Abstract
In the title compound, C7H10Cl2O2, the seven-membered ring displays a chair conformation. In the crystal, the hydroxy H atom is equally disordered over two orientations, and links with an adjacent molecule via an O—H⋯O hydrogen bond in both cases. Weak intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonding is also a feature of the crystal structure.
Related literature
For background to syn-bis-epoxides, see: Balcı (1981 ▶); Akbulut et al. (1987 ▶); Menzek & Balcı (1993 ▶); Saraçoğlu et al. (1999 ▶). For background to unsaturated bicyclic endopexide, see: Menzek et al. (2005 ▶). For background to epoxide and bis-epoxide, see: Şengül et al. (2008 ▶).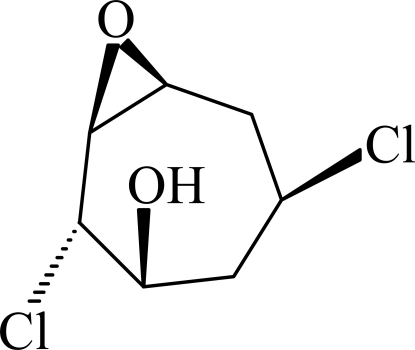
Experimental
Crystal data
C7H10Cl2O2
M r = 197.05
Orthorhombic,

a = 21.9202 (5) Å
b = 9.9343 (3) Å
c = 8.1005 (2) Å
V = 1763.98 (8) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.68 mm−1
T = 294 K
0.32 × 0.20 × 0.15 mm
Data collection
Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID-S diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (Blessing, 1995 ▶) T min = 0.845, T max = 0.900
32813 measured reflections
1801 independent reflections
1267 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.110
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.088
wR(F 2) = 0.190
S = 1.18
1801 reflections
115 parameters
2 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.28 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.34 e Å−3
Data collection: CrystalClear (Rigaku/MSC, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: CrystalClear; data reduction: CrystalClear; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and Mercury (Macrae et al., 2006 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811013304/xu5182sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811013304/xu5182Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2—H2A⋯O2i | 0.83 (11) | 1.96 (11) | 2.746 (7) | 159 (12) |
| O2—H2B⋯O2ii | 0.85 | 1.84 | 2.692 (8) | 174 |
| C2—H21⋯O1iii | 0.97 | 2.43 | 3.398 (7) | 172 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to the Department of Chemistry, Atatürk University, Erzurum, Turkey, for the use of X-ray diffractometer purchased under grant No. 2003/219 of the University Research Fund.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Unsaturated bicyclic endopexides are important compounds for versatile chemical transformations in organic chemistry. In these endoperoxides, diradicals formed by thermal cleavage of the weak O-O bonds react to give the syn-bis-epoxides (Balcı, 1981; Akbulut et al., 1987; Menzek & Balcı, 1993; Saraçoğlu et al., 1999).
Unsaturated bicyclic endopexide, (1), (Scheme 1) was synthesized by the literature method (Menzek et al., 2005). Reaction of endoperoxide, (1), by heating at 453 (5) K gave a mixture of products (Scheme 1). The title compound, (2), was isolated from these mixtures. The other products were not identified. According to the NMR data of dichloride, (2), it was not easy to establish the exact configuration of the molecule. Therefore, the exact structure of dichloride, (2), was determined by X-ray single crystal analysis.
To rationalize the formation of dichloride, (2), we propose the following reaction mechanism as favourable mechanism (Scheme 1). Bis-epoxide, (3), is produced via diradicals formed by thermal cleavage of the weak O-O bonds. HCl formed by elimination from reaction products such as (3) can attack bis-epoxide, (3), to give intermediate (4). Cl- can attack intermediate (4) to give dichloride, (2), as a nucleophile. An epoxide or bis-epoxide ring (Şengül et al., 2008) may be opened by as a nucleophile.
In the title compound, the seven-membered ring A (C1-C7) is, of course, not planar. The planar moieties B (O1/C1/C7), C (C3-C5), D (C2/C3/C5/C6) and E (C1/C2/C6/C7) are oriented at dihedral angles of B/C = 68.75 (46)°, B/D = 13.84 (28)°, B/E = 74.48 (32)°, C/D = 54.91 (42)°, C/E = 6.00 (42)° and D/E = 60.65 (30)°.
In the crystal, intermolecular O—H···O and C—H···O hydrogen bonds link the molecules into a three-dimensional network (Table 1 and Fig. 2).
Experimental
For the preparation of the title compound, a mixture of endoproxide (0.5 g, 2.6 mmol) and benzene (5 ml) was placed into a test tube, sealed under vacuum and heated at 453 (5) K for 3 d. After cooling to room temperature, the solvent was evaporated. The residue was submitted to column chromatography (silica gel, 90 g) with AcOEt/hexane (1:6) as eluant. Dichloride (yield: 0.056 g, 9%, m. p. 366-368 K) and a mixture of unidentified products were obtained. Dichloride was crystallized from ethyl acetate/hexane (1:1) as colorless block crystals.
Refinement
H1, H7, H21, H22 and H41, H42 atoms were positioned geometrically with C—H = 0.98 and 0.97 Å, respectively, and constrained to ride on their parent atoms, with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C). The remaining H-atoms were located in a difference Fourier map and refined isotropically. The H atom of the OH group was disordered over two orientations. During the refinement process, the disordered H2A and H2B atoms were refined with equal occupancies.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title molecule with the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 40% probability level.
Fig. 2.
A view of the crystal packing of the title compound. The O-H···O and C-H···O hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C7H10Cl2O2 | F(000) = 816 |
| Mr = 197.05 | Dx = 1.484 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, Pbcn | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2n 2ab | Cell parameters from 4978 reflections |
| a = 21.9202 (5) Å | θ = 2.3–26.4° |
| b = 9.9343 (3) Å | µ = 0.68 mm−1 |
| c = 8.1005 (2) Å | T = 294 K |
| V = 1763.98 (8) Å3 | Block, colorless |
| Z = 8 | 0.32 × 0.20 × 0.15 mm |
Data collection
| Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID-S diffractometer | 1801 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1267 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.110 |
| ω scans | θmax = 26.4°, θmin = 2.3° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (Blessing, 1995) | h = −27→27 |
| Tmin = 0.845, Tmax = 0.900 | k = −12→12 |
| 32813 measured reflections | l = −9→10 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.088 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.190 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.18 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.020P)2 + 5.1831P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 1801 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 115 parameters | Δρmax = 0.28 e Å−3 |
| 2 restraints | Δρmin = −0.34 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| Cl1 | 0.59049 (9) | 0.41547 (16) | 0.1157 (2) | 0.0883 (6) | |
| Cl2 | 0.62620 (9) | 1.07361 (16) | 0.1076 (2) | 0.0841 (6) | |
| O1 | 0.7389 (2) | 0.8227 (5) | 0.1601 (7) | 0.1017 (17) | |
| O2 | 0.5199 (2) | 0.8930 (5) | 0.0928 (7) | 0.0941 (16) | |
| H2A | 0.511 (7) | 0.945 (11) | 0.017 (12) | 0.090* | 0.50 |
| H2B | 0.5050 | 0.8950 | 0.1900 | 0.090* | 0.50 |
| C1 | 0.7119 (3) | 0.7145 (7) | 0.0682 (10) | 0.084 (2) | |
| H1 | 0.7361 | 0.6806 | −0.0247 | 0.101* | |
| C2 | 0.6766 (2) | 0.6091 (6) | 0.1650 (9) | 0.0732 (18) | |
| H21 | 0.7003 | 0.5271 | 0.1751 | 0.088* | |
| H22 | 0.6672 | 0.6421 | 0.2748 | 0.088* | |
| C3 | 0.6182 (3) | 0.5825 (6) | 0.0692 (8) | 0.0604 (15) | |
| H3 | 0.628 (3) | 0.578 (7) | −0.042 (9) | 0.10 (2)* | |
| C4 | 0.5669 (2) | 0.6810 (5) | 0.1042 (8) | 0.0610 (14) | |
| H41 | 0.5303 | 0.6467 | 0.0516 | 0.073* | |
| H42 | 0.5595 | 0.6806 | 0.2223 | 0.073* | |
| C5 | 0.5748 (2) | 0.8269 (6) | 0.0507 (8) | 0.0582 (14) | |
| H5 | 0.580 (2) | 0.832 (5) | −0.066 (7) | 0.057 (16)* | |
| C6 | 0.6294 (3) | 0.8926 (5) | 0.1265 (7) | 0.0558 (13) | |
| H6 | 0.636 (2) | 0.873 (5) | 0.231 (7) | 0.066 (18)* | |
| C7 | 0.6885 (2) | 0.8499 (6) | 0.0502 (8) | 0.0703 (17) | |
| H7 | 0.6993 | 0.8954 | −0.0531 | 0.084* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.1032 (13) | 0.0592 (9) | 0.1024 (14) | −0.0091 (8) | −0.0189 (11) | 0.0044 (9) |
| Cl2 | 0.1150 (14) | 0.0573 (9) | 0.0799 (11) | −0.0025 (9) | 0.0052 (10) | −0.0046 (8) |
| O1 | 0.067 (3) | 0.095 (4) | 0.143 (5) | −0.021 (3) | −0.030 (3) | 0.028 (3) |
| O2 | 0.067 (3) | 0.084 (3) | 0.132 (5) | 0.024 (2) | 0.023 (3) | 0.012 (3) |
| C1 | 0.049 (3) | 0.097 (5) | 0.107 (6) | 0.011 (3) | 0.009 (4) | 0.011 (5) |
| C2 | 0.055 (3) | 0.069 (4) | 0.096 (5) | 0.014 (3) | −0.016 (3) | 0.010 (3) |
| C3 | 0.066 (4) | 0.052 (3) | 0.063 (4) | 0.001 (3) | 0.001 (3) | −0.005 (3) |
| C4 | 0.049 (3) | 0.058 (3) | 0.075 (4) | 0.001 (2) | −0.009 (3) | −0.004 (3) |
| C5 | 0.050 (3) | 0.064 (3) | 0.061 (4) | 0.008 (3) | −0.001 (3) | 0.004 (3) |
| C6 | 0.066 (3) | 0.049 (3) | 0.052 (3) | 0.001 (2) | −0.009 (3) | 0.000 (3) |
| C7 | 0.052 (3) | 0.075 (4) | 0.084 (4) | −0.006 (3) | 0.009 (3) | 0.014 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cl1—C3 | 1.806 (6) | C3—C2 | 1.520 (8) |
| Cl2—C6 | 1.806 (6) | C3—C4 | 1.518 (7) |
| O1—C1 | 1.434 (8) | C3—H3 | 0.93 (7) |
| O1—C7 | 1.443 (7) | C4—C5 | 1.522 (8) |
| O2—C5 | 1.413 (7) | C4—H41 | 0.9700 |
| O2—H2B | 0.853 (5) | C4—H42 | 0.9700 |
| O2—H2A | 0.82 (2) | C5—H5 | 0.95 (5) |
| C1—C7 | 1.447 (9) | C6—C5 | 1.497 (8) |
| C1—H1 | 0.9800 | C6—C7 | 1.497 (8) |
| C2—C1 | 1.521 (8) | C6—H6 | 0.88 (6) |
| C2—H21 | 0.9700 | C7—H7 | 0.9800 |
| C2—H22 | 0.9700 | ||
| C5—O2—H2B | 124.0 (5) | C3—C4—H41 | 107.7 |
| C5—O2—H2A | 109 (10) | C3—C4—H42 | 107.7 |
| H2B—O2—H2A | 125 (10) | C5—C4—H41 | 107.7 |
| C1—O1—C7 | 60.4 (4) | C5—C4—H42 | 107.7 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 117.3 (6) | H42—C4—H41 | 107.1 |
| O1—C1—C7 | 60.1 (4) | O2—C5—C4 | 106.1 (5) |
| O1—C1—H1 | 115.7 | O2—C5—C6 | 112.3 (5) |
| C2—C1—H1 | 115.7 | O2—C5—H5 | 109 (3) |
| C7—C1—C2 | 120.7 (5) | C4—C5—H5 | 110 (3) |
| C7—C1—H1 | 115.7 | C6—C5—C4 | 112.9 (5) |
| C1—C2—H21 | 110.4 | C6—C5—H5 | 107 (3) |
| C1—C2—H22 | 110.4 | Cl2—C6—H6 | 108 (4) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 106.6 (5) | C5—C6—Cl2 | 111.6 (4) |
| C3—C2—H21 | 110.4 | C5—C6—C7 | 113.6 (5) |
| C3—C2—H22 | 110.4 | C5—C6—H6 | 116 (4) |
| H21—C2—H22 | 108.6 | C7—C6—Cl2 | 106.3 (4) |
| Cl1—C3—H3 | 104 (4) | C7—C6—H6 | 101 (4) |
| C2—C3—Cl1 | 109.6 (4) | O1—C7—C1 | 59.5 (4) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 108 (4) | O1—C7—C6 | 117.4 (6) |
| C4—C3—Cl1 | 107.7 (4) | O1—C7—H7 | 115.4 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 114.6 (5) | C1—C7—C6 | 122.0 (5) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 113 (4) | C1—C7—H7 | 115.4 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 118.4 (5) | C6—C7—H7 | 115.4 |
| C7—O1—C1—C2 | −111.5 (6) | C3—C4—C5—O2 | 177.8 (5) |
| C1—O1—C7—C6 | 112.7 (6) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | −58.7 (7) |
| O1—C1—C7—C6 | −105.2 (7) | Cl2—C6—C5—O2 | −44.3 (6) |
| C2—C1—C7—O1 | 105.9 (8) | Cl2—C6—C5—C4 | −164.2 (4) |
| C2—C1—C7—C6 | 0.7 (10) | C7—C6—C5—O2 | −164.5 (5) |
| C3—C2—C1—O1 | 135.8 (5) | C7—C6—C5—C4 | 75.6 (7) |
| C3—C2—C1—C7 | 66.0 (8) | Cl2—C6—C7—C1 | 168.9 (6) |
| Cl1—C3—C2—C1 | 154.6 (5) | Cl2—C6—C7—O1 | 99.4 (5) |
| C4—C3—C2—C1 | −84.1 (7) | C5—C6—C7—O1 | −137.5 (5) |
| Cl1—C3—C4—C5 | −170.8 (4) | C5—C6—C7—C1 | −68.0 (8) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 66.8 (7) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O2—H2A···O2i | 0.83 (11) | 1.96 (11) | 2.746 (7) | 159 (12) |
| O2—H2B···O2ii | 0.85 | 1.84 | 2.692 (8) | 174 |
| C2—H21···O1iii | 0.97 | 2.43 | 3.398 (7) | 172 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+2, −z; (ii) −x+1, y, −z+1/2; (iii) −x+3/2, y−1/2, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: XU5182).
References
- Akbulut, N., Menzek, A. & Balcı, M. (1987). Tetrahedron Lett. 28, 1689–1692.
- Balcı, M. (1981). Chem. Rev. 81, 91–108.
- Blessing, R. H. (1995). Acta Cryst. A51, 33–38. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 837–838.
- Macrae, C. F., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Shields, G. P., Taylor, R., Towler, M. & van de Streek, J. (2006). J. Appl. Cryst. 39, 453–457.
- Menzek, A. & Balcı, M. (1993). Aust. J. Chem. 46, 1613–1621.
- Menzek, A., Şengül, M. E., Çetinkaya, Y. & Ceylan, S. (2005). J. Chem. Res. pp. 209–214.
- Rigaku/MSC (2005). CrystalClear Rigaku/MSC, The Woodlands, Texas, USA.
- Saraçoğlu, N., Menzek, A., Sayan, Ş., Salzner, U. & Balcı, M. (1999). J. Org. Chem. 64, 6670–6676. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Şengül, M. E., Menzek, A., Şahin, E., Arık, M. & Saracoğlu, N. (2008). Tetrahedron, 64, 7289–7294.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811013304/xu5182sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811013304/xu5182Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




