Abstract
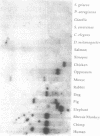
Recently an HMG-box protein denoted SSRP1, for structure-specific recognition protein 1, has been discovered which binds to specific DNA structural elements such as the bent, unwound conformations that occur upon the formation of intrastrand crosslinks by the anticancer drug cisplatin. The SSRP family includes the mouse protein T160, which recognizes recombination signal sequences. In order to delineate functional domains more clearly, a homolog of SSRP1 was cloned from Drosophila melanogaster. This homolog maps to polytene region 60A (1-4) and shares 54% identity with human SSRP1. Comparison of the predicted amino acid sequences among SSRP family members reveals 48% identity, with structural conservation in the carboxy terminus of the HMG box as well as domains of highly charged residues. Interestingly, however, the most highly conserved regions of the protein are in the less well understood amino terminus, strongly suggesting that this portion of the protein is critical for its function.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellon S. F., Coleman J. H., Lippard S. J. DNA unwinding produced by site-specific intrastrand cross-links of the antitumor drug cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II). Biochemistry. 1991 Aug 13;30(32):8026–8035. doi: 10.1021/bi00246a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellon S. F., Lippard S. J. Bending studies of DNA site-specifically modified by cisplatin, trans-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) and cis-[Pt(NH3)2(N3-cytosine)Cl]+. Biophys Chem. 1990 Apr;35(2-3):179–188. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(90)80007-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi M. E., Beltrame M., Paonessa G. Specific recognition of cruciform DNA by nuclear protein HMG1. Science. 1989 Feb 24;243(4894 Pt 1):1056–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.2922595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi M. E., Falciola L., Ferrari S., Lilley D. M. The DNA binding site of HMG1 protein is composed of two similar segments (HMG boxes), both of which have counterparts in other eukaryotic regulatory proteins. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1055–1063. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05144.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruhn S. L., Pil P. M., Essigmann J. M., Housman D. E., Lippard S. J. Isolation and characterization of human cDNA clones encoding a high mobility group box protein that recognizes structural distortions to DNA caused by binding of the anticancer agent cisplatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2307–2311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustin M., Lehn D. A., Landsman D. Structural features of the HMG chromosomal proteins and their genes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jul 30;1049(3):231–243. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90092-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao C. C., Huang S. L., Lee L. Y., Lin-Chao S. Identification of inducible damage-recognition proteins that are overexpressed in HeLa cells resistant to cis-diamminedichloroplatinum (II). Biochem J. 1991 Aug 1;277(Pt 3):875–878. doi: 10.1042/bj2770875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Conformational parameters for amino acids in helical, beta-sheet, and random coil regions calculated from proteins. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):211–222. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Chang E. Xeroderma pigmentosum group E cells lack a nuclear factor that binds to damaged DNA. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):564–567. doi: 10.1126/science.3175673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Stillman B. A close relative of the nuclear, chromosomal high-mobility group protein HMG1 in yeast mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7864–7868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Stillman B. DNA binding properties of an HMG1-related protein from yeast mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3368–3374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue B. A., Augot M., Bellon S. F., Treiber D. K., Toney J. H., Lippard S. J., Essigmann J. M. Characterization of a DNA damage-recognition protein from mammalian cells that binds specifically to intrastrand d(GpG) and d(ApG) DNA adducts of the anticancer drug cisplatin. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 19;29(24):5872–5880. doi: 10.1021/bi00476a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastman A. The formation, isolation and characterization of DNA adducts produced by anticancer platinum complexes. Pharmacol Ther. 1987;34(2):155–166. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(87)90009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einck L., Bustin M. The intracellular distribution and function of the high mobility group chromosomal proteins. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Feb;156(2):295–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90539-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Amsterdam A., Grosschedl R. DNA-binding properties of the HMG domain of the lymphoid-specific transcriptional regulator LEF-1. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2567–2578. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Cox J., Grosschedl R. The HMG domain of lymphoid enhancer factor 1 bends DNA and facilitates assembly of functional nucleoprotein structures. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90129-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubbay J., Collignon J., Koopman P., Capel B., Economou A., Münsterberg A., Vivian N., Goodfellow P., Lovell-Badge R. A gene mapping to the sex-determining region of the mouse Y chromosome is a member of a novel family of embryonically expressed genes. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):245–250. doi: 10.1038/346245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada H., Bustin M. Hierarchy of binding sites for chromosomal proteins HMG 1 and 2 in supercoiled deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1985 Mar 12;24(6):1428–1433. doi: 10.1021/bi00327a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley V. R., Jackson D. I., Hextall P. J., Hawkins J. R., Berkovitz G. D., Sockanathan S., Lovell-Badge R., Goodfellow P. N. DNA binding activity of recombinant SRY from normal males and XY females. Science. 1992 Jan 24;255(5043):453–456. doi: 10.1126/science.1734522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes E. N., Engelsberg B. N., Billings P. C. Purification of nuclear proteins that bind to cisplatin-damaged DNA. Identity with high mobility group proteins 1 and 2. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13520–13527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh N., Slemmon J. R., Hawke D. H., Williamson R., Morita E., Itakura K., Roberts E., Shively J. E., Crawford G. D., Salvaterra P. M. Cloning of Drosophila choline acetyltransferase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4081–4085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Admon A., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Nucleolar transcription factor hUBF contains a DNA-binding motif with homology to HMG proteins. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):830–836. doi: 10.1038/344830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loehrer P. J., Einhorn L. H. Drugs five years later. Cisplatin. Ann Intern Med. 1984 May;100(5):704–713. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-5-704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max E. E., Seidman J. G., Leder P. Sequences of five potential recombination sites encoded close to an immunoglobulin kappa constant region gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3450–3454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasrin N., Buggs C., Kong X. F., Carnazza J., Goebl M., Alexander-Bridges M. DNA-binding properties of the product of the testis-determining gene and a related protein. Nature. 1991 Nov 28;354(6351):317–320. doi: 10.1038/354317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parisi M. A., Clayton D. A. Similarity of human mitochondrial transcription factor 1 to high mobility group proteins. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):965–969. doi: 10.1126/science.2035027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pil P. M., Lippard S. J. Specific binding of chromosomal protein HMG1 to DNA damaged by the anticancer drug cisplatin. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):234–237. doi: 10.1126/science.1566071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson B., Suzuki E. Conformational properties of amino acid residues in globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1976 Nov 5;107(3):327–356. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Hüppi K., Heinrich G., Tonegawa S. Sequences at the somatic recombination sites of immunoglobulin light-chain genes. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):288–294. doi: 10.1038/280288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakata M., Hüppi K., Usuda S., Okazaki K., Yoshida K., Sakano H. HMG1-related DNA-binding protein isolated with V-(D)-J recombination signal probes. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4528–4536. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair A. H., Berta P., Palmer M. S., Hawkins J. R., Griffiths B. L., Smith M. J., Foster J. W., Frischauf A. M., Lovell-Badge R., Goodfellow P. N. A gene from the human sex-determining region encodes a protein with homology to a conserved DNA-binding motif. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):240–244. doi: 10.1038/346240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh J., Dixon G. H. High mobility group proteins 1 and 2 function as general class II transcription factors. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 3;29(26):6295–6302. doi: 10.1021/bi00478a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toney J. H., Donahue B. A., Kellett P. J., Bruhn S. L., Essigmann J. M., Lippard S. J. Isolation of cDNAs encoding a human protein that binds selectively to DNA modified by the anticancer drug cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8328–8332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis A., Amsterdam A., Belanger C., Grosschedl R. LEF-1, a gene encoding a lymphoid-specific protein with an HMG domain, regulates T-cell receptor alpha enhancer function [corrected]. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):880–894. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremethick D. J., Molloy P. L. Effects of high mobility group proteins 1 and 2 on initiation and elongation of specific transcription by RNA polymerase II in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 9;16(23):11107–11123. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.23.11107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremethick D. J., Molloy P. L. High mobility group proteins 1 and 2 stimulate transcription in vitro by RNA polymerases II and III. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):6986–6992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waga S., Mizuno S., Yoshida M. Chromosomal protein HMG1 removes the transcriptional block caused by the cruciform in supercoiled DNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19424–19428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waga S., Mizuno S., Yoshida M. Nonhistone protein HMG1 removes the transcriptional block caused by left-handed Z-form segment in a supercoiled DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 31;153(1):334–339. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81227-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman M. L., Fischer W. H., Jones K. A. A thymus-specific member of the HMG protein family regulates the human T cell receptor C alpha enhancer. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):656–669. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt F., Molloy P. L. High mobility group proteins 1 and 2 stimulate binding of a specific transcription factor to the adenovirus major late promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1471–1486. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]