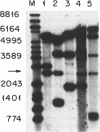
Abstract
Autonomously replicating sequence (ARS) elements function as plasmid replication origins. Our studies of the H4 ARS and ARS307 have established the requirement for a DNA unwinding element (DUE), a broad easily-unwound sequence 3' to the essential consensus that likely facilitates opening of the origin. In this report, we examine the intrinsic ease of unwinding a variety of ARS elements using (1) a single-strand-specific nuclease to probe for DNA unwinding in a negatively-supercoiled plasmid, and (2) a computer program that calculates DNA helical stability from the nucleotide sequence. ARS elements that are associated with replication origins on chromosome III are nuclease hypersensitive, and the helical stability minima correctly predict the location and hierarchy of the hypersensitive sites. All well-studied ARS elements in which the essential consensus sequence has been identified by mutational analysis contain a 100-bp region of low helical stability immediately 3' to the consensus, as do ARS elements created by mutation within the prokaryotic M13 vector. The level of helical stability is, in all cases, below that of ARS307 derivatives inactivated by mutations in the DUE. Our findings indicate that the ease of DNA unwinding at the broad region directly 3' to the ARS consensus is a conserved property of yeast replication origins.
Full text
PDF

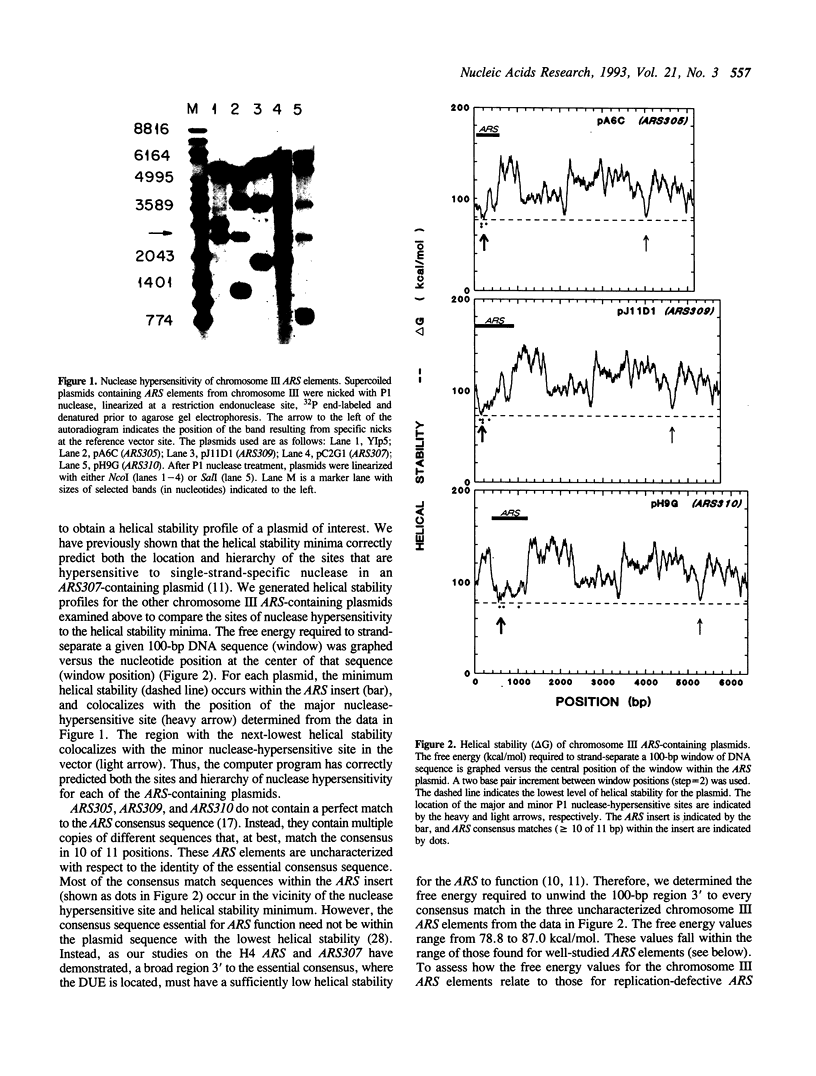
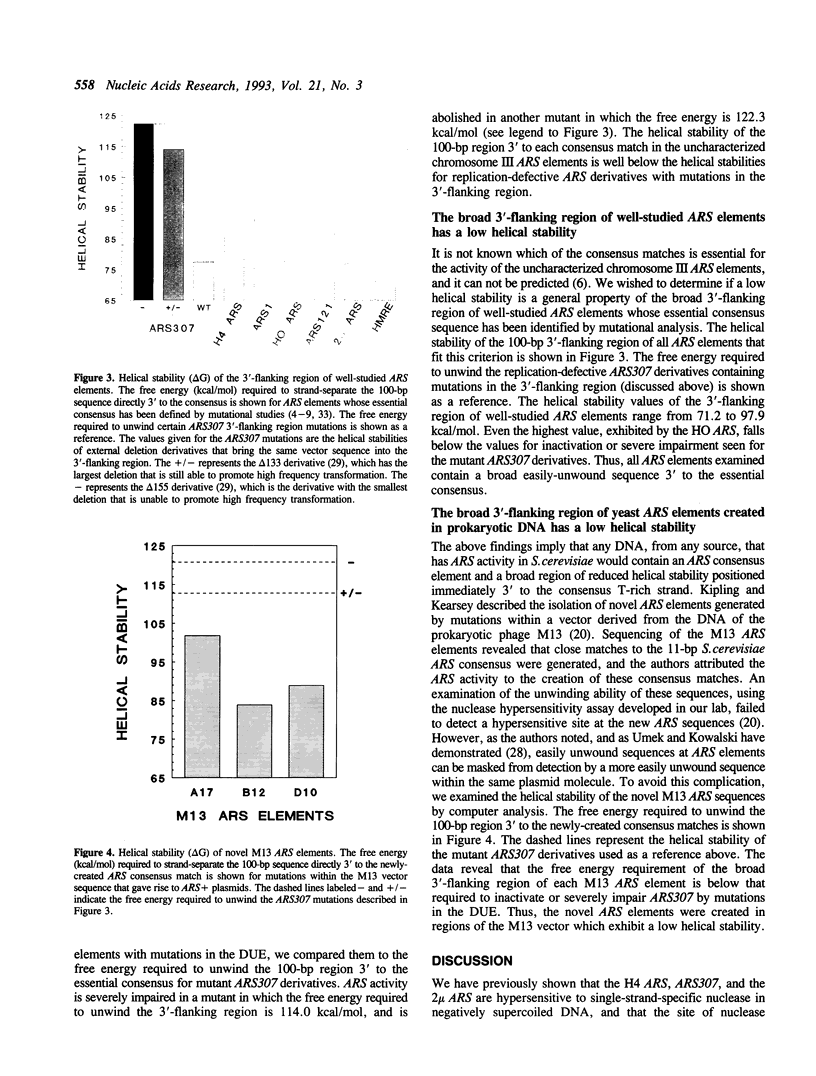


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bouton A. H., Smith M. M. Fine-structure analysis of the DNA sequence requirements for autonomous replication of Saccharomyces cerevisiae plasmids. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2354–2363. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramhill D., Kornberg A. Duplex opening by dnaA protein at novel sequences in initiation of replication at the origin of the E. coli chromosome. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):743–755. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90412-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand A. H., Micklem G., Nasmyth K. A yeast silencer contains sequences that can promote autonomous plasmid replication and transcriptional activation. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):709–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslauer K. J., Frank R., Blöcker H., Marky L. A. Predicting DNA duplex stability from the base sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3746–3750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J., Fangman W. L. The localization of replication origins on ARS plasmids in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):463–471. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90642-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broach J. R., Li Y. Y., Feldman J., Jayaram M., Abraham J., Nasmyth K. A., Hicks J. B. Localization and sequence analysis of yeast origins of DNA replication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):1165–1173. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Kimmerly W. J., Rine J., Kornberg R. D. Two DNA-binding factors recognize specific sequences at silencers, upstream activating sequences, autonomously replicating sequences, and telomeres in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):210–225. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francesconi S. C., Eisenberg S. Purification and characterization of OBF1: a Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein that binds to autonomously replicating sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2906–2913. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfeder S. A., Newlon C. S. A replication map of a 61-kb circular derivative of Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome III. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Sep;3(9):999–1013. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.9.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Spotila L. D., Nawotka K. A., el-Assouli S. M., Davis L. R. The in vivo replication origin of the yeast 2 microns plasmid. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):473–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90643-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Zhu J. G., Davis L. R., Newlon C. S. Close association of a DNA replication origin and an ARS element on chromosome III of the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14A):6373–6384. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearsey S. Structural requirements for the function of a yeast chromosomal replicator. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90326-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kipling D., Kearsey S. E. Reversion of autonomously replicating sequence mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: creation of a eucaryotic replication origin within procaryotic vector DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):265–272. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski D. Changes in site specificity of single-strand-specific endonucleases on supercoiled PM2 DNA with temperature and ionic environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7071–7086. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski D., Eddy M. J. The DNA unwinding element: a novel, cis-acting component that facilitates opening of the Escherichia coli replication origin. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4335–4344. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08620.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski D., Natale D. A., Eddy M. J. Stable DNA unwinding, not "breathing," accounts for single-strand-specific nuclease hypersensitivity of specific A+T-rich sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9464–9468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski D., Sanford J. P. Action of mung bean nuclease on supercoiled PM2 DNA. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7820–7825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marahrens Y., Stillman B. A yeast chromosomal origin of DNA replication defined by multiple functional elements. Science. 1992 Feb 14;255(5046):817–823. doi: 10.1126/science.1536007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natale D. A., Schubert A. E., Kowalski D. DNA helical stability accounts for mutational defects in a yeast replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2654–2658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newlon C. S. Yeast chromosome replication and segregation. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Dec;52(4):568–601. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.4.568-601.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palzkill T. G., Newlon C. S. A yeast replication origin consists of multiple copies of a small conserved sequence. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):441–450. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90164-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palzkill T. G., Oliver S. G., Newlon C. S. DNA sequence analysis of ARS elements from chromosome III of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: identification of a new conserved sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6247–6264. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radloff R., Bauer W., Vinograd J. A dye-buoyant-density method for the detection and isolation of closed circular duplex DNA: the closed circular DNA in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1514–1521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umek R. M., Kowalski D. The DNA unwinding element in a yeast replication origin functions independently of easily unwound sequences present elsewhere on a plasmid. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6601–6605. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umek R. M., Kowalski D. The ease of DNA unwinding as a determinant of initiation at yeast replication origins. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):559–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90469-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umek R. M., Kowalski D. Thermal energy suppresses mutational defects in DNA unwinding at a yeast replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2486–2490. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umek R. M., Kowalski D. Yeast regulatory sequences preferentially adopt a non-B conformation in supercoiled DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4467–4480. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Houten J. V., Newlon C. S. Mutational analysis of the consensus sequence of a replication origin from yeast chromosome III. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3917–3925. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S. S., Francesconi S. C., Eisenberg S. A DNA replication enhancer in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4665–4669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]