Abstract
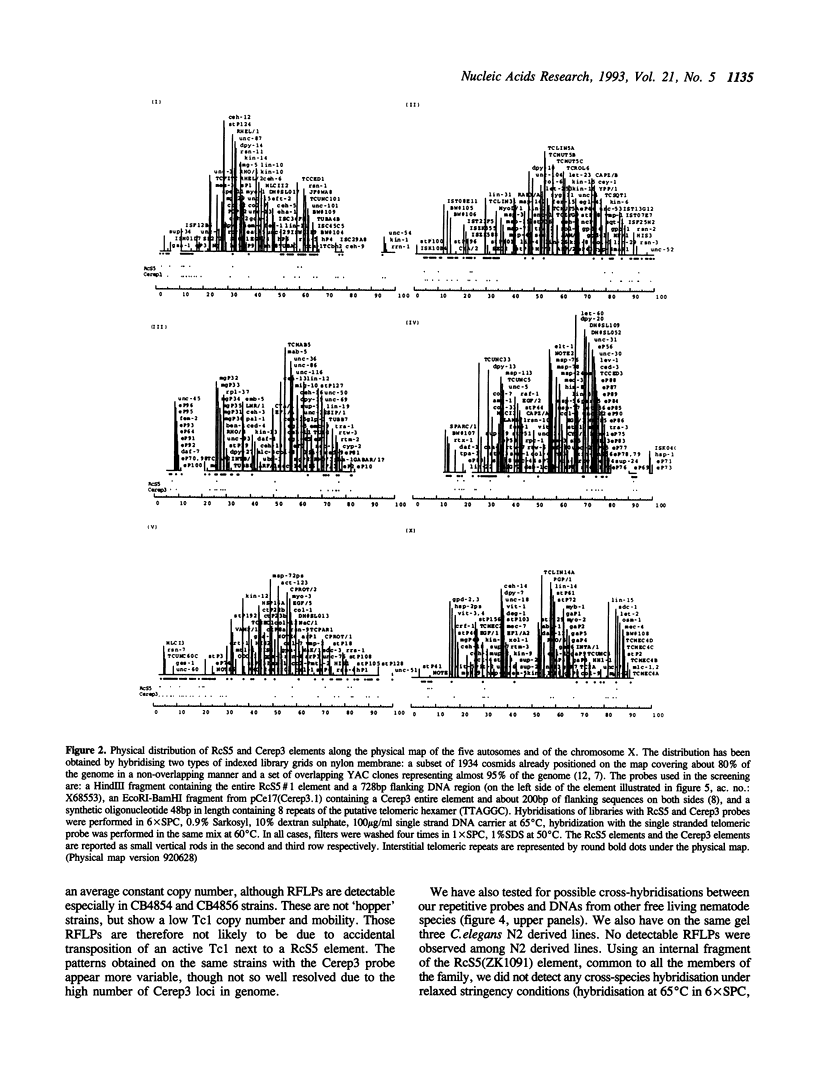
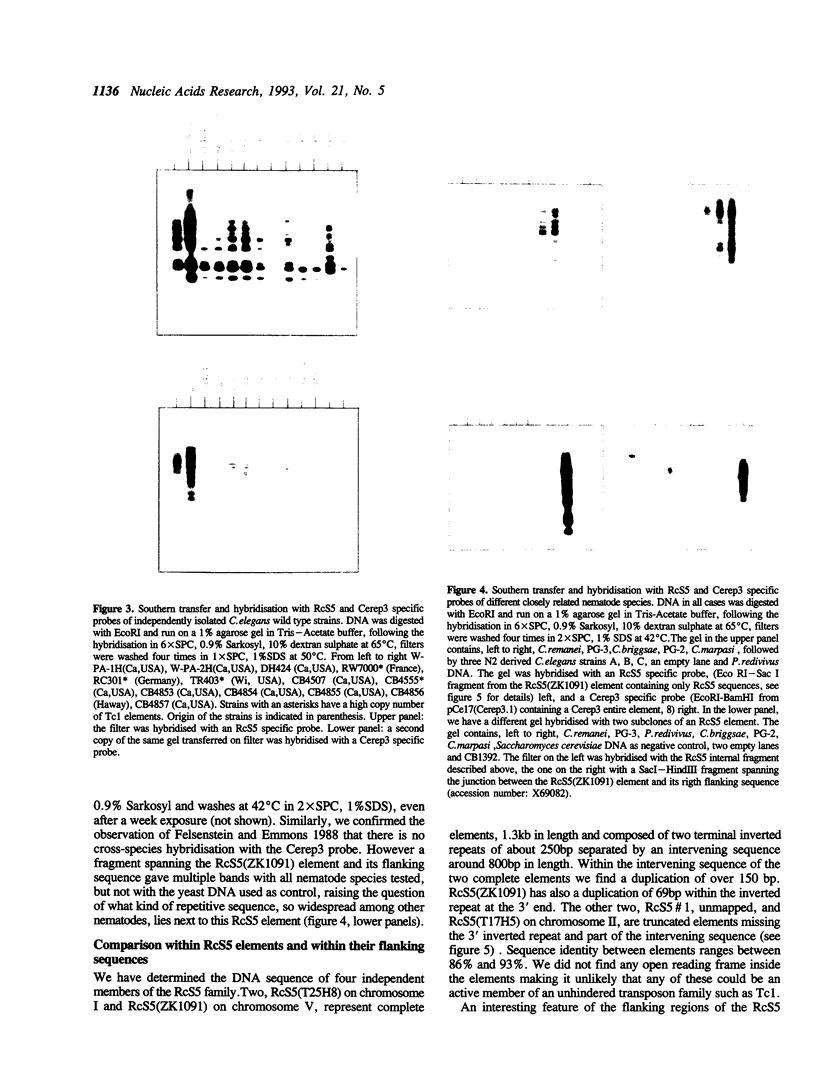
We describe the distribution along the chromosomes of Caenorhabditis elegans of two repetitive DNA families, RcS5 and Cerep3 and interstitial telomeric sequences. Both families show, among other interesting features, a preferential location in the terminal 30% of the chromosomes. It is known that in these regions of the genome the frequency of recombination is much higher than in the central portion, genes are rarer and sequences important for chromosome disjunction may lie.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albertson D. G., Thomson J. N. The kinetochores of Caenorhabditis elegans. Chromosoma. 1982;86(3):409–428. doi: 10.1007/BF00292267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cangiano G., Ameer H., Waterston R., La Volpe A. Use of repetitive DNA probes as physical mapping strategy in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5077–5081. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry J. M., Blackburn E. H. The internally located telomeric sequences in the germ-line chromosomes of Tetrahymena are at the ends of transposon-like elements. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90248-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J., Saari B., Anderson P. Activation of a transposable element in the germ line but not the soma of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1987 Aug 20;328(6132):726–728. doi: 10.1038/328726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran L. M., Thompson J. K., Walliker D., Kemp D. J. Homologous recombination within subtelomeric repeat sequences generates chromosome size polymorphisms in P. falciparum. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):807–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90097-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson A., Kozono Y., Lutterbach B., Shownkeen R., Sulston J., Waterston R. YACs and the C. elegans genome. Bioessays. 1991 Aug;13(8):413–417. doi: 10.1002/bies.950130809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson A., Waterston R., Kiff J., Sulston J., Kohara Y. Genome linking with yeast artificial chromosomes. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):184–186. doi: 10.1038/335184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G. A. DNA turnover and the molecular clock. J Mol Evol. 1987;26(1-2):47–58. doi: 10.1007/BF02111281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G. Molecular drive: a cohesive mode of species evolution. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):111–117. doi: 10.1038/299111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
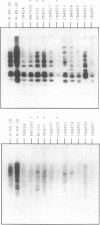
- Felsenstein K. M., Emmons S. W. Nematode repetitive DNA with ARS and segregation function in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):875–883. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson T. J., Rosenthal A., Waterston R. H. Lorist6, a cosmid vector with BamHI, NotI, ScaI and HindIII cloning sites and altered neomycin phosphotransferase gene expression. Gene. 1987;53(2-3):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S. T., Petes T. D. Instability of simple sequence DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2749–2757. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman R. K., Madl J. E., Kari C. K. Duplications in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1979 Jun;92(2):419–435. doi: 10.1093/genetics/92.2.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrick G., Cartinhour S., Dawson D., Ang D., Sheets R., Lee A., Williams K. Mobile elements bounded by C4A4 telomeric repeats in Oxytricha fallax. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):759–768. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90249-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin J., Horvitz H. R., Brenner S. Nondisjunction Mutants of the Nematode CAENORHABDITIS ELEGANS. Genetics. 1979 Jan;91(1):67–94. doi: 10.1093/genetics/91.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz H., Thorburn P., Haber J. E. Rearrangements of highly polymorphic regions near telomeres of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2509–2517. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter D. J., Williams K., Cartinhour S., Herrick G. Precise excision of telomere-bearing transposons during Oxytricha fallax macronuclear development. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2101–2112. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klion A. D., Raghavan N., Brindley P. J., Nutman T. B. Cloning and characterization of a species-specific repetitive DNA sequence from Loa loa. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Apr;45(2):297–305. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90098-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKim K. S., Rose A. M. Chromosome I duplications in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1990 Jan;124(1):115–132. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Szostak J. W. Chromosome segregation in mitosis and meiosis. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:289–315. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller F., Wicky C., Spicher A., Tobler H. New telomere formation after developmentally regulated chromosomal breakage during the process of chromatin diminution in Ascaris lumbricoides. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):815–822. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90076-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naclerio G., Cangiano G., Coulson A., Levitt A., Ruvolo V., La Volpe A. Molecular and genomic organization of clusters of repetitive DNA sequences in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jul 5;226(1):159–168. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pays E., Steinert M. Control of antigen gene expression in African trypanosomes. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:107–126. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.000543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluta A. F., Zakian V. A. Recombination occurs during telomere formation in yeast. Nature. 1989 Feb 2;337(6206):429–433. doi: 10.1038/337429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulston J., Du Z., Thomas K., Wilson R., Hillier L., Staden R., Halloran N., Green P., Thierry-Mieg J., Qiu L. The C. elegans genome sequencing project: a beginning. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):37–41. doi: 10.1038/356037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulston J., Mallett F., Staden R., Durbin R., Horsnell T., Coulson A. Software for genome mapping by fingerprinting techniques. Comput Appl Biosci. 1988 Mar;4(1):125–132. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/4.1.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterston R., Martin C., Craxton M., Huynh C., Coulson A., Hillier L., Durbin R., Green P., Shownkeen R., Halloran N. A survey of expressed genes in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat Genet. 1992 May;1(2):114–123. doi: 10.1038/ng0592-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]