Abstract
The title molecule, C22H23N3O2, was obtained via an intramolecular cycloaddition of an azomethine ylide and an alkene tethered by a benzimidazole unit. The benzoimidazole unit is essentially planar, with an r.m.s. deviation of 0.0087 Å from the nine constituent atoms. It has a cis fusion of the two pyrrolidine rings as well as a cis ester appendage. The two pyrrolidine rings rings have envelope conformations. The crystal packing is stabilized by aromatic π–π stacking of parallel benzimidazole ring systems, with a centroid-to-centroid distance of 3.518 (6) Å. Weak intermolecular C—H⋯O contacts may also play a role in the stability of the packing.
Related literature
Polycyclic nitrogen-containing heterocycles form the basic skeleton of numerous alkaloids and physiologically active compounds, see: Southon & Buckingham (1989 ▶). Conformational studies have been reported for related pyrrolidino[3,4-b]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylates obtained from intramolecular cycloaddition of azomethine ylides, see: Cheng et al. (2001 ▶); Meng et al. (2007 ▶). For related literature on the pharmaceutical properties of benzimidazole and pyrrolidine, see: Gudmundsson et al. (2000 ▶); Hamilton & Steiner (1997 ▶). For related literature on the azomethine ylide cycloaddition in similar systems, Pedrosa et al. (2006 ▶); Yang et al. (2006 ▶).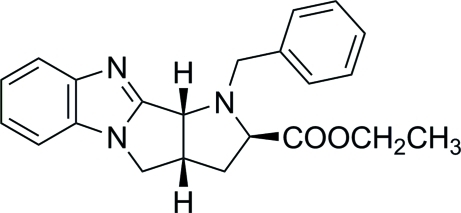
Experimental
Crystal data
C22H23N3O2
M r = 361.43
Monoclinic,

a = 9.2498 (5) Å
b = 13.8999 (7) Å
c = 14.2258 (7) Å
β = 90.345 (1)°
V = 1829.00 (16) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 90 K
0.39 × 0.16 × 0.13 mm
Data collection
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.037
wR(F 2) = 0.095
S = 1.09
4194 reflections
336 parameters
All H-atom parameters refined
Δρmax = 0.37 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.27 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2002 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: XP in SHELXTL/PC (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811014292/wn2427sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811014292/wn2427Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C11—H11B⋯O12i | 1.005 (15) | 2.399 (15) | 3.3344 (17) | 154.5 (12) |
| C18—H18⋯O12ii | 0.968 (15) | 2.514 (16) | 3.3505 (17) | 144.6 (12) |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Science Foundation (grant No. CHE-0910870) and the National Institutes of Health (grant No. GM0891583) for financial support of this work.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Polycyclic nitrogen-containing heterocycles form the basic skeleton of numerous alkaloids and physiologically active compounds (Southon & Buckingham, 1989). The title polycyclic N-heterocycle, ethyl 1-benzylpyrrolidino[2',3':3,4]pyrrolidino[1,2-a] benzimidazole-2-carboxylate, was obtained via an intramolecular azomethine ylide cycloaddition and possesses two medicinally relevant pharmacophores – benzimidazole and pyrrolidine (Gudmundsson et al., 2000; Hamilton & Steiner, 1997)– in one rigid molecule; the title compound may afford important bioactivity.
In the structure of the title compound (Fig. 1), the benzoimidazole unit is essentially planar, with a root mean square deviation of 0.0087 Å from the nine constituent atoms. The two pyrrolidine rings have envelope forms and are cis fused, which is consistent with conventional azomethine ylide cycloadditions in similar systems (Pedrosa et al., 2006; Yang et al., 2006). However, unlike the previously reported analogues obtained from an intramolecular azomethine ylide and alkene cycloaddition tethered by an oxazolidin-2-one (Cheng et al., 2001), the ester appendage in the title structure was unambiguously assigned as cis to the angular protons H2A and H10A by X-ray crystallography. The crystal packing (Fig. 2) exhibits π–π stacking of parallel benzimidazole ring systems, with a Cg1···Cg2 distance of 3.518 Å [Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the C3A–C8A benzene ring in one molecule and the C2B/N2/C3A/C8A/N8 imidazole ring in the other molecule, respectively]. Intermolecular C—H···O contacts may also play a role in the stability of the packing.
Experimental
The title compound was prepared from 1-allyl-1H-benzimidazole-2-carbaldehyde, N-benzylglycine ethyl ester hydrochloride, and triethylamine according to the procedure reported by Meng et al. (2007). Colourless blocks of the title compound were obtained by recrystallization from EtOAc/n-hexane 1:1 with slow evaporation at room temperature. These crystals were suitable for X-ray crystallography.
Refinement
H atoms were located directly in a difference Fourier map and then allowed to refine freely throughout the final convergence stage. The final structure was refined to convergence [Δ/σ≤ 0.001]. The final difference Fourier map was featureless, indicating that the structure is both correct and complete.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound. Ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are represented as small spheres of arbitrary radius.
Fig. 2.
The crystal packing of the title compound with a view of the C—H···O (dashed lines) and π–π interactions.
Crystal data
| C22H23N3O2 | F(000) = 768 |
| Mr = 361.43 | Dx = 1.313 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 7133 reflections |
| a = 9.2498 (5) Å | θ = 2.6–27.5° |
| b = 13.8999 (7) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 14.2258 (7) Å | T = 90 K |
| β = 90.345 (1)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 1829.00 (16) Å3 | 0.39 × 0.16 × 0.13 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART1000 CCD area-detector diffractometer | 4194 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3080 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.037 |
| ω and φ scans | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 2.1° |
| Absorption correction: numerical (SADABS; Blessing, 1995; Sheldrick, 2007) | h = −12→12 |
| Tmin = 0.962, Tmax = 0.989 | k = −18→18 |
| 16147 measured reflections | l = −18→18 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.037 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.095 | All H-atom parameters refined |
| S = 1.09 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0417P)2 + 0.3839P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4194 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 336 parameters | Δρmax = 0.37 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.27 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. A colourless block with approximate orthogonal dimensions 0.39 × 0.16 × 0.13 mm3 was placed and optically centered on the Bruker SMART1000 CCD system at -183°C. The initial unit cell was indexed using a least-squares analysis of a random set of reflections collected from three series of 0.3° wide ω scans, 10 s per frame, and 25 frames per series that were well distributed in reciprocal space. Four ω-scan data frame series were collected [Mo Kα] with 0.3° wide scans, 30 s per frame and 606, 435, 606, 435 frames collected per series at varying φ angles (φ = 0°, 90°, 180°, 270°), respectively. |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. The crystal to detector distance was 4.123 cm, thus providing a complete sphere of data to 2θmax = 55.06°. A total of 23465 reflections were collected and corrected for Lorentz and polarization effects and absorption using Blessing's method (Blessing, 1995) as incorporated into the program SADABS with 4390 unique. All crystallographic calculations were performed on a personal computer (PC) with a Pentium 3.20 GHz processor and 1 GB of extended memory. The SHELXTL program package was implemented to determine the probable space group and set up the initial files. System symmetry, systematic absences and intensity statistics indicated the centrosymmetric monoclinic non-standard space group P21/n (No. 14). The structure was determined by direct methods with the successful location of a majority of the molecule within the asymmetric unit using the program XS. The structure was refined with XL. The 23465 data collected were merged based upon identical indices yielding 16536 data [R(int) = 0.0245] that were truncated to 2θmax = 55.0° resulting in 16147 data that were further merged during least-squares refinement to 4194 unique data [R(int) = 0.0373]. A single least-squares difference Fourier cycle was required to locate the remaining non-H atoms. All non-H atoms were refined anisotropically. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.11370 (13) | 0.83406 (9) | 0.93388 (9) | 0.0171 (3) | |
| H1 | 0.1841 (15) | 0.8014 (10) | 0.8905 (10) | 0.016 (3)* | |
| N1 | −0.03076 (11) | 0.79245 (7) | 0.92753 (7) | 0.0167 (2) | |
| C2A | −0.02373 (14) | 0.70281 (9) | 0.98214 (9) | 0.0168 (3) | |
| H2A | −0.1230 (16) | 0.6828 (10) | 0.9972 (10) | 0.021 (4)* | |
| C2B | 0.05845 (13) | 0.61970 (9) | 0.93939 (9) | 0.0164 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.04725 (11) | 0.56851 (8) | 0.86159 (7) | 0.0188 (2) | |
| C3A | 0.15526 (14) | 0.49885 (9) | 0.87233 (9) | 0.0178 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.19276 (15) | 0.42310 (10) | 0.81285 (9) | 0.0215 (3) | |
| H4 | 0.1418 (16) | 0.4118 (10) | 0.7547 (11) | 0.024 (4)* | |
| C5 | 0.30288 (15) | 0.36208 (10) | 0.84115 (10) | 0.0239 (3) | |
| H5 | 0.3296 (16) | 0.3071 (11) | 0.8029 (11) | 0.024 (4)* | |
| C6 | 0.37646 (15) | 0.37548 (10) | 0.92687 (10) | 0.0231 (3) | |
| H6 | 0.4508 (16) | 0.3301 (11) | 0.9460 (10) | 0.025 (4)* | |
| C7 | 0.34082 (14) | 0.44980 (10) | 0.98730 (10) | 0.0205 (3) | |
| H7 | 0.3892 (16) | 0.4588 (10) | 1.0466 (11) | 0.023 (4)* | |
| C8A | 0.22957 (14) | 0.51062 (9) | 0.95859 (9) | 0.0176 (3) | |
| N8 | 0.16544 (11) | 0.58997 (8) | 0.99883 (7) | 0.0173 (2) | |
| C9 | 0.16669 (15) | 0.63878 (10) | 1.08991 (9) | 0.0191 (3) | |
| H9A | 0.2688 (16) | 0.6555 (10) | 1.1086 (10) | 0.021 (4)* | |
| H9B | 0.1242 (15) | 0.5967 (10) | 1.1379 (10) | 0.022 (4)* | |
| C10A | 0.07245 (14) | 0.72792 (9) | 1.06910 (9) | 0.0180 (3) | |
| H10A | 0.0137 (14) | 0.7435 (9) | 1.1239 (10) | 0.013 (3)* | |
| C11 | 0.15928 (15) | 0.81681 (10) | 1.03687 (9) | 0.0193 (3) | |
| H11A | 0.2653 (18) | 0.8059 (11) | 1.0440 (11) | 0.029 (4)* | |
| H11B | 0.1335 (16) | 0.8755 (11) | 1.0745 (11) | 0.025 (4)* | |
| C12 | 0.11502 (14) | 0.93996 (9) | 0.90881 (9) | 0.0182 (3) | |
| O12 | 0.01249 (10) | 0.98789 (7) | 0.88602 (7) | 0.0248 (2) | |
| C13 | 0.27147 (16) | 1.07485 (10) | 0.89143 (10) | 0.0225 (3) | |
| H13A | 0.2190 (16) | 1.1145 (11) | 0.9382 (11) | 0.023 (4)* | |
| H13B | 0.2268 (16) | 1.0867 (10) | 0.8302 (11) | 0.022 (4)* | |
| O13 | 0.25101 (10) | 0.97384 (6) | 0.91573 (6) | 0.0201 (2) | |
| C14 | 0.43191 (16) | 1.09273 (11) | 0.89238 (11) | 0.0251 (3) | |
| H14A | 0.4769 (18) | 1.0798 (12) | 0.9539 (13) | 0.037 (5)* | |
| H14B | 0.4516 (18) | 1.1615 (13) | 0.8784 (11) | 0.038 (5)* | |
| H14C | 0.4819 (17) | 1.0527 (12) | 0.8441 (12) | 0.035 (4)* | |
| C15 | −0.08571 (14) | 0.78122 (10) | 0.83087 (9) | 0.0179 (3) | |
| H15A | −0.0297 (15) | 0.7327 (10) | 0.7948 (10) | 0.018 (4)* | |
| H15B | −0.0739 (15) | 0.8460 (11) | 0.8007 (10) | 0.018 (4)* | |
| C16 | −0.24288 (14) | 0.75165 (9) | 0.82970 (9) | 0.0178 (3) | |
| C17 | −0.28700 (15) | 0.66465 (10) | 0.79108 (9) | 0.0205 (3) | |
| H17 | −0.2161 (17) | 0.6209 (11) | 0.7651 (11) | 0.030 (4)* | |
| C18 | −0.43276 (15) | 0.63824 (10) | 0.79093 (9) | 0.0228 (3) | |
| H18 | −0.4629 (16) | 0.5773 (11) | 0.7644 (11) | 0.027 (4)* | |
| C19 | −0.53434 (15) | 0.69891 (11) | 0.83067 (9) | 0.0232 (3) | |
| H19 | −0.6361 (17) | 0.6801 (11) | 0.8303 (10) | 0.024 (4)* | |
| C20 | −0.49157 (15) | 0.78651 (10) | 0.86906 (9) | 0.0224 (3) | |
| H20 | −0.5630 (16) | 0.8300 (11) | 0.8959 (10) | 0.022 (4)* | |
| C21 | −0.34683 (14) | 0.81280 (10) | 0.86831 (9) | 0.0205 (3) | |
| H21 | −0.3146 (16) | 0.8746 (11) | 0.8952 (10) | 0.022 (4)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0135 (6) | 0.0187 (6) | 0.0189 (6) | 0.0002 (5) | 0.0018 (5) | −0.0014 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0149 (5) | 0.0182 (6) | 0.0170 (5) | −0.0009 (4) | −0.0002 (4) | 0.0011 (4) |
| C2A | 0.0146 (6) | 0.0196 (7) | 0.0161 (6) | −0.0012 (5) | 0.0012 (5) | 0.0005 (5) |
| C2B | 0.0145 (6) | 0.0186 (6) | 0.0162 (6) | −0.0027 (5) | 0.0009 (5) | 0.0025 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0194 (6) | 0.0191 (6) | 0.0180 (5) | 0.0006 (4) | 0.0011 (4) | 0.0000 (4) |
| C3A | 0.0165 (6) | 0.0193 (6) | 0.0177 (6) | −0.0013 (5) | 0.0030 (5) | 0.0042 (5) |
| C4 | 0.0244 (7) | 0.0236 (7) | 0.0164 (7) | −0.0002 (6) | 0.0044 (5) | 0.0006 (5) |
| C5 | 0.0251 (7) | 0.0226 (7) | 0.0242 (7) | 0.0017 (6) | 0.0096 (6) | 0.0001 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0172 (7) | 0.0221 (7) | 0.0300 (8) | 0.0013 (6) | 0.0049 (6) | 0.0053 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0159 (7) | 0.0225 (7) | 0.0230 (7) | −0.0026 (5) | 0.0004 (5) | 0.0050 (5) |
| C8A | 0.0173 (6) | 0.0179 (6) | 0.0177 (6) | −0.0027 (5) | 0.0028 (5) | 0.0026 (5) |
| N8 | 0.0170 (6) | 0.0184 (5) | 0.0165 (5) | −0.0004 (4) | −0.0005 (4) | 0.0013 (4) |
| C9 | 0.0207 (7) | 0.0208 (7) | 0.0157 (6) | −0.0023 (5) | −0.0014 (5) | −0.0002 (5) |
| C10A | 0.0179 (6) | 0.0216 (7) | 0.0146 (6) | −0.0013 (5) | 0.0022 (5) | −0.0014 (5) |
| C11 | 0.0194 (7) | 0.0182 (7) | 0.0204 (7) | −0.0005 (5) | −0.0029 (5) | 0.0004 (5) |
| C12 | 0.0187 (7) | 0.0213 (7) | 0.0146 (6) | 0.0013 (5) | 0.0022 (5) | −0.0021 (5) |
| O12 | 0.0232 (5) | 0.0226 (5) | 0.0284 (5) | 0.0044 (4) | −0.0022 (4) | 0.0015 (4) |
| C13 | 0.0289 (8) | 0.0154 (7) | 0.0233 (7) | −0.0024 (6) | −0.0026 (6) | 0.0023 (5) |
| O13 | 0.0207 (5) | 0.0161 (5) | 0.0235 (5) | −0.0020 (4) | 0.0003 (4) | 0.0015 (4) |
| C14 | 0.0297 (8) | 0.0199 (7) | 0.0257 (8) | −0.0066 (6) | −0.0002 (6) | 0.0008 (6) |
| C15 | 0.0159 (6) | 0.0221 (7) | 0.0156 (6) | 0.0008 (5) | 0.0010 (5) | 0.0000 (5) |
| C16 | 0.0173 (7) | 0.0229 (7) | 0.0130 (6) | 0.0012 (5) | −0.0013 (5) | 0.0031 (5) |
| C17 | 0.0201 (7) | 0.0248 (7) | 0.0164 (6) | 0.0032 (6) | −0.0009 (5) | 0.0009 (5) |
| C18 | 0.0242 (7) | 0.0247 (7) | 0.0193 (7) | −0.0027 (6) | −0.0052 (5) | 0.0014 (6) |
| C19 | 0.0165 (7) | 0.0322 (8) | 0.0209 (7) | −0.0019 (6) | −0.0033 (5) | 0.0043 (6) |
| C20 | 0.0171 (7) | 0.0305 (8) | 0.0195 (7) | 0.0047 (6) | −0.0005 (5) | 0.0010 (6) |
| C21 | 0.0206 (7) | 0.0232 (7) | 0.0177 (6) | 0.0010 (6) | −0.0011 (5) | −0.0008 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—N1 | 1.4582 (16) | C10A—C11 | 1.5448 (18) |
| C1—C12 | 1.5147 (18) | C10A—H10A | 0.977 (14) |
| C1—C11 | 1.5409 (18) | C11—H11A | 0.997 (16) |
| C1—H1 | 1.008 (14) | C11—H11B | 1.005 (15) |
| N1—C2A | 1.4696 (16) | C12—O12 | 1.2019 (16) |
| N1—C15 | 1.4714 (16) | C12—O13 | 1.3462 (15) |
| C2A—C2B | 1.5126 (18) | C13—O13 | 1.4584 (16) |
| C2A—C10A | 1.5590 (17) | C13—C14 | 1.505 (2) |
| C2A—H2A | 0.984 (15) | C13—H13A | 0.993 (15) |
| C2B—N2 | 1.3193 (16) | C13—H13B | 0.976 (15) |
| C2B—N8 | 1.3620 (16) | C14—H14A | 0.983 (18) |
| N2—C3A | 1.3990 (17) | C14—H14B | 0.994 (18) |
| C3A—C4 | 1.3959 (18) | C14—H14C | 0.999 (17) |
| C3A—C8A | 1.4125 (18) | C15—C16 | 1.5108 (18) |
| C4—C5 | 1.383 (2) | C15—H15A | 0.994 (14) |
| C4—H4 | 0.963 (16) | C15—H15B | 1.004 (15) |
| C5—C6 | 1.405 (2) | C16—C17 | 1.3885 (19) |
| C5—H5 | 0.971 (15) | C16—C21 | 1.3982 (18) |
| C6—C7 | 1.385 (2) | C17—C18 | 1.3973 (19) |
| C6—H6 | 0.971 (16) | C17—H17 | 0.969 (16) |
| C7—C8A | 1.3912 (18) | C18—C19 | 1.386 (2) |
| C7—H7 | 0.961 (15) | C18—H18 | 0.967 (16) |
| C8A—N8 | 1.3785 (16) | C19—C20 | 1.391 (2) |
| N8—C9 | 1.4625 (16) | C19—H19 | 0.977 (15) |
| C9—C10A | 1.5425 (18) | C20—C21 | 1.3879 (19) |
| C9—H9A | 1.006 (15) | C20—H20 | 0.975 (15) |
| C9—H9B | 0.983 (15) | C21—H21 | 0.986 (15) |
| N1—C1—C12 | 112.30 (10) | C9—C10A—H10A | 110.0 (8) |
| N1—C1—C11 | 104.04 (10) | C11—C10A—H10A | 110.6 (8) |
| C12—C1—C11 | 111.87 (11) | C2A—C10A—H10A | 111.4 (8) |
| N1—C1—H1 | 112.2 (8) | C1—C11—C10A | 105.48 (10) |
| C12—C1—H1 | 106.7 (8) | C1—C11—H11A | 112.6 (9) |
| C11—C1—H1 | 109.7 (8) | C10A—C11—H11A | 111.2 (9) |
| C1—N1—C2A | 105.42 (10) | C1—C11—H11B | 108.4 (9) |
| C1—N1—C15 | 114.29 (10) | C10A—C11—H11B | 111.5 (9) |
| C2A—N1—C15 | 114.70 (10) | H11A—C11—H11B | 107.8 (12) |
| N1—C2A—C2B | 117.12 (10) | O12—C12—O13 | 124.14 (12) |
| N1—C2A—C10A | 104.65 (10) | O12—C12—C1 | 126.49 (12) |
| C2B—C2A—C10A | 101.79 (10) | O13—C12—C1 | 109.37 (11) |
| N1—C2A—H2A | 108.5 (8) | O13—C13—C14 | 106.64 (11) |
| C2B—C2A—H2A | 110.1 (9) | O13—C13—H13A | 108.1 (9) |
| C10A—C2A—H2A | 114.8 (8) | C14—C13—H13A | 112.9 (9) |
| N2—C2B—N8 | 114.23 (11) | O13—C13—H13B | 108.6 (9) |
| N2—C2B—C2A | 135.40 (12) | C14—C13—H13B | 113.1 (9) |
| N8—C2B—C2A | 110.31 (11) | H13A—C13—H13B | 107.4 (12) |
| C2B—N2—C3A | 103.25 (11) | C12—O13—C13 | 116.23 (10) |
| C4—C3A—N2 | 129.48 (12) | C13—C14—H14A | 112.9 (10) |
| C4—C3A—C8A | 119.52 (12) | C13—C14—H14B | 109.8 (10) |
| N2—C3A—C8A | 110.99 (11) | H14A—C14—H14B | 106.1 (14) |
| C5—C4—C3A | 118.11 (13) | C13—C14—H14C | 111.3 (10) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.4 (9) | H14A—C14—H14C | 108.3 (14) |
| C3A—C4—H4 | 121.5 (9) | H14B—C14—H14C | 108.2 (13) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.55 (13) | N1—C15—C16 | 111.48 (10) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.6 (9) | N1—C15—H15A | 112.1 (8) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 117.8 (9) | C16—C15—H15A | 108.3 (8) |
| C7—C6—C5 | 121.44 (13) | N1—C15—H15B | 105.5 (8) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 118.8 (9) | C16—C15—H15B | 110.3 (8) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.7 (9) | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.2 (11) |
| C6—C7—C8A | 116.70 (13) | C17—C16—C21 | 118.93 (12) |
| C6—C7—H7 | 122.1 (9) | C17—C16—C15 | 121.45 (12) |
| C8A—C7—H7 | 121.2 (9) | C21—C16—C15 | 119.62 (12) |
| N8—C8A—C7 | 133.13 (12) | C16—C17—C18 | 120.71 (13) |
| N8—C8A—C3A | 104.19 (11) | C16—C17—H17 | 119.9 (9) |
| C7—C8A—C3A | 122.68 (12) | C18—C17—H17 | 119.3 (9) |
| C2B—N8—C8A | 107.32 (10) | C19—C18—C17 | 119.74 (13) |
| C2B—N8—C9 | 114.28 (11) | C19—C18—H18 | 119.8 (9) |
| C8A—N8—C9 | 137.56 (11) | C17—C18—H18 | 120.4 (9) |
| N8—C9—C10A | 101.61 (10) | C18—C19—C20 | 120.07 (13) |
| N8—C9—H9A | 110.0 (8) | C18—C19—H19 | 119.4 (9) |
| C10A—C9—H9A | 113.2 (8) | C20—C19—H19 | 120.6 (9) |
| N8—C9—H9B | 109.8 (9) | C21—C20—C19 | 119.96 (13) |
| C10A—C9—H9B | 112.6 (9) | C21—C20—H20 | 119.7 (9) |
| H9A—C9—H9B | 109.4 (12) | C19—C20—H20 | 120.3 (9) |
| C9—C10A—C11 | 113.90 (11) | C20—C21—C16 | 120.58 (13) |
| C9—C10A—C2A | 106.95 (10) | C20—C21—H21 | 121.1 (9) |
| C11—C10A—C2A | 103.81 (10) | C16—C21—H21 | 118.4 (9) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C11—H11B···O12i | 1.005 (15) | 2.399 (15) | 3.3344 (17) | 154.5 (12) |
| C18—H18···O12ii | 0.968 (15) | 2.514 (16) | 3.3505 (17) | 144.6 (12) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+2, −z+2; (ii) −x−1/2, y−1/2, −z+3/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: WN2427).
References
- Blessing, R. H. (1995). Acta Cryst. A51, 33–38. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2002). SMART Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2007). SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cheng, Q., Zhang, W., Tagamia, Y. & Oritani, T. (2001). J. Chem. Soc Perkin Trans. 1, pp. 452–456.
- Gudmundsson, K. S., Tidwell, J., Lippa, N., Koszalka, G. W., van Draanen, N., Ptak, R. G., Drach, J. C. & Townsend, L. B. (2000). J. Med. Chem. 43, 2464–2472. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, G. S. & Steiner, J. P. (1997). Curr. Pharm. Des. 3, 405–428.
- Meng, L., Fettinger, C. J. & Kurth, J. M. (2007). Org. Lett. 9, 5055–5058. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Pedrosa, R., Andres, C., Nieto, J., Perez-Cuadrado, C. & Francisco, I. S. (2006). Eur. J. Org. Chem. pp. 3259–3265.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2007). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Southon, I. W. & Buckingham, J. (1989). Editors. Dictionary of Alkaloids New York: Chapman & Hall.
- Yang, X., Luo, S., Fang, F., Liu, P., Lu, Y., He, M. & Zhai, H. (2006). Tetrahedron, 62, 2240–2246.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811014292/wn2427sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811014292/wn2427Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




