Abstract
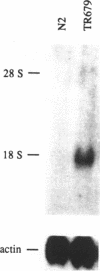
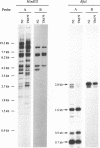
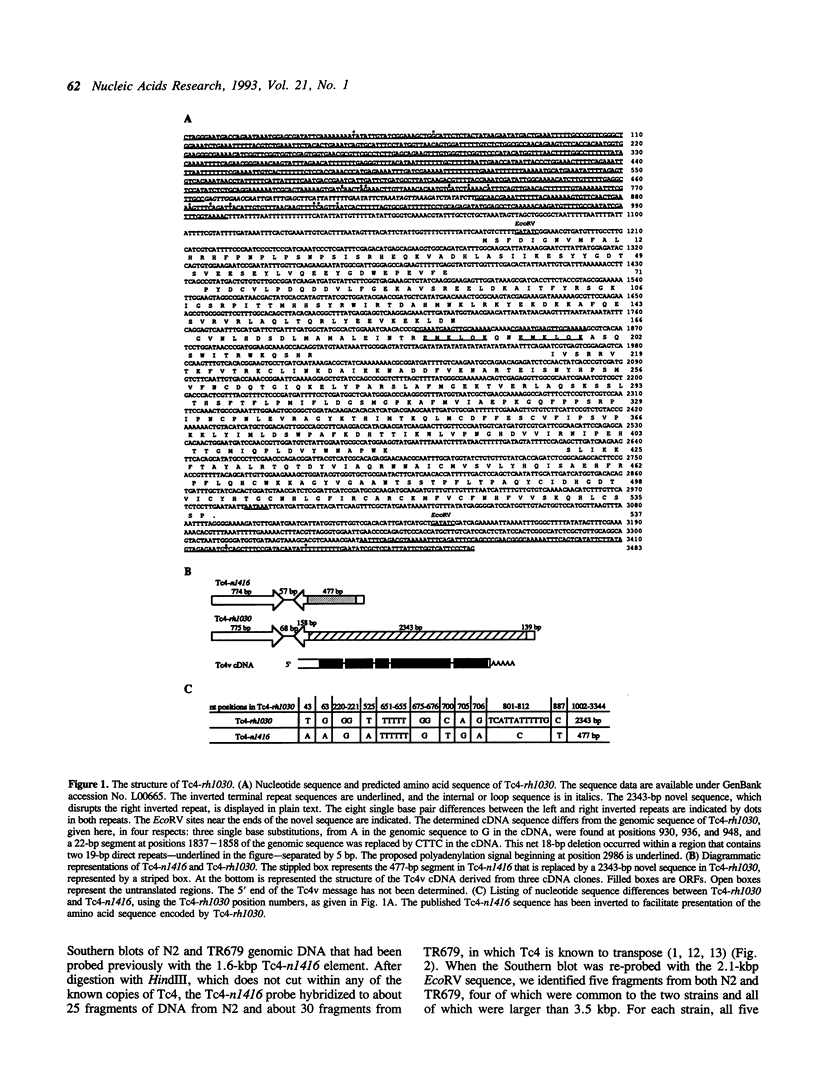
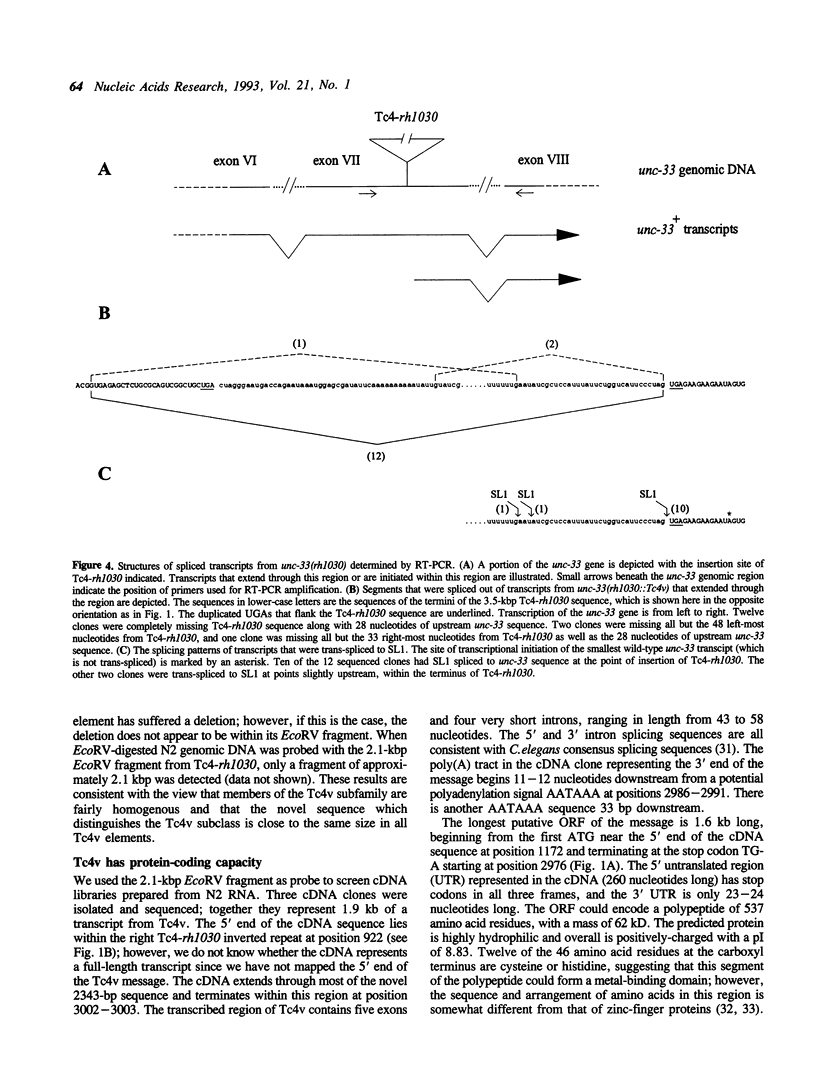
A variant C. elegans Tc4 transposable element, Tc4-rh1030, has been sequenced and is 3483 bp long. The Tc4 element that had been analyzed previously is 1605 bp long, consists of two 774-bp nearly perfect inverted terminal repeats connected by a 57-bp loop, and lacks significant open reading frames. In Tc4-rh1030, by comparison, a 2343-bp novel sequence is present in place of a 477-bp segment in one of the inverted repeats. The novel sequence of Tc4-rh1030 is present about five times per haploid genome and is invariably associated with Tc4 elements; we have used the designation Tc4v to denote this variant subfamily of Tc4 elements. Sequence analysis of three cDNA clones suggests that a Tc4v element contains at least five exons that could encode a novel basic protein of 537 amino acid residues. On northern blots, a 1.6-kb Tc4v-specific transcript was detected in the mutator strain TR679 but not in the wild-type strain N2; Tc4 elements are known to transpose in TR679 but appear to be quiescent in N2. We have analyzed transcripts produced by an unc-33 gene that has the Tc4-rh1030 insertional mutation in its transcribed region; all or almost all of the Tc4v sequence is frequently spliced out of the mutant unc-33 transcripts, sometimes by means of non-consensus splice acceptor sites.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Zinc finger domains: hypotheses and current knowledge. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1990;19:405–421. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.19.060190.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner S. The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1974 May;77(1):71–94. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brierley H. L., Potter S. S. Distinct characteristics of loop sequences of two Drosophila foldback transposable elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 25;13(2):485–500. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.2.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J., Forbes E., Anderson P. The Tc3 family of transposable genetic elements in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1989 Jan;121(1):47–55. doi: 10.1093/genetics/121.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J., Saari B., Anderson P. Activation of a transposable element in the germ line but not the soma of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1987 Aug 20;328(6132):726–728. doi: 10.1038/328726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus D. H., Emmons S. W. A transposon-related palindromic repetitive sequence from C. elegans. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19(8):1871–1877. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.8.1871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmons S. W., Klass M. R., Hirsh D. Analysis of the constancy of DNA sequences during development and evolution of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1333–1337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmons S. W., Yesner L., Ruan K. S., Katzenberg D. Evidence for a transposon in Caenorhabditis elegans. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):55–65. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90496-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Files J. G., Hirsh D. Ribosomal DNA of Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 25;149(2):223–240. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90299-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finney M., Ruvkun G., Horvitz H. R. The C. elegans cell lineage and differentiation gene unc-86 encodes a protein with a homeodomain and extended similarity to transcription factors. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):757–769. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90132-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III in DNA sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:156–165. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson A. Purification and fractionation of poly(A)+ RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:254–261. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause M., Hirsh D. A trans-spliced leader sequence on actin mRNA in C. elegans. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):753–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90613-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause M., Wild M., Rosenzweig B., Hirsh D. Wild-type and mutant actin genes in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1989 Aug 5;208(3):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90503-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt A., Emmons S. W. The Tc2 transposon in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3232–3236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W., Herman R. K., Shaw J. E. Analysis of the Caenorhabditis elegans axonal guidance and outgrowth gene unc-33. Genetics. 1992 Nov;132(3):675–689. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebermann D., Hoffman-Liebermann B., Weinthal J., Childs G., Maxson R., Mauron A., Cohen S. N., Kedes L. An unusual transposon with long terminal inverted repeats in the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):342–347. doi: 10.1038/306342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter S. S. DNA sequence of a foldback transposable element in Drosophila. Nature. 1982 May 20;297(5863):201–204. doi: 10.1038/297201a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenzweig B., Liao L. W., Hirsh D. Sequence of the C. elegans transposable element Tc1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):4201–4209. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.4201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvolo V., Hill J. E., Levitt A. The Tc2 transposon of Caenorhabditis elegans has the structure of a self-regulated element. DNA Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;11(2):111–122. doi: 10.1089/dna.1992.11.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheen J. Y., Seed B. Electrolyte gradient gels for DNA sequencing. Biotechniques. 1988 Nov-Dec;6(10):942–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templeton N. S., Potter S. S. Complete foldback transposable elements encode a novel protein found in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1887–1894. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03585.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truett M. A., Jones R. S., Potter S. S. Unusual structure of the FB family of transposable elements in Drosophila. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):753–763. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessler S. R. The maize transposable Ds1 element is alternatively spliced from exon sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6192–6196. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan J. Y., Finney M., Tsung N., Horvitz H. R. Tc4, a Caenorhabditis elegans transposable element with an unusual fold-back structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3334–3338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]