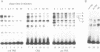Abstract
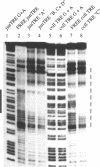
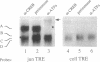
Several promoter elements with sequence similarity to the prototype TPA-responsive element (TRE) were compared by mobility-shift analyses. Activities within whole cell extracts were identified that bind to the TRE-like elements in the collagenase, the somatostatin, and the c-jun promoters. The corresponding factors appeared to differ in their degree of selectivity for these TRE-like sequences. One protein species bound equally well to all TREs. In addition, a subset of specific activities recognised only the somatostatin and the c-jun-derived element and one DNA-protein complex had exclusive specificity for the TRE present in the c-jun promoter. By antibody 'supershift' assays some of the protein components of the specific complexes were identified as CREB- and ATF-related products. Based on these data we postulate that bZip protein dimers differ in their ability to tolerate variations from the canonical TRE sequence. We propose that TRE-like promoter elements are distinguished by this ability to bind to different subsets of a family of related transcription factors.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Allegretto E. A., Okino S. T., Hattori K., Boyle W. J., Hunter T., Karin M. Oncogene jun encodes a sequence-specific trans-activator similar to AP-1. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):166–171. doi: 10.1038/332166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Baumann I., Stein B., Delius H., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate induction of the human collagenase gene is mediated by an inducible enhancer element located in the 5'-flanking region. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2256–2266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbrook D. M., Jones N. C. Heterodimer formation between CREB and JUN proteins. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):295–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Bos T. J., Admon A., Nishimura T., Vogt P. K., Tjian R. Human proto-oncogene c-jun encodes a DNA binding protein with structural and functional properties of transcription factor AP-1. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1386–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2825349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch S. J., Sassone-Corsi P. Dimers, leucine zippers and DNA-binding domains. Trends Genet. 1990 Feb;6(2):36–40. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90071-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatton B., Bocco J. L., Gaire M., Hauss C., Reimund B., Goetz J., Kedinger C. Transcriptional activation by the adenovirus larger E1a product is mediated by members of the cellular transcription factor ATF family which can directly associate with E1a. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):561–570. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Van Beveren C., Verma I. M. Viral and cellular fos proteins are complexed with a 39,000-dalton cellular protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):167–172. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T., Curran T. Cross-family dimerization of transcription factors Fos/Jun and ATF/CREB alters DNA binding specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3720–3724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst H. C., Masson N., Jones N. C., Lee K. A. The cellular transcription factor CREB corresponds to activating transcription factor 47 (ATF-47) and forms complexes with a group of polypeptides related to ATF-43. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6192–6203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Smeal T. Control of transcription factors by signal transduction pathways: the beginning of the end. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):418–422. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabayashi I., Chiu R., Gachelin G., Yokoyama K. E1A dependent up-regulation of c-jun/AP-1 activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 11;19(3):649–655. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.3.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovary K., Bravo R. Expression of different Jun and Fos proteins during the G0-to-G1 transition in mouse fibroblasts: in vitro and in vivo associations. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2451–2459. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwabara M. D., Sigman D. S. Footprinting DNA-protein complexes in situ following gel retardation assays using 1,10-phenanthroline-copper ion: Escherichia coli RNA polymerase-lac promoter complexes. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 17;26(23):7234–7238. doi: 10.1021/bi00397a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F., Green M. R. A specific member of the ATF transcription factor family can mediate transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1217–1224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90686-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masquilier D., Sassone-Corsi P. Transcriptional cross-talk: nuclear factors CREM and CREB bind to AP-1 sites and inhibit activation by Jun. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22460–22466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller C. R., Maire P., Schibler U. DBP, a liver-enriched transcriptional activator, is expressed late in ontogeny and its tissue specificity is determined posttranscriptionally. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):279–291. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90808-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., Bravo R. c-JUN, JUN B, and JUN D differ in their binding affinities to AP-1 and CRE consensus sequences: effect of FOS proteins. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):533–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Ransone L. J., Verma I. M. Cross-talk in signal transduction: TPA-inducible factor jun/AP-1 activates cAMP-responsive enhancer elements. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):427–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. E., Papavassiliou A. G. A coupled Southwestern--DNase I footprinting assay. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 11;20(19):5239–5240. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.19.5239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. K., Gonzalez G. A., Biggs W. H., 3rd, Montminy M. R. Phosphorylation-induced binding and transcriptional efficacy of nuclear factor CREB. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):494–498. doi: 10.1038/334494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Chiu R., Karin M. Elevation of AP1 activity during F9 cell differentiation is due to increased c-jun transcription. New Biol. 1990 Apr;2(4):351–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimarino V., Wu C. Induction of sequence-specific binding of Drosophila heat shock activator protein without protein synthesis. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):727–730. doi: 10.1038/327727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot R., Foulkes N., Mulder M., Kruijer W., Sassone-Corsi P. Positive regulation of jun/AP-1 by E1A. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):192–201. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]