Abstract
Objective
To examine the association of lipid-lowering drugs, change in diet and physical activity with a decline in low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol in middle age.
Design
A prospective cohort study.
Setting
The Whitehall II study.
Participants
4469 British civil servants (72% men) aged 39–62 years at baseline.
Main Outcome Measure
Change in LDL-cholesterol concentrations between the baseline (1991–3) and follow-up (2003–4).
Results
Mean LDL-cholesterol decreased from 4.38 to 3.52 mmol/l over a mean follow-up of 11.3 years. In a mutually adjusted model, a decline in LDL-cholesterol was greater among those who were taking lipid-lowering treatment at baseline (−1.14 mmol/l, n=34), or started treatment during the follow-up (−1.77 mmol/l, n=481) compared with untreated individuals (n=3954; p<0.001); among those who improved their diet—especially the ratio of white to red meat consumption and the ratio of polyunsaturated to saturated fatty acids intake—(−0.07 mmol/l, n=717) compared with those with no change in diet (n=3071; p=0.03) and among those who increased physical activity (−0.10 mmol/l, n=601) compared with those with no change in physical activity (n=3312; p=0.005). Based on these estimates, successful implementation of lipid-lowering drug treatment for high-risk participants (n=858) and favourable changes in diet (n=3457) and physical activity (n=2190) among those with non-optimal lifestyles would reduce LDL-cholesterol by 0.90 to 1.07 mmol/l in the total cohort.
Conclusions
Both lipid-lowering pharmacotherapy and favourable changes in lifestyle independently reduced LDL-cholesterol levels in a cohort of middle-aged men and women, supporting the use of multifaceted intervention strategies for prevention.
Keywords: Cohort study, diet, epidemiology, LDL-cholesterol, lipid lowering, lipid-lowering drug, lipoproteins, physical activity, public health
Blood cholesterol, low density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol in particular, is a major risk factor for coronary heart disease (CHD).1 Large randomised controlled trials and meta-analyses2–4 have established the clinical benefits of lowering LDL-cholesterol. A decrease of 1 mmol/l in LDL-cholesterol concentrations has been shown to be associated with a 23% lower risk of myocardial infarction or coronary death.4 Similarly, a 10% reduction in total cholesterol was associated with a 20% reduction in the risk of CHD.5
There is now consistent evidence for a secular decline in total cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol levels among adults in industrialised countries.6–19 For example, the MONICA study showed total cholesterol in adults aged 35–64 years to have declined between the mid-1980s and mid-1990s in approximately half of the European populations included in the study.6 Similar findings have been reported in other European populations,8–12 the USA,13–16 Canada,17 Australia18 and New Zealand.19
Clinical guidelines recommend a multifaceted approach to lowering LDL-cholesterol.1 20 However, the extent to which a healthy diet, physical activity and lipid-lowering drugs independently explain the decline in LDL-cholesterol levels currently being observed at the population level is unknown. We therefore examined associations of lipid-lowering drug use and 11-year change in diet and physical activity with declining LDL-cholesterol trends in an occupational cohort of middle-aged British civil servants participating in the Whitehall II study.
Subjects and methods
Study sample
The Whitehall II study is a prospective cohort study of 10 308 (67% men) London-based British civil servants aged 35–55 years in 1985.21 The baseline examination (phase 1) took place during 1985–8 and involved a clinical examination and self-administered questionnaire. Subsequent phases of data collection have alternated between postal questionnaire alone (phases 2 (1988–90), 4 (1995–6), 6 (2001) and 8 (2006)), and postal questionnaire accompanied by a medical screening (phases 3 (1991–3), 5 (1997–9) and 7 (2002–4)).
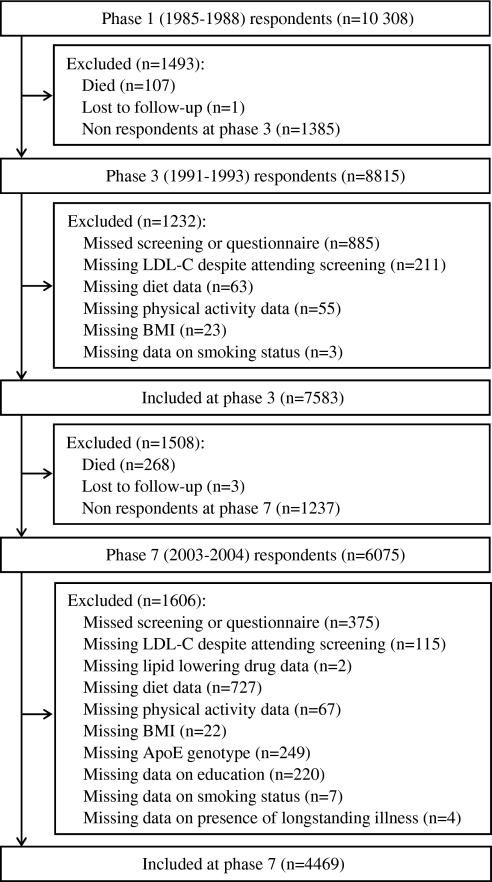
Detailed lipid data were not available at phase 1 so the data used in the current analysis were drawn from phases 3–7, making phase 3 the baseline for the present study. The mean follow-up between phases 3 and 7 was 11.3 years (SD=0.5). Participants not included in the analysis were those who did not undertake the medical screening at phases 3 or 7, and those with missing data on any of the predictors (lipid-lowering drugs, diet and physical activity) or potential confounders (ethnicity, body mass index, level of education, smoking status and the presence of long-standing illness) either at phase 3 or phase 7 (figure 1). A total of 4469 participants was eligible and constituted the study sample. Ethical approval for the Whitehall II study was obtained from the University College London Medical School committee on the ethics of human research (London, UK).
Figure 1.
Selection of the study participants. ApoE, apolipoprotein E; BMI, body mass index; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
Biochemical analyses
Blood samples were collected at phases 3 and 7, following either an 8-h overnight fast (participants presenting to the clinic in the morning) or at least a 4-h fast after a light fat-free breakfast (participants presenting in the afternoon). Venepuncture of the left antecubital vein was performed with tourniquet. Blood was collected into plain and fluoride Sarstedt (Neumbrecht, Germany) monovettes. Serum for lipid analyses was refrigerated at −4°C and assayed within 72 h.22 Total cholesterol was determined by an enzymatic procedure using the CHOD–PAP method at phases 3 and 7. Serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol concentrations were measured from the supernatant after the precipitation of non-HDL-cholesterol with dextran sulphate–magnesium at phase 3 and with a direct homogeneous assay at phase 7,23 using at both phases the CHOD–PAP method. Serum triglyceride was determined by the enzymatic colorimetric method (GPO–PAP) at both phases. The concentration of LDL-cholesterol was calculated using the Friedewald formula when serum triglycerides were lower than 4.5 mmol/l.24 Technical error was estimated by assaying blinded duplicate samples for 5% of subjects. Coefficients of variation were 2.0–6.6%. After both screenings, participants were sent a letter that informed them of their results and summarised whether or not they were ‘at increased risk of heart disease or angina’. For example, when a total cholesterol level of 8.5 mmol/l or higher was recorded at baseline (n=185), the letter suggested the participant see his or her general practitioner for a repeat test. The same envelope contained a similar unsealed letter addressed to the participant's general practitioner.
Potential predictors
Lipid-lowering drugs
At phases 3 and 7, participants were asked whether they had taken any medication in the past 14 days and, if so, to provide the name of the medication. Medications were coded using British National Formulary codes. We did not distinguish statins from other lipid-lowering drugs, such as fibrates, nicotinic acid and its derivatives, cholesterol absorption inhibitors, or omega-3 fatty acid compounds. Our measure thus included all lipid-lowering drugs combined together.
Diet quality using the AHEI
Diet quality was measured using the alternate healthy eating index (AHEI).25 Based on the 127-item anglicised version of Willett's food frequency questionnaire (FFQ),26 27 it has been found to yield a satisfactory estimate of food intake among Whitehall II participants compared with biomarkers and 7-day diet diaries.27 The AHEI includes nine food components; food items listed on the FFQ were assigned to their appropriate food groups, using the FFQ serving sizes identified. Eight of the nine components (vegetables, fruit, nuts and soy protein, ratio of white to red meat, dietary fibre, trans fat, ratio of polyunsaturated to saturated fatty acids and alcohol) contributed 0–10 points to the total AHEI score. A score of 10 indicates that recommendations were fully met, whereas a score of 0 represents the least healthy dietary behaviour. Intermediate intakes were scored proportionally between 0 and 10. The final component, long-term multivitamin use, was dichotomised, contributing either 2.5 points (for non-use) or 7.5 points (for use) to the total score. All component scores were summed to obtain a total AHEI score ranging from 2.5 (worst) to 87.5 (best).25 Nutrient intake estimates were calculated using a computerised system developed for the Whitehall II dietary data.27
Physical activity
At baseline (phase 3), participants were asked the duration (number of hours per week) of their participation in moderately energetic (eg, dancing, cycling, leisurely swimming, lawn mowing) and vigorous (eg, running, hard swimming, playing squash) physical activity. At phase 7, the questionnaire was modified to include 20 items on the duration of participation in different physical activities (eg, running, cycling, other sports, housework and gardening activities) that were used to compute hours per week at each intensity level. At both phases, physical activity was defined as the total number of hours per week spent in moderate and vigorous activity.
Covariates
Other variables included in the analysis were: sex; age at baseline (<45, 45–54, ≥55 years); self-reported ethnicity (white, non-white); education (none, lower secondary, A-levels, university or higher); current smoking (categorised as yes or no); and long-standing illness (categorised as yes or no). Prevalent CHD was defined using the MONICA criteria,28 positive responses to questions about chest pain29 and physician diagnoses, evidence from medical records, or ECG findings. Prevalent diabetes mellitus was defined as reported doctor-diagnosed diabetes mellitus or the use of diabetes medication.30 Body mass index (BMI) was calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in metres squared and categorised as normal (BMI <25), overweight (25 ≤BMI <30), or obese (BMI ≥30).31
Statistical analyses
The 11-year change in LDL-cholesterol was calculated as phase 7 minus phase 3 values. In the analysis we wanted to determine the impact of the predictors assessed at baseline (phase 3) and their values over the 11-year follow-up. In order to simplify the interpretation of the coefficients, we categorised the predictors in the following way: lipid-lowering drug use was categorised as no use, treated at baseline, or treatment started during the follow-up. Change in diet was estimated by subtracting the AHEI score at baseline from that at phase 7, standardised to a z-score (mean 0, SD 1) and categorised as ‘increase’ (z-score ≥1), ‘stable’ (−1≤ z-score <1) and ‘decrease’ (z-score ≤−1). This procedure was first applied to the total AHEI score and then to the nine components of the score. Change in physical activity was calculated by subtracting the number of hours per week of physical activity at baseline from that at phase 7. The difference in duration was standardised and categorised as an ‘increase’ (z-score ≥1), ‘stable’ (−1≤ z-score <1), ‘decrease’ (z-score ≤−1) level of physical activity.
As 11-year changes in LDL-cholesterol, diet score and physical activity were all normally distributed, parametric statistical tests were used in the analysis. To examine the unadjusted impact of the predictors (lipid-lowering drug, diet and physical activity) and the covariates we first conducted univariate analysis using linear regression with change in LDL-cholesterol as the dependent variable. The interaction terms between the predictors and sex and age had p values greater than 0.05, negating any necessity to stratify the analyses by age or sex. For the quantitative predictors (diet and physical activity) and for change in BMI, we tested the interaction between continuous values at baseline and the change measures expressed as ‘increase’, ‘stable’, or ‘decrease’. Only the interaction term between BMI at baseline and change in BMI was significant (p<0.05) and was consequently included in further analyses as a covariate.
We constructed three models to examine associations between the predictors and concomitant change in LDL-cholesterol. Model 1 included only non-modifiable covariates (sex, age at baseline, ethnicity) and the duration of follow-up. Model 2 further included education, BMI and long-standing illness at baseline. Model 3 included all three predictors together with the covariates already in model 2. To examine the role of regression to the mean in declining LDL-cholesterol trends, we repeated model 3 among participants in the highest quintile of LDL-cholesterol at baseline (in this subgroup regression to the mean is particularly likely),32 and compared the results with those from the main analysis. In addition, for lipid-lowering medication we removed any potential regression to the mean effect by comparing those with lipid-lowering medication during follow-up with a group without medication selected such that their mean LDL-cholesterol values at baseline were identical.
Using the covariates and predictors in model 3, we conducted several supplementary analyses to determine: (1) whether specific components of the nine-item AHEI scale were associated with the reduction in LDL-cholesterol; (2) the effect of moderate and vigorous physical activity separately on change in LDL-cholesterol; (3) the impact of further adjusting model 3 for change in BMI and the interaction term between change in BMI and BMI at baseline; and (4) whether replacing the variable ‘presence of a long-standing illness at baseline’ by the variables ‘presence of at least one non-fatal CHD event at baseline’ and ‘presence of diabetes mellitus at baseline’ changed estimates.
The squared multiple correlation, also called coefficient of determination (R2), was used to estimate the proportion of variation in LDL-cholesterol change explained by the predictors. We assessed change in R2 when each predictor was entered individually into the initial model adjusted for sex, age at baseline, ethnicity, duration of follow-up, education level, BMI at baseline and long-standing illness at baseline; the model above plus mutual adjustment for the predictors.33
To examine potential beneficial effects related to lipid-lowering drug treatment and favourable changes in diet and physical activity, we estimated the reduction in LDL-cholesterol that would be observed if all participants in need of lipid-lowering drugs at baseline (n=858) were treated, all individuals with a non-optimal diet (AHEI score <60, n=3457) improved their diet, defined as an increased AHEI score of at least 1 SD (0.6 point), and those who undertake less than the recommended level of physical activity (<2.5 h/week, n=2190) increased their physical activity, defined as a minimum increase of 17 min (1 SD) physical activity per week. Following European guidelines,20 participants with prevalent CHD or diabetes and those with a ‘high risk’ of cardiovascular disease (CVD) defined as having a 10-year risk of CVD death of 5% or more based on the systematic coronary risk evaluation (SCORE) charts,34 were deemed to be in need of lipid-lowering therapy. The benefits of lipid-lowering treatment, improved diet (≥1 SD) and increased physical activity levels (≥1 SD) for the total population were estimated based on model 3 estimates using the following equation:
= intercept + β1 Itreatment at baseline + β2 Itreatment during the follow-up + β3 Ione or more SD decrease in AHEI score + β4 Ione or more SD increase in AHEI score + β5 Ione or more SD decrease in hours of physical activity + β6 Ione or more SD increase in hours of physical activity + β7 men + β8 age at baseline + β9 ethnicity + β7 Iintermediate education + β8 Ihigh education + β9 BMI at baseline + β10 long-standing illness + β11 duration of follow-up,
where is a change in LDL cholesterol and I an indicator variable (1 vs 0). All analyses were performed using SAS software, version 9.
Results
Description of the study participants
Of the 10 308 participants at recruitment to the study, 7583 had complete data at phase 3 and 4469 were included in the analysis reported here (figure 1, comparison of the participants included in the analyses with those excluded is provided in supplementary appendix, eTable 1, available online only). Table 1 describes the characteristics of those included at baseline and follow-up. The mean age at baseline was 49.3 years and 72.0% were men. From baseline to follow-up, the mean LDL-cholesterol concentration dropped from 4.38 to 3.52 mmol/l. At the same time the use of lipid-lowering drugs increased from 0.8% to 10.8%. There was a small increase in the mean total AHEI score (from 50.7 to 51.2) and the mean number of hours per week spent in moderate or vigorous physical activity (from 3.4 to 3.7 h/week).
Table 1.
Baseline (phase 3) and follow-up (phase 7) characteristics of the 4469 study participants
| Baseline (1991–3) | Phase 7 (2003–4) | |||
| N | %/Mean (SD) | N | %/Mean (SD) | |
| Sex | ||||
| Men | 3217 | 72.0 | – | – |
| Women | 1252 | 28.0 | – | – |
| Age (years) | ||||
| <45 | 1198 | 26.8 | – | – |
| 45–55 | 2169 | 48.5 | – | – |
| ≥55 | 1102 | 24.7 | – | – |
| All | 4469 | 49.3 (5.9) | – | – |
| Ethnicity | ||||
| White | 4189 | 93.7 | – | – |
| Non-white | 280 | 6.3 | – | – |
| Education | ||||
| No or lower secondary | 1969 | 44.1 | – | – |
| A-levels | 1171 | 26.2 | – | – |
| University or higher | 1329 | 29.7 | – | – |
| BMI (kg/m2) | ||||
| Normal (<25) | 2463 | 55.1 | 1718 | 38.4 |
| Overweight (25–30) | 1667 | 37.3 | 1999 | 44.7 |
| Obese (≥30) | 339 | 7.6 | 752 | 16.8 |
| All | 4469 | 25.0 (3.5) | 4469 | 26.5 (4.2) |
| Current smoking | ||||
| No | 4000 | 89.5 | 4159 | 93.1 |
| Yes | 469 | 10.5 | 310 | 6.9 |
| Long-standing illness | ||||
| No | 2993 | 67.0 | 1767 | 39.5 |
| Yes | 1476 | 33.0 | 2702 | 60.5 |
| Total cholesterol concentrations (mmol/l) | 4469 | 6.4 (1.1) | 4469 | 5.7 (1.0) |
| HDL-cholesterol concentrations (mmol/l) | 4469 | 1.4 (0.4) | 4469 | 1.6 (0.4) |
| Triglyceride concentrations (mmol/l) | 4469 | 1.3 (0.7) | 4469 | 1.3 (0.7) |
| LDL-cholesterol concentrations (mmol/l) | 4469 | 4.4 (1.0) | 4469 | 3.5 (0.9) |
| Lipid-lowering drugs use | ||||
| No | 4435 | 99.2 | 3987 | 89.2 |
| Yes | 34 | 0.8 | 482 | 10.8 |
| AHEI score, mean (SD) | 4469 | 50.7 (11.9) | 4469 | 51.2 (12.5) |
| Physical activity (h/week) | 4469 | 3.4 (3.4) | 4469 | 3.7 (3.1) |
AHEI, alternate healthy eating index; BMI, body mass index; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; LDL, low-density lipoprotein.
At baseline, 858 participants had a high risk of CVD according to the European guidelines,20 had diabetes or had experienced a validated non-fatal CHD event at baseline, or took lipid-lowering medication at baseline or follow-up. Only 60.0% (n=515) of them were taking lipid-lowering medication at follow-up.
Multivariate analysis of change in lipid levels during follow-up
Univariate analyses provided strong evidence of associations between changes in LDL-cholesterol and all the covariates, with the exception of smoking (see supplementary appendix eTable 2, available online only). Table 2 presents multivariable-adjusted absolute changes in LDL-cholesterol as a function of lipid-lowering medication and changes in diet and physical activity. These results show that LDL-cholesterol declined in all groups. Table 3 shows the corresponding changes in relative terms. Compared with those not on lipid-lowering drugs, the decline in LDL-cholesterol was greater among those who were on treatment at baseline or during the follow-up. Compared with those with a stable diet, individuals who improved their diet showed a greater decline in LDL-cholesterol, whereas those whose diet worsened showed a smaller decline. Similar results were observed for physical activity. All relative differences persisted after serial adjustments for multiple covariates (table 3). The results were largely similar in a subgroup of participants in the top quintile of LDL-cholesterol at baseline and when, for lipid-lowering medication, potential regression to the mean effects were totally removed (see supplementary appendix eTable 3, available online only).
Table 2.
Absolute change in serum LDL-cholesterol between the baseline (1991–3) and follow-up (2003–4) screening as a function of the use of lipid-lowering drugs, healthy diet and physical activity (N=4469)
| n | Mean absolute change in LDL-cholesterol (95% CI), mmol/l | |||
| Model 1* | Model 2† | Model 3‡ | ||
| Start of lipid-lowering drugs | ||||
| None | 3954 | −0.61 (−0.66 to −0.56) | −0.60 (−0.65 to −0.56) | −0.59 (−0.65 to −0.53) |
| Baseline | 34 | −1.70 (−1.96 to −1.43) | −1.70 (−1.96 to −1.43) | −1.73 (−1.99 to −1.46) |
| During follow-up | 481 | −2.42 (−2.50 to −2.34) | −2.38 (−2.46 to −2.30) | −2.36 (−2.45 to −2.28) |
| Change in AHEI score | ||||
| Increase (≥1 SD) | 717 | −0.99 (−1.08 to −0.91) | −0.99 (−1.07 to −0.90) | −1.65 (−1.76 to −1.53) |
| Stable (−1≤ SD <1) | 3071 | −0.85 (−0.92 to −0.79) | −0.84 (−0.90 to −0.78) | −1.58 (−1.68 to −1.47) |
| Decrease (<−1 SD) | 681 | −0.76 (−0.85 to −0.67) | −0.75 (−0.83 to −0.66) | −1.46 (−1.57 to −1.35) |
| Change in physical activity | ||||
| Increase (≥1 SD) | 601 | −0.98 (−1.07 to −0.88) | −0.95 (−1.05 to −0.86) | −1.66 (−1.78 to −1.54) |
| Stable (−1≤ SD <1) | 3312 | −0.86 (−0.92 to −0.80) | −0.85 (−0.91 to −0.79) | −1.56 (−1.66 to −1.46) |
| Decrease (<−1 SD) | 556 | −0.77 (−0.87 to −0.68) | −0.76 (−0.85 to −0.66) | −1.46 (−1.58 to −1.34) |
Model 1: Adjusted for sex, age at baseline, ethnicity and duration of follow-up.
Model 2: As model 1 and additionally adjusted for education level, BMI at baseline and long-standing illness at baseline.
Model 3: As model 2 with predictors mutually adjusted.
AHEI, alternate healthy eating index; BMI, body mass index; LDL, low-density lipoprotein.
Table 3.
Relative change in serum LDL-cholesterol (mmol/l) between the baseline (1991–3) and follow-up (2003–4) screening as a function of the use of lipid-lowering drugs, healthy diet and physical activity (N=4469)
| n | Mean relative change in LDL-cholesterol (mmol/l) and p value for difference | ||||||
| Model 1* | Model 2† | Model 3‡ | |||||
| Start of lipid-lowering drugs | |||||||
| None | 3954 | 0 | Reference | 0 | Reference | 0 | Reference |
| Baseline | 34 | −1.09 | <0.001 | −1.09 | <0.001 | −1.14 | <0.001 |
| During follow-up | 481 | −1.81 | <0.001 | −1.77 | <0.001 | −1.77 | <0.001 |
| Change in AHEI score | |||||||
| Increase (≥1 SD) | 717 | −0.14 | <0.001 | −0.14 | <0.001 | −0.07 | 0.03 |
| Stable (−1≤ SD <1) | 3071 | 0 | Reference | 0 | Reference | 0 | Reference |
| Decrease (<−1 SD) | 681 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.12 | <0.001 |
| Change in physical activity | |||||||
| Increase (≥1 SD) | 601 | −0.11 | 0.007 | −0.10 | 0.02 | −0.10 | 0.005 |
| Stable (−1≤ SD <1) | 3312 | 0 | Reference | 0 | Reference | 0 | Reference |
| Decrease (<−1 SD) | 556 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.004 |
Model 1: Adjusted for sex, age at baseline, ethnicity and duration of follow-up.
Model 2: As model 1 and additionally adjusted for education level, BMI at baseline and long-standing illness at baseline.
Model 3: As model 2 with predictors mutually adjusted.
AHEI, alternate healthy eating index; BMI, body mass index; LDL, low-density lipoprotein.
More detailed analyses of the nine components of the AHEI diet score and intensity of physical activity are shown in supplementary appendix eTables 4 and 5 (available online only). Briefly, the decline in LDL-cholesterol change was significantly associated with an increase in the ratio of white to red meat consumption (p<0.001), the ratio of polyunsaturated to saturated fatty acids (p<0.001), an increase in fruit consumption (p=0.04) and a decrease in trans fats (p=0.04). Decreases in both moderate and vigorous physical activity were associated with a smaller decrease in LDL-cholesterol.
In sensitivity analyses, we examined the role of BMI by adding the following covariates to model 3: change in BMI and the interaction term between change in BMI and BMI at baseline. The results remained largely unchanged. Similarly, when the variable ‘presence of a long-standing illness at baseline’ was replaced by the variables ‘presence of at least one non-fatal CHD event at baseline’ and ‘presence of diabetes mellitus at baseline’, respectively, in model 3, the results were much the same (data not shown).
Multivariate analyses of changes in other lipid fractions are provided in supplementary appendix, eTable 6 (available online only). An increase in physical activity was associated with a 0.05 mmol/l greater increase in HDL-cholesterol compared with those who had a stable level of physical activity. Participants whose BMI increased over the follow-up showed a 0.01 mmol/l decrease in HDL-cholesterol and a 0.27 mmol/l increase in triglycerides; among those with stable BMI, HDL-cholesterol increased by 0.11 mmol/l and triglycerides decreased by 0.07 mmol/l. Participants whose alcohol consumption increased had a 0.08 mmol/l greater increase in HDL-cholesterol than those whose alcohol consumption was stable. Among participants who stopped smoking during follow-up, there was a 0.04 mmol/l greater increase in HDL-cholesterol compared with never smokers.
Relative importance of medications, diet and physical activity in explaining LDL-cholesterol trends
The baseline model for this analysis, including sex, ethnicity, duration of follow-up and baseline measures of age, education, BMI and long-standing illness as covariates, explained 11.6% of the variability in the change in LDL-cholesterol. Adding lipid-lowering drugs to this model increased the coefficient of determination (R2) by 29.4%. AHEI diet score and physical activity, when added into the baseline model, explained only 0.5% and 0.3% of the variability in the change in LDL-cholesterol concentrations, respectively. Each predictor had an independent effect in the mutually adjusted model. (see supplementary appendix eTable 7, available online only).
Estimated population-level benefits of lipid-lowering drugs and improved lifestyle
Based on model 3 estimates, if all 858 participants with prevalent CHD or diabetes or a high risk of CVD death at baseline had been on lipid-lowering medication, as suggested in the European guidelines, then the decline in LDL-cholesterol would have been 2.77 mmol/l greater than the observed value (table 4). If all 3457 participants who did not have an optimal diet (AHEI score <60) had improved their diet, the corresponding additional decline in LDL-cholesterol would have been 0.08 mmol/l. The adoption of a more physically active lifestyle by the 2190 participants who undertook less than 2.5 h of moderate or vigorous activities per week would have produced an additional decline in LDL-cholesterol of 0.11 mmol/l. These estimations applied to the total cohort (n=4469) suggest that successful implementation of lipid-lowering therapy and change in lifestyle would each reduce LDL-cholesterol levels by 0.90 to 1.07 mmol/l (table 4).
Table 4.
Estimated beneficial effect of lipid-lowering drugs, healthy diet and physical activity on LDL change in the population at risk and the total cohort
| Intervention | Mean LDL-cholesterol (mmol/l) change | ||||
| Population at risk at baseline | Total cohort (n=4469) | ||||
| Total N (N already following the intervention)* | Observed | After intervention† | Observed | After intervention† | |
| Start lipid-lowering drugs | 858‡ (515) | −1.04 | −3.81 | −0.86 | −1.07 |
| ≥1 SD increase in the AHEI diet score* | 3457§ (684) | −0.84 | −0.92 | −0.86 | −0.91 |
| ≥1 SD increase in the no of hours of physical activity* | 2190¶ (383) | −0.85 | −0.96 | −0.86 | −0.90 |
Here intervention stands for use of a lipid-lowering drug among those needing such a treatment according to the European guidelines, improving diet among those with an AHEI score less than 60, or increasing the duration of physical activity among those with less than 2.5 h/week. 1 SD increase in the AHEI score is 0.6 point and 1 SD increase in physical activity is 17 min/week
Decline in LDL-cholesterol estimated for participants who met the criteria for intervention based on effects shown in table 3, model 3.
Participants with cardiovascular disease risk score of 5% or greater or prevalent coronary heart disease or diabetes at baseline, or lipid-lowering medication at baseline or follow-up.
Participants with an AHEI score of less than 60 at baseline.
Participants with physical activity for less than 2.5 h/week at baseline.
AHEI, alternate healthy eating index; LDL, low-density lipoprotein.
Discussion
We found an overall decrease in the LDL-cholesterol concentration in the Whitehall II cohort of civil servants over 11 years of follow-up. The degree of decline was associated with an increased use of lipid-lowering drugs, improvements in diet—especially the ratio of white to red meat consumption and the ratio of polyunsaturated to saturated fatty acids intake—and an increase in physical activity. In this population, the contribution of changes in diet and physical activity were modest compared with pharmacological treatment among individuals at high risk of CVD. However, a successful implementation of lipid-lowering drug treatment for the relatively small group of high-risk individuals and a favourable change in diet and physical activity in the large group of people with a non-optimal lifestyle were estimated to result in largely similar declines in LDL-cholesterol in the total cohort. These findings support the use of multifaceted intervention strategies for prevention.
In many previous studies, a decrease in the LDL-cholesterol concentration has been assessed by comparing cross-sectional surveys repeated over time: in the INTERGENE and GOT–MONICA study (1985, 1990, 1995 and 2002),9 in the French MONICA study (1996 and 2007),10 in the studies conducted in Catalonia, Spain (1992 and 2003)11 and in Gerona, Spain (1995, 2000 and 2005).12 This design captures time trends but, unlike the prospective cohort design employed in the present study, does not allow an estimation of within-subject changes in LDL-cholesterol, or in their predictors.
Our study confirms the findings of the few previous cohort studies on changes in total or LDL-cholesterol among middle-aged individuals. In an Australian population-based cohort study, Buyken et al35 reported a decrease of 0.7 mmol/l in LDL-cholesterol between 1992 and 2004, comparable with the 0.9 mmol/l decrease in our study. Two other cohort studies, the New Zealand Workforce Diabetes Survey19 and the American Physicians' Health Study,36 also reported a decline in LDL-cholesterol from 1988 to 1997 and from 1982 to 1997, respectively. In the Framingham Heart Study,37 there was a slight increase in LDL-cholesterol over time, but these analyses did not include individuals on lipid-lowering or hormone replacement therapies, or those with prevalent CVD. Randomised trials have shown lipid-lowering drugs,38 39 diet modification39–42 and endurance exercise training42–44 to be effective in lowering LDL-cholesterol concentrations. The present results, obtained from an observational study, add to the knowledge from randomised controlled trials in which the effect size is dependent on specific interventions.
There are a few caveats to the results reported here. First, total cholesterol and triglycerides were not measured using the same enzymatic methods at both study phases; but HDL-cholesterol was assessed using the dextran sulphate–magnesium precipitation method at baseline and the direct homogeneous method at follow-up.23 These protocol changes might have affected the estimation of absolute LDL levels. However, this is an unlikely source of major bias because both methods have been validated and certified by the Cholesterol Reference Method Laboratory Network at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention,45 46 and agreement between the methods is high, with a correlation coefficient of 0.98, slope 0.98 and mean bias 0.05 mmol/l.47 If the level of HDL-cholesterol was ‘overestimated’ by 0.05 mmol/l at follow-up in the present study, the method-related decrease in LDL-cholesterol between baseline and follow-up would have been approximately 0.06 mmol/l, which is small compared with the mean observed decrease of 0.86 mmol/l. Furthermore, bias resulting from the change in the method of assessing HDL-cholesterol is likely to be independent of the measurement of the predictors and thus should not unduly bias our findings on relative differences in changes in LDL-cholesterol between subgroups.
Second, physical activity and, to a greater extent, dietary intake, are difficult to measure accurately; whereas it is likely that the use of lipid-lowering drugs is recalled with greater precision. We may therefore have underestimated the effects of diet and physical activity on LDL-cholesterol decline. Furthermore, it is possible that we underestimated the contribution of diet because our analysis did not fully capture effects arising from externally driven secular changes in dietary patterns. For example, recommendations from the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence encourage manufacturers, caterers and producers to reduce the amount of saturated and trans fatty acids in all food products and replace them, if needed, by polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fatty acids.48 Such guidance, if successful in reducing ‘bad’ cholesterol in marketed foods, could, potentially, have a notable impact on the number of cardiovascular events at the population level, as is clear from the results from the recent meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.49
Third, regression towards the mean is a potential source of bias in observational studies with repeat outcome measures.32 Regression to the mean arises from random errors in measurement and should be relatively independent of the use of lipid-lowering drugs or lifestyle. In the present study, these factors remained important predictors of reduced LDL levels in a subgroup of participants with particularly high LDL-cholesterol at baseline, a group whose measures are likely to contain more measurement error, suggesting that regression to the mean had, if anything, little impact on our findings.
Fourth, by definition, occupational cohorts such as Whitehall II are fitter than the general population due to the healthy worker effect. The feedback provided to participants after medical screening phases of the study about their coronary risk factors may also have promoted healthier lifestyles, as discussed in relation to the Framingham study.37 Further research is therefore needed to examine the generalisability of our findings.
With the limitations of our study in mind, we conclude that declining trends in LDL-cholesterol seem to be independently associated with the use of lipid-lowering therapy and favourable lifestyle changes. Our findings suggest that more should be done to reduce the under-treatment of dyslipidaemia and promote lifestyle modifications in order to accelerate further the favourable population trends in LDL-cholesterol.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all participating men and women in the Whitehall II Study; all participating Civil Service departments and their welfare, personnel and establishment officers; the Occupational Health and Safety Agency and the Council of Civil Service Unions. The Whitehall II Study team comprises research scientists, statisticians, study coordinators, nurses, data managers, administrative assistants and data entry staff, who make the study possible. They would also like to thank Drs Anthony Wierzbicki and Gill Rumsby for providing information on cholesterol measurements.
Footnotes
Funding: The Whitehall II study has been supported by grants from the Medical Research Council, UK, Economic and Social Research Council, UK, British Heart Foundation, UK, Health and Safety Executive, UK, Department of Health, UK, BUPA Foundation, UK, National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (R01HL036310), USA and NIH: National Institute on Aging (R01AG013196; R01AG034454), USA. GDB is a Wellcome Trust Fellow (WBS U.1300.00.006.00012.01), UK. MJS is supported by the British Heart Foundation. MK is supported by the BUPA Foundation, UK, the Academy of Finland, Finland, and the EU OSH ERA research programme.
Competing interests: None.
Ethics approval: This study was conducted with the approval of the University College London Medical School committee on the ethics of human research (London, UK).
Contributors: All authors contributed to the conception and design, and to analysis and interpretation of data; or wrote the first draft of the article and revised it critically for important intellectual content. All approved the final version to be published.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
References
- 1.Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults Executive Summary of the Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 2001;285:2486–97 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hebert PR, Gaziano JM, Chan KS, et al. Cholesterol lowering with statin drugs, risk of stroke, and total mortality. An overview of randomized trials. JAMA 1997;278:313–21 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Heart Protection Study Collaborative Group MRC/BHF Heart Protection Study of cholesterol lowering with simvastatin in 20,536 high-risk individuals: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2002;360:7–2212114036 [Google Scholar]
- 4.Baigent C, Keech A, Kearney PM, et al. Efficacy and safety of cholesterol-lowering treatment: prospective meta-analysis of data from 90,056 participants in 14 randomised trials of statins. Lancet 2005;366:1267–78 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Probstfield JL, Rifkind BM. The Lipid Research Clinics Coronary Primary Prevention Trial: design, results, and implications. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1991;40(Suppl 1):S69–75 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kuulasmaa K, Tunstall-Pedoe H, Dobson A, et al. Estimation of contribution of changes in classic risk factors to trends in coronary-event rates across the WHO MONICA Project populations. Lancet 2000;355:675–87 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kotseva K, Wood D, De Backer G, et al. EUROASPIRE Study Group Cardiovascular prevention guidelines in daily practice: a comparison of EUROASPIRE I, II, and III surveys in eight European countries. Lancet 2009;373:929–40 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Unal B, Critchley JA, Capewell S. Modelling the decline in coronary heart disease deaths in England and Wales, 1981–2000: comparing contributions from primary prevention and secondary prevention. BMJ 2005;331:614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Berg CM, Lissner L, Aires N, et al. Trends in blood lipid levels, blood pressure, alcohol and smoking habits from 1985 to 2002: results from INTERGENE and GOT–MONICA. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil 2005;12:115–25 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ferrieres J, Bongard V, Dallongeville J, et al. Trends in plasma lipids, lipoproteins and dyslipidaemias in French adults, 1996–2007. Arch Cardiovasc Dis 2009;102:293–301 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Serra-Majem L, Pastor-Ferrer MC, Castell C, et al. Trends in blood lipids and fat soluble vitamins in Catalonia, Spain (1992–2003). Public Health Nutr 2007;10:1379–88 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Grau M, Subirana I, Elosua R, et al. Trends in cardiovascular risk factor prevalence (1995–2000–2005) in northeastern Spain. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil 2007;14:653–9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Li M, Ong KL, Tse HF, et al. Utilization of lipid lowering medications among adults in the United States 1999–2006. Atherosclerosis 2010;208:456–60 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Carroll MD, Lacher DA, Sorlie PD, et al. Trends in serum lipids and lipoproteins of adults, 1960–2002. JAMA 2005;294:1773–81 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Arnett DK, Jacobs DR, Jr, Luepker RV, et al. Twenty-year trends in serum cholesterol, hypercholesterolemia, and cholesterol medication use: the Minnesota Heart Survey, 1980–1982 to 2000–2002. Circulation 2005;112:3884–91 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kuklina EV, Yoon PW, Keenan NL. Trends in high levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in the United States, 1999–2006. JAMA 2009;302:2104–10 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Neutel CI, Morrison H, Campbell NR, et al. Statin use in Canadians: trends, determinants and persistence. Can J Public Health 2007;98:412–16 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hobbs MS, Knuiman MW, Briffa T, et al. Plasma cholesterol levels continue to decline despite the rising prevalence of obesity: population trends in Perth, Western Australia, 1980–1999. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil 2008;15:319–24 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Metcalf PA, Scragg RK, Swinburn BA, et al. Factors associated with changes in serum total cholesterol levels over 7 years in middle-aged New Zealand men and women: a prospective study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2001;11:298–305 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Graham I, Atar D, Borch-Johnsen K, et al. European guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice: full text. Fourth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and other societies on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice (constituted by representatives of nine societies and by invited experts). Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil 2007;14(Suppl 2):S1–113 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Marmot M, Brunner E. Cohort profile: the Whitehall II study. Int J Epidemiol 2005;34:251–6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Brunner EJ, Marmot MG, Nanchahal K, et al. Social inequality in coronary risk: central obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Evidence from the Whitehall II study. Diabetologia 1997;40:1341–9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Warnick GR, Nauck M, Rifai N. Evolution of methods for measurement of HDL-cholesterol: from ultracentrifugation to homogeneous assays. Clin Chem 2001;47:1579–96 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem 1972;18:499–502 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.McCullough ML, Feskanich D, Stampfer MJ, et al. Diet quality and major chronic disease risk in men and women: moving toward improved dietary guidance. Am J Clin Nutr 2002;76:1261–71 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Willett WC, Sampson L, Stampfer MJ, et al. Reproducibility and validity of a semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire. Am J Epidemiol 1985;122:51–65 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Brunner E, Stallone D, Juneja M, et al. Dietary assessment in Whitehall II: comparison of 7 d diet diary and food-frequency questionnaire and validity against biomarkers. Br J Nutr 2001;86:405–14 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tunstall-Pedoe H, Kuulasmaa K, Amouyel P, et al. Myocardial infarction and coronary deaths in the World Health Organization MONICA Project. Registration procedures, event rates, and case-fatality rates in 38 populations from 21 countries in four continents. Circulation 1994;90:583–612 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Rose GA, Blackburn H, Gillum RF, et al. Cardiovascular survey methods. 2nd edn Geneva, Switzerland: WHO, 1982 [Google Scholar]
- 30.World Health Organization Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO, 1997 [Google Scholar]
- 31.World Health Organization Physical status: the use and interpretation of anthropometry: report of a WHO expert committee. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO, 1995 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Morton V, Torgerson DJ. Effect of regression to the mean on decision making in health care. BMJ 2003;326:1083–4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Chao YC, Zhao Y, Kupper LL, et al. Quantifying the relative importance of predictors in multiple linear regression analyses for public health studies. J Occup Environ Hyg 2008;5:519–29 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Conroy RM, Pyorala K, Fitzgerald AP, et al. Estimation of ten-year risk of fatal cardiovascular disease in Europe: the SCORE project. Eur Heart J 2003;24:987–1003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Buyken AE, Flood V, Rochtchina E, et al. Modifications in dietary fat quality are associated with changes in serum lipids of older adults independently of lipid medication. J Nutr 2010;140:88–94 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Scranton R, Sesso HD, Stampfer MJ, et al. Predictors of 14-year changes in the total cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio in men. Am Heart J 2004;147:1033–8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ingelsson E, Massaro JM, Sutherland P, et al. Contemporary trends in dyslipidemia in the Framingham Heart Study. Arch Intern Med 2009;169:279–86 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Cui Y, Watson DJ, Girman CJ, et al. Effects of increasing high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and decreasing low-density lipoprotein cholesterol on the incidence of first acute coronary events (from the Air Force/Texas Coronary Atherosclerosis Prevention Study). Am J Cardiol 2009;104:829–34 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Nakamura H, Arakawa K, Itakura H, et al. Primary prevention of cardiovascular disease with pravastatin in Japan (MEGA Study): a prospective randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2006;368:1155–63 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Brunner E, Rees K, Ward K, et al. Dietary advice for reducing cardiovascular risk. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2007;(4):CD002128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Howard BV, Van HL, Hsia J, et al. Low-fat dietary pattern and risk of cardiovascular disease: the Women's Health Initiative Randomized Controlled Dietary Modification Trial. JAMA 2006;295:655–66 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Varady KA, Jones PJ. Combination diet and exercise interventions for the treatment of dyslipidemia: an effective preliminary strategy to lower cholesterol levels? J Nutr 2005;135:1829–35 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Halverstadt A, Phares DA, Wilund KR, et al. Endurance exercise training raises high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and lowers small low-density lipoprotein and very low-density lipoprotein independent of body fat phenotypes in older men and women. Metabolism 2007;56:444–50 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Wilund KR, Feeney LA, Tomayko EJ, et al. Effects of endurance exercise training on markers of cholesterol absorption and synthesis. Physiol Res 2009;58:545–52 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kimberly MM, Leary ET, Cole TG, et al. Selection, validation, standardization, and performance of a designated comparison method for HDL-cholesterol for use in the cholesterol reference method laboratory network. Clin Chem 1999;45:1803–12 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Laboratory quality assurance and standardization programs: cholesterol reference method laboratory network. http://www.cdc.gov/labstandards/crmln.html (accessed 21 Dec 2010).
- 47.Bairaktari E, Elisaf M, Katsaraki A, et al. Homogeneous HDL-cholesterol assay versus ultracentrifugation/dextran sulfate-Mg2+ precipitation and dextran sulfate-Mg2+ precipitation in healthy population and in hemodialysis patients. Clin Biochem 1999;32:339–46 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.NHS National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Prevention of cardiovascular disease at population level. http://guidance.nice.org.uk/PH25 (accessed 21 Dec 2010).
- 49.Mozaffarian D, Micha R, Wallace S. Effects on coronary heart disease of increasing polyunsaturated fat in place of saturated fat: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS Med 2010;7:e1000252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]