Abstract
We have devised a simple method for ordering markers on a chromosome and determining the distances between them. It uses haploid equivalents of DNA and the polymerase chain reaction, hence 'happy mapping'. Our approach is analogous to classical linkage mapping; we replace its two essential elements, chromosome breakage and segregation, by in vitro analogues. DNA from any source is broken randomly by gamma-irradiation or shearing. Markers are then segregated by diluting the resulting fragments to give aliquots containing approximately 1 haploid genome equivalent. Linked markers tend to be found together in an aliquot. After detecting markers using the polymerase chain reaction, map order and distance can be deduced from the frequency with which markers 'co-segregate'. We have mapped 7 markers scattered over 1.24 Mbp using only 140 aliquots. Using the 'whole-genome' chain reaction, we also show how the approach might be used to map thousands of markers scattered throughout the genome. The method is powerful because the frequency of chromosome breakage can be optimized to suit the resolution required.
Full text
PDF

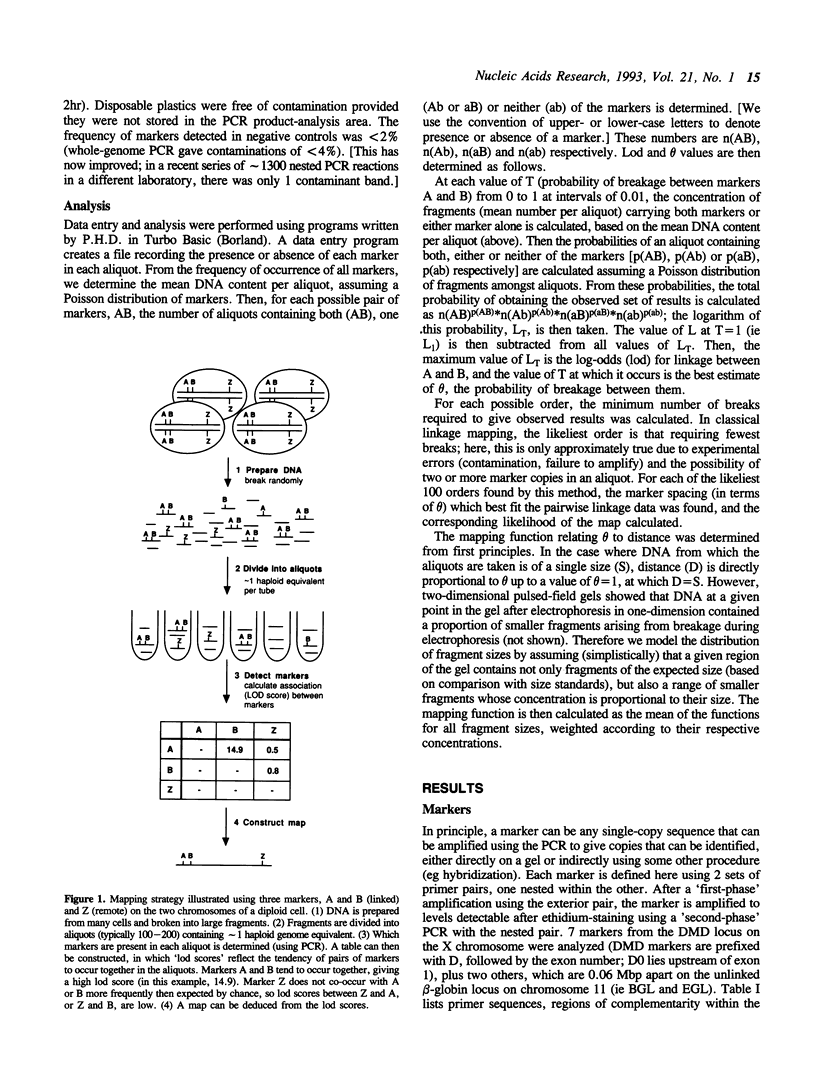
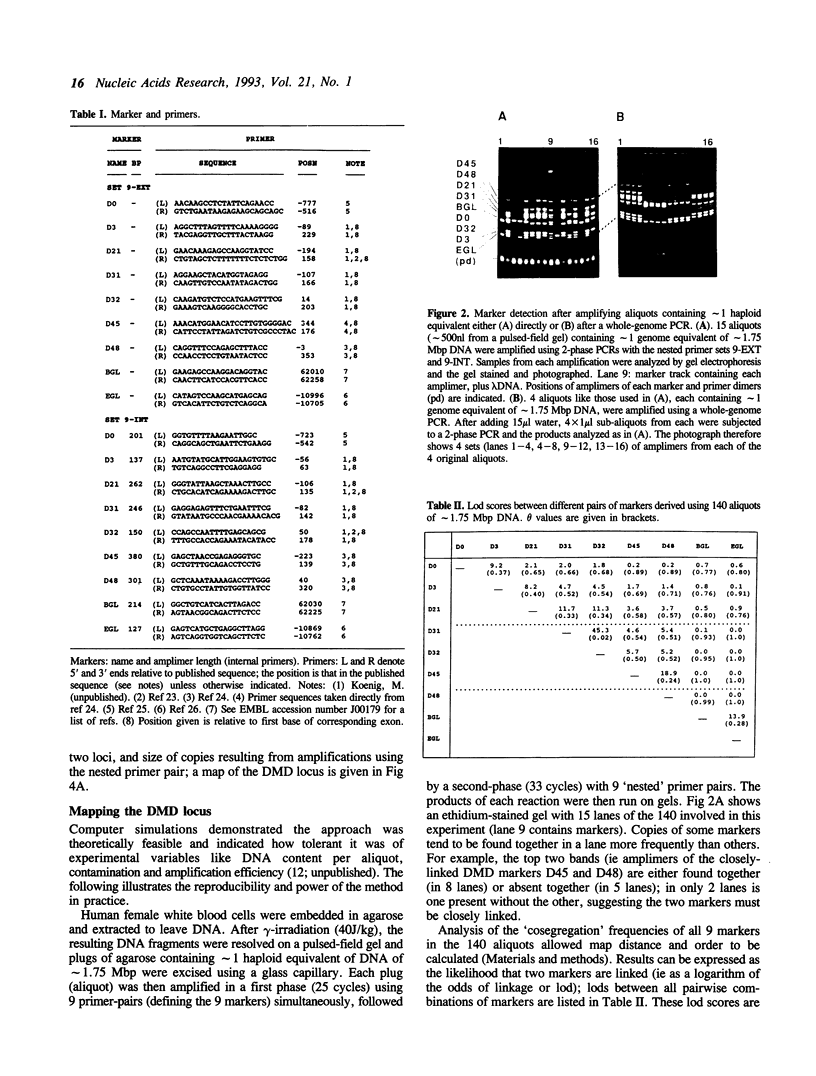
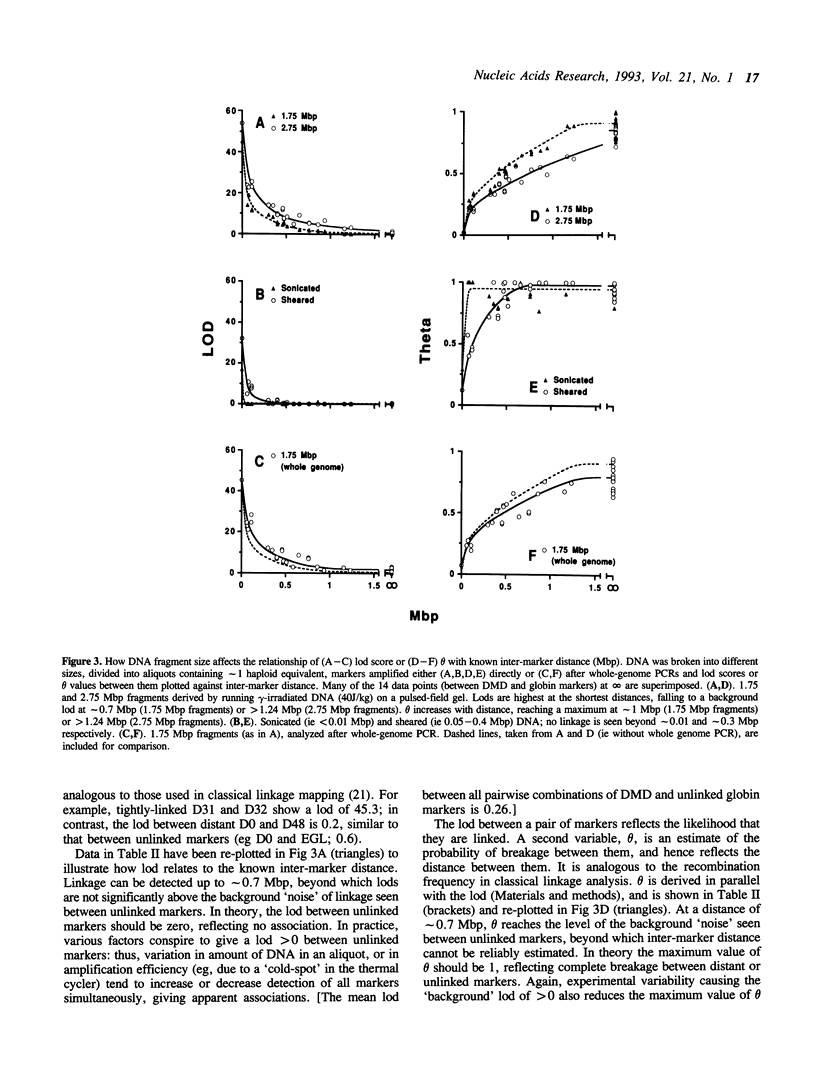



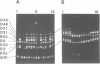
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. D., Dubnick M., Kerlavage A. R., Moreno R., Kelley J. M., Utterback T. R., Nagle J. W., Fields C., Venter J. C. Sequence identification of 2,375 human brain genes. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):632–634. doi: 10.1038/355632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellanné-Chantelot C., Lacroix B., Ougen P., Billault A., Beaufils S., Bertrand S., Georges I., Glibert F., Gros I., Lucotte G. Mapping the whole human genome by fingerprinting yeast artificial chromosomes. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):1059–1068. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90254-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. S., Gibbs R. A., Ranier J. E., Nguyen P. N., Caskey C. T. Deletion screening of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus via multiplex DNA amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 9;16(23):11141–11156. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.23.11141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chumakov I., Rigault P., Guillou S., Ougen P., Billaut A., Guasconi G., Gervy P., LeGall I., Soularue P., Grinas L. Continuum of overlapping clones spanning the entire human chromosome 21q. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):380–387. doi: 10.1038/359380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R. A general method for preparing intact nuclear DNA. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1837–1842. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02056.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R., Brazell I. A. Conformational constraints in nuclear DNA. J Cell Sci. 1976 Nov;22(2):287–302. doi: 10.1242/jcs.22.2.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. R., Burmeister M., Price E. R., Kim S., Myers R. M. Radiation hybrid mapping: a somatic cell genetic method for constructing high-resolution maps of mammalian chromosomes. Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):245–250. doi: 10.1126/science.2218528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cui X. F., Li H. H., Goradia T. M., Lange K., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Galas D., Arnheim N. Single-sperm typing: determination of genetic distance between the G gamma-globin and parathyroid hormone loci by using the polymerase chain reaction and allele-specific oligomers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9389–9393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dear P. H., Cook P. R. Happy mapping: a proposal for linkage mapping the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 12;17(17):6795–6807. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.17.6795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Den Dunnen J. T., Grootscholten P. M., Bakker E., Blonden L. A., Ginjaar H. B., Wapenaar M. C., van Paassen H. M., van Broeckhoven C., Pearson P. L., van Ommen G. J. Topography of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) gene: FIGE and cDNA analysis of 194 cases reveals 115 deletions and 13 duplications. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Dec;45(6):835–847. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drmanac R., Petrović N., Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R. A calculation of fragment lengths obtainable from human DNA with 78 restriction enzymes: an aid for cloning and mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4691–4692. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klamut H. J., Gangopadhyay S. B., Worton R. G., Ray P. N. Molecular and functional analysis of the muscle-specific promoter region of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):193–205. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Beggs A. H., Moyer M., Scherpf S., Heindrich K., Bettecken T., Meng G., Müller C. R., Lindlöf M., Kaariainen H. The molecular basis for Duchenne versus Becker muscular dystrophy: correlation of severity with type of deletion. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Oct;45(4):498–506. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Monaco A. P., Kunkel L. M. The complete sequence of dystrophin predicts a rod-shaped cytoskeletal protein. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. B., Singer R. H., McNeil J. A. Interphase and metaphase resolution of different distances within the human dystrophin gene. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):928–932. doi: 10.1126/science.2203143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H. H., Gyllensten U. B., Cui X. F., Saiki R. K., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Amplification and analysis of DNA sequences in single human sperm and diploid cells. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):414–417. doi: 10.1038/335414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Q., Powers P. A., Smithies O. Nucleotide sequence of 16-kilobase pairs of DNA 5' to the human epsilon-globin gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):14901–14910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little P. Human Genome Project: Mapping the way ahead. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):367–368. doi: 10.1038/359367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R., Lalouel J. M. Sets of linked genetic markers for human chromosomes. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:259–279. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.001355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyman A. R., Wolfe L. B., Botstein D. Propagation of some human DNA sequences in bacteriophage lambda vectors requires mutant Escherichia coli hosts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2880–2884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang L., Cui X., Schmitt K., Hubert R., Navidi W., Arnheim N. Whole genome amplification from a single cell: implications for genetic analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5847–5851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Engh G., Sachs R., Trask B. J. Estimating genomic distance from DNA sequence location in cell nuclei by a random walk model. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1410–1412. doi: 10.1126/science.1388286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]