Abstract
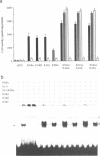
The binding affinity of retinoic acid receptors (RARs) to their response elements is strongly enhanced in vitro by the formation of heterodimers with retinoid X receptors (RXRs) suggesting that heterodimerization with RXR may be a prerequisite for a RAR-mediated transcriptional response. We found that in Drosophila SL-3 cells that are devoid of endogenous RARs and RXRs the presence of RAR is sufficient to confer a response to all-trans retinoic acid (RA). The transfection of both RAR and RXR and stimulation with their respective ligands all-trans and 9-cis RA leads to a synergistic response. On point mutations of the RAR beta 2 gene promoter RA response element (RARE) the stimulation by RARs showed distinct differences in the absence and presence of RXR. The same differences in transcriptional activity are observed, if mammalian cells containing endogenous RARs and RXRs are stimulated with all-trans RA only or additionally with 9-cis RA. This establishes an RXR-independent and an RXR-dependent pathway of all-trans RA action in Drosophila SL-3 cells as well as in mammalian cells. The presence or absence of 9-cis RA determines by which of the two pathways a response to all-trans RA is mediated.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. DNA binding specificity of steroid receptors. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1065–1068. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand N., Petkovich M., Krust A., Chambon P., de Thé H., Marchio A., Tiollais P., Dejean A. Identification of a second human retinoic acid receptor. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):850–853. doi: 10.1038/332850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugge T. H., Pohl J., Lonnoy O., Stunnenberg H. G. RXR alpha, a promiscuous partner of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptors. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1409–1418. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duester G., Shean M. L., McBride M. S., Stewart M. J. Retinoic acid response element in the human alcohol dehydrogenase gene ADH3: implications for regulation of retinoic acid synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1638–1646. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawell S. E., Lees J. A., White R., Parker M. G. Characterization and colocalization of steroid binding and dimerization activities in the mouse estrogen receptor. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):953–962. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90343-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguere V., Ong E. S., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a receptor for the morphogen retinoic acid. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):624–629. doi: 10.1038/330624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., DiRenzo J., Kurokawa R., Han Z. H. Regulation of gene expression by retinoic acid receptors. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;10(9):623–638. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Chambon P. Nuclear receptors enhance our understanding of transcription regulation. Trends Genet. 1988 Nov;4(11):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Chambon P. Oestradiol induction of a glucocorticoid-responsive gene by a chimaeric receptor. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):75–78. doi: 10.1038/325075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyman R. A., Mangelsdorf D. J., Dyck J. A., Stein R. B., Eichele G., Evans R. M., Thaller C. 9-cis retinoic acid is a high affinity ligand for the retinoid X receptor. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90479-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann B., Lehmann J. M., Zhang X. K., Hermann T., Husmann M., Graupner G., Pfahl M. A retinoic acid receptor-specific element controls the retinoic acid receptor-beta promoter. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Nov;4(11):1727–1736. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-11-1727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husmann M., Lehmann J., Hoffmann B., Hermann T., Tzukerman M., Pfahl M. Antagonism between retinoic acid receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4097–4103. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S. A., Umesono K., Mangelsdorf D. J., Evans R. M. Retinoid X receptor interacts with nuclear receptors in retinoic acid, thyroid hormone and vitamin D3 signalling. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):446–449. doi: 10.1038/355446a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krust A., Kastner P., Petkovich M., Zelent A., Chambon P. A third human retinoic acid receptor, hRAR-gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5310–5314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Chambon P. The estrogen receptor binds tightly to its responsive element as a ligand-induced homodimer. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann J. M., Zhang X. K., Pfahl M. RAR gamma 2 expression is regulated through a retinoic acid response element embedded in Sp1 sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):2976–2985. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.2976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Chambon P. Multiplicity generates diversity in the retinoic acid signalling pathways. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90014-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Lyons R., Nakshatri H., Saunders M., Zacharewski T., Chen J. Y., Staub A., Garnier J. M., Mader S. Purification, cloning, and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):377–395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90478-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy P., Nakshatri H., Chambon P. Mouse retinoic acid receptor alpha 2 isoform is transcribed from a promoter that contains a retinoic acid response element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10138–10142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin A. A., Sturzenbecker L. J., Kazmer S., Bosakowski T., Huselton C., Allenby G., Speck J., Kratzeisen C., Rosenberger M., Lovey A. 9-cis retinoic acid stereoisomer binds and activates the nuclear receptor RXR alpha. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):359–361. doi: 10.1038/355359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Borgmeyer U., Heyman R. A., Zhou J. Y., Ong E. S., Oro A. E., Kakizuka A., Evans R. M. Characterization of three RXR genes that mediate the action of 9-cis retinoic acid. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):329–344. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Ong E. S., Dyck J. A., Evans R. M. Nuclear receptor that identifies a novel retinoic acid response pathway. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):224–229. doi: 10.1038/345224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Umesono K., Kliewer S. A., Borgmeyer U., Ong E. S., Evans R. M. A direct repeat in the cellular retinol-binding protein type II gene confers differential regulation by RXR and RAR. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):555–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. S., Hallenbeck P. L., Nagata T., Segars J. H., Appella E., Nikodem V. M., Ozato K. H-2RIIBP (RXR beta) heterodimerization provides a mechanism for combinatorial diversity in the regulation of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone responsive genes. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1419–1435. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05187.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez E., Givel F., Wahli W. A common ancestor DNA motif for invertebrate and vertebrate hormone response elements. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):263–268. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07946.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagpal S., Saunders M., Kastner P., Durand B., Nakshatri H., Chambon P. Promoter context- and response element-dependent specificity of the transcriptional activation and modulating functions of retinoic acid receptors. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):1007–1019. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90250-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oro A. E., McKeown M., Evans R. M. Relationship between the product of the Drosophila ultraspiracle locus and the vertebrate retinoid X receptor. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):298–301. doi: 10.1038/347298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. C., Nakshatri H., Leroy P., Rees J., Chambon P. A retinoic acid response element is present in the mouse cellular retinol binding protein I (mCRBPI) promoter. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2223–2230. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07758.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sucov H. M., Murakami K. K., Evans R. M. Characterization of an autoregulated response element in the mouse retinoic acid receptor type beta gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5392–5396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabin C. J. Retinoids, homeoboxes, and growth factors: toward molecular models for limb development. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):199–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90612-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Carlstedt-Duke J., Weigel N. L., Dahlman K., Gustafsson J. A., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Molecular interactions of steroid hormone receptor with its enhancer element: evidence for receptor dimer formation. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Evans R. M. Determinants of target gene specificity for steroid/thyroid hormone receptors. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1139–1146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Murakami K. K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Direct repeats as selective response elements for the thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and vitamin D3 receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1255–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90020-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasios G. W., Gold J. D., Petkovich M., Chambon P., Gudas L. J. A retinoic acid-responsive element is present in the 5' flanking region of the laminin B1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9099–9103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vivanco Ruiz M. M., Bugge T. H., Hirschmann P., Stunnenberg H. G. Functional characterization of a natural retinoic acid responsive element. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3829–3838. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04952.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao T. P., Segraves W. A., Oro A. E., McKeown M., Evans R. M. Drosophila ultraspiracle modulates ecdysone receptor function via heterodimer formation. Cell. 1992 Oct 2;71(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90266-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. C., Delsert C., Andersen B., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., När A. M., Kim S. Y., Boutin J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. RXR beta: a coregulator that enhances binding of retinoic acid, thyroid hormone, and vitamin D receptors to their cognate response elements. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1251–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90301-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Hoffmann B., Tran P. B., Graupner G., Pfahl M. Retinoid X receptor is an auxiliary protein for thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):441–446. doi: 10.1038/355441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Lehmann J., Hoffmann B., Dawson M. I., Cameron J., Graupner G., Hermann T., Tran P., Pfahl M. Homodimer formation of retinoid X receptor induced by 9-cis retinoic acid. Nature. 1992 Aug 13;358(6387):587–591. doi: 10.1038/358587a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Vivanco-Ruiz M. M., Tiollais P., Stunnenberg H., Dejean A. Identification of a retinoic acid responsive element in the retinoic acid receptor beta gene. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):177–180. doi: 10.1038/343177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]