Abstract
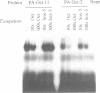
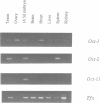
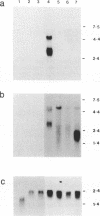
POU domain genes encode a family of highly conserved transacting factors that influence the transcriptional activity of several cell type-specific and ubiquitous genes. We have cloned and sequenced cDNAs encoding a novel mouse POU domain protein, Oct-11, that is closely related within the POU domain to the POU class II proteins, Oct-1 and Oct-2. Recombinant Oct-11 protein binds specifically to an octamer sequence in vitro. The Oct-11 gene is expressed during mouse embryogenesis and in the adult thymus and testis. In addition, it is abundant in the myeloma cell line P3/NS-1/1-Ag4.1. We describe the structure of Oct-11 and its chromosomal localization, and discuss the evidence that the POU class II gene family has evolved by duplication and divergence of a common ancestral gene.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashworth A., Skene B., Swift S., Lovell-Badge R. Zfa is an expressed retroposon derived from an alternative transcript of the Zfx gene. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1529–1534. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08271.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aurora R., Herr W. Segments of the POU domain influence one another's DNA-binding specificity. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):455–467. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltzinger M., Stiegler P., Remy P. Cloning and sequencing of POU-boxes expressed in Xenopus laevis neurula embryos. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6131–6131. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billin A. N., Cockerill K. A., Poole S. J. Isolation of a family of Drosophila POU domain genes expressed in early development. Mech Dev. 1991 Jun;34(2-3):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodner M., Castrillo J. L., Theill L. E., Deerinck T., Ellisman M., Karin M. The pituitary-specific transcription factor GHF-1 is a homeobox-containing protein. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):505–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botti A. C., Verma R. S. The molecular biology of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (review). Anticancer Res. 1990 Mar-Apr;10(2B):519–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunzow J. R., Van Tol H. H., Grandy D. K., Albert P., Salon J., Christie M., Machida C. A., Neve K. A., Civelli O. Cloning and expression of a rat D2 dopamine receptor cDNA. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):783–787. doi: 10.1038/336783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürglin T. R., Finney M., Coulson A., Ruvkun G. Caenorhabditis elegans has scores of homoeobox-containing genes. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):239–243. doi: 10.1038/341239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., LeBowitz J. H., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. The B-cell-specific Oct-2 protein contains POU box- and homeo box-type domains. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1570–1581. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. B., Unger T., Rechavi G., Canaani E., Givol D. Rearrangement of the oncogene c-mos in mouse myeloma NSI and hybridomas. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):797–799. doi: 10.1038/306797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Development and applications of a molecular genetic linkage map of the mouse genome. Trends Genet. 1991 Apr;7(4):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90455-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Silan C. M., Kingsley D. M., Jenkins N. A., Cannizzaro L. A., Croce C. M., Huebner K., Sims J. E. Chromosomal location of murine and human IL-1 receptor genes. Genomics. 1991 Jan;9(1):44–50. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan N. J., Secher D. S., Milstein C. Intracellular immunoglobulin chain synthesis in non-secreting variants of a mouse myeloma: detection of inactive light-chain messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1974 Dec 25;90(4):691–701. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90533-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny P., Swift S., Connor F., Ashworth A. An SRY-related gene expressed during spermatogenesis in the mouse encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3705–3712. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05455.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finney M., Ruvkun G., Horvitz H. R. The C. elegans cell lineage and differentiation gene unc-86 encodes a protein with a homeodomain and extended similarity to transcription factors. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):757–769. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90132-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Blanco M. A., Clerc R. G., Sharp P. A. The DNA-binding homeo domain of the Oct-2 protein. Genes Dev. 1989 Jun;3(6):739–745. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.6.739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gattoni-Celli S., Hsiao W. L., Weinstein I. B. Rearranged c-mos locus in a MOPC 21 murine myeloma cell line and its persistence in hybridomas. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):795–796. doi: 10.1038/306795a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Balmaceda C. G., Roeder R. G. The cell type-specific octamer transcription factor OTF-2 has two domains required for the activation of transcription. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1635–1643. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08283.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Roeder R. G. A herpesvirus trans-activating protein interacts with transcription factor OTF-1 and other cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6347–6351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsborough A., Ashworth A., Willison K. Cloning and sequencing of POU-boxes expressed in mouse testis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 25;18(6):1634–1634. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.6.1634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatzopoulos A. K., Stoykova A. S., Erselius J. R., Goulding M., Neuman T., Gruss P. Structure and expression of the mouse Oct2a and Oct2b, two differentially spliced products of the same gene. Development. 1990 Jun;109(2):349–362. doi: 10.1242/dev.109.2.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley R. G., Shulman M. J., Murialdo H., Gibson D. M., Hozumi N. Mutant immunoglobulin genes have repetitive DNA elements inserted into their intervening sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7425–7429. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X., Treacy M. N., Simmons D. M., Ingraham H. A., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Expression of a large family of POU-domain regulatory genes in mammalian brain development. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):35–41. doi: 10.1038/340035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Sturm R. A., Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A., Ingraham H. A., Rosenfeld M. G., Finney M., Ruvkun G. The POU domain: a large conserved region in the mammalian pit-1, oct-1, oct-2, and Caenorhabditis elegans unc-86 gene products. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1513–1516. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horibata K., Harris A. W. Mouse myelomas and lymphomas in culture. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Apr;60(1):61–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90489-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh C. L., Sturm R., Herr W., Francke U. The gene for the ubiquitous octamer-binding protein Oct-1 is on human chromosome 1, region cen-q32, and near Ly-22 and Ltw-4 on mouse chromosome 1. Genomics. 1990 Apr;6(4):666–672. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90502-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham H. A., Chen R. P., Mangalam H. J., Elsholtz H. P., Flynn S. E., Lin C. R., Simmons D. M., Swanson L., Rosenfeld M. G. A tissue-specific transcription factor containing a homeodomain specifies a pituitary phenotype. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):519–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham H. A., Flynn S. E., Voss J. W., Albert V. R., Kapiloff M. S., Wilson L., Rosenfeld M. G. The POU-specific domain of Pit-1 is essential for sequence-specific, high affinity DNA binding and DNA-dependent Pit-1-Pit-1 interactions. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1021–1033. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90067-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Organization, distribution, and stability of endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia virus DNA sequences in chromosomes of Mus musculus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):26–36. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.26-36.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. A., Hirsh J. Binding of a Drosophila POU-domain protein to a sequence element regulating gene expression in specific dopaminergic neurons. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):467–470. doi: 10.1038/343467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney J. F., Radbruch A., Liesegang B., Rajewsky K. A new mouse myeloma cell line that has lost immunoglobulin expression but permits the construction of antibody-secreting hybrid cell lines. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1548–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsley D. M., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. A molecular genetic linkage map of mouse chromosome 9 with regional localizations for the Gsta, T3g, Ets-1 and Ldlr loci. Genetics. 1989 Sep;123(1):165–172. doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko H. S., Fast P., McBride W., Staudt L. M. A human protein specific for the immunoglobulin octamer DNA motif contains a functional homeobox domain. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):135–144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koprowski H., Gerhard W., Croce C. M. Production of antibodies against influenza virus by somatic cell hybrids between mouse myeloma and primed spleen cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2985–2988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. At least six nucleotides preceding the AUG initiator codon enhance translation in mammalian cells. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):947–950. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBowitz J. H., Clerc R. G., Brenowitz M., Sharp P. A. The Oct-2 protein binds cooperatively to adjacent octamer sites. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1625–1638. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemke H., Hammerling G. J., Hohmann C., Rajewsky K. Hybrid cell lines secreting monoclonal antibody specific for major histocompatibility antigens of the mouse. Nature. 1978 Jan 19;271(5642):249–251. doi: 10.1038/271249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S., Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Rawson E. J., Simmons D. M., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Dwarf locus mutants lacking three pituitary cell types result from mutations in the POU-domain gene pit-1. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):528–533. doi: 10.1038/347528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S., Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Rawson E. J., Simmons D. M., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Dwarf locus mutants lacking three pituitary cell types result from mutations in the POU-domain gene pit-1. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):528–533. doi: 10.1038/347528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer D., Graus A., Kraay R., Langeveld A., Mulder M. P., Grosveld G. The octamer binding factor Oct6: cDNA cloning and expression in early embryonic cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7357–7365. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monuki E. S., Kuhn R., Weinmaster G., Trapp B. D., Lemke G. Expression and activity of the POU transcription factor SCIP. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1300–1303. doi: 10.1126/science.1975954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. M., Ruppert S., Schaffner W., Matthias P. A cloned octamer transcription factor stimulates transcription from lymphoid-specific promoters in non-B cells. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):544–551. doi: 10.1038/336544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadeau J. H., Kosowsky M. Mouse map of paralogous genes. Mamm Genome. 1991;1(Spec No):S433–S460. doi: 10.1007/BF00656503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B., Abrahmsén L., Uhlén M. Immobilization and purification of enzymes with staphylococcal protein A gene fusion vectors. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):1075–1080. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03741.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Okazawa H., Okuda A., Sakai M., Muramatsu M., Hamada H. A novel octamer binding transcription factor is differentially expressed in mouse embryonic cells. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):461–472. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90597-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petryniak B., Staudt L. M., Postema C. E., McCormack W. T., Thompson C. B. Characterization of chicken octamer-binding proteins demonstrates that POU domain-containing homeobox transcription factors have been highly conserved during vertebrate evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1099–1103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner M. H., Vigano M. A., Ozato K., Timmons P. M., Poirier F., Rigby P. W., Staudt L. M. A POU-domain transcription factor in early stem cells and germ cells of the mammalian embryo. Nature. 1990 Jun 21;345(6277):686–692. doi: 10.1038/345686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Cromlish J. A., Gerster T., Kawakami K., Balmaceda C. G., Currie R. A., Roeder R. G. A human lymphoid-specific transcription factor that activates immunoglobulin genes is a homoeobox protein. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):551–557. doi: 10.1038/336551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Identification of a novel lymphoid specific octamer binding protein (OTF-2B) by proteolytic clipping bandshift assay (PCBA). EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4221–4229. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Hatzopoulos A. K., Balling R., Suzuki N., Gruss P. A family of octamer-specific proteins present during mouse embryogenesis: evidence for germline-specific expression of an Oct factor. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2543–2550. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08392.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R. Octamania: the POU factors in murine development. Trends Genet. 1991 Oct;7(10):323–329. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90422-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Ruppert S., Suzuki N., Chowdhury K., Gruss P. New type of POU domain in germ line-specific protein Oct-4. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):435–439. doi: 10.1038/344435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. B., Senapathy P. RNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7155–7174. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siracusa L. D., Rosner M. H., Vigano M. A., Gilbert D. J., Staudt L. M., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Chromosomal location of the octamer transcription factors, Otf-1, Otf-2, and Otf-3, defines multiple Otf-3-related sequences dispersed in the mouse genome. Genomics. 1991 Jun;10(2):313–326. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90314-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. P., Old R. W. Nucleotide sequence of Xenopus laevis Oct-1 cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 25;18(2):369–369. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Clerc R. G., Singh H., LeBowitz J. H., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. Cloning of a lymphoid-specific cDNA encoding a protein binding the regulatory octamer DNA motif. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):577–580. doi: 10.1126/science.3399892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Tanaka M., Herr W. The Oct-1 homoeodomain directs formation of a multiprotein-DNA complex with the HSV transactivator VP16. Nature. 1989 Oct 19;341(6243):624–630. doi: 10.1038/341624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Use of bacteriophage T7 lysozyme to improve an inducible T7 expression system. J Mol Biol. 1991 May 5;219(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90855-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R. A., Das G., Herr W. The ubiquitous octamer-binding protein Oct-1 contains a POU domain with a homeo box subdomain. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1582–1599. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R. A., Herr W. The POU domain is a bipartite DNA-binding structure. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):601–604. doi: 10.1038/336601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita T., Totsuka T., Saito M., Yamasaki K., Taga T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Functional murine interleukin 6 receptor with the intracisternal A particle gene product at its cytoplasmic domain. Its possible role in plasmacytomagenesis. J Exp Med. 1990 Jun 1;171(6):2001–2009. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.6.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Rohdewohld H., Neuman T., Gruss P., Schöler H. R. Oct-6: a POU transcription factor expressed in embryonal stem cells and in the developing brain. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3723–3732. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07585.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svasti J., Milstein C. The complete amino acid sequence of a mouse kappa light chain. Biochem J. 1972 Jun;128(2):427–444. doi: 10.1042/bj1280427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Herr W. Differential transcriptional activation by Oct-1 and Oct-2: interdependent activation domains induce Oct-2 phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90589-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treacy M. N., He X., Rosenfeld M. G. I-POU: a POU-domain protein that inhibits neuron-specific gene activation. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):577–584. doi: 10.1038/350577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrijzer C. P., Kal A. J., van der Vliet P. C. The oct-1 homeo domain contacts only part of the octamer sequence and full oct-1 DNA-binding activity requires the POU-specific domain. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1964–1974. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrijzer C. P., van Oosterhout J. A., van der Vliet P. C. The Oct-1 POU domain mediates interactions between Oct-1 and other POU proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):542–551. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss J. W., Wilson L., Rosenfeld M. G. POU-domain proteins Pit-1 and Oct-1 interact to form a heteromeric complex and can cooperate to induce expression of the prolactin promoter. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1309–1320. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth T., Priess A., Annweiler A., Zwilling S., Oeler B. Multiple Oct2 isoforms are generated by alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):43–51. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]