Abstract
In the title compound, C21H16F2N2, the seven-membered 1,4-diazepine ring of the benzodiazepine ring system adopts a distorted-boat conformation. The benzene ring of this system makes dihedral angles of 18.6 (2) and 78.8 (2)° with those of two fluorophenyl substituents. In the crystal, inversion dimers linked by two weak C—H⋯F hydrogen bonds generate R 2 2(20) ring motifs. There are also weak N—H⋯π and C—H⋯π interactions.
Related literature
For related structures, see: An et al. (2007 ▶); Bibila Mayaya Bisseyou et al. (2010 ▶); Harrison et al. (2005 ▶); Peeters et al. (1997 ▶). For puckering parameters, see: Cremer & Pople (1975 ▶). For graph-set nomenclature of hydrogen bonds, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶).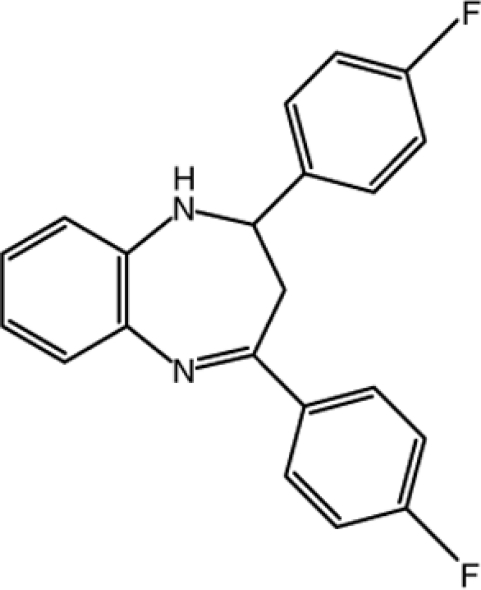
Experimental
Crystal data
C21H16F2N2
M r = 334.36
Monoclinic,

a = 12.9151 (4) Å
b = 6.0438 (3) Å
c = 21.2851 (7) Å
β = 92.147 (3)°
V = 1660.27 (11) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.10 mm−1
T = 294 K
0.20 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID-S diffractometer
Absorption correction: refined from ΔF (XABS2; Parkin et al., 1995 ▶) T min = 0.981, T max = 0.981
3413 measured reflections
3413 independent reflections
1226 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.061
wR(F 2) = 0.151
S = 1.04
3413 reflections
233 parameters
2 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.16 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3
Data collection: CrystalClear (Rigaku/MSC, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: CrystalClear; data reduction: CrystalClear; program(s) used to solve structure: SIR97 (Altomare et al., 1999 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811015455/hb5848sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811015455/hb5848Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811015455/hb5848Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the benzene rings of the two fluorophenyl substituents (C10–C15 and C16–C21, respectively).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C5—H5⋯F1i | 0.93 | 2.54 | 3.469 (6) | 175 |
| N1—H1N⋯Cg2i | 0.86 (3) | 2.82 (5) | 3.601 (4) | 151 (4) |
| C2—H2⋯Cg1ii | 0.93 | 2.89 | 3.640 (5) | 138 |
| C11—H11⋯Cg2 | 0.93 | 2.79 | 3.494 (5) | 134 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
ZB and MA thank the Unit of the Scientific Research Projects of Erciyes University, Turkey for the research grant FBD-10–2949, and for support of the data collection at Atatürk University, Turkey. SS and BN thank Mangalore University and the UGC SAP for financial assistance for the purchase of chemicals. HSY thanks the UOM for sabbatical leave.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The crystal structures of some 1,5-benzodiazepines, viz., 2-[2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-1,5-benzodiazepin-4-yl]phenol (Bibila Mayaya Bisseyou et al., 2010), 1-(2-bromo-5-methoxyphenyl)-8-chloro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazolo[4,3-a][1,4] benzodiazepine (Harrison et al., 2005), 5-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,8-dimethyl-2-(p-toluoylaminomethyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-1,4-benzodiazepine monohydrate (Peeters et al., 1997) and 2,4-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-2-methyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-1,5-benzodiazepine (An et al., 2007) have been reported. In continuation of this work, the title compound, (I), is synthesized and its crystal structure is reported here.
The seven-membered 1,4-diazepine ring (C1/C6–C9/N1/N2) of the benzodiazepine ring system (C1–C9/N1/N2) adopts a distorted-boat conformation [the puckering parameters (Cremer & Pople, 1975) for this eleven-membered ring system are: Q2 = 0.917 (4) Å, Q3 = 0.155 (4) Å, φ2 = 16.6 (3)° and φ3 = 92.6 (17)°] as shown in Fig. 1. The benzene ring (C1–C6) of this system forms dihedral angles of 18.6 (2)° and 78.8 (2)° with the benzene rings (C10–C15 and C16–C21) of two fluorophenyl fragments, respectively which make a dihedral angle of 62.1 (2)° with each other.
In the crystal, the two weak C—H···F hydrogen bonds link pairs of inversion-related molecules to form cyclic centrosymmetric dimers containing the R22(20) ring motif (Bernstein et al., 1995; Table 1, Fig. 2). In addtion, three C—H···π interactions are observed (Table 1).
Experimental
To a solution of 4,4'-difluoro chalcone (2.44 g, 0.01 mol) in ethanol (30 ml) a few drops of piperidine and 1, 2-diaminobenzene (1.08 g, 01 mol) were added. The mixture was heated under reflux for 10 h. The reaction mixture was cooled and poured into 50 ml ice-cold water. The precipitate was collected by filtration and purified by recrystallization from ethanol. Pale yellow blocks of (I) were grown from DMF by slow evaporation method in 66% yield (m. p.: 409 K).
Refinement
The amine and methine H atoms were placed from a Fourier map and positional parameters were constrained to ride on their parent atom by applying the N–H and C–H DFIX restraints of 0.86 (1) and 0.98 (1) Å, respectively. Their isotropic displacement parameters were set to be 1.2Ueq of the carrier atoms. The other H atoms were positioned geometrically [C—H = 0.93 and 0.97Å for aromatic and methylene H atoms, respectively] and allowed to ride on their parent C atoms, with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C). Owing to the large number of weak high-angle reflections, the ratio of observed to unique reflections is low (36%).
Figures
Fig. 1.
View of the structure of (I) with displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms drawn at the 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.
Packing diagram of the title compound viewed down the b axis. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dotted lines.
Crystal data
| C21H16F2N2 | F(000) = 696 |
| Mr = 334.36 | Dx = 1.338 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 1691 reflections |
| a = 12.9151 (4) Å | θ = 2.5–26.3° |
| b = 6.0438 (3) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| c = 21.2851 (7) Å | T = 294 K |
| β = 92.147 (3)° | Block, pale yellow |
| V = 1660.27 (11) Å3 | 0.20 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID-S diffractometer | 3413 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Sealed Tube | 1226 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite Monochromator | Rint = 0.000 |
| Detector resolution: 10.0000 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.5°, θmin = 3.2° |
| dtprofit.ref scans | h = −16→16 |
| Absorption correction: part of the refinement model (ΔF) [XABS2 (Parkin et al., 1995); Cubic fit to sinθ/λ, 24 parameters] | k = 0→7 |
| Tmin = 0.981, Tmax = 0.981 | l = 0→26 |
| 3413 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.061 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.151 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.04 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.P)2 + 1.2828P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3413 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 233 parameters | Δρmax = 0.16 e Å−3 |
| 2 restraints | Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement on F2 for ALL reflections except those flagged by the user for potential systematic errors. Weighted R-factors wR and all goodnesses of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The observed criterion of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating -R-factor-obs etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| F1 | 0.2985 (2) | 0.5093 (5) | 0.38988 (13) | 0.1156 (16) | |
| F2 | 0.6025 (2) | −0.0519 (5) | 0.58369 (17) | 0.1365 (18) | |
| N1 | −0.0014 (3) | 0.2319 (7) | 0.60658 (19) | 0.0764 (17) | |
| N2 | 0.1477 (3) | −0.0519 (6) | 0.67436 (16) | 0.0667 (16) | |
| C1 | 0.0446 (4) | −0.0259 (7) | 0.6923 (2) | 0.0649 (17) | |
| C2 | 0.0114 (4) | −0.1609 (7) | 0.7400 (2) | 0.0747 (19) | |
| C3 | −0.0881 (4) | −0.1566 (8) | 0.7601 (2) | 0.084 (2) | |
| C4 | −0.1587 (4) | −0.0156 (9) | 0.7299 (2) | 0.090 (2) | |
| C5 | −0.1280 (4) | 0.1161 (8) | 0.6815 (2) | 0.083 (2) | |
| C6 | −0.0273 (4) | 0.1150 (7) | 0.6613 (2) | 0.0669 (17) | |
| C7 | 0.0768 (4) | 0.4074 (7) | 0.6097 (2) | 0.0674 (17) | |
| C8 | 0.1593 (3) | 0.3499 (7) | 0.66113 (19) | 0.0675 (17) | |
| C9 | 0.2006 (3) | 0.1161 (7) | 0.6576 (2) | 0.0635 (17) | |
| C10 | 0.3074 (3) | 0.0767 (7) | 0.6375 (2) | 0.0652 (17) | |
| C11 | 0.3591 (4) | 0.2231 (8) | 0.6009 (2) | 0.080 (2) | |
| C12 | 0.4584 (4) | 0.1818 (9) | 0.5813 (2) | 0.095 (3) | |
| C13 | 0.5044 (4) | −0.0120 (10) | 0.6017 (3) | 0.094 (3) | |
| C14 | 0.4580 (4) | −0.1612 (8) | 0.6392 (2) | 0.085 (2) | |
| C15 | 0.3579 (4) | −0.1181 (7) | 0.6567 (2) | 0.0735 (17) | |
| C16 | 0.1258 (3) | 0.4366 (7) | 0.5464 (2) | 0.0628 (17) | |
| C17 | 0.1274 (3) | 0.2722 (7) | 0.5013 (2) | 0.0710 (17) | |
| C18 | 0.1843 (4) | 0.2974 (9) | 0.4478 (2) | 0.083 (2) | |
| C19 | 0.2394 (4) | 0.4894 (10) | 0.4416 (2) | 0.081 (2) | |
| C20 | 0.2382 (4) | 0.6561 (8) | 0.4837 (2) | 0.080 (2) | |
| C21 | 0.1800 (3) | 0.6298 (7) | 0.5363 (2) | 0.0721 (17) | |
| H1N | −0.060 (2) | 0.265 (10) | 0.588 (2) | 0.1640* | |
| H2 | 0.05840 | −0.25840 | 0.75920 | 0.0900* | |
| H3 | −0.10780 | −0.24590 | 0.79310 | 0.1010* | |
| H4 | −0.22690 | −0.01050 | 0.74250 | 0.1080* | |
| H5 | −0.17630 | 0.20920 | 0.66170 | 0.1000* | |
| H7 | 0.048 (4) | 0.552 (4) | 0.621 (2) | 0.1640* | |
| H8A | 0.21670 | 0.45220 | 0.65810 | 0.0810* | |
| H8B | 0.12960 | 0.37130 | 0.70190 | 0.0810* | |
| H11 | 0.32650 | 0.35440 | 0.58870 | 0.0960* | |
| H12 | 0.49230 | 0.28040 | 0.55560 | 0.1140* | |
| H14 | 0.49250 | −0.28860 | 0.65270 | 0.1020* | |
| H15 | 0.32380 | −0.21960 | 0.68140 | 0.0880* | |
| H17 | 0.08980 | 0.14290 | 0.50700 | 0.0850* | |
| H18 | 0.18500 | 0.18780 | 0.41710 | 0.0990* | |
| H20 | 0.27570 | 0.78520 | 0.47760 | 0.0960* | |
| H21 | 0.17710 | 0.74420 | 0.56540 | 0.0860* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| F1 | 0.117 (3) | 0.135 (3) | 0.098 (2) | 0.027 (2) | 0.0457 (19) | 0.034 (2) |
| F2 | 0.080 (2) | 0.133 (3) | 0.199 (4) | 0.019 (2) | 0.040 (2) | 0.037 (3) |
| N1 | 0.065 (3) | 0.093 (3) | 0.071 (3) | −0.011 (2) | 0.002 (2) | 0.014 (2) |
| N2 | 0.063 (3) | 0.064 (2) | 0.073 (3) | 0.001 (2) | 0.003 (2) | 0.001 (2) |
| C1 | 0.065 (3) | 0.066 (3) | 0.064 (3) | −0.005 (3) | 0.006 (2) | 0.001 (2) |
| C2 | 0.078 (4) | 0.070 (3) | 0.076 (3) | 0.000 (3) | 0.002 (3) | 0.003 (3) |
| C3 | 0.088 (4) | 0.088 (4) | 0.077 (4) | 0.001 (3) | 0.020 (3) | 0.014 (3) |
| C4 | 0.073 (4) | 0.109 (4) | 0.090 (4) | 0.005 (3) | 0.015 (3) | 0.011 (3) |
| C5 | 0.069 (3) | 0.098 (4) | 0.083 (4) | 0.009 (3) | 0.013 (3) | 0.012 (3) |
| C6 | 0.066 (3) | 0.072 (3) | 0.063 (3) | 0.001 (3) | 0.008 (2) | 0.002 (2) |
| C7 | 0.069 (3) | 0.069 (3) | 0.064 (3) | 0.004 (3) | 0.000 (2) | 0.004 (3) |
| C8 | 0.072 (3) | 0.064 (3) | 0.066 (3) | −0.001 (2) | −0.003 (2) | −0.003 (2) |
| C9 | 0.064 (3) | 0.061 (3) | 0.065 (3) | 0.005 (2) | −0.004 (2) | 0.000 (2) |
| C10 | 0.062 (3) | 0.067 (3) | 0.066 (3) | −0.004 (3) | −0.006 (2) | 0.000 (2) |
| C11 | 0.062 (3) | 0.082 (4) | 0.096 (4) | 0.001 (3) | 0.000 (3) | 0.015 (3) |
| C12 | 0.071 (4) | 0.102 (4) | 0.113 (5) | 0.003 (3) | 0.013 (3) | 0.031 (3) |
| C13 | 0.056 (3) | 0.105 (5) | 0.123 (5) | 0.012 (3) | 0.015 (3) | 0.010 (4) |
| C14 | 0.067 (4) | 0.078 (4) | 0.109 (4) | 0.005 (3) | 0.003 (3) | 0.010 (3) |
| C15 | 0.069 (3) | 0.067 (3) | 0.084 (3) | −0.007 (3) | −0.002 (3) | −0.001 (3) |
| C16 | 0.061 (3) | 0.061 (3) | 0.066 (3) | 0.004 (2) | −0.004 (2) | 0.002 (2) |
| C17 | 0.073 (3) | 0.068 (3) | 0.072 (3) | 0.003 (3) | 0.003 (3) | 0.001 (3) |
| C18 | 0.091 (4) | 0.084 (4) | 0.074 (4) | 0.016 (3) | 0.007 (3) | −0.006 (3) |
| C19 | 0.078 (4) | 0.099 (4) | 0.067 (3) | 0.020 (3) | 0.017 (3) | 0.023 (3) |
| C20 | 0.080 (4) | 0.074 (4) | 0.085 (4) | 0.006 (3) | 0.006 (3) | 0.017 (3) |
| C21 | 0.077 (3) | 0.068 (3) | 0.071 (3) | 0.002 (3) | −0.002 (3) | 0.001 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| F1—C19 | 1.368 (5) | C14—C15 | 1.384 (7) |
| F2—C13 | 1.359 (6) | C16—C21 | 1.382 (6) |
| N1—C6 | 1.413 (6) | C16—C17 | 1.382 (6) |
| N1—C7 | 1.464 (6) | C17—C18 | 1.387 (6) |
| N2—C1 | 1.408 (6) | C18—C19 | 1.370 (8) |
| N2—C9 | 1.282 (6) | C19—C20 | 1.349 (7) |
| N1—H1N | 0.86 (3) | C20—C21 | 1.381 (6) |
| C1—C6 | 1.406 (7) | C2—H2 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.383 (6) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.370 (7) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.388 (7) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.372 (7) | C7—H7 | 0.98 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.385 (7) | C8—H8A | 0.9700 |
| C7—C8 | 1.539 (6) | C8—H8B | 0.9700 |
| C7—C16 | 1.520 (6) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C8—C9 | 1.513 (6) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C9—C10 | 1.479 (6) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C10—C11 | 1.369 (6) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C10—C15 | 1.400 (6) | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C11—C12 | 1.386 (7) | C18—H18 | 0.9300 |
| C12—C13 | 1.376 (8) | C20—H20 | 0.9300 |
| C13—C14 | 1.358 (8) | C21—H21 | 0.9300 |
| C6—N1—C7 | 120.6 (4) | F1—C19—C18 | 117.4 (4) |
| C1—N2—C9 | 120.4 (4) | C18—C19—C20 | 123.3 (4) |
| C7—N1—H1N | 116 (4) | C19—C20—C21 | 118.2 (5) |
| C6—N1—H1N | 105 (3) | C16—C21—C20 | 121.2 (4) |
| N2—C1—C6 | 123.7 (4) | C1—C2—H2 | 119.00 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 119.0 (5) | C3—C2—H2 | 119.00 |
| N2—C1—C2 | 117.1 (4) | C2—C3—H3 | 121.00 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 122.6 (4) | C4—C3—H3 | 121.00 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 118.3 (4) | C3—C4—H4 | 120.00 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.0 (5) | C5—C4—H4 | 120.00 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 122.1 (5) | C4—C5—H5 | 119.00 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 117.9 (4) | C6—C5—H5 | 119.00 |
| N1—C6—C1 | 121.1 (4) | N1—C7—H7 | 113 (3) |
| N1—C6—C5 | 120.5 (4) | C8—C7—H7 | 107 (3) |
| N1—C7—C16 | 110.7 (4) | C16—C7—H7 | 107 (2) |
| N1—C7—C8 | 109.1 (3) | C7—C8—H8A | 109.00 |
| C8—C7—C16 | 110.9 (4) | C7—C8—H8B | 109.00 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 114.3 (3) | C9—C8—H8A | 109.00 |
| N2—C9—C8 | 122.2 (4) | C9—C8—H8B | 109.00 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 119.9 (4) | H8A—C8—H8B | 108.00 |
| N2—C9—C10 | 117.8 (4) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.00 |
| C9—C10—C15 | 118.7 (4) | C12—C11—H11 | 119.00 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 122.7 (4) | C11—C12—H12 | 122.00 |
| C11—C10—C15 | 118.6 (4) | C13—C12—H12 | 122.00 |
| C10—C11—C12 | 122.1 (4) | C13—C14—H14 | 121.00 |
| C11—C12—C13 | 116.9 (5) | C15—C14—H14 | 121.00 |
| C12—C13—C14 | 123.8 (5) | C10—C15—H15 | 120.00 |
| F2—C13—C14 | 119.0 (5) | C14—C15—H15 | 120.00 |
| F2—C13—C12 | 117.3 (5) | C16—C17—H17 | 119.00 |
| C13—C14—C15 | 118.1 (5) | C18—C17—H17 | 120.00 |
| C10—C15—C14 | 120.7 (4) | C17—C18—H18 | 121.00 |
| C17—C16—C21 | 118.6 (4) | C19—C18—H18 | 121.00 |
| C7—C16—C17 | 123.3 (4) | C19—C20—H20 | 121.00 |
| C7—C16—C21 | 117.8 (4) | C21—C20—H20 | 121.00 |
| C16—C17—C18 | 120.9 (4) | C16—C21—H21 | 119.00 |
| C17—C18—C19 | 117.7 (4) | C20—C21—H21 | 119.00 |
| F1—C19—C20 | 119.3 (5) | ||
| C6—N1—C7—C8 | 32.4 (5) | C7—C8—C9—N2 | −74.6 (5) |
| C6—N1—C7—C16 | 154.7 (4) | N2—C9—C10—C11 | 159.0 (4) |
| C7—N1—C6—C1 | −67.0 (6) | N2—C9—C10—C15 | −21.1 (6) |
| C7—N1—C6—C5 | 120.7 (5) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −24.2 (6) |
| C9—N2—C1—C6 | 40.9 (6) | C8—C9—C10—C15 | 155.7 (4) |
| C9—N2—C1—C2 | −144.4 (4) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −178.6 (4) |
| C1—N2—C9—C8 | 5.1 (6) | C15—C10—C11—C12 | 1.5 (7) |
| C1—N2—C9—C10 | −178.2 (4) | C9—C10—C15—C14 | −179.7 (4) |
| N2—C1—C6—C5 | 176.5 (4) | C11—C10—C15—C14 | 0.2 (7) |
| N2—C1—C2—C3 | −177.7 (4) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −1.6 (7) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −2.7 (7) | C11—C12—C13—F2 | −178.8 (5) |
| N2—C1—C6—N1 | 3.9 (7) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.1 (8) |
| C2—C1—C6—N1 | −170.7 (4) | F2—C13—C14—C15 | −179.6 (5) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 1.8 (6) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 1.5 (8) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 2.0 (7) | C13—C14—C15—C10 | −1.6 (7) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.5 (7) | C7—C16—C17—C18 | −171.8 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.3 (7) | C21—C16—C17—C18 | 1.7 (6) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.4 (7) | C7—C16—C21—C20 | 171.2 (4) |
| C4—C5—C6—N1 | 172.2 (4) | C17—C16—C21—C20 | −2.6 (6) |
| N1—C7—C8—C9 | 48.6 (5) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | 0.6 (7) |
| N1—C7—C16—C21 | 163.2 (4) | C17—C18—C19—F1 | 177.5 (4) |
| C8—C7—C16—C17 | 97.9 (5) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | −2.2 (8) |
| C8—C7—C16—C21 | −75.6 (5) | F1—C19—C20—C21 | −178.4 (4) |
| N1—C7—C16—C17 | −23.3 (6) | C18—C19—C20—C21 | 1.3 (8) |
| C16—C7—C8—C9 | −73.5 (4) | C19—C20—C21—C16 | 1.2 (7) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 108.7 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the benzene rings of the two fluorophenyl substituents (C10–C15 and C16–C21, respectively). |
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C5—H5···F1i | 0.93 | 2.54 | 3.469 (6) | 175 |
| N1—H1N···Cg2i | 0.86 (3) | 2.82 (5) | 3.601 (4) | 151 (4) |
| C2—H2···Cg1ii | 0.93 | 2.89 | 3.640 (5) | 138 |
| C11—H11···Cg2 | 0.93 | 2.79 | 3.494 (5) | 134 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) −x+1/2, y−1/2, −z+3/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HB5848).
References
- Altomare, A., Burla, M. C., Camalli, M., Cascarano, G. L., Giacovazzo, C., Guagliardi, A., Moliterni, A. G. G., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 115–119.
- An, L.-T., Ding, F.-Q., Zou, J.-P. & Lu, X.-H. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o3272–o3273.
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Bibila Mayaya Bisseyou, Y., Adjou, A., Yapo, Y. M., Bany, G. E. & Kakou-Yao, R. C. A. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o87–o88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97, 1354–1358.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 837–838.
- Harrison, W. T. A., Yathirajan, H. S., Anilkumar, H. G., Sarojini, B. K., Narayana, B. & Lobo, K. G. (2005). Acta Cryst. E61, o3810–o3812. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Parkin, S., Moezzi, B. & Hope, H. (1995). J. Appl. Cryst. 28, 53–56.
- Peeters, O. M., Blaton, N. M. & de Ranter, C. J. (1997). Acta Cryst. C53, 95–97.
- Rigaku/MSC (2005). CrystalClear Rigaku/MSC, The Woodlands, Texas, USA.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811015455/hb5848sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811015455/hb5848Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811015455/hb5848Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




