Abstract
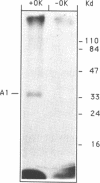
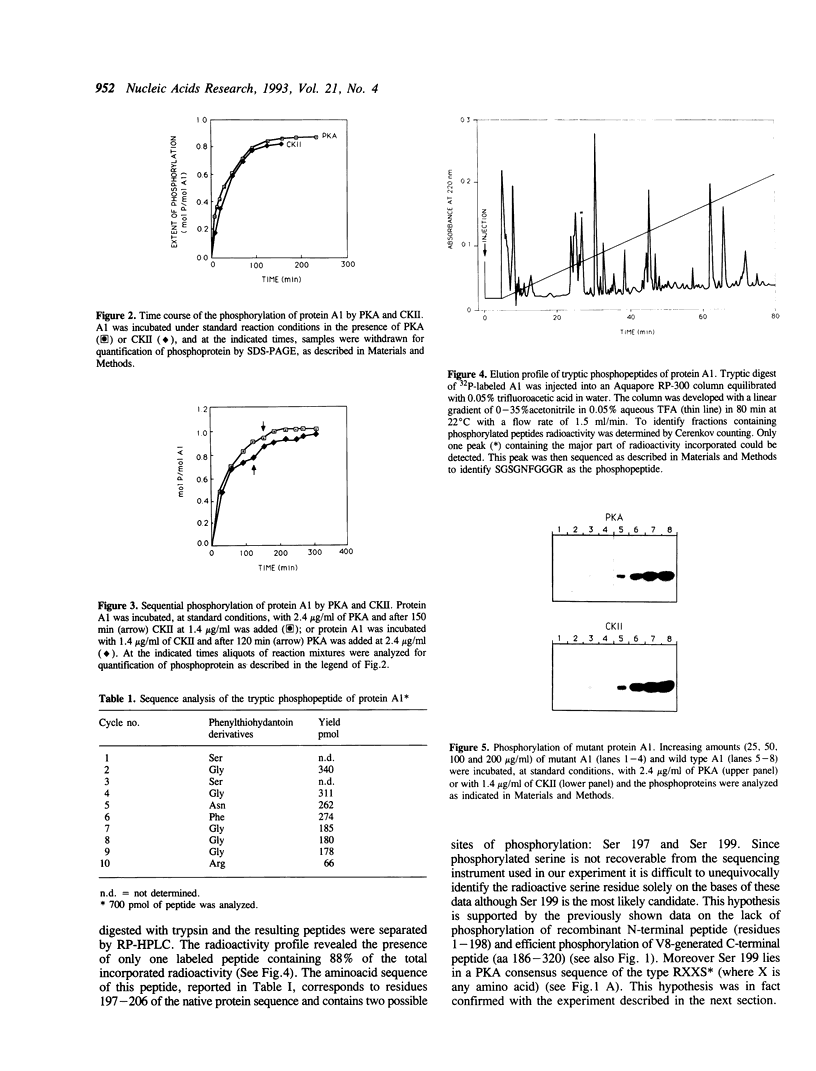
In HeLa cells metabolically labeled in vivo with [32P] orthophosphate in the presence of okadaic acid the concentration of phosphorylated A1 protein was increased significantly as compared to controls. Purified recombinant hnRNP protein A1 served as an excellent substrate in vitro for the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) and for casein kinase II (CKII). Thin layer electrophoresis of A1 acid hydrolysates showed the protein to be phosphorylated exclusively on serine residue by both kinases. V8 phosphopeptide maps revealed that the target site(s) of in vitro phosphorylation are located in the C-terminal region of A1. Phosphoamino acid sequence analysis and site directed mutagenesis identified Ser 199 as the sole phosphoamino acid in the protein phosphorylated by PKA. Phosphorylation introduced by PKA resulted in the suppression of the ability of protein A1 to promote strand annealing in vitro, without any detectable effect on its nucleic acid binding capacity. This finding indicates that phosphorylation of a single serine residue in the C-terminal domain may significantly alter the properties of protein A1.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso A., Fischer J., König N., Kinzel V. Structural analysis of hnRNP particles approached by in vitro phosphorylation using exogenous protein kinase and l gamma 32 P1 ATP. Eur J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;26(1):208–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandziulis R. J., Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. RNA-binding proteins as developmental regulators. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):431–437. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M., Piñol-Roma S., Staknis D., Dreyfuss G., Reed R. Differential binding of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins to mRNA precursors prior to spliceosome assembly in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3165–3175. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothwell A. L., Ballard D. W., Philbrick W. M., Lindwall G., Maher S. E., Bridgett M. M., Jamison S. F., Garcia-Blanco M. A. Murine polypyrimidine tract binding protein. Purification, cloning, and mapping of the RNA binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24657–24663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buvoli M., Cobianchi F., Biamonti G., Riva S. Recombinant hnRNP protein A1 and its N-terminal domain show preferential affinity for oligodeoxynucleotides homologous to intron/exon acceptor sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6595–6600. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buvoli M., Cobianchi F., Riva S. Interaction of hnRNP A1 with snRNPs and pre-mRNAs: evidence for a possible role of A1 RNA annealing activity in the first steps of spliceosome assembly. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 11;20(19):5017–5025. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.19.5017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobianchi F., Karpel R. L., Williams K. R., Notario V., Wilson S. H. Mammalian heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein complex protein A1. Large-scale overproduction in Escherichia coli and cooperative binding to single-stranded nucleic acids. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):1063–1071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobianchi F., SenGupta D. N., Zmudzka B. Z., Wilson S. H. Structure of rodent helix-destabilizing protein revealed by cDNA cloning. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3536–3543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Holmes C. F., Tsukitani Y. Okadaic acid: a new probe for the study of cellular regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):98–102. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90192-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Swanson M. S., Piñol-Roma S. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles and the pathway of mRNA formation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Mar;13(3):86–91. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho S. N., Hunt H. D., Horton R. M., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):51–59. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90358-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B. Protein kinase recognition sequence motifs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Sep;15(9):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90073-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiledjian M., Dreyfuss G. Primary structure and binding activity of the hnRNP U protein: binding RNA through RGG box. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2655–2664. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05331.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Casas-Finet J. R., Luneau C. J., Karpel R. L., Merrill B. M., Williams K. R., Wilson S. H. Mammalian heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1. Nucleic acid binding properties of the COOH-terminal domain. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17094–17100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Wilson S. H. Studies of the strand-annealing activity of mammalian hnRNP complex protein A1. Biochemistry. 1990 Dec 4;29(48):10717–10722. doi: 10.1021/bi00500a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leser G. P., Martin T. E. Changes in heterogeneous nuclear RNP core polypeptide complements during the cell cycle. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):2083–2094. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.2083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeda A., Krainer A. R. Regulation of alternative pre-mRNA splicing by hnRNP A1 and splicing factor SF2. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90477-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrand S. H., Pederson T. Crosslinking of hnRNP proteins to pre-mRNA requires U1 and U2 snRNPs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3307–3318. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermoud J. E., Cohen P., Lamond A. I. Ser/Thr-specific protein phosphatases are required for both catalytic steps of pre-mRNA splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 25;20(20):5263–5269. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.20.5263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill B. M., LoPresti M. B., Stone K. L., Williams K. R. High pressure liquid chromatography purification of UP1 and UP2, two related single-stranded nucleic acid-binding proteins from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):878–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill B. M., Stone K. L., Cobianchi F., Wilson S. H., Williams K. R. Phenylalanines that are conserved among several RNA-binding proteins form part of a nucleic acid-binding pocket in the A1 heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3307–3313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munroe S. H., Dong X. F. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 catalyzes RNA.RNA annealing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):895–899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton J. G., Mayer S. A., Tempst P., Nadal-Ginard B. Characterization and molecular cloning of polypyrimidine tract-binding protein: a component of a complex necessary for pre-mRNA splicing. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1237–1251. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piñol-Roma S., Dreyfuss G. Transcription-dependent and transcription-independent nuclear transport of hnRNP proteins. Science. 1991 Jul 19;253(5017):312–314. doi: 10.1126/science.1857966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontius B. W., Berg P. Renaturation of complementary DNA strands mediated by purified mammalian heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 protein: implications for a mechanism for rapid molecular assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8403–8407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riva S., Morandi C., Tsoulfas P., Pandolfo M., Biamonti G., Merrill B., Williams K. R., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Werr H. Mammalian single-stranded DNA binding protein UP I is derived from the hnRNP core protein A1. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2267–2273. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04494.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. RNA binding specificity of hnRNP proteins: a subset bind to the 3' end of introns. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3519–3529. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03228.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson R. P., Williams C. H., Jr, Massey V., Ronchi S., Minchiotti L., Galliano M., Curti B. The primary structure of D-amino acid oxidase from pig kidney. I. Isolation and sequence of the tryptic peptides. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8817–8823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilk H. E., Werr H., Friedrich D., Kiltz H. H., Schäfer K. P. The core proteins of 35S hnRNP complexes. Characterization of nine different species. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jan 2;146(1):71–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08621.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks A. F., Knowler J. T. The phosphorylation of the proteins of rat liver heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein particles by an endogenous kinase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jan 29;652(1):228–233. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90226-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. R., Stone K. L., LoPresti M. B., Merrill B. M., Planck S. R. Amino acid sequence of the UP1 calf thymus helix-destabilizing protein and its homology to an analogous protein from mouse myeloma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5666–5670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woppmann A., Patschinsky T., Bringmann P., Godt F., Lührmann R. Characterisation of human and murine snRNP proteins by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and phosphopeptide analysis of U1-specific 70K protein variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4427–4438. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.15.4427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]