600 |
| N5—C9 | 1.337 (2) | C13—H13C | 0.9600 |
| N5—C10 | 1.336 (3) | C14—H14A | 0.9600 |
| N6—C9 | 1.323 (2) | C14—H14B | 0.9600 |
| N6—C12 | 1.357 (2) | C14—H14C | 0.9600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.373 (3) | ||
| H6A—O6—H6B | 101 (4) | C1—C6—C7 | 113.88 (17) |
| O1—N1—O2 | 123.7 (2) | O5—C7—N3 | 123.49 (18) |
| O1—N1—C2 | 118.43 (19) | O5—C7—C6 | 119.51 (17) |
| O2—N1—C2 | 117.9 (2) | N3—C7—C6 | 117.00 (16) |
| O4—N2—O3 | 123.56 (19) | N4—C8—N3 | 115.18 (16) |
| O4—N2—C4 | 118.69 (17) | N4—C8—S1 | 117.87 (14) |
| O3—N2—C4 | 117.75 (18) | N3—C8—S1 | 126.94 (14) |
| C8—N3—C7 | 125.51 (17) | N6—C9—N5 | 128.26 (17) |
| C8—N3—H3N | 114.5 (14) | N6—C9—N4 | 119.63 (16) |
| C7—N3—H3N | 119.9 (14) | N5—C9—N4 | 112.11 (16) |
| C8—N4—C9 | 132.86 (16) | N5—C10—C11 | 121.06 (18) |
| C8—N4—H4N | 114.2 (14) | N5—C10—C14 | 116.15 (18) |
| C9—N4—H4N | 112.9 (14) | C11—C10—C14 | 122.79 (19) |
| C9—N5—C10 | 115.67 (17) | C12—C11—C10 | 118.78 (18) |
| C9—N6—C12 | 115.51 (16) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.6 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 119.31 (19) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.6 |
| C2—C1—H1 | 120.3 | N6—C12—C11 | 120.68 (17) |
| C6—C1—H1 | 120.3 | N6—C12—C13 | 116.40 (17) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 122.81 (18) | C11—C12—C13 | 122.92 (18) |
| C1—C2—N1 | 118.21 (19) | C12—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—N1 | 118.97 (18) | C12—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 116.83 (18) | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 121.6 | C12—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 121.6 | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 123.19 (19) | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—N2 | 117.74 (17) | C10—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—N2 | 119.06 (17) | C10—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 118.16 (17) | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.9 | C10—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.9 | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 119.68 (17) | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 126.44 (17) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N4—H4N···O6 | 0.88 (2) | 1.97 (2) | 2.849 (2) | 171.9 (19) |
| N3—H3N···N6 | 0.83 (2) | 2.00 (2) | 2.705 (2) | 141.8 (19) |
| O6—H6A···O3i | 0.82 (4) | 2.32 (4) | 3.119 (3) | 168 (4) |
| O6—H6B···O2ii | 0.73 (4) | 2.44 (4) | 3.143 (3) | 164 (4) |
| O6—H6B···O1ii | 0.73 (4) | 2.62 (4) | 3.248 (3) | 146 (4) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1/2, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (ii) x−1/2, −y+3/2, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: PV2402).
References
- Altomare, A., Cascarano, G., Giacovazzo, C., Guagliardi, A., Burla, M. C., Polidori, G. & Camalli, M. (1994). J. Appl. Cryst. 27, 435.
- Bruker (2007). SAINT and SMART Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Saeed, S., Rashid, N., Jones, P. G. & Tahir, A. (2011). J. Heterocycl. Chem. 48, 74–84.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2004). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811012323/pv2402sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811012323/pv2402Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




