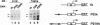Abstract
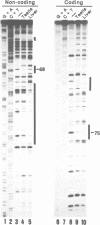
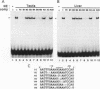
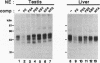
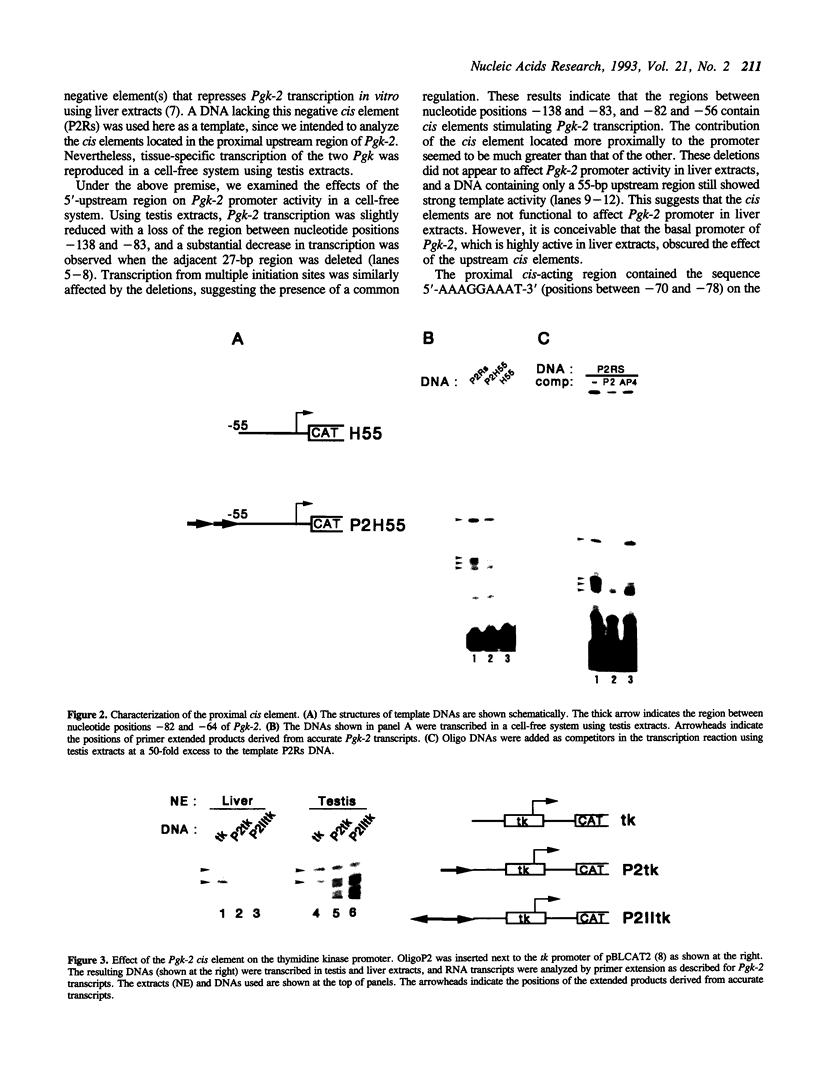
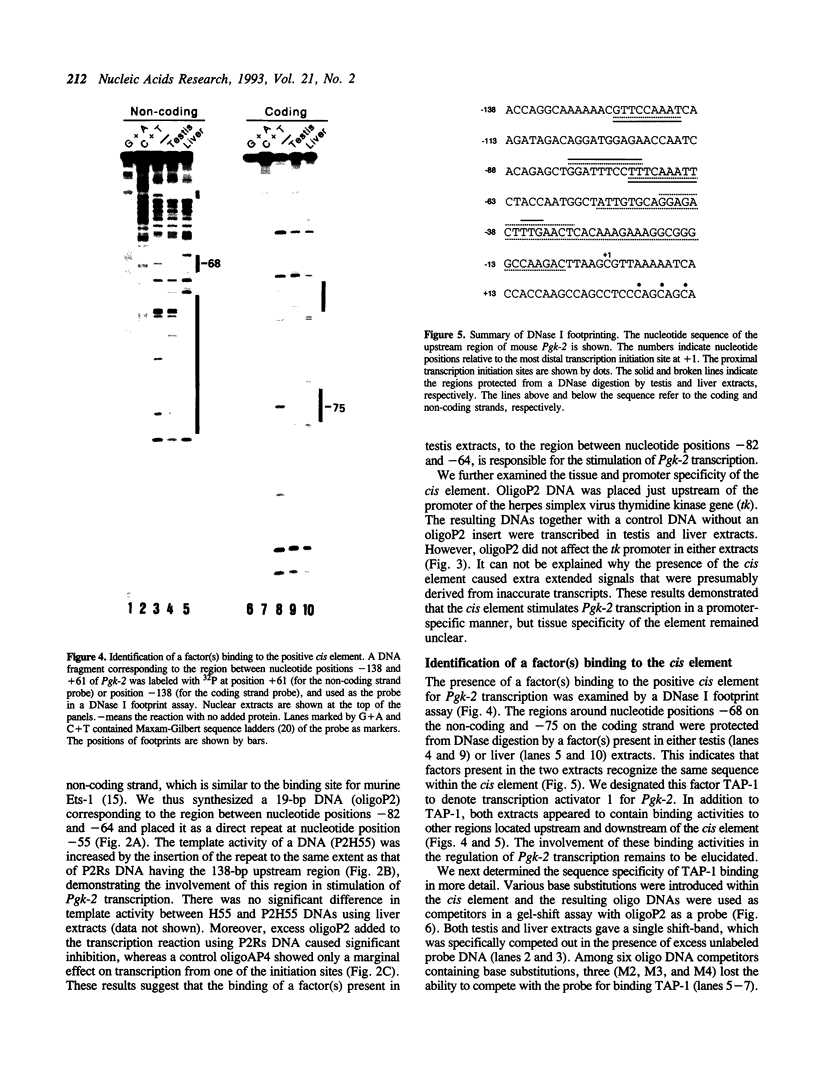
The glycolytic enzyme phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) consists of two isozymes, somatic-type PGK-1 and testis-specific PGK-2. The isozyme switch from PGK-1 to PGK-2 occurs during spermatogenesis at the mRNA level. The distal upstream region of the gene encoding mouse PGK-2 (Pgk-2) possesses a silencer-like negative cis element. In the present study, a positive cis element located in the proximal upstream region and factor(s) bound to it were analyzed in vitro. Cell-free transcription using nuclear extracts of rat organs demonstrated that the region between nucleotide positions -82 and -64, relative to the most distal transcription initiation site at +1, stimulates transcription in testis extracts. The cis element did not act on the promoter of the thymidine kinase gene, suggesting that it stimulates Pgk-2 transcription in a promoter-specific manner. The cis element bound a nuclear factor(s), which we designated TAP-1. Introducing various base substitutions within the cis element revealed that TAP-1-binding to the element requires the sequence 5'-GGAA-3', which is the binding motif for Ets oncoproteins. We previously reported that TIN-1, a transcription inhibitor of Pgk-1, binds to a sequence similar to the Ets-binding site. The addition of an oligo DNA containing the TIN-1-binding sequence of Pgk-1 prevented TAP-1 from binding to the Pgk-2 cis element, and vice versa. These results suggest that both TIN-1 and TAP-1, which are presumably involved in transcription regulation of the two Pgk genes, recognize DNA sequences related to the Ets-binding motif.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Two transcription factors, NF-kappa B and H2TF1, interact with a single regulatory sequence in the class I major histocompatibility complex promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):723–727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson R. P. Post-meiotic gene expression. Trends Genet. 1990 Aug;6(8):264–269. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90209-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebara M. M., McCarrey J. R. Protein-DNA interactions associated with the onset of testis-specific expression of the mammalian Pgk-2 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1422–1431. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto M., Koji T., Mizuno K., Tamaru M., Koikeda S., Nakane P. K., Mori N., Masamune Y., Nakanishi Y. Transcription switch of two phosphoglycerate kinase genes during spermatogenesis as determined with mouse testis sections in situ. Exp Cell Res. 1990 Feb;186(2):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(90)90306-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto M., Tamura T., Mikoshiba K., Masamune Y., Nakanishi Y. Transcription inhibition of the somatic-type phosphoglycerate kinase 1 gene in vitro by a testis-specific factor that recognizes a sequence similar to the binding site for Ets oncoproteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3959–3963. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Baltimore D. NF-kappa B: a pleiotropic mediator of inducible and tissue-specific gene control. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90833-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macleod K., Leprince D., Stehelin D. The ets gene family. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jul;17(7):251–256. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90404-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., Williams T. J., Tjian R. Enhancer binding factors AP-4 and AP-1 act in concert to activate SV40 late transcription in vitro. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):557–561. doi: 10.1038/332557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno K., Goto M., Masamune Y., Nakanishi Y. A silencer-like cis element for the testis-specific phosphoglycerate-kinase-2-encoding gene. Gene. 1992 Oct 1;119(2):293–297. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90286-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi Y., Kihara K., Mizuno K., Masamune Y., Yoshitake Y., Nishikawa K. Direct effect of basic fibroblast growth factor on gene transcription in a cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5216–5220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nye J. A., Petersen J. M., Gunther C. V., Jonsen M. D., Graves B. J. Interaction of murine ets-1 with GGA-binding sites establishes the ETS domain as a new DNA-binding motif. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):975–990. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Propst F., Rosenberg M. P., Vande Woude G. F. Proto-oncogene expression in germ cell development. Trends Genet. 1988 Jul;4(7):183–187. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaru M., Nagao Y., Taira M., Tatibana M., Masamune Y., Nakanishi Y. Selective activation of testis-specific genes in cultured rat spermatogenic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jul 30;1049(3):331–338. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90106-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]