Abstract
The repetitive sequence (AGGGCCCTAGAGGGGCCC-TAG)n was previously shown to be curved by gel mobility assays. Here we show, using hydroxy radical/DNase I digestion and differential helical phasing experiments that the curvature is directed towards the major groove and is located in the GGGCCC, but not the CTAGAG segments. The effect of the GC step in the context of the GGGCCC motif is apparently about as large as that of AA/TT, i.e. enough to cancel the macroscopic curvature of helically phased A-tracts. These data are in agreement with positive roll-like curvature of the GCC/GGC motif, predicted from nucleosome packing data and the 3D structure of the GGGGCCCC octamer, but they are not in agreement with the dinucleotide-based roll angle values predicted for AG/CT, TA, GG/CC and GC steps. Our results thus indicate the importance of interactions beyond the dinucleotide steps in predictive models of DNA curvature.
Full text
PDF

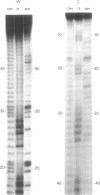
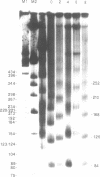
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolshoy A., McNamara P., Harrington R. E., Trifonov E. N. Curved DNA without A-A: experimental estimation of all 16 DNA wedge angles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2312–2316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenowitz M., Senear D. F., Shea M. A., Ackers G. K. "Footprint" titrations yield valid thermodynamic isotherms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8462–8466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brukner I., Jurukovski V., Konstantinović M., Savić A. Curved DNA without AA/TT dinucleotide step. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3549–3551. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brukner I., Jurukovski V., Savic A. Sequence-dependent structural variations of DNA revealed by DNase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):891–894. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhoff A. M., Tullius T. D. Structural details of an adenine tract that does not cause DNA to bend. Nature. 1988 Feb 4;331(6155):455–457. doi: 10.1038/331455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhoff A. M., Tullius T. D. The unusual conformation adopted by the adenine tracts in kinetoplast DNA. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):935–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90702-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calladine C. R., Drew H. R., McCall M. J. The intrinsic curvature of DNA in solution. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 5;201(1):127–137. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90444-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calladine C. R., Drew H. R. Principles of sequence-dependent flexure of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 20;192(4):907–918. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrera P., Martínez-Balbás M. A., Portugal J., Azorín F. Identification of sequence elements contributing to the intrinsic curvature of the mouse satellite DNA repeat. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5639–5644. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Santis P., Palleschi A., Savino M., Scipioni A. Validity of the nearest-neighbor approximation in the evaluation of the electrophoretic manifestations of DNA curvature. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 2;29(39):9269–9273. doi: 10.1021/bi00491a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann S., Mazzarelli J. M., McLaughlin L. W., von Kitzing E., Travers A. A. DNA curvature does not require bifurcated hydrogen bonds or pyrimidine methyl groups. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jun 5;225(3):729–738. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90397-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. DNA bending and its relation to nucleosome positioning. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 20;186(4):773–790. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90396-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. DNA structural variations in the E. coli tyrT promoter. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fratini A. V., Kopka M. L., Drew H. R., Dickerson R. E. Reversible bending and helix geometry in a B-DNA dodecamer: CGCGAATTBrCGCG. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14686–14707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman P. J. Straightening out the bends in curved DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jun 15;1131(2):125–132. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann U., Alings C., Bansal M. Double helix conformation, groove dimensions and ligand binding potential of a G/C stretch in B-DNA. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1931–1939. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05246.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Crothers D. M. Calibration of DNA curvature and a unified description of sequence-directed bending. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1763–1767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. DNA bending at adenine . thymine tracts. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):501–506. doi: 10.1038/320501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahm A., Suck D. DNase I-induced DNA conformation. 2 A structure of a DNase I-octamer complex. J Mol Biol. 1991 Dec 5;222(3):645–667. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90502-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall M., Brown T., Kennard O. The crystal structure of d(G-G-G-G-C-C-C-C). A model for poly(dG).poly(dC). J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 5;183(3):385–396. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara P. T., Harrington R. E. Characterization of inherent curvature in DNA lacking polyadenine runs. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12548–12554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson H. C., Finch J. T., Luisi B. F., Klug A. The structure of an oligo(dA).oligo(dT) tract and its biological implications. Nature. 1987 Nov 19;330(6145):221–226. doi: 10.1038/330221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satchwell S. C., Drew H. R., Travers A. A. Sequence periodicities in chicken nucleosome core DNA. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 20;191(4):659–675. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90452-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shliakhtenko L. S., Liubchenko Iu L., Chernov B. K., Zhurkin V. B. Vliianie temperatury i ionnoi sily na élektroforeticheskuiu podvizhnost' sinteticheskikh fragmentov DNK. Mol Biol (Mosk) 1990 Jan-Feb;24(1):79–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suck D., Lahm A., Oefner C. Structure refined to 2A of a nicked DNA octanucleotide complex with DNase I. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):464–468. doi: 10.1038/332464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhurkin V. B., Ulyanov N. B., Gorin A. A., Jernigan R. L. Static and statistical bending of DNA evaluated by Monte Carlo simulations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7046–7050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkel S. S., Crothers D. M. DNA bend direction by phase sensitive detection. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):178–181. doi: 10.1038/328178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]