Abstract
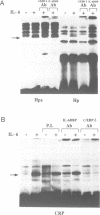
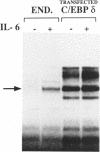
The promoter regions of three IL-6 inducible genes, hemopexin (Hpx), haptoglobin (Hp) and C-reactive protein (CRP) contain cis-acting IL-6 responsive elements (IL-6REs) which are necessary and sufficient to induce IL-6 transcription activation. Transcription factors of the C/EBP family interact with IL-6REs. Among these, IL-6DBP/NF-IL6 plays a key role in IL-6 signal transduction because its trans-activation potential is induced by IL-6 in the human hepatoma cell line Hep3B. We show here that a different C/EBP-related factor, C/EBP delta/NF-IL6 beta, is the major IL-6 induced protein interacting with IL-6REs in the nuclei of Hep3B cells. In contrast to IL-6DBP/NF-IL6, whose activity in Hep3B cells is modulated by IL-6 via a post-translational mechanism, C/EBP delta/NF-IL6 beta is transcriptionally induced by IL-6. Another contrasting feature is that the C/EBP delta cDNA transfected in Hep3B cells activates transcription from an IL-6RE synthetic promoter in a constitutive manner which is not further enhanced by IL-6. Therefore, in Hep3B cells, two distinct members of the C/EBP family are recruited in the IL-6 signal transduction pathway via different mechanisms.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Sugita T., Tanabe O., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Nakajima T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1897–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Gauldie J. Regulation of hepatic acute phase plasma protein genes by hepatocyte stimulating factors and other mediators of inflammation. Mol Biol Med. 1990 Apr;7(2):147–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Richards C., Gauldie J. Interaction among hepatocyte-stimulating factors, interleukin 1, and glucocorticoids for regulation of acute phase plasma proteins in human hepatoma (HepG2) cells. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4122–4128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Wong G. G. Hepatocyte-stimulating factor III shares structural and functional identity with leukemia-inhibitory factor. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1163–1167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Wong G. G. Hepatocyte-stimulating factor III shares structural and functional identity with leukemia-inhibitory factor. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1163–1167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasier A. R., Ron D., Tate J. E., Habener J. F. A family of constitutive C/EBP-like DNA binding proteins attenuate the IL-1 alpha induced, NF kappa B mediated trans-activation of the angiotensinogen gene acute-phase response element. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3933–3944. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasier A. R., Ron D., Tate J. E., Habener J. F. A family of constitutive C/EBP-like DNA binding proteins attenuate the IL-1 alpha induced, NF kappa B mediated trans-activation of the angiotensinogen gene acute-phase response element. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3933–3944. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Z., Umek R. M., McKnight S. L. Regulated expression of three C/EBP isoforms during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1538–1552. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlington G. J., Wilson D. R., Lachman L. B. Monocyte-conditioned medium, interleukin-1, and tumor necrosis factor stimulate the acute phase response in human hepatoma cells in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):787–793. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Chojkier M., Lichtsteiner S., Falvey E., Schibler U. LAP, a novel member of the C/EBP gene family, encodes a liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1541–1551. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauldie J., Richards C., Harnish D., Lansdorp P., Baumann H. Interferon beta 2/B-cell stimulatory factor type 2 shares identity with monocyte-derived hepatocyte-stimulating factor and regulates the major acute phase protein response in liver cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7251–7255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauldie J., Richards C., Harnish D., Lansdorp P., Baumann H. Interferon beta 2/B-cell stimulatory factor type 2 shares identity with monocyte-derived hepatocyte-stimulating factor and regulates the major acute phase protein response in liver cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7251–7255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibi M., Murakami M., Saito M., Hirano T., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Molecular cloning and expression of an IL-6 signal transducer, gp130. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1149–1157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90411-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T. Interleukin 6 (IL-6) and its receptor: their role in plasma cell neoplasias. Int J Cell Cloning. 1991 May;9(3):166–184. doi: 10.1002/stem.5530090303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isshiki H., Akira S., Sugita T., Nishio Y., Hashimoto S., Pawlowski T., Suematsu S., Kishimoto T. Reciprocal expression of NF-IL6 and C/EBP in hepatocytes: possible involvement of NF-IL6 in acute phase protein gene expression. New Biol. 1991 Jan;3(1):63–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama R., Sasai Y., Nakanishi S. Molecular characterization of transcription factors that bind to the cAMP responsive region of the substance P precursor gene. cDNA cloning of a novel C/EBP-related factor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15525–15531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita S., Akira S., Kishimoto T. A member of the C/EBP family, NF-IL6 beta, forms a heterodimer and transcriptionally synergizes with NF-IL6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1473–1476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis T. E. Microinjected antibodies against the cytoplasmic domain of vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein block its transport to the cell surface. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):931–941. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The DNA binding domain of the rat liver nuclear protein C/EBP is bipartite. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1681–1688. doi: 10.1126/science.2494700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Bindereif A., Green M. R. A small-scale procedure for preparation of nuclear extracts that support efficient transcription and pre-mRNA splicing. Gene Anal Tech. 1988 Mar-Apr;5(2):22–31. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(88)90023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The interplay of DNA-binding proteins on the promoter of the mouse albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):963–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90583-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Cabrera M., Letovsky J., Hu K. Q., Siddiqui A. Multiple liver-specific factors bind to the hepatitis B virus core/pregenomic promoter: trans-activation and repression by CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5069–5073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majello B., Arcone R., Toniatti C., Ciliberto G. Constitutive and IL-6-induced nuclear factors that interact with the human C-reactive protein promoter. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):457–465. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08131.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz R., Ziff E. cAMP stimulates the C/EBP-related transcription factor rNFIL-6 to trans-locate to the nucleus and induce c-fos transcription. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1754–1766. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrone G., Ciliberto G., Oliviero S., Arcone R., Dente L., Content J., Cortese R. Recombinant interleukin 6 regulates the transcriptional activation of a set of human acute phase genes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12554–12558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrone G., Cortese R., Sorrentino V. Post-transcriptional control of negative acute phase genes by transforming growth factor beta. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3767–3771. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08553.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima K., Wall R. Interleukin-6 signals activating junB and TIS11 gene transcription in a B-cell hybridoma. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1409–1418. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natsuka S., Isshiki H., Akira S., Kishimoto T. Augmentation of haptoglobin production in Hep3B cell line by a nuclear factor NF-IL6. FEBS Lett. 1991 Oct 7;291(1):58–62. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81103-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliviero S., Cortese R. The human haptoglobin gene promoter: interleukin-6-responsive elements interact with a DNA-binding protein induced by interleukin-6. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1145–1151. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03485.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei D. Q., Shih C. H. Transcriptional activation and repression by cellular DNA-binding protein C/EBP. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1517–1522. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1517-1522.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli V., Cortese R. Interleukin 6 induces a liver-specific nuclear protein that binds to the promoter of acute-phase genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8202–8206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli V., Mancini F. P., Cortese R. IL-6DBP, a nuclear protein involved in interleukin-6 signal transduction, defines a new family of leucine zipper proteins related to C/EBP. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):643–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90459-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards C. D., Brown T. J., Shoyab M., Baumann H., Gauldie J. Recombinant oncostatin M stimulates the production of acute phase proteins in HepG2 cells and rat primary hepatocytes in vitro. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 15;148(6):1731–1736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman C., Platero J. S., Shuman J., Calame K. Ig/EBP-1: a ubiquitously expressed immunoglobulin enhancer binding protein that is similar to C/EBP and heterodimerizes with C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1404–1415. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Habener J. F. CHOP, a novel developmentally regulated nuclear protein that dimerizes with transcription factors C/EBP and LAP and functions as a dominant-negative inhibitor of gene transcription. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):439–453. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. Interleukin-6: an overview. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:253–278. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.001345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. C., Cantwell C. A., Johnson P. F. A family of C/EBP-related proteins capable of forming covalently linked leucine zipper dimers in vitro. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1553–1567. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo P., Sipe J., Dinarello C. A., Colten H. R. Structure of a human serum amyloid A gene and modulation of its expression in transfected L cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15790–15795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki K., Taga T., Hirata Y., Yawata H., Kawanishi Y., Seed B., Taniguchi T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Cloning and expression of the human interleukin-6 (BSF-2/IFN beta 2) receptor. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):825–828. doi: 10.1126/science.3136546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]