Abstract
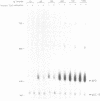
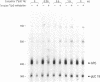
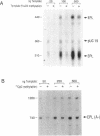
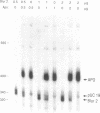
Methylation at CpG dinucleotides to produce 5 methyl cytosine (5me-C) has been proposed to regulate the transcriptional expression of human Alu repeats. Similarly, methylation has been proposed to indirectly favor the transpositional activity of young Alu repeats by transcriptionally inactivating older Alu's through the very rapid transition of 5me-C to T. Both hypotheses are examined here by RNA polymerase III (Pol III) in vitro transcription of Alu templates using HeLa cell extracts. A limiting factor represses the template activity of methylated Alu repeats. Competition by methylated prokaryotic vector DNA's relieves repression, showing that the factor is not sequence specific. This competitor has no effect on the activity of unmethylated templates showing that the repressor is highly specific toward methylated DNA. While methylation of a single pair of CpG dinucleotides in the A box of the Poll III promoter is sufficient to cause repression, methylation elsewhere within the template also causes repression. The repressor causing these effects on the Pol III directed transcription of Alu repeats is thought to be a previously reported, repressor for Pol II directed templates. Young Alu repeats are transcriptionally more active templates than a representative older Alu subfamily member. Also, younger Alu's form stable transcriptional complexes faster, potentially giving them an additional advantage. The mutation of three CpG's to CpA's within and near the A box drastically decreases both the template activity and rate of stable complex formation by a young Alu member. The sensitivity of Alu template activity to CpG transitions within the A box partially explains the selective transpositional advantage enjoyed by young Alu members.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Besser D., Götz F., Schulze-Forster K., Wagner H., Kröger H., Simon D. DNA methylation inhibits transcription by RNA polymerase III of a tRNA gene, but not of a 5S rRNA gene. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 3;269(2):358–362. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81193-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyes J., Bird A. DNA methylation inhibits transcription indirectly via a methyl-CpG binding protein. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1123–1134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90267-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L., Batzer M. A., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H. Master genes in mammalian repetitive DNA amplification. Trends Genet. 1992 Sep;8(9):307–311. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90262-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L., Jolly D. J., Rubin C. M., Friedmann T., Schmid C. W. Base sequence studies of 300 nucleotide renatured repeated human DNA clones. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 5;151(1):17–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Segni G., Carrara G., Tocchini-Valentini G. R., Shoulders C. C., Baralle F. E. Selective in vitro transcription of one of the two Alu family repeats present in the 5' flanking region of the human epsilon-globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6709–6722. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman S. A., Deininger P. L., LaPorte P., Friedmann T., Geiduschek E. P. Analysis of transcription of the human Alu family ubiquitous repeating element by eukaryotic RNA polymerase III. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6439–6456. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:873–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs P. E., Zielinski R., Boyd C., Dugaiczyk A. Structure, polymorphism, and novel repeated DNA elements revealed by a complete sequence of the human alpha-fetoprotein gene. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 10;26(5):1332–1343. doi: 10.1021/bi00379a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstetter H., Kressman A., Birnstiel M. L. A split promoter for a eucaryotic tRNA gene. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):573–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90348-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurka J., Milosavljevic A. Reconstruction and analysis of human Alu genes. J Mol Evol. 1991 Feb;32(2):105–121. doi: 10.1007/BF02515383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jüttermann R., Hosokawa K., Kochanek S., Doerfler W. Adenovirus type 2 VAI RNA transcription by polymerase III is blocked by sequence-specific methylation. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1735–1742. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1735-1742.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Transcription of class III genes: formation of preinitiation complexes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):740–748. doi: 10.1126/science.6356356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeflang E. P., Liu W. M., Hashimoto C., Choudary P. V., Schmid C. W. Phylogenetic evidence for multiple Alu source genes. J Mol Evol. 1992 Jul;35(1):7–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00160256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu W. M., Leeflang E. P., Schmid C. W. Unusual sequences of two old, inactive human Alu repeats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Oct 20;1132(3):306–308. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90165-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo S. M., Hernandez N. A 7 bp mutation converts a human RNA polymerase II snRNA promoter into an RNA polymerase III promoter. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90402-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matera A. G., Hellmann U., Hintz M. F., Schmid C. W. Recently transposed Alu repeats result from multiple source genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6019–6023. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matera A. G., Hellmann U., Schmid C. W. A transpositionally and transcriptionally competent Alu subfamily. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5424–5432. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meehan R. R., Lewis J. D., McKay S., Kleiner E. L., Bird A. P. Identification of a mammalian protein that binds specifically to DNA containing methylated CpGs. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):499–507. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90430-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Di Liegro C., Melli M. The in vitro transcription of the 7SK RNA gene by RNA polymerase III is dependent only on the presence of an upstream promoter. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. M., Folk W. R. Unraveling the complexities of transcription by RNA polymerase III. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Aug;15(8):300–304. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paolella G., Lucero M. A., Murphy M. H., Baralle F. E. The Alu family repeat promoter has a tRNA-like bipartite structure. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):691–696. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01486.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Stable C., Ayres T. M., Shen C. K. Distinctive sequence organization and functional programming of an Alu repeat promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5291–5295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rideout W. M., 3rd, Coetzee G. A., Olumi A. F., Jones P. A. 5-Methylcytosine as an endogenous mutagen in the human LDL receptor and p53 genes. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1288–1290. doi: 10.1126/science.1697983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan S. C., Dugaiczyk A. Newly arisen DNA repeats in primate phylogeny. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9360–9364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaack J., Sharp S., Dingermann T., Söll D. Transcription of eukaryotic tRNA genes in vitro. II. Formation of stable complexes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2447–2453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid C. W. Human Alu subfamilies and their methylation revealed by blot hybridization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5613–5617. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selker E. U. DNA methylation and chromatin structure: a view from below. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):103–107. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90193-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen C. K., Maniatis T. The organization, structure, and in vitro transcription of Alu family RNA polymerase III transcription units in the human alpha-like globin gene cluster: precipitation of in vitro transcripts by lupus anti-La antibodies. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):343–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen M. R., Batzer M. A., Deininger P. L. Evolution of the master Alu gene(s). J Mol Evol. 1991 Oct;33(4):311–320. doi: 10.1007/BF02102862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinnett D., Richer C., Deragon J. M., Labuda D. Alu RNA transcripts in human embryonal carcinoma cells. Model of post-transcriptional selection of master sequences. J Mol Biol. 1992 Aug 5;226(3):689–706. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90626-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullu E., Weiner A. M. Upstream sequences modulate the internal promoter of the human 7SL RNA gene. 1985 Nov 28-Dec 4Nature. 318(6044):371–374. doi: 10.1038/318371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Deininger P. L., Efstratiadis A. Nonviral retroposons: genes, pseudogenes, and transposable elements generated by the reverse flow of genetic information. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:631–661. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. J., Stott D., Rigby P. W. Regulation of RNA polymerase III transcription in response to F9 embryonal carcinoma stem cell differentiation. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1081–1092. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90764-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]