Abstract
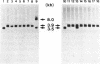
We studied the ability of single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) to participate in targeted recombination in mammalian cells. A 5' end-deleted adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (aprt) gene was subcloned into M13 vector, and the resulting ssDNA and its double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) were transfected to APRT-Chinese hamster ovary cells with a deleted aprt gene. APRT+ recombinants with the ssDNA was obtained at a frequency of 3 x 10(-7) per survivor, which was almost equal to that with the double-stranded equivalent. Analysis of the genome in recombinant clones produced by ssDNA revealed that 12 of 14 clones resulted from correction of the deletion in the aprt locus. On the other hand, the locus of the remaining 2 was not corrected; instead, the 5' deletion of the vector was corrected by end extension, followed by integration into random sites of the genome. To exclude the possibility that input ssDNA was converted into its duplex form before participating in a recombination reaction, we compared the frequency of extrachromosomal recombination between noncomplementary ssDNAs, and between one ssDNA and one dsDNA, of two phage vectors. The frequency with the ssDNAs was 0.4 x 10(-5), being 10-fold lower than that observed with the ssDNA and the dsDNA, suggesting that as little as 10% of the transfected ssDNA was converted into duplex forms before the recombination event, hence 90% remained unchanged as single-stranded molecules. Nevertheless, the above finding that ssDNA was as efficient as dsDNA in targeted recombination suggests that ssDNA itself is able to participate directly in targeted recombination reactions in mammalian cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adair G. M., Nairn R. S., Wilson J. H., Seidman M. M., Brotherman K. A., MacKinnon C., Scheerer J. B. Targeted homologous recombination at the endogenous adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus in Chinese hamster cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4574–4578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aratani Y., Okazaki R., Koyama H. End extension repair of introduced targeting vectors mediated by homologous recombination in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 25;20(18):4795–4801. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.18.4795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilang R., Peterhans A., Bogucki A., Paszkowski J. Single-stranded DNA as a recombination substrate in plants as assessed by stable and transient recombination assays. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):329–336. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollag R. J., Waldman A. S., Liskay R. M. Homologous recombination in mammalian cells. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:199–225. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. R. Altering the genome by homologous recombination. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1288–1292. doi: 10.1126/science.2660260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. M., Lehman I. R. Enzymes of general recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:229–262. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. M., Lehman I. R. recA protein of Escherichia coli promotes branch migration, a kinetically distinct phase of DNA strand exchange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3433–3437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyon C., Faugeron G. Targeted transformation of Ascobolus immersus and de novo methylation of the resulting duplicated DNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2818–2827. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillemann D., Pühler A., Wohlleben W. Gene disruption and gene replacement in Streptomyces via single stranded DNA transformation of integration vectors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):727–731. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh P., Camerini-Otero R. D. Formation of joint DNA molecules by two eukaryotic strand exchange proteins does not require melting of a DNA duplex. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5089–5097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiec E., Holloman W. K. Homologous pairing of DNA molecules promoted by a protein from Ustilago. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B. H., Smithies O. Altering genes in animals by gene targeting. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:705–730. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.003421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Model for homologous recombination during transfer of DNA into mouse L cells: role for DNA ends in the recombination process. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1020–1034. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Recombination in mouse L cells between DNA introduced into cells and homologous chromosomal sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1391–1395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meselson M. S., Radding C. M. A general model for genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):358–361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishina Y., Shimokawa T., Kawasaki K., Arai N., Shibata T., Koyama H. Identification of two types of homologous DNA pairing activity in mouse cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jun 30;185(3):987–992. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91724-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S. P., Fishel R. Purification and characterization of a protein from human cells which promotes homologous pairing of DNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11108–11117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalbantoglu J., Hartley D., Phear G., Tear G., Meuth M. Spontaneous deletion formation at the aprt locus of hamster cells: the presence of short sequence homologies and dyad symmetries at deletion termini. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1199–1204. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04347.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauth S., Song K. Y., Ayares D., Wallace L., Moore P. D., Kucherlapati R. Transfection and homologous recombination involving single-stranded DNA substrates in mammalian cells and nuclear extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5587–5591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander M., Lowenhaupt K., Rich A. Drosophila Rrp1 protein: an apurinic endonuclease with homologous recombination activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6780–6784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata T., DasGupta C., Cunningham R. P., Radding C. M. Purified Escherichia coli recA protein catalyzes homologous pairing of superhelical DNA and single-stranded fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1638–1642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. R., Moore P. D. Homologous recombination between single-stranded DNA and chromosomal genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2329–2334. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. J., Berg P. Homologous recombination between defective neo genes in mouse 3T6 cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:171–181. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song K. Y., Schwartz F., Maeda N., Smithies O., Kucherlapati R. Accurate modification of a chromosomal plasmid by homologous recombination in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6820–6824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Orr-Weaver T. L., Rothstein R. J., Stahl F. W. The double-strand-break repair model for recombination. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90331-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by gene targeting in mouse embryo-derived stem cells. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90646-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss U., Wilson J. H. Repair of single-stranded loops in heteroduplex DNA transfected into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1619–1623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer A. Manipulating the genome by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1992;15:115–137. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.15.030192.000555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]