Abstract
We have solved the x-ray crystal structures of the RabGAP domains of human TBC1D1 and human TBC1D4 (AS160), at 2.2 and 3.5 Å resolution, respectively. Like the yeast Gyp1p RabGAP domain, whose structure was solved previously in complex with mouse Rab33B, the human TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 domains both have 16 α-helices and no β-sheet elements. We expected the yeast Gyp1p RabGAP/mouse Rab33B structure to predict the corresponding interfaces between cognate mammalian RabGAPs and Rabs, but found that residues were poorly conserved. We further tested the relevance of this model by Ala-scanning mutagenesis, but only one of five substitutions within the inferred binding site of the TBC1D1 RabGAP significantly perturbed catalytic efficiency. In addition, substitution of TBC1D1 residues with corresponding residues from Gyp1p did not enhance catalytic efficiency. We hypothesized that biologically relevant RabGAP/Rab partners utilize additional contacts not described in the yeast Gyp1p/mouse Rab33B structure, which we predicted using our two new human TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 structures. Ala substitution of TBC1D1 Met930, corresponding to a residue outside of the Gyp1p/Rab33B contact, substantially reduced catalytic activity. GLUT4 translocation assays confirmed the biological relevance of our findings. Substitutions with lowest RabGAP activity, including catalytically dead RK and Met930 and Leu1019 predicted to perturb Rab binding, confirmed that biological activity requires contacts between cognate RabGAPs and Rabs beyond those in the yeast Gyp1p RabGAP/mouse Rab33B structure.
Keywords: Adipose Tissue Metabolism, Cell Metabolism, Crystal Structure, Glucose Transport, Protein Structure, Glucose Transporter Protein, Rab, RabGAP
Introduction
The trafficking of intracellular vesicles is regulated by Rab GTPases (Rab), which participate in Rab-mediated vesicle budding, uncoating, docking, and fusion (1, 2). Insulin-stimulated glucose uptake utilizes these processes during translocation of glucose transporter protein (e.g. GLUT4)3 vesicles from intracellular pools to the cell surface (3). TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 (also known as AS160) are Rab GTPase-activating proteins (RabGAPs) in skeletal myocytes and adipocytes, respectively, with functions in GLUT4 vesicle trafficking (4, 5). TBC1D1- and TBC1D4-catalyzed hydrolysis of Rab-bound GTP (active) to GDP (inactive) leaves GLUT4 vesicles sequestered in an intracellular compartment. Insulin-stimulated Akt phosphorylation of TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 decreases GTP hydrolysis, which increases Rab·GTP concentrations, GLUT4 vesicle translocation, and glucose uptake. Of >60 Rab proteins in mammalian genomes (1, 2), <20 associate with GLUT4 vesicles, and among them only Rabs 2A, 8A, 10, and 14 have been shown to be potential substrates for TBC1D1 or TBC1D4 (6–8).
TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 each contain ∼1300 residues. Besides catalytic RabGAP domains at their carboxyl termini, each has two putative amino-terminal phosphotyrosine binding domains whose functions are under investigation. The second phosphotyrosine binding domain has been shown to bind insulin-regulated aminopeptidase, a marker for GLUT4 vesicle (9). TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 are closely related paralogs, with 47% overall identity and 76% identity within their RabGAP domains, but they are expressed in different tissues. To further underscore their important roles in normal metabolic function, naturally occurring loss-of-function mutations in TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 RabGAP domains have been genetically linked to protection against obesity in mice (10) and defective insulin signaling in humans (11), respectively.
The structure of the yeast Gyp1p RabGAP in complex with mouse Rab33B revealed an interaction surface as well as catalytic roles for specific Arg and Gln residues (12). However, it has been difficult to use this structure to generalize details about Rab/RabGAP specificity, first because the proteins used were from such evolutionarily divergent organisms, and second because RabGAP structures are also variable. We have solved the x-ray crystal structures of the human TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 RabGAP domains and used the structures to probe Rab/RabGAP interactions relevant to GLUT4 translocation.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Protein Expression and Purification
Fragments of cDNA encoding human TBC1D1 (residues 746–1072; DNA from Open Biosystem) and human TBC1D4 (residues 873–1172; DNA from Takahiro Nagase, Kazusa DNA Research Institute) RabGAP domains and mouse Rab14 (residues 1–175; DNA from Gus Lienhard, Dartmouth University) were PCR-cloned into pET28a (Novagen) vectors. The proteins were expressed with His6 tags in Escherichia coli strain BL21 (DE3) (Stratagene) using kanamycin selection (25 μg/ml) and isolated on Ni2+-nitrilotriacetic acid columns. His tags were removed with thrombin. The proteins were further purified using a Superdex 200 sizing column (Pharmacia) in 50 mm Tris, pH 7.5, 150 mm NaCl, and concentrated to 80–100 (TBC1D1) or 15–30 (TBC1D4) mg/ml by centrifugation (Amicon Centriprep). Rab14 was loaded with GTP by incubating 4 mg of protein with a 10-fold molar excess of GTP at 4 °C for 2–3 h in 50 mm Tris, pH 7.5, 150 mm NaCl, 5 mm EDTA, and 5 mm DTT. Free GTP was removed with a desalting column (Bio-Rad) preequilibrated with 50 mm Tris, pH 7.5, and 150 mm NaCl. Rab14 aliquots were stored at −80 °C for enzyme assays.
Crystallization and Data Collection
Conditions for crystallizing the TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 RabGAP domains were found using commercial screening solutions (Hampton Research). Optimized TBC1D1 RabGAP domain crystals appeared overnight under vapor diffusion conditions in 2-μl hanging drops containing 1:1 mixtures of protein and reservoir solutions: 2.0–3.2 m ammonium formate, 0.1 HEPES, pH 7.5, and 20–25% ethylene glycol. Osmium-derivatized crystals were obtained by soaking the crystals in 10 mm ammonium hexabromoosmate (IV) or 10 mm potassium osmate (VI) dissolved in the reservoir solution. Because prolonged exposure to osmium damaged the crystals, they were frozen in liquid nitrogen after a 2-h soaking. Diffraction data for both native (2.2 Å resolution) and osmium-soaked (3.2 Å resolution) TBC1D1 RabGAP domain crystals were collected under a 100 K nitrogen stream at the National Synchrotron Light Source at Brookhaven National Laboratory in New York (NSLS X29/X12C) on a CCD detector (ADSC Quantum 315/210). Diffraction data were processed using the HKL (13) program package (Table 1). The crystals belong to the P43212 space group; Patterson analysis on the osmium-soaked crystal dataset revealed two osmium atoms/asymmetric unit.
TABLE 1.
Data collection and phasing statistics
| Parameters | TBC1D1 |
TBC1D4 (AS160) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Native | Os-peak | Os-inflection | Os-remote | ||
| Wavelength (Å) | 1.0809 | 1.1394 | 1.1399 | 1.0876 | 1.0809 |
| Resolution (Å) | 50-2.2 | 50-3.20 | 50-3.20 | 50-3.20 | 50-3.50 |
| Highest shell | 2.28-2.20 | 3.31-3.20 | 3.31-3.20 | 3.31-3.20 | 3.63-3.50 |
| Completeness (%) | 100 (100) | 100 (100) | 100 (100) | 100 (100) | 99.7 (99.7) |
| Rmergea | 0.115 (0.580) | 0.105 (0.546) | 0.107 (0.561) | 0.112 (0.570) | 0.083 (0.554) |
| I/σ (I) | 28 (5.0) | 22 (4.1) | 22 (4.0) | 21 (3.9) | 20 (3.0) |
| Redundancy | 13.0 (11.9) | 7.8 (7.8) | 7.8 (7.8) | 7.8 (7.8) | 5.3 (4.9) |
| Beamline | NSLS (X29) | NSLS (X12C) | NSLS (X12C) | NSLS (X12C) | NSLS (X29) |
| Figure of merit | 0.52 (25-3.48 Å) | ||||
a Rmerge = ΣΣj|Ij − 〈I〉|/ΣΣj Ij.
Optimized TBC1D4 (AS160) RabGAP domain crystals appeared overnight in 5–8% PEG 8000, 0.1 Tris, pH 8.5, and 35% glycerol and had a space group of P3221, 3.5 Å diffraction, and one molecule in the asymmetric unit (151 Å × 151 Å × 53 Å). Diffraction data were collected at NSLS (X29) on a CCD detector (ADSC Quantum 315) and processed as described previously (Table 1).
Structure Determination and Refinement
The initial Cα trace of the TBC1D1 RabGAP domain was built manually using the XFIT (14) program from a 3.2 Å map that had been generated with SOLVE (15); this was further modified by solvent flattening using the program DM (16). The Cα traces were converted into polyalanine chains using the program COOT (17). The initial model and the native 2.2 Å resolution dataset were analyzed together using the program ARP/wARP (18) to register side chain positions. The ARP/wARP model (initial R-factor = 0.280/Rfree = 0.280) was iteratively modified using XFIT and refined using CNS software packages (19). The final model contains two molecules of TBC1D1 RabGAP domain (residue 750–1066) with R-factor = 0.197/Rfree = 0.236 (Table 2).
TABLE 2.
Refinement statistics
| Parameters | TBC1D1 | TBC1D4 |
|---|---|---|
| Space group unit cell dimensions | P43212 (a = b = 117.36 Å, c = 141.27 Å) | P3221 (a = b = 151.21 Å, c = 53.16 Å) |
| Resolution range (Å) | 50–2.2 | 50–3.5 |
| Unique reflections (test set) | 50,676 (4,876) | 8,683 (920) |
| Wilson B (Å2) | 38.61 | 143.87 |
| R-factora (Rfree) | 0.199 (0.239) | 0.246 (0.300) |
| No. of scatters (no. of residues) | A 750–821/829–1,066 (310) B 752–1,067 (316) | 875–1,169 (295) |
| No. of water molecules | 409 | 9 |
| r.m.s.d. bonds (Å) | 0.0106 | 0.0133 |
| r.m.s.d. angles (°) | 1.606 | 1.572 |
| Average B-factor (main chain) (Å2) | 44.49 | 101.31 |
| Average B-factor (side chain) (Å2) | 44.95 | 105.58 |
| Average B-factor (water) (Å2) | 51.00 | 62.17 |
a R-factor = Σ(|Fobs| − |Fcalc|)/Σ|Fobs|.
The TBC1D4 RabGAP domain structure was determined by molecular replacement using the program PHASER (20) and the previously solved TBC1D1 structure as a search model. An automated search routine found one molecule of TBC1D4. The initial model (R-factor = 0.357/Rfree = 0.324) was iteratively modified using XFIT and refined using CNS programs; the final model contains one molecule of TBC1D4 RabGAP domain (residue 875–1169) with R-factor = 0.246/Rfree = 0.300 (Table 2). Figures were generated using PyMOL (21).
GTPase Assays
Substitutions introduced into the human TBC1D1 RabGAP domain using QuikChange mutagenesis (Stratagene) were verified by DNA sequencing. The altered proteins were expressed and purified as described above; concentrations were quantified by absorption at λ = 280 nm and further confirmed by SDS-PAGE. Kinetics of TBC1D1 RabGAP-catalyzed Rab14·GTP hydrolysis were measured using EnzChek Phosphate Assay kit (Invitrogen). Briefly, solutions containing 50 mm Tris, pH 7.5, 11 mm MgCl2, 0.2 mm 2-amino-6-mercapto-7-methylpurine riboside (MESG), 1 unit/ml purine nucleoside phosphorylase, and 30 μm GTP-loaded mouse Rab14 were mixed with various concentrations of TBC1D1 RabGAP domain variants in 96-well microplates (Corning). Absorbance changes at 360 nm were monitored with a microplate reader. Time course data at nine concentrations ranging from 20 nm to 2 μm wild-type TBC1D1 RabGAP domain were fitted to a pseudo first-order Michaelis-Menten model to obtain kcat/Km values (12). Initial velocities obtained at constant 2 μm concentration were also used to measure relative kcat/Km values for the TBC1D1 RabGAP mutants.
GLUT4 Translocation Assays
M1017A and L1106A substitutions in mouse TBC1D1, corresponding to residues Met930 and Leu1019 of human TBC1D1, were introduced by QuikChange mutagenesis into the corresponding wild-type TBC1D1 in a pCAGGS vector (mouse TBC1D1 DNA was provided by Gus Lienhard). The wild-type and the substituted full-length proteins were expressed with amino-terminal HA (hemagglutinin) tags. DNA sequences spanning the ∼3800-bp coding sequence were verified by PCR; the catalytically inactive R941K protein and the empty pCAGGS vector were provided by An Ding and Laurie Goodyear (Joslin Diabetes Center).
Cultured mouse L6 muscle cells were co-transfected with plasmids encoding myc-GLUT4-GFP (construct from Peter Schjerling) and the TBC1D1 proteins using DharmaFECT Duo Transfection Reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific). After 24 h the transfected cells were serum-deprived overnight and stimulated or not with 100 nm insulin for 10 min. More than 80% of the cells expressed both myc-GLUT4-GFP and HA-TBC1D1 as verified by co-localization (see Fig. 8B) of GFP and anti-HA fluorescence (mouse anti-HA, Cell Signaling; Cy3-conjugated anti-mouse, Jackson ImmunoResearch). Separate sets of cells were fixed with 3.6% formaldehyde, and the myc-GLUT4-GFP at the cell surface was stained with mouse anti-myc (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) and Cy3-conjugated anti-mouse antibodies. Because the myc epitope is within an extracellular loop of GLUT4, Cy3 fluorescence at the cell periphery signifies translocation; >100 cells were counted for each TBC1D1 construct.
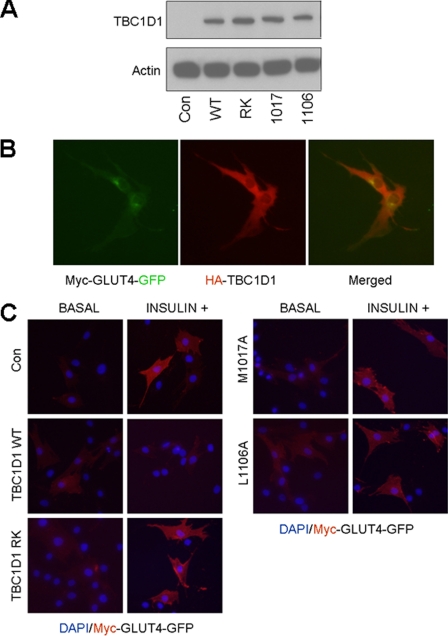
FIGURE 8.
GLUT4 translocation assay. A, equivalent expression of the TBC1D1 proteins was verified by Western blotting lysates from the transfected L6 myocytes using an anti-HA antibody. B, single-cell fluorescence assay shows co-expression of myc-GLUT4-GFP and HA-TBC1D1. C, differential effects of the HA-TBC1D1 proteins on insulin-induced myc-GLUT4-GFP translocation in L6 myocytes are shown. DAPI stains nuclei blue; Myc-GLUT4-GFP fluorescence is red due to binding of Cy3-conjugated secondary antibody.
RESULTS
Structures of the RabGAP Domains of Human TBC1D1 and TBC1D4
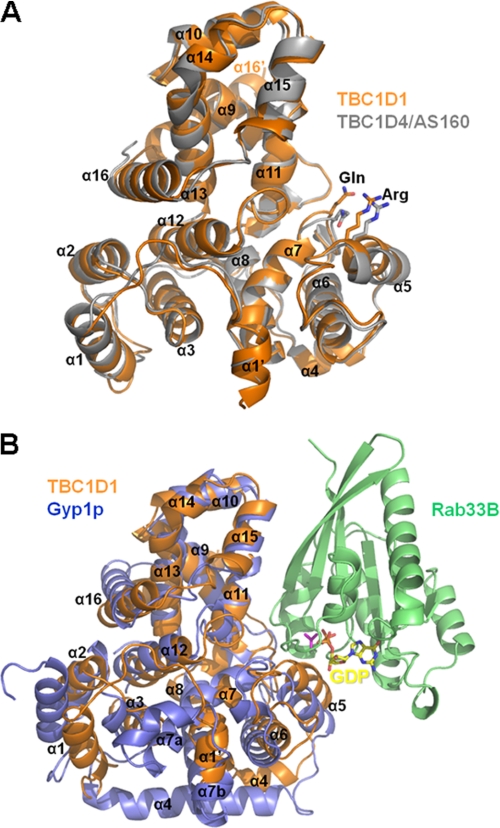
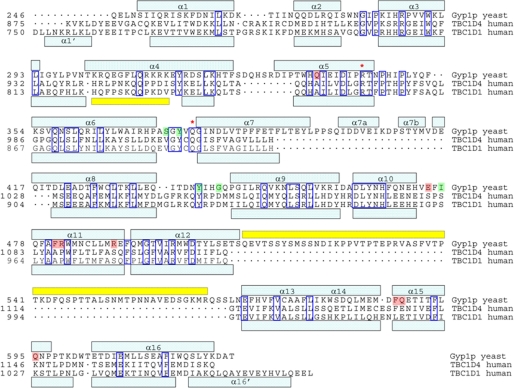
The structure of the human TBC1D1 RabGAP domain was solved at 2.2-Å resolution using multiwavelength anomalous diffraction phasing. Using this structure as a search model we subsequently solved the structure of the human TBC1D4 RabGAP domain at 3.5-Å resolution by molecular replacement. The crystals of TBC1D1 have two molecules in the asymmetric unit forming a nonsymmetrical dimer, whereas the crystals of TBC1D4 have only one molecule in the asymmetric unit. The TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 RabGAP domains share 76% identity, and their structures are accordingly similar (Cα r.m.s.d. = 0.865 Å; Fig. 1A). Like the Gyp1p RabGAP domain (22), the human TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 RabGAP domains have 16 α-helices and no β-sheet elements. The α-helices and the intervening loops are numbered sequentially from α1 to α16 as in yeast Gyp1p, with intervening loops named according to flanking helices (Fig. 2).
FIGURE 1.
Superimposed structures of TBC1D1, TBC1D4, and Gyp1p RabGAP domains. A, schematic ribbon diagrams of the superimposed TBC1D1 (orange) and TBC1D4 (gray) RabGAP domain structures are shown with catalytic residues and α-helices labeled. The structures are highly similar (Cα r.m.s.d. = 0.865 Å), with minor differences within the loops connecting the amino-terminal three helices. B, structures of the yeast Gyp1p (lavender), mouse Rab33B (green), GDP (yellow) complex (PDB 2G77), with TBC1D1 (orange) are superimposed on Gyp1p.
FIGURE 2.
Structure-based sequence alignment of Gyp1p, TBC1D1, and TBC1D4 RabGAP domains. Alignments are according to common structural elements (light blue boxes) and protein sequence. Disordered regions are denoted by yellow boxes, asterisks indicate catalytic residues, and dots denote gaps in sequence relative to other domains. Gyp1p residues important for Rab33B binding via main chain and side chain interactions are shaded green and red, respectively.
The previously reported structure of the yeast Gyp1p RabGAP domain in complex with mouse Rab33B predicted the importance of catalytic active site Arg and Gln residues as accelerators of GTP hydrolysis through a novel dual-finger mechanism (22). TBC1D1 Arg854 and TBC1D4 Arg973 in α5 and TBC1D1 Gln891 (TBC1D4 Gln1010) in the α6/α7 loops are parts of the highly conserved RabGAP signature motifs (IXXDXXR and YXQ) that are clearly seen as solvent-exposed residues in our structures (Fig. 1).
The previously reported Gyp1p RabGAP/Rab33B structure also revealed a Rab/RabGAP interaction surface, which we used to predict the potential interaction surfaces for the TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 domains and corresponding Rabs by superimposing the RabGAP domain structures (12) (Figs. 1B and 2). The Rab binding surface of Gyp1p comprises side chains of residues in α5, α11, and α15, and main-chain interactions with residues in the α6/α7, α8/α9, and α10/α11 loops (Fig. 2).
Comparison of the Structures of Human TBC1D1 and Yeast Gyp1p RabGAP
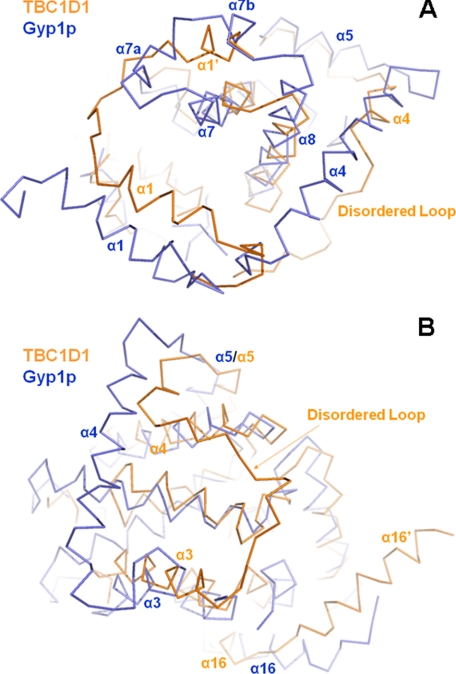
Yeast Gyp1p and the human TBC1D1 (or TBC1D4) RabGAP domains share weaker 19% sequence identity and have correspondingly significantly lower structural similarities (Cα r.m.s.d. = 1.89 Å). This is true even when the most closely overlapping 231 residues of 390 total Gyp1p residues and 320 total TBC1D1 residues are compared (Figs. 1B and 2). The most obvious structural differences between the Gyp1p and TBC1D1 RabGAP domains are the lengths of the α-helices and the intervening loops. At the amino terminus of TBC1D1 and preceding α1 is an ancillary helix, termed α1′, which is not present in the Gyp1p domain (Fig. 2). Carboxyl- and amino-terminal extensions of α7 and α8, respectively, and two short ancillary helices α7a and α7b in the Gyp1p domain, are not found in TBC1D1, but the corresponding space in the TBC1D1 structure is alternatively occupied by the ancillary α1′ helix (Fig. 3A). Other structural element that distinguish the TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 domains relative to the Gyp1p domain are extended α3 and shortened α4 segments, which shift the α3/α4 loops to significantly different orientations (Figs. 2 and 3B). The α3/α4 loops in both TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 also have high temperature factors, indicating substantial motion and flexibility in these regions of the structures.
FIGURE 3.
Structural comparisons among TBC1D1, TBC1D4, and Gyp1p RabGAP domains. A, significant differences between Gyp1p and TBC1D1 or TBC1D4 are the residues between Gyp1p α7 and α8, creating α7a and α7b, which are absent in TBC1D1 and TBC1D4. The space occupied by these short helices in Gyp1p is occupied in TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 by the alternative ancillary helix α1′. B, α4 in Gyp1p is also much longer than in the TBC1D domains. Much of this region in TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 is a disordered loop.
In addition, α16 at the carboxyl terminus of TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 is followed by an ancillary helix, termed α16′, which is not present in Gyp1p. The longitudinal axes of α16 and α16′ are at ∼110° angles relative to one another. TBC1D1 molecules form nonsymmetrical dimers in the crystals through interactions of α16′ from one subunit with α16 of the other subunit via an antiparallel α-helix bundle. This likely represents crystallographic packing, and not a biologically relevant interaction, as TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 RabGAP domains appear to be monomeric in solution.4
RabGAP Activities of Human TBC1D1 and TBC1D4
GTPase hydrolysis kinetics were determined for human TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 RabGAP domains using mouse Rab14·GTP as the substrate. Rab14 was chosen because only it and Rabs 2A, 8A, and 10, of <20 total Rabs in mammalian proteomes that co-purify with GLUT4 vesicles, have been shown to be in vitro substrates for TBC1D1 or TBC1D4 (6). We also attempted to use Rab10 as a substrate for TBC1D4 (9), but were unable to generate the quantities of purified recombinant Rab10 needed for these assays.
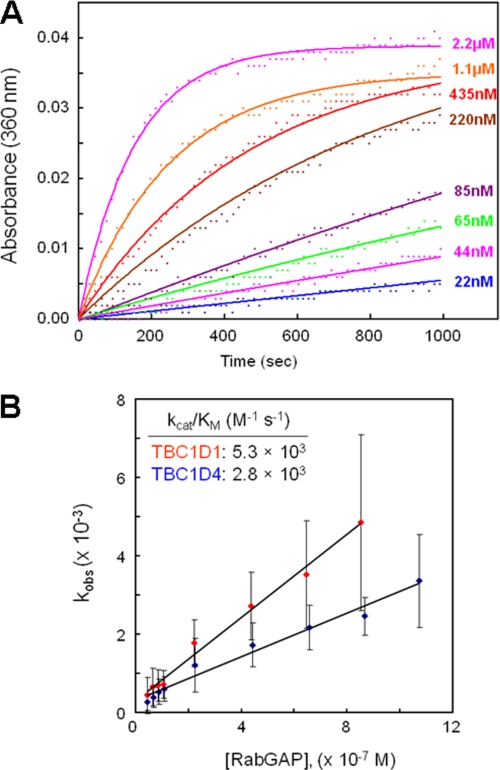
Free phosphate generated in the assays by TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 RabGAP-catalyzed GTP hydrolysis was detected spectrophotometrically (Fig. 4A). With Rab14·GTP as the substrate, catalytic efficiency parameters kcat/Km for TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 RabGAP domains were 5300 and 2800 m−1s−1, respectively (Fig. 4B). As anticipated, RabGAP activity was abolished by substitution of invariant residues R854A, Q891A, and D851A within the catalytic pocket (see Fig. 7A).
FIGURE 4.
Catalytic activities of TBC1D1 RabGAP domains. A, TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 RabGAP domains were used to catalyze hydrolysis of Rab14-loaded GTP. For each RabGAP domain concentration, kobs was fitted using a pseudo first-order Michaelis-Menten model (A(t) = (A∞ − A0) (1 − exp(−kobst)) + A0). B, the catalytic efficiency parameter, Kcat/Km, was calculated by plotting kobs against TBC1D1 concentration, and the slopes of the best fit lines provide kcat/Km values.
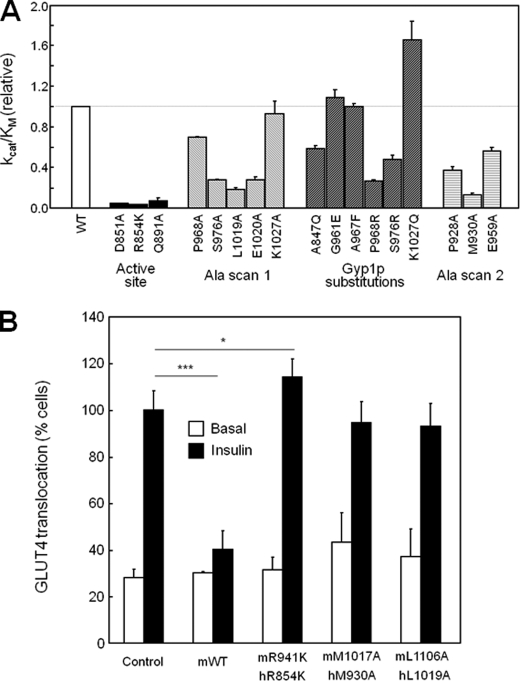
FIGURE 7.
Assay results for catalytic activity and GLUT4 translocation. A, relative kcat/Km values for RabGAPs against GTP-loaded Rab14 are plotted relative to WT protein kcat/Km. B, L6 muscle cells expressing a myc-GLUT4-GFP reporter were transfected with plasmids expressing WT or substituted mouse TBC1D1 proteins (numbering for the human protein provided for comparison). *, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.0005.
Catalytic Activities of Substituted TBC1D1 Proteins
Direct binding assays would have been useful to assess the importance of residues at the Rab/RabGAP interfaces, but neither we nor others in the field have successfully detected binding (results not shown).5 We therefore used the GTPase assay as a very useful measure that integrates binding with catalysis. From the structure of the yeast Gyp1p RabGAP·mouse Rab33B complex, we predicted potential interaction surfaces between Rabs and TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 (Figs. 1B and 2). We expected that relevant residues along α5, α11, and α15, where side chain interactions with Rab are observed, to be conserved between Gyp1p and both TBC1D1/TBC1D4. However, our structures showed that the side chains of Gyp1p that participate in Rab33B binding through either hydrogen bonds (Gln336, Glu475, Arg482, Arg490, and Gln603) or hydrophobic clusters (Phe481, Phe595, and Gln596) are not conserved in TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 (Fig. 5A, Gyp1p/TBC1D1/TBC1D4: Gln336/Ala847/Ala866, Glu475/Gly961/Ser980, Arg482/Pro968/Pro987, Arg490/Ser976/Ser995, Gln603/Lys1027/Lys1046, Phe481/Ala967/Ala986, Phe595/Leu1019/Phe1038, and Gln596/Glu1020/Glu1039). On the other hand, the side chains of mouse Rab33B interacting with the side chains of Gyp1p residues are well conserved in putative TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 Rab partners, including mammalian Rab10 and Rab14 (Fig. 6). This also suggests that side chain residues different from those predicted by the Gyp1p/Rab33B structure may participate in forming TBC1D1 RabGAP/Rab interfaces.
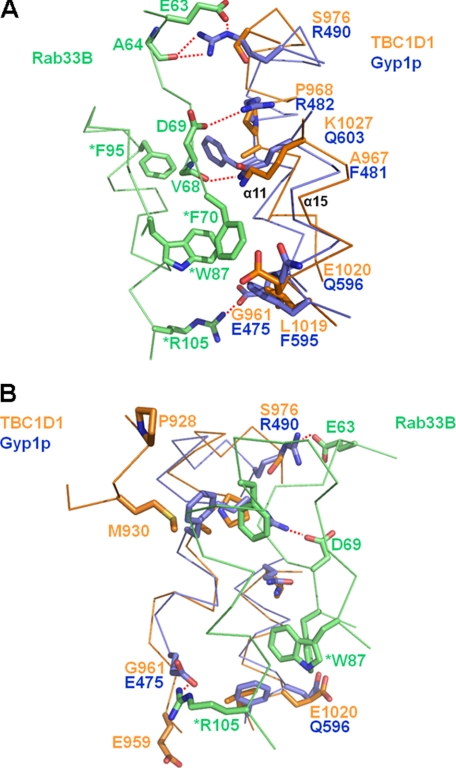
FIGURE 5.
Lack of sequence similarity at Rab binding surfaces of TBC1D1 and Gyp1p. A, Rab binding surfaces predicted by the Gyp1p/Rab33B structure are poorly conserved between TBC1D1 and Gyp1p. B, because the sequence conservation is so low, we predicted additional solvent-exposed residues of TBC1D1 (Pro928, Met930, and Glu959) that might participate in Rab binding.
FIGURE 6.
Sequence alignment of mammalian Rab proteins at the predicted RabGAP interface. The buried region of mouse Rab33B at the yeast Gyp1p interface was aligned with other human Rab proteins reported potentially to interact with TBC1D proteins during GLUT4 trafficking. Rab residues important for Gyp1p RabGAP binding via main chain and side chain interactions are colored green and red, respectively.
Although there was little sequence conservation at the relevant RabGAP surface, we constructed a series of TBC1D1 domains containing Ala residues in place of the residues of Gyp1p that interact with Rab33B (P968A, S976A, L1019A, E1020A, and K1027A) in the crystal structure (12). The Ala-substituted TBC1D1 RabGAPs were tested for catalytic activities against Rab14·GTP (attempts to pull down Rab14 with either TBC1D1 or TBC1D4, or to induce complex formation using either a nonhydrolyzable GTP analog or the transition state mimetic, GDP-AlFx, have consistently failed). Of note, the bacterial expression efficiencies, protein solubilities, and aggregation states of the substituted proteins were similar to those of the wild-type protein (results not shown), suggesting proper protein folding. Nevertheless, two of the five substituted proteins (P968A, K1027A) had near-normal catalytic efficiencies, two were reduced ∼3-fold (S976A, E1020A), and only one, the L1019A substitution, diminished GTP hydrolysis >5-fold (Fig. 7A). Leu1019 of TBC1D1 aligns with Phe595 of Gyp1p, whose side chain participates in a hydrophobic cluster at the Gyp1p/Rab33B interface. The corresponding residue of TBC1D4 is Phe1038, suggesting that either Leu or Phe may be accommodated at this site. The fact that two of the substitutions lacked effects suggests that side chains Pro968 and Lys1027 of TBC1D1 are unimportant for binding and catalysis, which counters predictions from the Gyp1p/Rab33B structure.
Because the residues are well conserved among mammalian Rabs (Fig. 6), we also asked whether changing TBC1D1 residues to the corresponding Gyp1p residues improved TBC1D1 catalytic efficiency toward Rab14·GTP. None of the mutants (P968R, S976R, K1027Q, A847Q, G961E, and A967F) showed >2-fold increase in the efficiency of GTP hydrolysis (Fig. 7A). These results suggest that although general modes of Rab binding may be conserved between TBC1D1 and Gyp1p, the contact residues between the TBC1D1 and Rab14 likely differ significantly from those at the yeast Gyp1p/mouse Rab33B interface.
To further test whether the Gyp1p:Rab33B structure predicts mammalian RabGAP/Rab binding in general, and TBC1D1/Rab14 binding in particular, we substituted residues at the periphery of the defined Gyp1p and Rab33B interface (Fig. 5B). The three selected residues of TBC1D1, Pro928 and Met930 in the α8/α9 loop and Glu959 in the α10/α11 loop, correspond to residues of Gyp1p that make main chain but not side chain contacts with Rab33B. M930A in particular resulted in >5-fold decrease in catalytic efficiency, indicating that the hydrophobic side chain of Met930 in the α8/α9 loop is important in TBC1D1/Rab14 interactions (Fig. 7A).
To summarize, we compared the previously solved structure of a yeast Gyp1p RabGAP·mouse Rab33B complex with the new structures of human TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 RabGAP domains reported here to predict residues potentially involved in TBC1D1 or TBC1D4 RabGAP·Rab binding. Because it has not been possible to study binding directly, we used enzymatic assays as a surrogate method for assessing binding. Based on diminished activity for TBC1D1 substitutions L1019A and M930A, we conclude that these residues are involved at relevant mammalian TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 RabGAP/Rab interfaces.
TBC1D1/Endogenous Rab Interactions in GLUT4 Translocation Assays
Subsequent experiments determined whether the predictions and conclusions from the aforementioned structure-function studies apply to interactions between TBC1D1 proteins and endogenous Rabs in living cells. To accomplish this we expressed wild-type and alanine-substituted TBC1D1 proteins in cultured mouse L6 muscle cells that had been engineered to monitor GLUT4 translocation through the stable expression of labeled GLUT4. The substituted residues that reduced human TBC1D1 RabGAP activity in the enzymatic GTPase assays (M930A and L1019A) were incorporated into the conserved sites of full-length mouse TBC1D1 (M1017A and L1106A) and expressed in the L6 myocytes (Fig. 8A). Cells expressing wild-type or catalytically inactive mouse R941K (human R854K) TBC1D1 served as positive and dominant negative controls, respectively, and numbers of cells positive for insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation were determined (23).
Insulin stimulated a 3–4-fold increase in the number of cells with GLUT4 at the surface in cells transfected with the empty vector control. By contrast, the expression of catalytically active wild-type TBC1D1, which converts active RabGTP to inactive RabGDP, blocked insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation to the cell surface (Figs. 7B and 8C) (23). The expression of R854K TBC1D1, with a catalytically inactive RabGAP domain, mildly stimulated GLUT4 translocation (Figs. 7B and 8C). This is consistent with a dominant inhibitory effect of the R854K mutant, which retains Rab binding but lacks catalytic activity, thus suppressing normal insulin signaling mediated by endogenous proteins. Expression of the L1019A- and M930A-substituted TBC1D1 proteins had no effect on GLUT4 translocation. The results from the myocyte GLUT4 translocation assays agree with results from the in vitro TBC1D1/Rab14 GTPase assays, which showed that these substitutions rendered TBC1D1 catalytically inactive. However, our structures predicted that the L1019A and M930A substitutions would inhibit TBC1D1/Rab binding, which therefore inhibits catalysis through a distinct mechanism that is not dominant inhibitory, compared with the R854K mutant protein. These data confirm the biological relevance of Leu1019 and Met930 on interactions of TBC1D1 with endogenous Rab partner proteins.
DISCUSSION
We have solved structures of the RabGAP domains of human TBC1D1 and TBC1D4, two proteins directly involved in the trafficking and translocation of GLUT4-containing vesicles and insulin-stimulated glucose uptake into cells. Although the two RabGAP structures resemble the previously determined yeast Gyp1p RabGAP domain, as each has 16 α-helices and the same protein fold, the length of the helical elements and the loops connecting the helices differ. For example, the two short ancillary helices (α7a and α7b) between α7 and α8 of yeast Gyp1p are not present in TBC1D1 or TBC1D4. The corresponding space in TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 is occupied instead by an ancillary helix (α1′) unique among RabGAPs. The α7/α8 loops of RabGAPs vary significantly in both sequence and length, even among yeast Gyp RabGAP homologs, and the function of this region is unknown (21). Another significant difference between TBC1D1 (and TBC1D4) and Gyp1p is in α3 and α4, which changes the orientation of the α3/α4 loop. However, these differences may not affect Rab binding affinity or specificity because they are opposite the catalytic active site. Determining the functional relevance of these structural differences requires further experimentation.
We measured catalytic activities for TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 RabGAPs using Rab14·GTP as the substrate. For TBC1D1, kcat/Km = 5300 m−1s−1 whereas for TBC1D4, kcat/Km = 2800 m−1s−1. These are lower than the kcat/Km value of 100,000 m−1s−1 reported for yeast Gyp1p RabGAP toward mouse Rab33B·GTP (12), but within a typical range for yeast Gyp1p toward native yeast substrates (Sec4p kcat/Km = 2000 m−1s−1; Ypt1p kcat/Km = 26,000 m−1s−1) (12). The relatively high Km value (low affinity) for TBC1D1 toward Rab14·GTP helps to explain why we and others have been unsuccessful at co-precipitating either GLUT4 vesicle-associating Rabs or recombinant Rab14 using TBC1D1 or TBC1D4 RabGAP proteins. This has been especially problematic for studies aimed at identifying biologically relevant Rab partners for TBC1D1 and TBC1D4, which remain unknown. It is possible that our reported kcat/Km values underestimate in vivo catalytic efficiencies, as the recombinant RabGAP proteins used for these measurements are taken out of the context of the intact TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 proteins. Other regions likely participate in protein/membrane or protein/protein interactions, including the phosphotyrosine binding domains of TBC1D1 and TBC1D4. Their phosphotyrosine binding domains may interact with insulin-regulated aminopeptidase in GLUT4 vesicles (11), which would increase the local concentrations of TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 near membrane-bound Rabs.
We had hoped that the structure of yeast Gyp1p RabGAP in complex with mouse Rab33B (12) would accurately predict corresponding interactions between TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 RabGAPs and biologically relevant, same-species Rab partners. This is partly true, but there also appear to be differences. The residues of Gyp1p that form hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic clusters at the Rab33B interface are not conserved in TBC1D1 and TBC1D4, suggesting that TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 recognize biologically relevant Rab partners differently. We tested this using an alanine-scanning approach to probe the functional relevance of corresponding residues of TBC1D1 and TBC1D4. We were surprised to find that two substitutions (P968A and K1027A) had little effect, two others had modest effects (S976A and E1020A), and only one substitution (L1019A) of the five tested showed >5-fold effect on catalytic efficiency. Based on these results, we asked whether additional residues of TBC1D1 corresponding to the buried surface of Gyp1p, but not actually present in Gyp1p, might also participate. Using this approach we found that substitution of Met930, in the α8/α9 loop of TBC1D1, reduced RabGAP activity. Side chains of residues in the corresponding loop of Gyp1p are not at the Gyp1p/Rab33B interface and thus do not participate in binding. The cellular GLUT4 translocation assays provided a very important confirmation that Leu1019 and Met930 are critical for TBC1D1 interactions with endogenous Rabs, as either substitution alone was sufficient to abrogate GLUT4 translocation.
In conclusion, althoughTBC1D1 and TBC1D4 share general modes of RabGAP/Rab binding with Gyp1p/Rab33B, additional structural elements (e.g. side chains of residues in the α8/α9 loop, including Met930) not identified in the yeast/mouse hybrid structure contribute to the molecular contact surface between corresponding mammalian RabGAP/Rab proteins. The perfect complementarity of proteins within biologically relevant complexes results during and requires co-evolution, the fundamental driver of biological specificity. It is therefore not surprising that the Gyp1p/Rab33B structure provides an incomplete picture of mammalian RabGAP/Rab interactions, given up to a billion years of evolutionary distance between yeast and mammals. Gyp1p and TBC1D1/4 are also more structurally divergent than Gyp1p and certain other mammalian RabGAP proteins, such as TBC1D22B, which may further diminish our capacity to extrapolate from the Gyp1p/Rab33B structure. Although we had aimed to crystallize TBC1D1 and TBC1D4 RabGAPs in complex with relevant same-species Rabs, to date this has not been successful. The Gyp1p/Rab33B structure remains the only high resolution structure of any RabGAP/Rab complex. A more complete picture TBC1D1 or TBC1D4 RabGAP/Rab binding thus awaits the successful solutions of such same-species protein complexes.
This work was supported, in whole or in part, by National Institutes of Health Grants R01 DK43123 and R01 DK51729 (to S. E. S.), F32 DK77485 (to S.-Y. P.), and P30 DK36836 (to the Joslin Diabetes Center). Data were collected at beams X29A and X12C of National Synchrotron Light Source, Brookhaven National Laboratory, which is supported by the United States Department of Energy, Division of Materials Sciences and Division of Chemical Sciences, Contract DE-AC02-98CH10886.
The atomic coordinates and structure factors (codes 3QYB and 3QYE) have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank, Research Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformatics, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, NJ (http://www.rcsb.org/).
S.-Y. Park, unpublished results.
Gus Lienhard, unpublished results.
- GLUT4
- glucose transporter 4
- RabGAP
- RabGTPase-activating protein
- r.m.s.d.
- root mean square deviation
- TBC1D
- Tre-2, Bub2, and Cdc16-1 domain.
REFERENCES
- 1. Zerial M., McBride H. (2001) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2, 107–117 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Stenmark H. (2009) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 10, 513–525 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Watson R. T., Pessin J. E. (2006) Trends Biochem. Sci. 31, 215–222 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Kane S., Sano H., Liu S. C., Asara J. M., Lane W. S., Garner C. C., Lienhard G. E. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 22115–22118 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Sano H., Kane S., Sano E., Mîinea C. P., Asara J. M., Lane W. S., Garner C. W., Lienhard G. E. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278, 14599–14602 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Mîinea C. P., Sano H., Kane S., Sano E., Fukuda M., Peränen J., Lane W. S., Lienhard G. E. (2005) Biochem. J. 391, 87–93 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Sano H., Eguez L., Teruel M. N., Fukuda M., Chuang T. D., Chavez J. A., Lienhard G. E., McGraw T. E. (2007) Cell Metab. 5, 293–303 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Sano H., Roach W. G., Peck G. R., Fukuda M., Lienhard G. E. (2008) Biochem. J. 411, 89–95 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Peck G. R., Ye S., Pham V., Fernando R. N., Macaulay S. L., Chai S. Y., Albiston A. L. (2006) Mol. Endocrinol. 20, 2576–2583 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Chadt A., Leicht K., Deshmukh A., Jiang L. Q., Scherneck S., Bernhardt U., Dreja T., Vogel H., Schmolz K., Kluge R., Zierath J. R., Hultschig C., Hoeben R. C., Schürmann A., Joost H. G., Al-Hasani H. (2008) Nat. Genet. 40, 1354–1359 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Dash S., Sano H., Rochford J. J., Semple R. K., Yeo G., Hyden C. S., Soos M. A., Clark J., Rodin A., Langenberg C., Druet C., Fawcett K. A., Tung Y. C., Wareham N. J., Barroso I., Lienhard G. E., O'Rahilly S., Savage D. B. (2009) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 9350–9355 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Pan X., Eathiraj S., Munson M., Lambright D. G. (2006) Nature 442, 303–306 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Otwinowski Z., Minor W. (1997) Methods Enzymol. 276, 307–326 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. McRee D. E. (1999) J. Struct. Biol. 125, 156–165 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Terwilliger T. C., Berendzen J. (1999) Acta Crystallogr. D 55, 849–861 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Cowtan K. (1994) Joint CCP4 and ESF-EACBM Newsletter on Protein Crystallography 31, 34–38 [Google Scholar]
- 17. Emsley P., Cowtan K. (2004) Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 60, 2126–2132 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Perrakis A., Morris R., Lamzin V. S. (1999) Nat. Struct. Biol. 6, 458–463 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Brünger A. T., Adams P. D., Clore G. M., DeLano W. L., Gros P., Grosse-Kunstleve R. W., Jiang J. S., Kuszewski J., Nilges M., Pannu N. S., Read R. J., Rice L. M., Simonson T., Warren G. L. (1998) Acta Crystallogr. D 54, 905–921 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. McCoy A. J., Grosse-Kunstleve R. W., Storoni L. C., Read R. J. (2005) Acta Crystallogr. D 61, 458–464 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. DeLano W. L. (2010) The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, version 1.3r1, Schrödinger, LLC, New York [Google Scholar]
- 22. Rak A., Fedorov R., Alexandrov K., Albert S., Goody R. S., Gallwitz D., Scheidig A. J. (2000) EMBO J. 19, 5105–5113 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Roach W. G., Chavez J. A., Mîinea C. P., Lienhard G. E. (2007) Biochem. J. 403, 353–358 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]