Abstract
In the title compound, C18H16N2O2, the central pyridazine ring forms dihedral angles of 77.08 (5)° and 84.62 (5)° with the two benzene rings. The dihedral angle between the two benzene rings is 68.18 (4)°. A very weak intramolecular C—H⋯N hydrogen bond and an intramolecular C—H⋯π interaction occur. The crystal structure is stabilized by weak intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and weak C—H⋯π and π–π stacking interactions [centroid–centroid distance = 3.6867 (10) Å].
Related literature
For applications of pyridazinone analogues as highly selective anti-HIV agents, see: Loksha et al. (2007 ▶). For applications as pesticide agents, see: Li et al. (2005 ▶); Selby et al. (2002 ▶). For applications as herbicides, see: Xu et al. (2006 ▶). For related structures, see: Liu et al. (2005 ▶).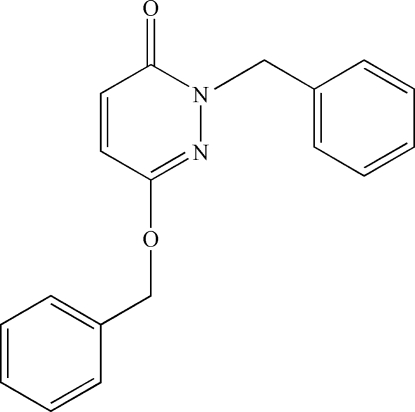
Experimental
Crystal data
C18H16N2O2
M r = 292.33
Monoclinic,

a = 32.741 (4) Å
b = 10.9198 (14) Å
c = 8.1228 (10) Å
β = 95.92 (2)°
V = 2888.6 (6) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 113 K
0.20 × 0.18 × 0.12 mm
Data collection
Rigaku Saturn CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku/MSC, 2009 ▶) T min = 0.982, T max = 0.989
18031 measured reflections
3448 independent reflections
2142 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.063
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.047
wR(F 2) = 0.116
S = 0.95
3448 reflections
199 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.23 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3
Data collection: CrystalClear (Rigaku/MSC, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: CrystalClear; data reduction: CrystalClear; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: CrystalStructure (Rigaku/MSC, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: CrystalStructure.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811011597/fj2404sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811011597/fj2404Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg3 is the centroid of the C13–C18 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2—H2⋯O1i | 0.95 | 2.38 | 3.2906 (19) | 161 (19) |
| C11—H11⋯N2 | 0.95 | 2.49 | 3.126 (2) | 124 |
| C11—H11⋯Cg3 | 0.95 | 2.98 | 3.7103 (17) | 135 |
| C17—H17⋯Cg3ii | 0.95 | 2.98 | 3.6991 (17) | 133 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. 20972143), the Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province Educational Committee, China (grant Nos. 2010 A150021 and 2007150036) and the High-level Talents Foundation of Xuchang University (grant No. 2010 GC033).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Pyridazinone analogues have been reported to have a variety of biological activities, such as highly-selective anti-HIV agents (Loksha et al., 2007), pesticide(Li et al., 2005), highly herbicidal activity (Xu et al., 2006). In order to discover further biologically active Pyridazinone analogues, the title compound, (I), was synthesized and its crystal structure determined (Fig. 1).
In a continuation of our studies on the crystal structures of Pyridazinone analogues (Liu et al., 2005), we report here the synthesis and crystal structure of the title molecule, the central pyridazine ring forms dihedral angles of 77.08 (5)° and 84.62 (5)° with the two benzene rings, The dihedral angle between two benzene rings is 68.18 (4)°. The Crystal structure is stabilized by a weak intramolecular C—H···N hydrogen bond (Table 1), a weak intermolecular C—H···O hydrogen bond (Table 1), C—H···Cgπ—ring (Table 1) and π-π stacking interactions where Cg(1)—Cg(1) (1/2 - x, 1/2 - y, 1 - z) is 3.6867 (10) Å [Cg(1) is the centroid of the N1,N2, C1—C4 ring] (Table 2).
Experimental
Maleic hydrazide(0.56 g, 5 mmol), Benzyl chloride(1.52 g, 12 mmol) and K2CO3 (1.66 g, 12 mmol) were added to absolute ethanol(30 ml). The mixture was stirred in the room temperature for 6 h. The suspension was filtered and the residue was washed with absolute ethanol. The title compound was recrystallized from the mother solution and single crystals of (I) were obtained by slow evaporation.
Refinement
All H atoms were placed in calculated positions, with C—H = 0.95 Å and C—H = 0.99 Å, and included in the final cycles of refinement using a riding model, with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The asymmetric unit of the title compound, (I), with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 30% probability level.
Crystal data
| C18H16N2O2 | F(000) = 1232 |
| Mr = 292.33 | Dx = 1.344 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -C 2yc | Cell parameters from 4881 reflections |
| a = 32.741 (4) Å | θ = 1.3–28.0° |
| b = 10.9198 (14) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 8.1228 (10) Å | T = 113 K |
| β = 95.92 (2)° | Prism, colorless |
| V = 2888.6 (6) Å3 | 0.20 × 0.18 × 0.12 mm |
| Z = 8 |
Data collection
| Rigaku Saturn CCD area-detector diffractometer | 3448 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: rotating anode | 2142 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| multilayer | Rint = 0.063 |
| Detector resolution: 14.63 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.9°, θmin = 1.3° |
| ω and φ scans | h = −43→41 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan CrystalClear | k = −14→14 |
| Tmin = 0.982, Tmax = 0.989 | l = −10→10 |
| 18031 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.047 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.116 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 0.95 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0548P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3448 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 199 parameters | Δρmax = 0.23 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.20711 (3) | 0.14159 (10) | 0.06099 (12) | 0.0315 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.20245 (3) | 0.38939 (9) | 0.62925 (12) | 0.0282 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.18498 (4) | 0.16470 (11) | 0.31678 (14) | 0.0221 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.18241 (4) | 0.22441 (11) | 0.46481 (14) | 0.0229 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.20713 (5) | 0.20250 (14) | 0.19094 (18) | 0.0241 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.22975 (5) | 0.31536 (14) | 0.22369 (18) | 0.0257 (4) | |
| H2 | 0.2460 | 0.3470 | 0.1432 | 0.031* | |
| C3 | 0.22792 (5) | 0.37578 (14) | 0.36727 (18) | 0.0253 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.2427 | 0.4499 | 0.3894 | 0.030* | |
| C4 | 0.20319 (5) | 0.32523 (14) | 0.48542 (17) | 0.0231 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.15786 (4) | 0.05874 (13) | 0.29089 (17) | 0.0232 (3) | |
| H5A | 0.1559 | 0.0173 | 0.3982 | 0.028* | |
| H5B | 0.1698 | 0.0000 | 0.2164 | 0.028* | |
| C6 | 0.11536 (5) | 0.09390 (13) | 0.21683 (17) | 0.0222 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.09415 (5) | 0.01638 (14) | 0.10195 (17) | 0.0257 (4) | |
| H7 | 0.1068 | −0.0570 | 0.0701 | 0.031* | |
| C8 | 0.05468 (5) | 0.04490 (15) | 0.03337 (18) | 0.0298 (4) | |
| H8 | 0.0406 | −0.0082 | −0.0461 | 0.036* | |
| C9 | 0.03585 (5) | 0.15088 (15) | 0.08102 (19) | 0.0304 (4) | |
| H9 | 0.0088 | 0.1706 | 0.0347 | 0.036* | |
| C10 | 0.05657 (5) | 0.22800 (14) | 0.19643 (19) | 0.0289 (4) | |
| H10 | 0.0436 | 0.3004 | 0.2299 | 0.035* | |
| C11 | 0.09614 (5) | 0.20016 (14) | 0.26341 (18) | 0.0261 (4) | |
| H11 | 0.1102 | 0.2540 | 0.3417 | 0.031* | |
| C12 | 0.17631 (5) | 0.34314 (15) | 0.74918 (18) | 0.0281 (4) | |
| H12A | 0.1835 | 0.3852 | 0.8562 | 0.034* | |
| H12B | 0.1818 | 0.2546 | 0.7665 | 0.034* | |
| C13 | 0.13136 (5) | 0.36113 (13) | 0.69709 (17) | 0.0246 (4) | |
| C14 | 0.10296 (5) | 0.28071 (14) | 0.75401 (18) | 0.0274 (4) | |
| H14 | 0.1122 | 0.2156 | 0.8260 | 0.033* | |
| C15 | 0.06137 (5) | 0.29469 (14) | 0.70671 (19) | 0.0301 (4) | |
| H15 | 0.0422 | 0.2389 | 0.7454 | 0.036* | |
| C16 | 0.04764 (5) | 0.39007 (14) | 0.60290 (19) | 0.0317 (4) | |
| H16 | 0.0191 | 0.3996 | 0.5698 | 0.038* | |
| C17 | 0.07560 (5) | 0.47139 (15) | 0.54761 (19) | 0.0317 (4) | |
| H17 | 0.0663 | 0.5371 | 0.4768 | 0.038* | |
| C18 | 0.11706 (5) | 0.45739 (14) | 0.59503 (18) | 0.0293 (4) | |
| H18 | 0.1360 | 0.5142 | 0.5575 | 0.035* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0356 (7) | 0.0367 (7) | 0.0229 (6) | −0.0022 (5) | 0.0066 (5) | −0.0036 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0292 (6) | 0.0304 (6) | 0.0252 (6) | −0.0038 (5) | 0.0037 (5) | −0.0070 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0246 (7) | 0.0239 (7) | 0.0177 (6) | −0.0016 (5) | 0.0020 (5) | −0.0007 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0239 (7) | 0.0255 (7) | 0.0191 (6) | 0.0017 (5) | 0.0009 (5) | −0.0020 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0244 (8) | 0.0282 (9) | 0.0194 (7) | 0.0034 (6) | 0.0016 (6) | 0.0022 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0243 (8) | 0.0280 (9) | 0.0247 (8) | −0.0005 (7) | 0.0026 (6) | 0.0038 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0223 (8) | 0.0243 (8) | 0.0288 (8) | −0.0007 (6) | 0.0003 (7) | 0.0015 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0221 (8) | 0.0253 (8) | 0.0213 (8) | 0.0022 (6) | −0.0008 (6) | −0.0018 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0266 (8) | 0.0211 (8) | 0.0220 (7) | −0.0021 (6) | 0.0029 (6) | −0.0001 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0248 (8) | 0.0228 (8) | 0.0193 (7) | −0.0019 (6) | 0.0032 (6) | 0.0028 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0300 (9) | 0.0251 (8) | 0.0225 (8) | −0.0044 (7) | 0.0059 (7) | −0.0006 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0301 (9) | 0.0333 (9) | 0.0256 (8) | −0.0082 (7) | 0.0006 (7) | −0.0015 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0274 (9) | 0.0332 (9) | 0.0298 (9) | −0.0029 (7) | −0.0008 (7) | 0.0063 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0304 (9) | 0.0259 (9) | 0.0304 (9) | 0.0019 (7) | 0.0028 (7) | 0.0021 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0283 (8) | 0.0245 (8) | 0.0247 (8) | −0.0005 (7) | −0.0011 (6) | −0.0018 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0322 (9) | 0.0329 (9) | 0.0194 (8) | −0.0013 (7) | 0.0034 (7) | −0.0020 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0336 (9) | 0.0216 (8) | 0.0190 (7) | 0.0002 (7) | 0.0047 (6) | −0.0041 (6) |
| C14 | 0.0357 (9) | 0.0240 (8) | 0.0222 (8) | 0.0001 (7) | 0.0023 (7) | 0.0001 (6) |
| C15 | 0.0327 (9) | 0.0292 (9) | 0.0289 (8) | −0.0041 (7) | 0.0057 (7) | −0.0016 (7) |
| C16 | 0.0314 (9) | 0.0340 (10) | 0.0294 (9) | 0.0024 (7) | 0.0020 (7) | −0.0030 (7) |
| C17 | 0.0385 (10) | 0.0275 (9) | 0.0293 (9) | 0.0056 (7) | 0.0036 (7) | 0.0030 (7) |
| C18 | 0.0345 (9) | 0.0259 (9) | 0.0283 (8) | −0.0012 (7) | 0.0071 (7) | 0.0034 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C1 | 1.2476 (17) | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| O2—C4 | 1.3647 (17) | C9—C10 | 1.385 (2) |
| O2—C12 | 1.4522 (18) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C1 | 1.3763 (19) | C10—C11 | 1.386 (2) |
| N1—N2 | 1.3780 (15) | C10—H10 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C5 | 1.4605 (18) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| N2—C4 | 1.2959 (18) | C12—C13 | 1.502 (2) |
| C1—C2 | 1.448 (2) | C12—H12A | 0.9900 |
| C2—C3 | 1.347 (2) | C12—H12B | 0.9900 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C13—C18 | 1.390 (2) |
| C3—C4 | 1.429 (2) | C13—C14 | 1.392 (2) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C14—C15 | 1.385 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.507 (2) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C5—H5A | 0.9900 | C15—C16 | 1.385 (2) |
| C5—H5B | 0.9900 | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C6—C11 | 1.391 (2) | C16—C17 | 1.383 (2) |
| C6—C7 | 1.392 (2) | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| C7—C8 | 1.389 (2) | C17—C18 | 1.381 (2) |
| C7—H7 | 0.9500 | C17—H17 | 0.9500 |
| C8—C9 | 1.385 (2) | C18—H18 | 0.9500 |
| C4—O2—C12 | 117.36 (12) | C10—C9—H9 | 120.1 |
| C1—N1—N2 | 126.19 (12) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.1 |
| C1—N1—C5 | 119.33 (12) | C9—C10—C11 | 120.34 (15) |
| N2—N1—C5 | 114.18 (11) | C9—C10—H10 | 119.8 |
| C4—N2—N1 | 115.86 (12) | C11—C10—H10 | 119.8 |
| O1—C1—N1 | 120.95 (14) | C10—C11—C6 | 120.47 (15) |
| O1—C1—C2 | 124.38 (14) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.8 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 114.67 (13) | C6—C11—H11 | 119.8 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.56 (14) | O2—C12—C13 | 113.20 (12) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.7 | O2—C12—H12A | 108.9 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.7 | C13—C12—H12A | 108.9 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 118.12 (14) | O2—C12—H12B | 108.9 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.9 | C13—C12—H12B | 108.9 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.9 | H12A—C12—H12B | 107.8 |
| N2—C4—O2 | 119.42 (13) | C18—C13—C14 | 118.68 (15) |
| N2—C4—C3 | 124.59 (13) | C18—C13—C12 | 121.80 (14) |
| O2—C4—C3 | 115.98 (13) | C14—C13—C12 | 119.51 (14) |
| N1—C5—C6 | 112.22 (12) | C15—C14—C13 | 120.64 (15) |
| N1—C5—H5A | 109.2 | C15—C14—H14 | 119.7 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 109.2 | C13—C14—H14 | 119.7 |
| N1—C5—H5B | 109.2 | C14—C15—C16 | 119.97 (16) |
| C6—C5—H5B | 109.2 | C14—C15—H15 | 120.0 |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 107.9 | C16—C15—H15 | 120.0 |
| C11—C6—C7 | 118.77 (14) | C17—C16—C15 | 119.76 (16) |
| C11—C6—C5 | 121.93 (14) | C17—C16—H16 | 120.1 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 119.28 (14) | C15—C16—H16 | 120.1 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 120.80 (15) | C18—C17—C16 | 120.19 (15) |
| C8—C7—H7 | 119.6 | C18—C17—H17 | 119.9 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 119.6 | C16—C17—H17 | 119.9 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 119.86 (15) | C17—C18—C13 | 120.74 (15) |
| C9—C8—H8 | 120.1 | C17—C18—H18 | 119.6 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 120.1 | C13—C18—H18 | 119.6 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 119.75 (15) | ||
| C1—N1—N2—C4 | −0.3 (2) | C11—C6—C7—C8 | 0.7 (2) |
| C5—N1—N2—C4 | −173.91 (12) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | 178.90 (13) |
| N2—N1—C1—O1 | −179.53 (13) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −0.9 (2) |
| C5—N1—C1—O1 | −6.3 (2) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 0.2 (2) |
| N2—N1—C1—C2 | 0.8 (2) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.5 (2) |
| C5—N1—C1—C2 | 174.04 (12) | C9—C10—C11—C6 | −0.6 (2) |
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | 179.70 (14) | C7—C6—C11—C10 | 0.0 (2) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −0.6 (2) | C5—C6—C11—C10 | −178.11 (14) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.1 (2) | C4—O2—C12—C13 | −72.05 (17) |
| N1—N2—C4—O2 | −179.59 (11) | O2—C12—C13—C18 | −28.7 (2) |
| N1—N2—C4—C3 | −0.3 (2) | O2—C12—C13—C14 | 152.30 (13) |
| C12—O2—C4—N2 | −3.1 (2) | C18—C13—C14—C15 | 1.5 (2) |
| C12—O2—C4—C3 | 177.58 (12) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −179.46 (14) |
| C2—C3—C4—N2 | 0.4 (2) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −0.6 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—O2 | 179.72 (13) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | −0.3 (2) |
| C1—N1—C5—C6 | −88.39 (16) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | 0.3 (2) |
| N2—N1—C5—C6 | 85.65 (14) | C16—C17—C18—C13 | 0.7 (2) |
| N1—C5—C6—C11 | −38.55 (18) | C14—C13—C18—C17 | −1.6 (2) |
| N1—C5—C6—C7 | 143.33 (13) | C12—C13—C18—C17 | 179.41 (14) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| Cg3 is the centroid of the C13–C18 ring. |
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C2—H2···O1i | 0.95 | 2.38 | 3.2906 (19) | 161 (19) |
| C11—H11···N2 | 0.95 | 2.49 | 3.126 (2) | 124 |
| C11—H11···Cg3 | 0.95 | 2.98 | 3.7103 (17) | 135 |
| C17—H17···Cg3ii | 0.95 | 2.98 | 3.6991 (17) | 133 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1/2, −y+1/2, −z; (ii) x, −y+1, z−1/2.
Table 2 Comparative geometrical parameters (Å) for selected Cg—Cg Π stacking interaction, Cg1 is the centroid of the N1,N2,C1-C4 ring (Symmetry codes: 1/2-X,1/2-Y,1-Z).
| CgI—CgJ | Cg—Cg(Å) | CgIPerp(Å) | CgjPerp(Å) | Slippage(Å) |
| Cg1—Cg1 | 3.6867 (10) | 3.224 | 3.224 | 1.789 |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: FJ2404).
References
- Li, H. S., Ling, Y., Guo, Y. L., Yang, X. L. & Chen, F. H. (2005). Chin. J. Org. Chem. 25, 204–207.
- Liu, W. D., Li, Z. W., Li, Z. Y., Wang, X. G. & Gao, B. D. (2005). Chin. J. Org. Chem. 25, 445–448.
- Loksha, Y. M., Pedersen, E. B., Colla, P. L. & Loddo, R. (2007). J. Heterocycl. Chem. , 44, 1351–1356.
- Rigaku/MSC (2009). CrystalClear and CrystalStructure Rigaku/MSC, The Woodlands, Texas, USA.
- Selby, T. P., Drumm, J. E., Coats, R. A., Coppo, F. T., Gee, S. K., Hay, J. V., Pasteris, R. J. & Stevenson, T. M. (2002). ACS Symposium Series, Vol. 800 (Synthesis and Chemistry of Agrochemicals VI), pp. 74–84.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Xu, H., Zou, X. M. & Yang, H. Z. (2006). Pest Manag. Sci. 62, 522–530. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811011597/fj2404sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811011597/fj2404Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



