Abstract
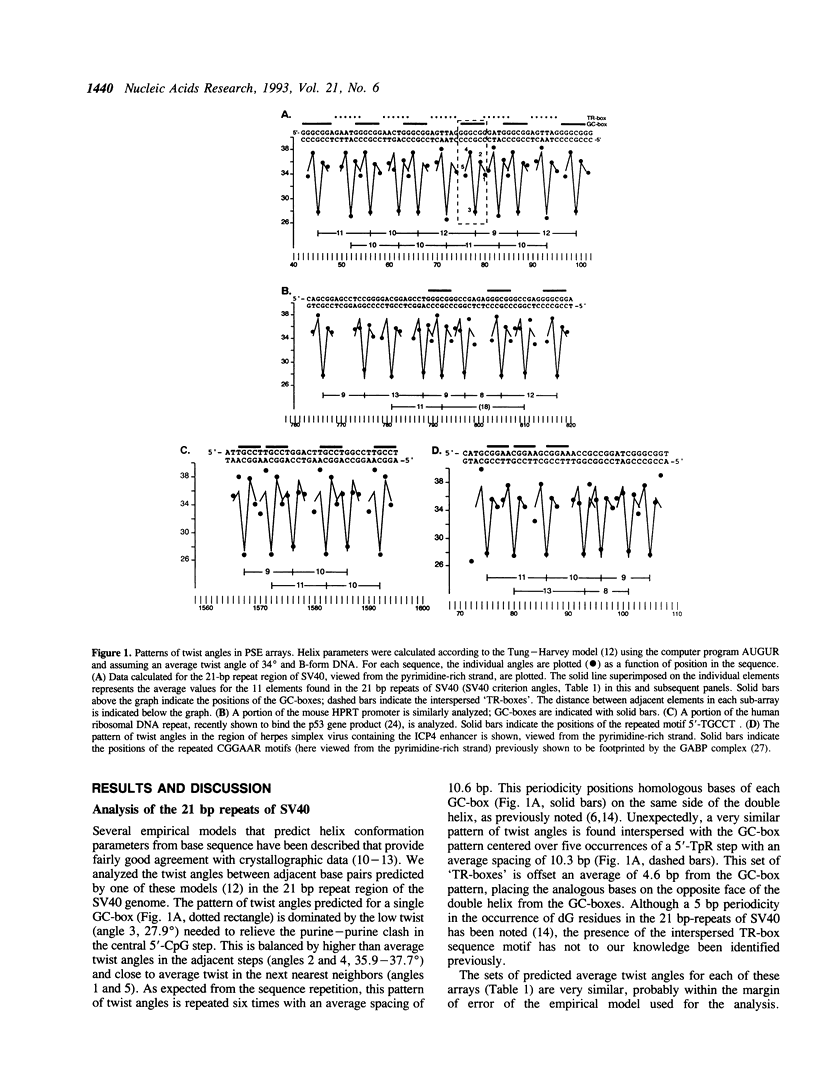
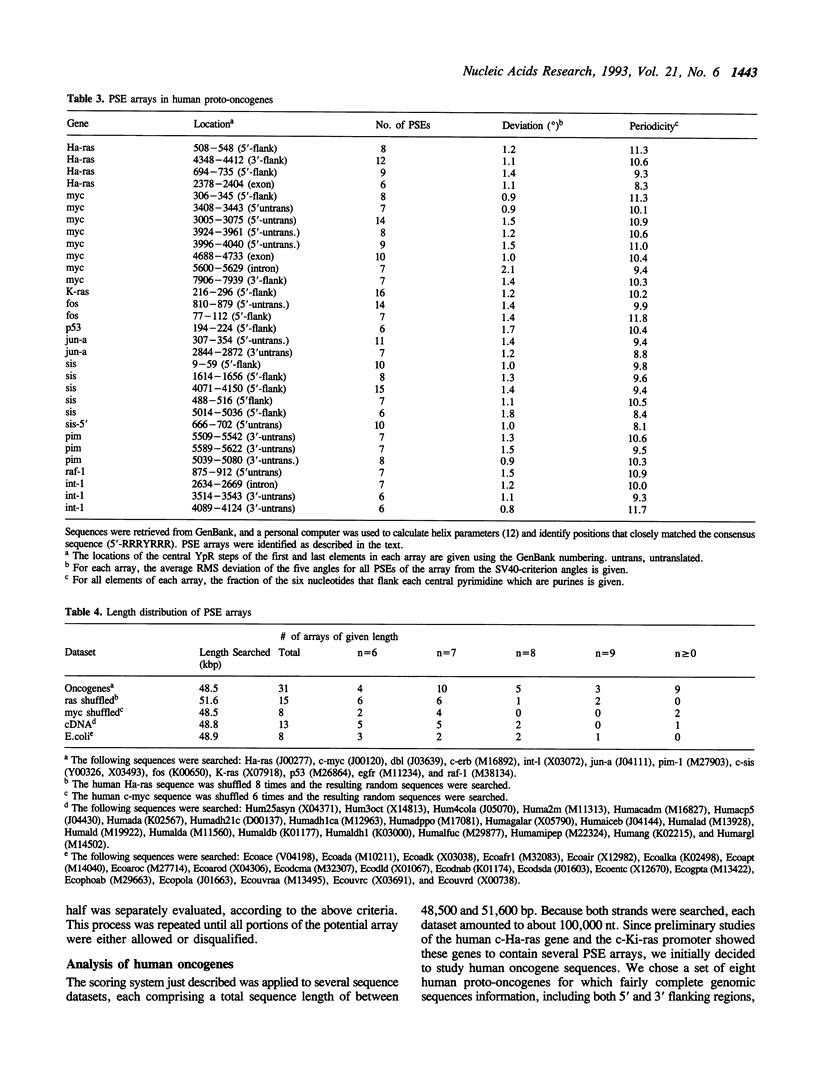
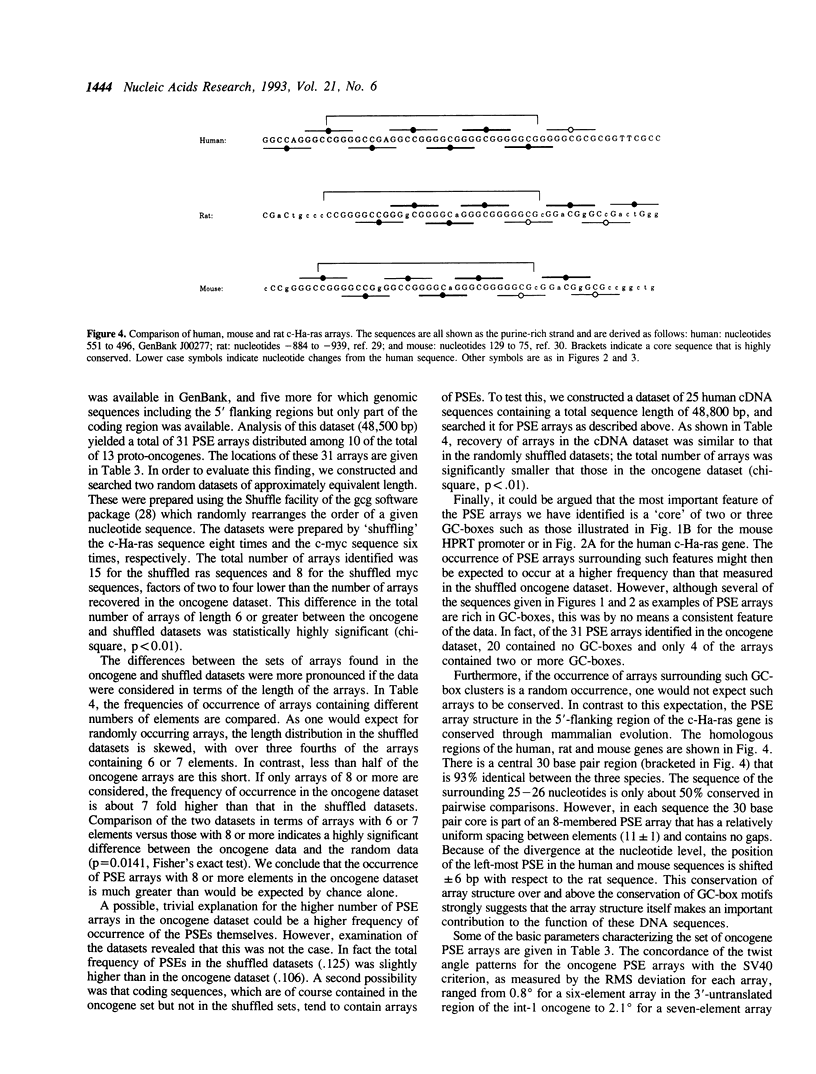
We have analyzed predicted helical twist angles in the 21-bp repeat region of the SV40 genome, using a semi-empirical model previously shown to accurately predict backbone conformations. Unexpectedly, the pattern of twist angles characteristic of the six GC-boxes is repeated an additional five times at positions that are regularly interspersed with the six GC-box sequences. These patterns of helical twist angles are associated with a second, imperfectly-repeated sequence motif, the TR-box 5'-RRNTRGG. Unrelated DNA sequences that interact with trans-acting factors (p53 and GABP) exhibit similar twist angle patterns, due to elements of the general form 5'-RRRYRRR that occur as interspersed arrays with a spacing of 10-11 bp and an offset of 4-6 bp. Arrays of these elements, which we call pyrimidine sandwich elements (PSEs), may play an important role in the interaction of trans-acting factors with DNA control regions. In 13 human proto-oncogenes analyzed, we identified 31 PSE arrays, 11 of which were in the 5'-flanking regions of the genes. The most extensive array was found in the promoter region of the K-ras gene. Extending over 80 bp of DNA, it contained 16 PSEs that showed an average deviation from the SV40 criterion pattern of angles of only 1.2 degrees.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrecht G. R., Cavallini B., Davidson I. Detection of specific protein binding to the SV40 early promoter in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7945–7963. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer T. K., Cordingley M. G., Wolford R. G., Hager G. L. Transcription factor access is mediated by accurately positioned nucleosomes on the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):688–698. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azizkhan J. C., Vaughn J. P., Christy R. J., Hamlin J. L. Nucleotide sequence and nuclease hypersensitivity of the Chinese hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene promoter region. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 7;25(20):6228–6236. doi: 10.1021/bi00368a059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargonetti J., Friedman P. N., Kern S. E., Vogelstein B., Prives C. Wild-type but not mutant p53 immunopurified proteins bind to sequences adjacent to the SV40 origin of replication. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1083–1091. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90560-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broderick T. P., Schaff D. A., Bertino A. M., Dush M. K., Tischfield J. A., Stambrook P. J. Comparative anatomy of the human APRT gene and enzyme: nucleotide sequence divergence and conservation of a nonrandom CpG dinucleotide arrangement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3349–3353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calladine C. R., Drew H. R. Principles of sequence-dependent flexure of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 20;192(4):907–918. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calladine C. R. Mechanics of sequence-dependent stacking of bases in B-DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Oct 25;161(2):343–352. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90157-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damante G., Filetti S., Rapoport B. Nucleotide sequence and characterization of the 5' flanking region of the rat Ha-ras protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):774–778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E. Base sequence and helix structure variation in B and A DNA. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 25;166(3):419–441. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Drew H. R. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer. II. Influence of base sequence on helix structure. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 15;149(4):761–786. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Calladine C. R. Sequence-specific positioning of core histones on an 860 base-pair DNA. Experiment and theory. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 5;195(1):143–173. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90333-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dush M. K., Sikela J. M., Khan S. A., Tischfield J. A., Stambrook P. J. Nucleotide sequence and organization of the mouse adenine phosphoribosyltransferase gene: presence of a coding region common to animal and bacterial phosphoribosyltransferases that has a variable intron/exon arrangement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2731–2735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A., Voss H., Rice P., Civitello A., Stegemann J., Schwager C., Zimmermann J., Erfle H., Caskey C. T., Ansorge W. Automated DNA sequencing of the human HPRT locus. Genomics. 1990 Apr;6(4):593–608. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90493-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Multiple specific contacts between a mammalian transcription factor and its cognate promoters. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):409–413. doi: 10.1038/312409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Kadonaga J. T., Barrera-Saldaña H., Takahashi K., Chambon P., Tjian R. Bidirectional SV40 transcription mediated by tandem Sp1 binding interactions. Science. 1985 Nov 1;230(4725):511–517. doi: 10.1126/science.2996137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch M., Gerwin N., Taubert H., Jäckle H. Competition for overlapping sites in the regulatory region of the Drosophila gene Krüppel. Science. 1992 Apr 3;256(5053):94–97. doi: 10.1126/science.1348871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R., Brady J. N., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Binding of the Sp1 transcription factor by the human Harvey ras1 proto-oncogene promoter. Science. 1986 Jun 13;232(4756):1410–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.3012774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch W., Sander C., Trifonov E. N. The ten helical twist angles of B-DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 11;10(3):1097–1104. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.3.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Kinzler K. W., Bruskin A., Jarosz D., Friedman P., Prives C., Vogelstein B. Identification of p53 as a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1708–1711. doi: 10.1126/science.2047879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. J., Onwuta U. S., Lee Y. I., Li R., Botchan M. R., Robbins P. D. The retinoblastoma gene product regulates Sp1-mediated transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2455–2463. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsley C., Winoto A. Cloning of GT box-binding proteins: a novel Sp1 multigene family regulating T-cell receptor gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4251–4261. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann J. M., Zhang X. K., Pfahl M. RAR gamma 2 expression is regulated through a retinoic acid response element embedded in Sp1 sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):2976–2985. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.2976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R., Knight J. D., Jackson S. P., Tjian R., Botchan M. R. Direct interaction between Sp1 and the BPV enhancer E2 protein mediates synergistic activation of transcription. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):493–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90467-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutter L. C. Kinetic analysis of deoxyribonuclease I cleavages in the nucleosome core: evidence for a DNA superhelix. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 15;124(2):391–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Carothers A. M., Han J. H., Harding J. D., Kas E., Venolia L., Chasin L. A. Multiple transcription start sites, DNase I-hypersensitive sites, and an opposite-strand exon in the 5' region of the CHO dhfr gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):425–440. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalbantoglu J., Phear G. A., Meuth M. Nucleotide sequence of hamster adenine phosphoribosyl transferase (aprt) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1914–1914. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park J. H., Taylor M. W. Analysis of signals controlling expression of the Chinese hamster ovary aprt gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2536–2544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann T., Wrange O. Specific glucocorticoid receptor binding to DNA reconstituted in a nucleosome. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3073–3079. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03172.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitluk Z. W., Ward D. C. Unusual Sp1-GC box interaction in a parvovirus promoter. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6661–6670. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6661-6670.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piña B., Brüggemeier U., Beato M. Nucleosome positioning modulates accessibility of regulatory proteins to the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):719–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90087-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piña B., Truss M., Ohlenbusch H., Postma J., Beato M. DNA rotational positioning in a regulatory nucleosome is determined by base sequence. An algorithm to model the preferred superhelix. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6981–6987. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumb M., Telliez J. B., Fee F., Daubersies P., Bailleul B., Balmain A. Structural analysis of the mouse c-Ha-ras gene promoter. Mol Carcinog. 1991;4(2):103–111. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940040205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. A., Basu S. K., Osborne T. F., Chin D. J., Gil G., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Luskey K. L. HMG CoA reductase: a negatively regulated gene with unusual promoter and 5' untranslated regions. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90549-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Klug A. An underlying repeat in some transcriptional control sequences corresponding to half a double helical turn of DNA. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):123–132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90866-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard-Foy H., Hager G. L. Sequence-specific positioning of nucleosomes over the steroid-inducible MMTV promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2321–2328. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02507.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider T. D., Stormo G. D., Gold L., Ehrenfeucht A. Information content of binding sites on nucleotide sequences. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 5;188(3):415–431. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrader T. E., Crothers D. M. Artificial nucleosome positioning sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7418–7422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrader T. E., Crothers D. M. Effects of DNA sequence and histone-histone interactions on nucleosome placement. J Mol Biol. 1990 Nov 5;216(1):69–84. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80061-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Hartzell G. W., 3rd Identifying protein-binding sites from unaligned DNA fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1183–1187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I. C., Workman J. L., Schuetz T. J., Kingston R. E. Facilitated binding of GAL4 and heat shock factor to nucleosomal templates: differential function of DNA-binding domains. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1285–1298. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. C., Brown T. A., McKnight S. L. Convergence of Ets- and notch-related structural motifs in a heteromeric DNA binding complex. Science. 1991 Aug 16;253(5021):762–768. doi: 10.1126/science.1876833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung C. S., Harvey S. C. Base sequence, local helix structure, and macroscopic curvature of A-DNA and B-DNA. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3700–3709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingender E. Compilation of transcription regulating proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):1879–1902. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Brown D. D. Developmental regulation of two 5S ribosomal RNA genes. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1626–1632. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambetti G. P., Bargonetti J., Walker K., Prives C., Levine A. J. Wild-type p53 mediates positive regulation of gene expression through a specific DNA sequence element. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1143–1152. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



