Abstract
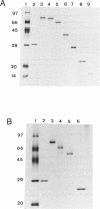
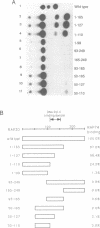
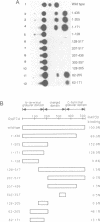
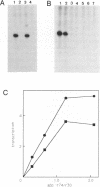
The structural and functional domains of a general transcription initiation factor, TFIIF (RAP30/74, FC), have been investigated using various deletion mutants of each subunit, both in vivo and in vitro. An in vivo assay showed that the N-terminal sequence containing residues of 1-110 of RAP30 that is located close to a sigma homology region interacts with a minimum sequence of residues 62-171 of RAP74 to form a heteromeric interaction. Reconstitution of in vitro transcription activity by deletion mutants of RAP74 clearly indicated that both N-terminal residues 73-205 and C-terminal residues 356-517 are essential for full activity, the former interacting with RAP30, thus complexing with RNA polymerase II. From these data, the functional significance of domain structure of TFIIF is discussed in terms of its sigma homology sequences and complex formation with RNA polymerase II in the initiation and elongation of transcription.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahearn J. M., Jr, Bartolomei M. S., West M. L., Cisek L. J., Corden J. L. Cloning and sequence analysis of the mouse genomic locus encoding the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10695–10705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison L. A., Moyle M., Shales M., Ingles C. J. Extensive homology among the largest subunits of eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA polymerases. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):599–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aso T., Vasavada H. A., Kawaguchi T., Germino F. J., Ganguly S., Kitajima S., Weissman S. M., Yasukochi Y. Characterization of cDNA for the large subunit of the transcription initiation factor TFIIF. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):461–464. doi: 10.1038/355461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengal E., Flores O., Krauskopf A., Reinberg D., Aloni Y. Role of the mammalian transcription factors IIF, IIS, and IIX during elongation by RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1195–1206. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggs J., Searles L. L., Greenleaf A. L. Structure of the eukaryotic transcription apparatus: features of the gene for the largest subunit of Drosophila RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):611–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90118-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Sopta M., Greenblatt J., Sharp P. A. RNA polymerase II-associated proteins are required for a DNA conformation change in the transcription initiation complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7509–7513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton Z. F., Killeen M., Sopta M., Ortolan L. G., Greenblatt J. RAP30/74: a general initiation factor that binds to RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1602–1613. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway J. W., Bond M. W., Conaway R. C. An RNA polymerase II transcription system from rat liver. Purification of an essential component. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8293–8297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway J. W., Conaway R. C. A multisubunit transcription factor essential for accurate initiation by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2357–2362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway J. W., Conaway R. C. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor shares functional properties with Escherichia coli sigma 70. Science. 1990 Jun 22;248(4962):1550–1553. doi: 10.1126/science.2193400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Egly J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Chambon P. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes between eukaryotic class B transcription factors and promoter sequences. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):680–686. doi: 10.1038/301680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein A., Kostrub C. F., Li J., Chavez D. P., Wang B. Q., Fang S. M., Greenblatt J., Burton Z. F. A cDNA encoding RAP74, a general initiation factor for transcription by RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):464–467. doi: 10.1038/355464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Ha I., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Purification and subunit composition of transcription factor IIF. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5629–5634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Lu H., Killeen M., Greenblatt J., Burton Z. F., Reinberg D. The small subunit of transcription factor IIF recruits RNA polymerase II into the preinitiation complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):9999–10003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.9999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Lu H., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Identification and characterization of factor IIH. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2786–2793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Maldonado E., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Factors IIE and IIF independently interact with RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8913–8921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ha I., Lane W. S., Reinberg D. Cloning of a human gene encoding the general transcription initiation factor IIB. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):689–695. doi: 10.1038/352689a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Elution of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate, and renaturation of enzymatic activity: results with sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase, wheat germ DNA topoisomerase, and other enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):76–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao C. C., Lieberman P. M., Schmidt M. C., Zhou Q., Pei R., Berk A. J. Cloning of a transcriptionally active human TATA binding factor. Science. 1990 Jun 29;248(4963):1646–1650. doi: 10.1126/science.2194289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen M. T., Greenblatt J. F. The general transcription factor RAP30 binds to RNA polymerase II and prevents it from binding nonspecifically to DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):30–37. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitajima S., Kawaguchi T., Yasukochi Y., Weissman S. M. Resolution and partial characterization of factors required for in vitro transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6106–6110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitajima S., Tanaka Y., Kawaguchi T., Nagaoka T., Weissman S. M., Yasukochi Y. A heteromeric transcription factor required for mammalian RNA polymerase II. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4843–4849. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koleske A. J., Buratowski S., Nonet M., Young R. A. A novel transcription factor reveals a functional link between the RNA polymerase II CTD and TFIID. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):883–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90298-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Segall J., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors required for accurate initiation of transcription by purified RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11992–11996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken S., Greenblatt J. Related RNA polymerase-binding regions in human RAP30/74 and Escherichia coli sigma 70. Science. 1991 Aug 23;253(5022):900–902. doi: 10.1126/science.1652156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mémet S., Gouy M., Marck C., Sentenac A., Buhler J. M. RPA190, the gene coding for the largest subunit of yeast RNA polymerase A. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2830–2839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma Y., Sumimoto H., Hoffmann A., Shimasaki S., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Structural motifs and potential sigma homologies in the large subunit of human general transcription factor TFIIE. Nature. 1991 Dec 5;354(6352):398–401. doi: 10.1038/354398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. G., Inostroza J., Maxon M. E., Flores O., Admon A., Reinberg D., Tjian R. Structure and functional properties of human general transcription factor IIE. Nature. 1991 Dec 5;354(6352):369–373. doi: 10.1038/354369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. G., Tanese N., Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Functional domains and upstream activation properties of cloned human TATA binding protein. Science. 1990 Jun 29;248(4963):1625–1630. doi: 10.1126/science.2363050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. H., Sluder A. E., Greenleaf A. L. Dynamic interaction between a Drosophila transcription factor and RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1465–1475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. H., Sluder A. E., Greenleaf A. L. Fractionation of transcription factors for RNA polymerase II from Drosophila Kc cell nuclear extracts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3244–3255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription in mammalian RNA polymerase II. Functional analysis of initiation factors IIA and IID and identification of a new factor operating at sequences downstream of the initiation site. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3322–3330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Purification and functional analysis of initiation factors IIB and IIE. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3310–3321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. L., Meisterernst M., Pognonec P., Roeder R. G. Cooperative interaction of an initiator-binding transcription initiation factor and the helix-loop-helix activator USF. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):245–248. doi: 10.1038/354245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ptashne M. A vector for expressing GAL4(1-147) fusions in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7539–7539. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels M., Fire A., Sharp P. A. Separation and characterization of factors mediating accurate transcription by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14419–14427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by human RNA polymerase II: analysis by a rapid and quantitative in vitro assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4394–4398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Sentenac A. RNA polymerase B (II) and general transcription factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:711–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.003431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sopta M., Burton Z. F., Greenblatt J. Structure and associated DNA-helicase activity of a general transcription initiation factor that binds to RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):410–414. doi: 10.1038/341410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sopta M., Carthew R. W., Greenblatt J. Isolation of three proteins that bind to mammalian RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10353–10360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumimoto H., Ohkuma Y., Sinn E., Kato H., Shimasaki S., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Conserved sequence motifs in the small subunit of human general transcription factor TFIIE. Nature. 1991 Dec 5;354(6352):401–404. doi: 10.1038/354401a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumimoto H., Ohkuma Y., Yamamoto T., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: identification of general transcription factor TFIIG. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9158–9162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweetser D., Nonet M., Young R. A. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic RNA polymerases have homologous core subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1192–1196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usheva A., Maldonado E., Goldring A., Lu H., Houbavi C., Reinberg D., Aloni Y. Specific interaction between the nonphosphorylated form of RNA polymerase II and the TATA-binding protein. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):871–881. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90297-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasavada H. A., Ganguly S., Germino F. J., Wang Z. X., Weissman S. M. A contingent replication assay for the detection of protein-protein interactions in animal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10686–10690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]