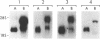Abstract
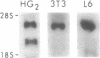
Plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 (PAI-1) is the primary physiologic inhibitor of the naturally occurring plasminogen activators. In higher primates two forms of mature PAI-1 mRNA (3.2 kb and 2.2 kb) arise by alternative cleavage and polyadenylation of PAI-1 hnRNA which is regulated in a tissue-specific fashion in humans. In other mammals only the 3.2 kb mRNA has been detected. The putative downstream polyadenylation site in humans that gives rise to the 3.2 kb PAI-1 mRNA consists of three overlapping copies of the consensus polyadenylation sequence while no consensus polyadenylation sequence is found upstream at a position that could generate the shorter mRNA species. To determine whether differential cleavage and polyadenylation of PAI-1 mRNA is due to species-specific differences in trans-acting factors that process PAI-1 mRNA or to the presence of a nonconsensus polyadenylation site acquired recently during primate evolution we prepared plasmids in which the 3' nontranslated region of the human PAI-1 gene or the mouse PAI-1 cDNA was inserted downstream of the neomycin gene in the plasmid pSV2neo. We show that the 3'-nontranslated region of the human PAI-1 gene but not the mouse PAI-1 cDNA conferred alternative cleavage and polyadenylation to the neomycin gene in transfected human Hep G2 cells as well as mouse NIH3T3 and rat L6 cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bohjanen P. R., Petryniak B., June C. H., Thompson C. B., Lindsten T. An inducible cytoplasmic factor (AU-B) binds selectively to AUUUA multimers in the 3' untranslated region of lymphokine mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3288–3295. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma P. J., Kooistra T. Different induction of two plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 mRNA species by phorbol ester in human hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):17845–17849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma P. J., van den Berg E. A., Kooistra T., Siemieniak D. R., Slightom J. L. Human plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene. Promoter and structural gene nucleotide sequences. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9129–9141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitbart R. E., Andreadis A., Nadal-Ginard B. Alternative splicing: a ubiquitous mechanism for the generation of multiple protein isoforms from single genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:467–495. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicila G. T., O'Connell T. M., Hahn W. C., Rheinwald J. G. Cloned cDNA sequence for the human mesothelial protein 'mesosecrin' discloses its identity as a plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) and a recent evolutionary change in transcript processing. J Cell Sci. 1989 Sep;94(Pt 1):1–10. doi: 10.1242/jcs.94.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etingin O. R., Hajjar D. P., Hajjar K. A., Harpel P. C., Nachman R. L. Lipoprotein (a) regulates plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression in endothelial cells. A potential mechanism in thrombogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2459–2465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fattal P. G., Schneider D. J., Sobel B. E., Billadello J. J. Post-transcriptional regulation of expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 mRNA by insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12412–12415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follo M., Ginsburg D. Structure and expression of the human gene encoding plasminogen activator inhibitor, PAI-1. Gene. 1989 Dec 14;84(2):447–453. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg D., Zeheb R., Yang A. Y., Rafferty U. M., Andreasen P. A., Nielsen L., Dano K., Lebo R. V., Gelehrter T. D. cDNA cloning of human plasminogen activator-inhibitor from endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1673–1680. doi: 10.1172/JCI112761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedén L. O., Hög J. O., Larsson K., Lake M., Lagerholm E., Holmgren A., Vallee B. L., Jörnvall H., von Bahr-Lindström H. cDNA clones coding for the beta-subunit of human liver alcohol dehydrogenase have differently sized 3'-non-coding regions. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 6;194(2):327–332. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80111-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins W. E., Westerhausen D. R., Jr, Sobel B. E., Billadello J. J. Transcriptional regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 mRNA in Hep G2 cells by epidermal growth factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):163–168. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucore C. L., Fujii S., Wun T. C., Sobel B. E., Billadello J. J. Regulation of the expression of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor in Hep G2 cells by epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):15845–15848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder V. J. Inhibiting the inhibitor. Circulation. 1992 Jan;85(1):386–387. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.85.1.386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimuro J., Loskutoff D. J. Purification of a protein from bovine plasma that binds to type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor and prevents its interaction with extracellular matrix. Evidence that the protein is vitronectin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):936–939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimuro J., Sawdey M., Hattori M., Luskutoff D. J. cDNA for bovine type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1). Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8872–8872. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ny T., Sawdey M., Lawrence D., Millan J. L., Loskutoff D. J. Cloning and sequence of a cDNA coding for the human beta-migrating endothelial-cell-type plasminogen activator inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6776–6780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Diamond L. E., Dahl D., Cole M. D. The c-myc-regulated gene mrl encodes plasminogen activator inhibitor 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1265–1269. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. C., Falck-Pedersen E. Varied poly(A) site efficiency in the adenovirus major late transcription unit. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8175–8181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J. How RNA polymerase II terminates transcription in higher eukaryotes. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Mar;14(3):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawdey M. S., Loskutoff D. J. Regulation of murine type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor gene expression in vivo. Tissue specificity and induction by lipopolysaccharide, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and transforming growth factor-beta. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1346–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI115440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler G. D., Cole M. D. GM-CSF and oncogene mRNA stabilities are independently regulated in trans in a mouse monocytic tumor. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1115–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90256-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thekkumkara T. J., Livingston W., 3rd, Kumar R. S., Sen G. C. Use of alternative polyadenylation sites for tissue-specific transcription of two angiotensin-converting enzyme mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 25;20(4):683–687. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.4.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerhausen D. R., Jr, Hopkins W. E., Billadello J. J. Multiple transforming growth factor-beta-inducible elements regulate expression of the plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 gene in Hep G2 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1092–1100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wun T. C., Kretzmer K. K. cDNA cloning and expression in E. coli of a plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI) related to a PAI produced by Hep G2 hepatoma cell. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jan 1;210(1):11–16. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81288-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]