Abstract
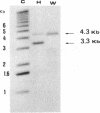
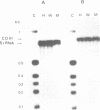
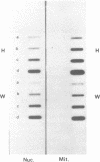
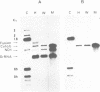
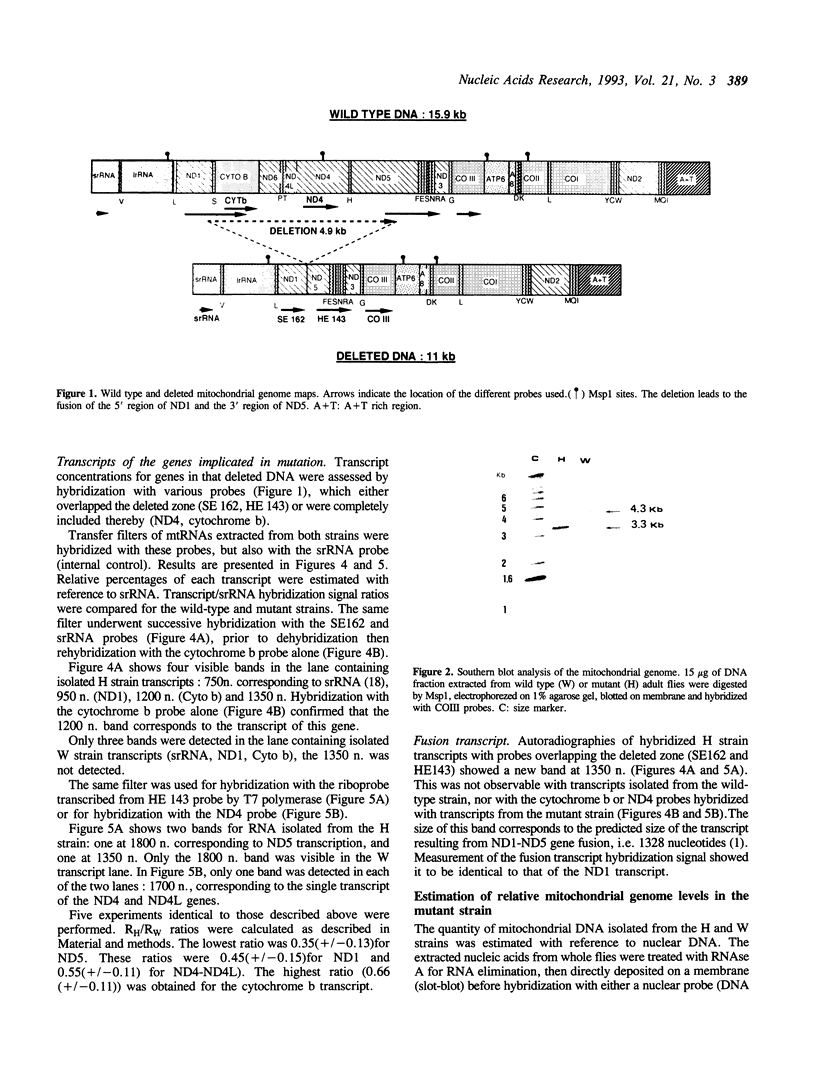
A mitochondrial mutant strain of D. subobscura has two mitochondrial genome populations (heteroplasmy): the first (20-30% of the population, 15.9 kb) is the same as could be found in the wild type; the second (70-80% of the population, 11 kb) has lost by deletion several genes coding for complex I and III subunits, and four tRNAs. In human pathology, this kind of mutation has been correlated with severe diseases such as the Kearns-Sayre syndrome, but the mutant strain, does not seem to be affected by the mutation (1). Studies reported here show that: a) Transcripts from genes not concerned by the mutation are present at the same level in both strains. b) In contrast, transcript concentrations from genes involved in the deletion are significantly decreased (30-50%) in the mutant. c) Deleted DNA was expressed as shown by the detection of the fusion transcript. d) The mtDNA/nuc.DNA ratio is 1.5 times higher in the mutant strain than in the wild type. The mutation leads to change in the transcript level equilibrium. The apparent innocuousness of the mutation may suggest some post-transcriptional compensation mechanisms. This drosophila strain is an interesting model to study the consequence of this type of mitochondrial genome deletion.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alziari S., Berthier F., Touraille S., Stepien G., Durand R. Mitochondrial DNA expression in Drosophila melanogaster: neosynthesized polypeptides in isolated mitochondria. Biochimie. 1985 Sep;67(9):1023–1034. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(85)80297-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthier F., Renaud M., Alziari S., Durand R. RNA mapping on Drosophila mitochondrial DNA: precursors and template strands. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4519–4533. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clary D. O., Wolstenholme D. R. The mitochondrial DNA molecular of Drosophila yakuba: nucleotide sequence, gene organization, and genetic code. J Mol Evol. 1985;22(3):252–271. doi: 10.1007/BF02099755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degoul F., Nelson I., Amselem S., Romero N., Obermaier-Kusser B., Ponsot G., Marsac C., Lestienne P. Different mechanisms inferred from sequences of human mitochondrial DNA deletions in ocular myopathies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 11;19(3):493–496. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.3.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMauro S., Bonilla E., Zeviani M., Nakagawa M., DeVivo D. C. Mitochondrial myopathies. Ann Neurol. 1985 Jun;17(6):521–538. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garesse R. Drosophila melanogaster mitochondrial DNA: gene organization and evolutionary considerations. Genetics. 1988 Apr;118(4):649–663. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.4.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto Y., Nonaka I., Horai S. A mutation in the tRNA(Leu)(UUR) gene associated with the MELAS subgroup of mitochondrial encephalomyopathies. Nature. 1990 Dec 13;348(6302):651–653. doi: 10.1038/348651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi J., Ohta S., Kikuchi A., Takemitsu M., Goto Y., Nonaka I. Introduction of disease-related mitochondrial DNA deletions into HeLa cells lacking mitochondrial DNA results in mitochondrial dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10614–10618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt I. J., Harding A. E., Cooper J. M., Schapira A. H., Toscano A., Clark J. B., Morgan-Hughes J. A. Mitochondrial myopathies: clinical and biochemical features of 30 patients with major deletions of muscle mitochondrial DNA. Ann Neurol. 1989 Dec;26(6):699–708. doi: 10.1002/ana.410260603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt I. J., Harding A. E., Morgan-Hughes J. A. Deletions of muscle mitochondrial DNA in patients with mitochondrial myopathies. Nature. 1988 Feb 25;331(6158):717–719. doi: 10.1038/331717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton P., Ruban A. V., Rees D., Pascal A. A., Noctor G., Young A. J. Control of the light-harvesting function of chloroplast membranes by aggregation of the LHCII chlorophyll-protein complex. FEBS Lett. 1991 Nov 4;292(1-2):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80819-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd S. J., Glover D. M. A DNA segment from D. melanogaster which contains five tandemly repeating units homologous to the major rDNA insertion. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90392-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lestienne P., Ponsot G. Kearns-Sayre syndrome with muscle mitochondrial DNA deletion. Lancet. 1988 Apr 16;1(8590):885–885. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91632-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mita S., Schmidt B., Schon E. A., DiMauro S., Bonilla E. Detection of "deleted" mitochondrial genomes in cytochrome-c oxidase-deficient muscle fibers of a patient with Kearns-Sayre syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9509–9513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakase H., Moraes C. T., Rizzuto R., Lombes A., DiMauro S., Schon E. A. Transcription and translation of deleted mitochondrial genomes in Kearns-Sayre syndrome: implications for pathogenesis. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Mar;46(3):418–427. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rötig A., Cormier V., Blanche S., Bonnefont J. P., Ledeist F., Romero N., Schmitz J., Rustin P., Fischer A., Saudubray J. M. Pearson's marrow-pancreas syndrome. A multisystem mitochondrial disorder in infancy. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1601–1608. doi: 10.1172/JCI114881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoffner J. M., Lott M. T., Lezza A. M., Seibel P., Ballinger S. W., Wallace D. C. Myoclonic epilepsy and ragged-red fiber disease (MERRF) is associated with a mitochondrial DNA tRNA(Lys) mutation. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):931–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90059-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoffner J. M., Lott M. T., Voljavec A. S., Soueidan S. A., Costigan D. A., Wallace D. C. Spontaneous Kearns-Sayre/chronic external ophthalmoplegia plus syndrome associated with a mitochondrial DNA deletion: a slip-replication model and metabolic therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7952–7956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace D. C. Mitochondrial DNA mutations and neuromuscular disease. Trends Genet. 1989 Jan;5(1):9–13. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90005-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeviani M., Moraes C. T., DiMauro S., Nakase H., Bonilla E., Schon E. A., Rowland L. P. Deletions of mitochondrial DNA in Kearns-Sayre syndrome. Neurology. 1988 Sep;38(9):1339–1346. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.9.1339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]