Abstract
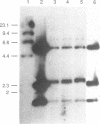
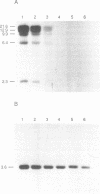
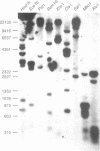
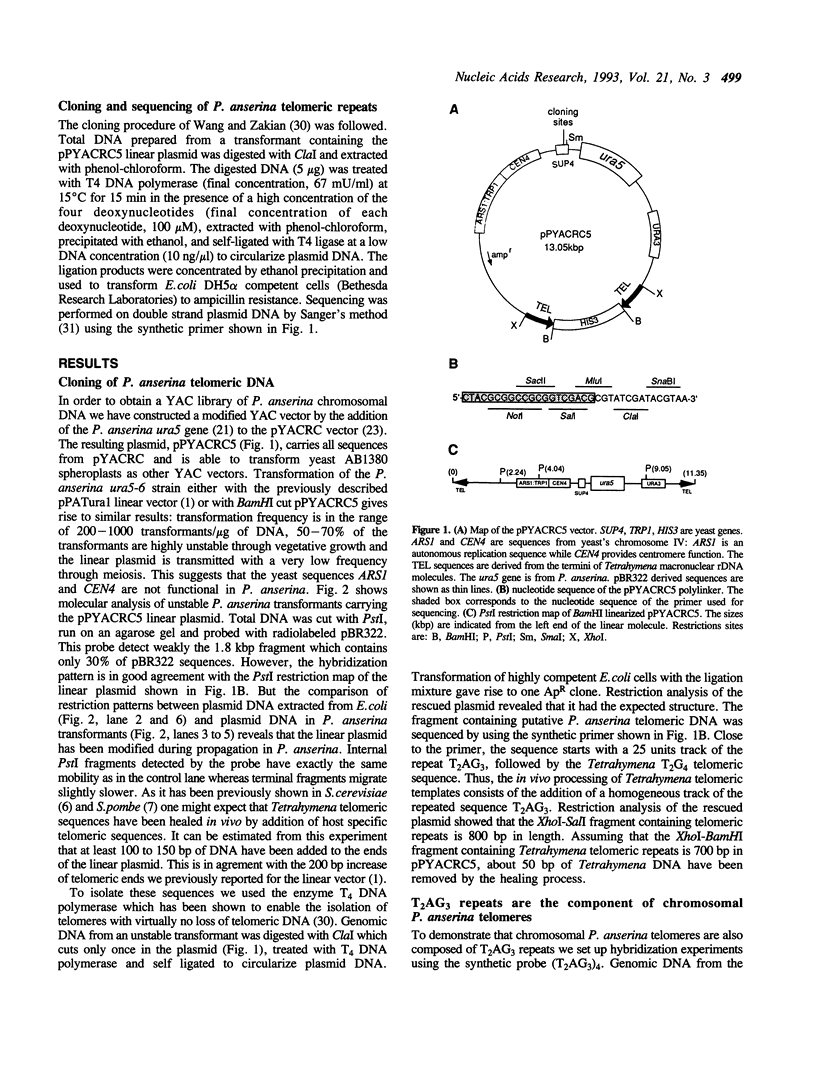
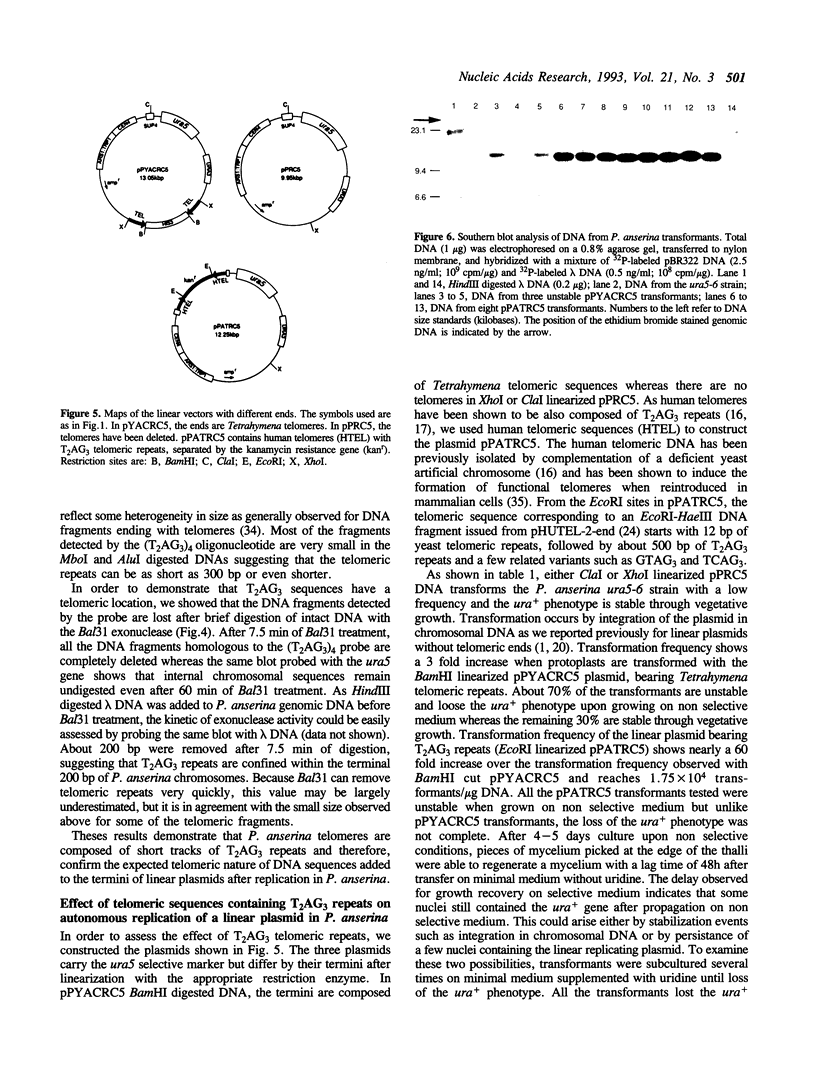
It has been previously shown that linear plasmids bearing Tetrahymena telomeric sequences are able to replicate autonomously in the filamentous fungus Podospora anserina (1). However, autonomous replication occurs in only 50-70% of the transformants, suggesting a defect in the recognition of the Tetrahymena telomeric template by the putative P. anserina telomerase so that only a fraction of entering DNA is stabilized into linear extrachromosomal molecules. We have cloned DNA sequences added to the Tetrahymena (T2G4)n ends of the linear plasmid. Nucleotide sequencing showed that these sequences are exclusively composed of T2AG3 repeat units. Hybridization experiments of Bal31 treated DNA showed that T2AG3 repeats are confined within 200 bp in chromosomal P. anserina telomeres. A new plasmid has been constructed so that after linearization, the terminal sequences contain T2AG3 repeats. This linear molecule transforms P. anserina with a high frequency (up to 1.75 x 10(4) transformants/micrograms), autonomous replication occurs in 100% of the transformants and the plasmid copy number is about 2-3 per nucleus. These results underscore the importance of the telomeric repeat nucleotide sequence for efficient recognition as functional telomeric DNA in vivo and provide the first step toward the development of an artificial chromosome cloning system for filamentous fungi.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergès T., Barreau C. Heat shock at an elevated temperature improves transformation efficiency of protoplasts from Podospora anserina. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Mar;135(3):601–604. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-3-601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H., Gall J. G. A tandemly repeated sequence at the termini of the extrachromosomal ribosomal RNA genes in Tetrahymena. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):33–53. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90294-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. Structure and function of telomeres. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):569–573. doi: 10.1038/350569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. The molecular structure of centromeres and telomeres. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:163–194. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R. Molecular cloning of human telomeres in yeast. Nature. 1989 Apr 27;338(6218):774–776. doi: 10.1038/338774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. T., Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):806–812. doi: 10.1126/science.3033825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bégueret J., Razanamparany V., Perrot M., Barreau C. Cloning gene ura5 for the orotidylic acid pyrophosphorylase of the filamentous fungus Podospora anserina: transformation of protoplasts. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):487–492. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad M. N., Wright J. H., Wolf A. J., Zakian V. A. RAP1 protein interacts with yeast telomeres in vivo: overproduction alters telomere structure and decreases chromosome stability. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):739–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90140-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross S. H., Allshire R. C., McKay S. J., McGill N. I., Cooke H. J. Cloning of human telomeres by complementation in yeast. Nature. 1989 Apr 27;338(6218):771–774. doi: 10.1038/338771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross S., Lindsey J., Fantes J., McKay S., McGill N., Cooke H. The structure of a subterminal repeated sequence present on many human chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6649–6657. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuBridge R. B., Tang P., Hsia H. C., Leong P. M., Miller J. H., Calos M. P. Analysis of mutation in human cells by using an Epstein-Barr virus shuttle system. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):379–387. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery H. S., Weiner A. M. An irregular satellite sequence is found at the termini of the linear extrachromosomal rDNA in Dictyostelium discoideum. Cell. 1981 Nov;26(3 Pt 1):411–419. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90210-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr C., Fantes J., Goodfellow P., Cooke H. Functional reintroduction of human telomeres into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7006–7010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. A telomeric sequence in the RNA of Tetrahymena telomerase required for telomere repeat synthesis. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):331–337. doi: 10.1038/337331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. Identification of a specific telomere terminal transferase activity in Tetrahymena extracts. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. The telomere terminal transferase of Tetrahymena is a ribonucleoprotein enzyme with two kinds of primer specificity. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90576-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahnenberger K. M., Baum M. P., Polizzi C. M., Carbon J., Clarke L. Construction of functional artificial minichromosomes in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):577–581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz H., Haber J. E. Identification of autonomously replicating circular subtelomeric Y' elements in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2369–2380. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss G. B., Amin A. A., Pearlman R. E. Two separate regions of the extrachromosomal ribosomal deoxyribonucleic acid of Tetrahymena thermophila enable autonomous replication of plasmids in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;1(6):535–543. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.6.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klobutcher L. A., Swanton M. T., Donini P., Prescott D. M. All gene-sized DNA molecules in four species of hypotrichs have the same terminal sequence and an unusual 3' terminus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3015–3019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig A. J., Kurtz S., Shore D. Involvement of the silencer and UAS binding protein RAP1 in regulation of telomere length. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):549–553. doi: 10.1126/science.2237406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchuk D., Collins F. S. pYAC-RC, a yeast artificial chromosome vector for cloning DNA cut with infrequently cutting restriction endonucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7743–7743. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin G. B. The human telomere terminal transferase enzyme is a ribonucleoprotein that synthesizes TTAGGG repeats. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):521–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Szostak J. W. Construction of artificial chromosomes in yeast. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):189–193. doi: 10.1038/305189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka A., Sugisaki H., Takanami M. Nucleotide sequence of the kanamycin resistance transposon Tn903. J Mol Biol. 1981 Apr 5;147(2):217–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90438-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrot M., Barreau C., Bégueret J. Nonintegrative transformation in the filamentous fungus Podospora anserina: stabilization of a linear vector by the chromosomal ends of Tetrahymena thermophila. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1725–1730. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluta A. F., Dani G. M., Spear B. B., Zakian V. A. Elaboration of telomeres in yeast: recognition and modification of termini from Oxytricha macronuclear DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1475–1479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell W. A., Kistler H. C. In vivo rearrangement of foreign DNA by Fusarium oxysporum produces linear self-replicating plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3163–3171. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3163-3171.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. M., Cech T. R. Properties of the telomeric DNA-binding protein from Oxytricha nova. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 24;28(2):769–774. doi: 10.1021/bi00428a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. M. Telomere structure in Euplotes crassus: characterization of DNA-protein interactions and isolation of a telomere-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3421–3431. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razanamparany V., Bégueret J. Positive screening and transformation of ura5 mutants in the fungus Podospora anserina: characterization of the transformants. Curr Genet. 1986;10(11):811–817. doi: 10.1007/BF00418527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shampay J., Szostak J. W., Blackburn E. H. DNA sequences of telomeres maintained in yeast. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):154–157. doi: 10.1038/310154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shippen-Lentz D., Blackburn E. H. Functional evidence for an RNA template in telomerase. Science. 1990 Feb 2;247(4942):546–552. doi: 10.1126/science.1689074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Blackburn E. H. Cloning yeast telomeres on linear plasmid vectors. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90109-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turcq B., Bégueret J. The ura5 gene of the filamentous fungus Podospora anserina: nucleotide sequence and expression in transformed strains. Gene. 1987;53(2-3):201–209. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. S., Zakian V. A. Sequencing of Saccharomyces telomeres cloned using T4 DNA polymerase reveals two domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4415–4419. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lange T. Human telomeres are attached to the nuclear matrix. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):717–724. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05104.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]