Abstract
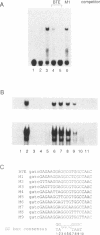
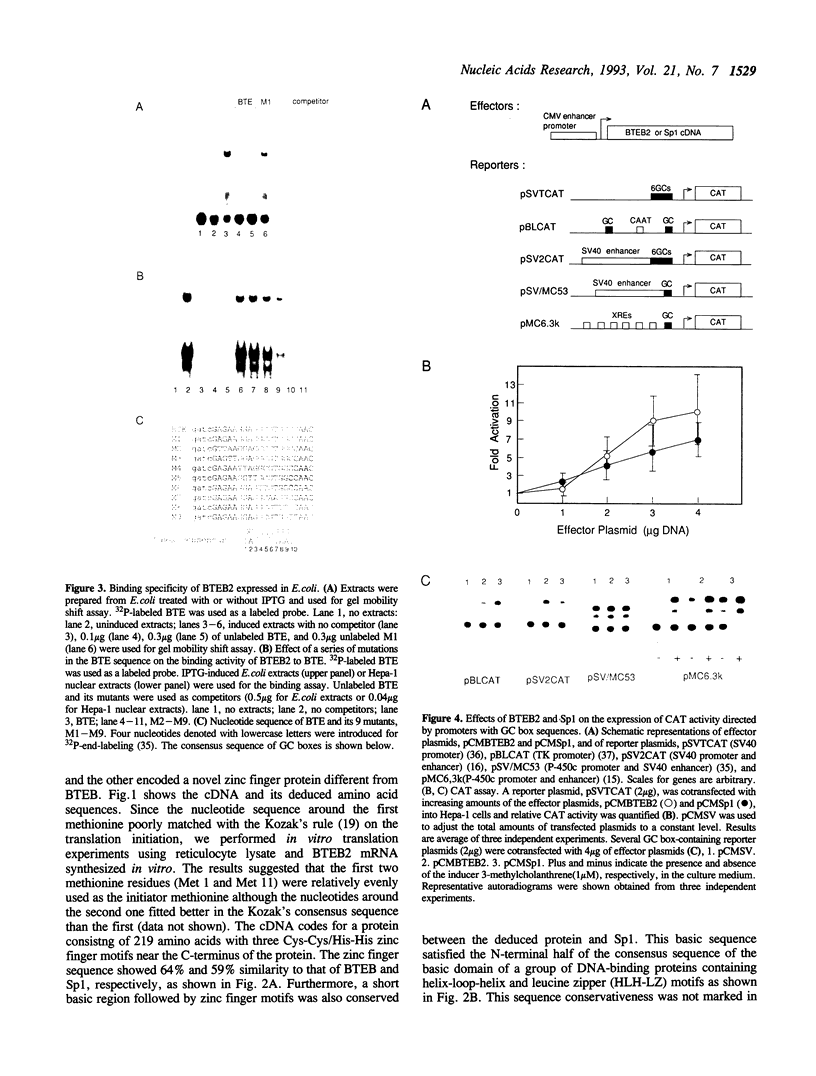
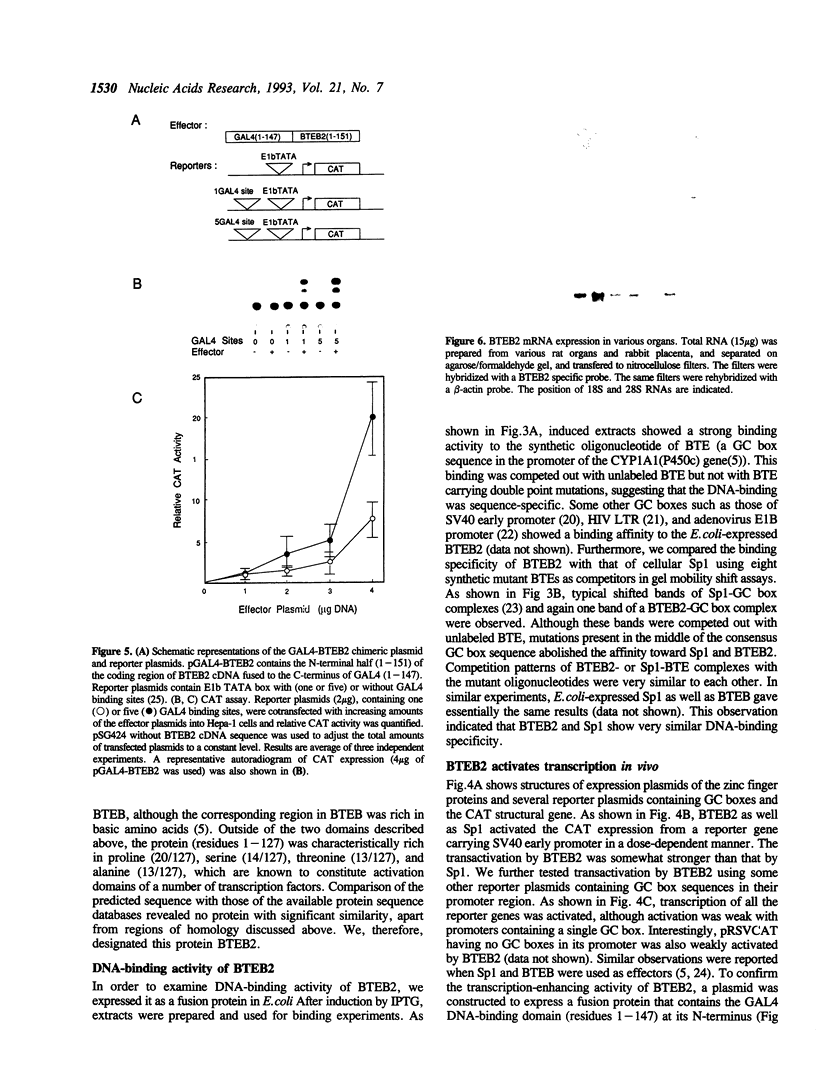
We have cloned a cDNA for a novel GC box-binding protein designated BTEB2 from a human placenta cDNA library using rat BTEB cDNA (Imataka et al. (1992). EMBO J. 11,3663-3671. as a hybridization probe. BTEB2 consists of 219 amino acids and contains three contiguous zinc finger motifs at its C-terminus. The zinc finger domains showed 59% and 64% sequence similarity to those of Sp1 and BTEB, respectively. Adjacent to the N-terminal of the zinc finger motifs, a short sequence rich in basic amino acids is conserved between BTEB2 and Sp1. Furthermore, This basic sequence concurs with the N-terminal half of the consensus sequence for basic domains of the proteins containing both helix-loop-helix and leucine zipper motifs. The other region of BTEB2 is notably rich in proline, serine, threonine, and alanine residues. BTEB2 expressed in Escherichia coli showed DNA-binding activity whose specificity was closely similar to that of Sp1. Cotransfection experiments using Hepa-1 cells (a mouse hepatoma cell line) with a BTEB2 expression plasmid and GC box-containing reporter plasmids revealed that BTEB2 apparently activated the expression of the CAT activity. Moreover, when BTEB2 was fused to GAL4 DNA-binding domain, the chimeric protein could enhance the transcription through promoters containing GAL4-binding sites. Analysis of the BTEB2 mRNA by RNA blot analysis demonstrated that the mRNA was expressed specifically in testis and placenta with different sizes, 20S and 28S, respectively, among various organs examined.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerji J., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Expression of a beta-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhard H. P., Darlington G. J., Ruddle F. H. Expression of liver phenotypes in cultured mouse hepatoma cells: synthesis and secretion of serum albumin. Dev Biol. 1973 Nov;35(1):83–96. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. S., Sander C., Argos P. The primary structure of transcription factor TFIIIA has 12 consecutive repeats. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 8;186(2):271–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80723-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Tjian R. Analysis of Sp1 in vivo reveals multiple transcriptional domains, including a novel glutamine-rich activation motif. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePinho R. A., Hatton K. S., Tesfaye A., Yancopoulos G. D., Alt F. W. The human myc gene family: structure and activity of L-myc and an L-myc pseudogene. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1311–1326. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ema M., Sogawa K., Watanabe N., Chujoh Y., Matsushita N., Gotoh O., Funae Y., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. cDNA cloning and structure of mouse putative Ah receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Apr 15;184(1):246–253. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91185-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. E., Carr C. S., Parent L. A., Sharp P. A. TFEB has DNA-binding and oligomerization properties of a unique helix-loop-helix/leucine-zipper family. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2342–2352. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa-Sehara A., Sogawa K., Nishi C., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Regulatory DNA elements localized remotely upstream from the drug-metabolizing cytochrome P-450c gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1465–1477. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imataka H., Sogawa K., Yasumoto K., Kikuchi Y., Sasano K., Kobayashi A., Hayami M., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Two regulatory proteins that bind to the basic transcription element (BTE), a GC box sequence in the promoter region of the rat P-4501A1 gene. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3663–3671. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05451.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue H., Watanabe N., Higashi Y., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Structures of regulatory regions in the human cytochrome P-450scc (desmolase) gene. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jan 30;195(2):563–569. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15738.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Luciw P. A., Tjian R. Activation of the AIDS retrovirus promoter by the cellular transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):755–759. doi: 10.1126/science.3008338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Carner K. R., Masiarz F. R., Tjian R. Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90594-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M. R. Transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):39–44. doi: 10.1038/338039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., O'Neill E. A., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. The proline-rich transcriptional activator of CTF/NF-I is distinct from the replication and DNA binding domain. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):741–753. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardelli J., Gibson T. J., Vesque C., Charnay P. Base sequence discrimination by zinc-finger DNA-binding domains. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):175–178. doi: 10.1038/349175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):809–817. doi: 10.1126/science.2028256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ptashne M. A vector for expressing GAL4(1-147) fusions in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7539–7539. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffer J. D., Jackson S. P., Annarella M. B. Developmental expression of Sp1 in the mouse. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2189–2199. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaufele F., West B. L., Reudelhuber T. L. Overlapping Pit-1 and Sp1 binding sites are both essential to full rat growth hormone gene promoter activity despite mutually exclusive Pit-1 and Sp1 binding. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17189–17196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. C., Zhou Q., Berk A. J. Sp1 activates transcription without enhancing DNA-binding activity of the TATA box factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3299–3307. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swick A. G., Blake M. C., Kahn J. W., Azizkhan J. C. Functional analysis of GC element binding and transcription in the hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9291–9304. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagida A., Sogawa K., Yasumoto K. I., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. A novel cis-acting DNA element required for a high level of inducible expression of the rat P-450c gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1470–1475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]