Abstract
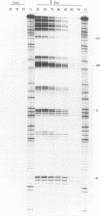
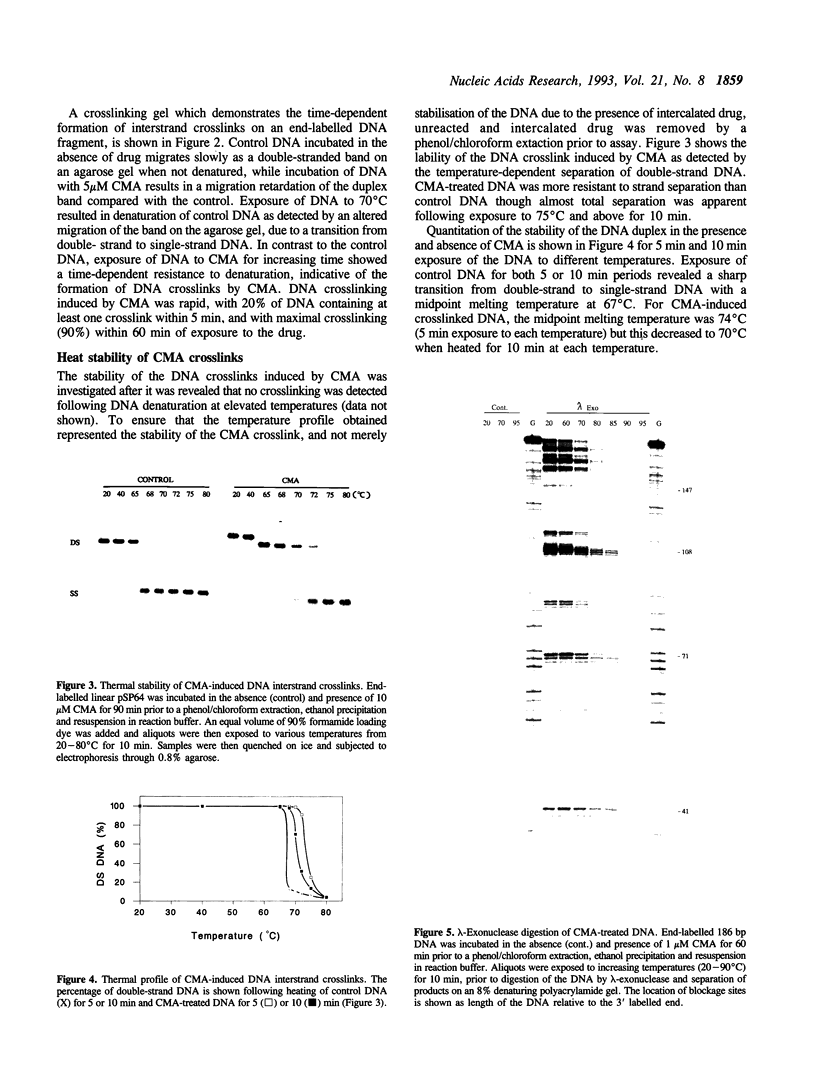
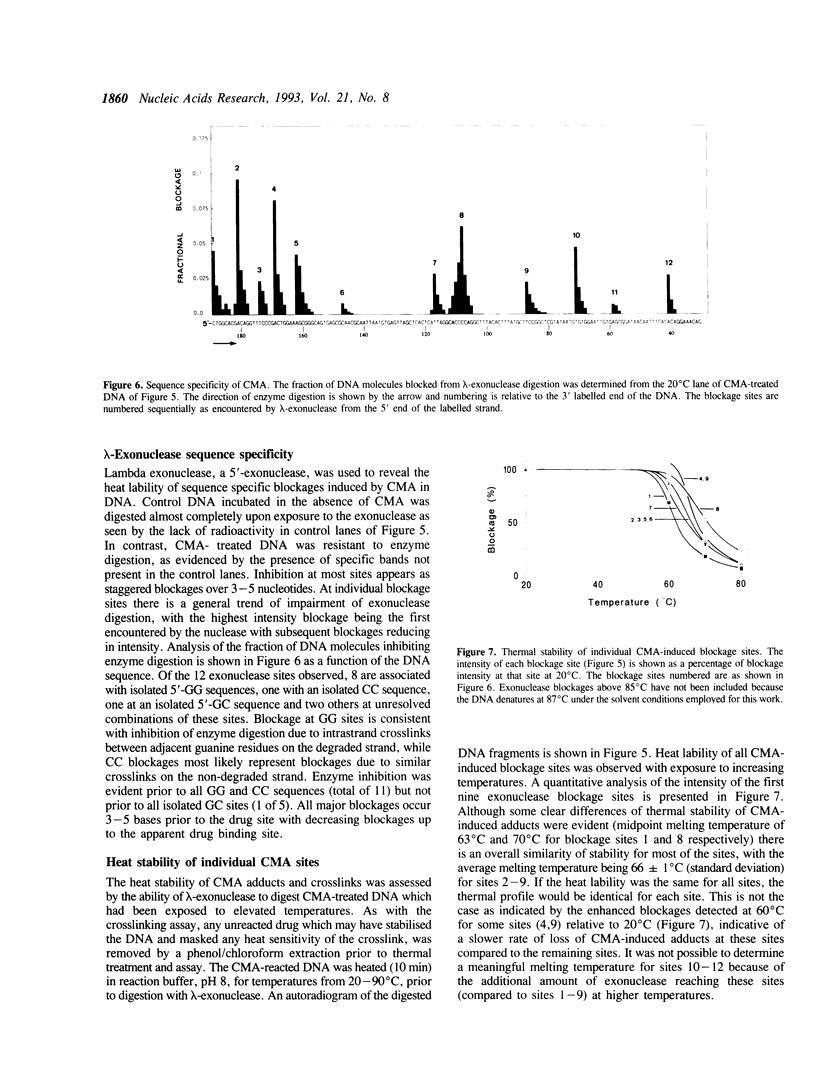
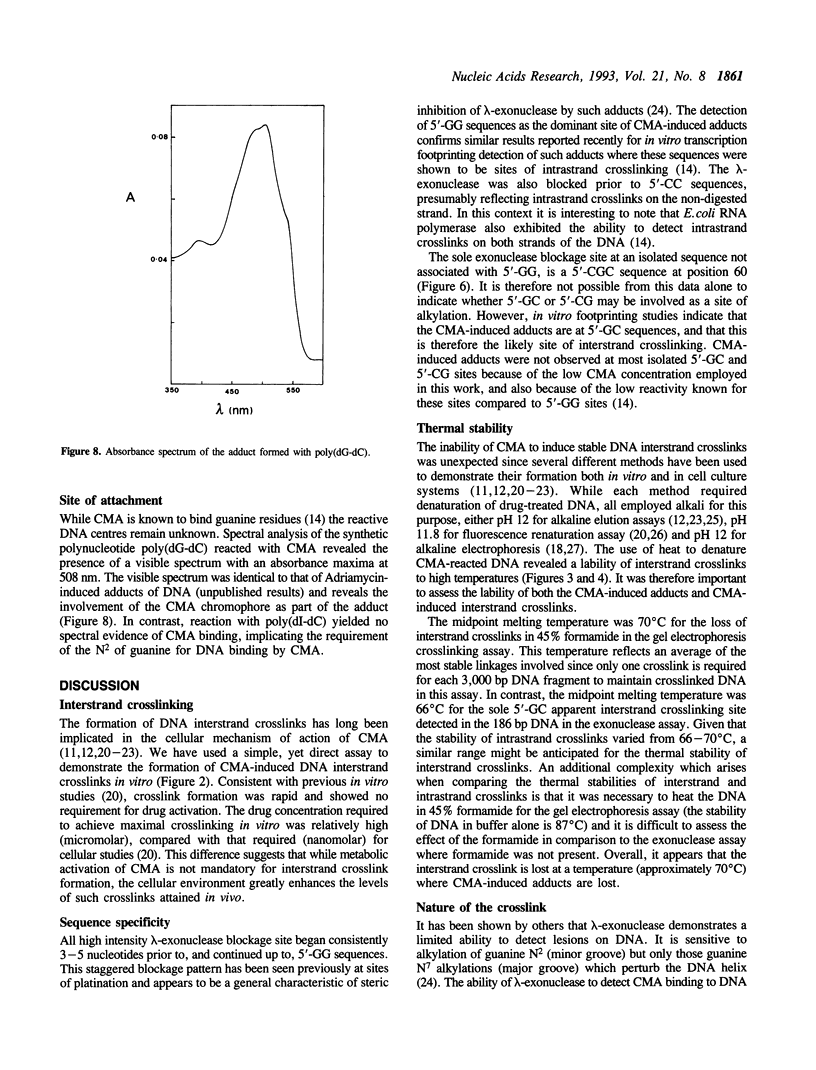
The Adriamycin derivative, cyanomorpholinoadriamycin (CMA) was reacted with DNA in vitro to form apparent interstrand crosslinks. The extent of interstrand crosslink formation was monitored by a gel electrophoresis assay and maximal crosslinking of DNA was observed within 1 hr with 5 microM of drug. The interstrand crosslinks were heat labile, with a midpoint melting temperature of 70 degrees C (10 min exposure to heat) in 45% formamide. When CMA-induced adducts were detected as blockages of lambda-exonuclease, 12 blockage sites were observed with 8 being prior to 5'-GG sequences, one prior to 5'-CC, one prior to 5'-GC and 2 at unresolved combinations of these sequences. These exonuclease-detected blockages reveal the same sites of CMA-induced crosslinking as detected by in vitro transcription footprinting and primer-extension blockages on single strand DNA, where the blockages at 5'-GG and 5'-CC were identified as sites of intrastrand crosslinking and the 5'-GC blockage as a probable site of interstrand crosslinking. The thermal stability of both types of crosslink (10 min exposure to heat) ranged from 63-70 degrees C at individual sites. High levels of adduct were detected with poly (dG-dC) but not with poly (dI-dC). These results suggest adduct formation involving an aminal linkage between the 3 position of the morpholino moiety and N2 of guanine.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acton E. M., Tong G. L., Mosher C. W., Wolgemuth R. L. Intensely potent morpholinyl anthracyclines. J Med Chem. 1984 May;27(5):638–645. doi: 10.1021/jm00371a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begleiter A., Johnston J. B. DNA crosslinking by 3'-(3-cyano-4-morpholinyl)-3'-deaminoadriamycin in HT-29 human colon carcinoma cells in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 30;131(1):336–338. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91807-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullinane C., Phillips D. R. In vitro transcription analysis of DNA adducts induced by cyanomorpholinoadriamycin. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 13;31(40):9513–9519. doi: 10.1021/bi00155a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullinane C., Phillips D. R. The DNA sequence specificity of cyanomorpholinoadriamycin. FEBS Lett. 1991 Nov 18;293(1-2):195–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81185-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu L. X., Waagstein F., Hjalmarson A. A new insight into adriamycin-induced cardiotoxicity. Int J Cardiol. 1990 Oct;29(1):15–20. doi: 10.1016/0167-5273(90)90267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. A., Berardini M. D., Souhami R. L. An agarose gel method for the determination of DNA interstrand crosslinking applicable to the measurement of the rate of total and "second-arm" crosslink reactions. Anal Biochem. 1991 Feb 15;193(1):131–134. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90052-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg R. P., Hecht S. M., Reynolds V. L., Molineux I. J., Hurley L. H. DNA sequence specificity of the pyrrolo[1,4]benzodiazepine antitumor antibiotics. Methidiumpropyl-EDTA-iron(II) footprinting analysis of DNA binding sites for anthramycin and related drugs. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 25;25(6):1249–1258. doi: 10.1021/bi00354a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesson M. I., Johnston J. B., Robotham E., Begleiter A. Characterization of the DNA-DNA cross-linking activity of 3'-(3-cyano-4-morpholinyl)-3'-deaminoadriamycin. Cancer Res. 1989 Dec 15;49(24 Pt 1):7031–7036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau D. H., Durán G. E., Sikic B. I. Characterization of covalent DNA binding of morpholino and cyanomorpholino derivatives of doxorubicin. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992 Oct 21;84(20):1587–1592. doi: 10.1093/jnci/84.20.1587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lown J. W., Begleiter A., Johnson D., Morgan A. R. Studies related to antitumor antibiotics. Part V. Reactions of mitomycin C with DNA examined by ethidium fluorescence assay. Can J Biochem. 1976 Feb;54(2):110–119. doi: 10.1139/o76-018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lown J. W., Joshua A. V., Lee J. S. Molecular mechanisms of binding and single-strand scission of deoxyribonucleic acid by the antitumor antibiotics saframycins A and C. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 2;21(3):419–428. doi: 10.1021/bi00532a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattes W. B. Lesion selectivity in blockage of lambda exonuclease by DNA damage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3723–3730. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrusek R. L., Anderson G. L., Garner T. F., Fannin Q. L., Kaplan D. J., Zimmer S. G., Hurley L. H. Pyrrol[1,4]benzodiazepine antibiotics. Proposed structures and characteristics of the in vitro deoxyribonucleic acid adducts of anthramycin, tomaymycin, sibiromycin, and neothramycins A and B. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1111–1119. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao K. E., Lown J. W. DNA sequence selectivities in the covalent bonding of antibiotic saframycins Mx1, Mx3, A, and S deduced from MPE.Fe(II) footprinting and exonuclease III stop assays. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 8;31(48):12076–12082. doi: 10.1021/bi00163a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scudder S. A., Brown J. M., Sikic B. I. DNA cross-linking and cytotoxicity of the alkylating cyanomorpholino derivative of doxorubicin in multidrug-resistant cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1988 Oct 19;80(16):1294–1298. doi: 10.1093/jnci/80.16.1294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha B. K. Free radicals in anticancer drug pharmacology. Chem Biol Interact. 1989;69(4):293–317. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(89)90117-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skorobogaty A., White R. J., Phillips D. R., Reiss J. A. Elucidation of the DNA sequence preferences of daunomycin. Drug Des Deliv. 1988 Jul;3(2):125–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassermann K., Markovits J., Jaxel C., Capranico G., Kohn K. W., Pommier Y. Effects of morpholinyl doxorubicins, doxorubicin, and actinomycin D on mammalian DNA topoisomerases I and II. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;38(1):38–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassermann K., Zwelling L. A., Mullins T. D., Silberman L. E., Andersson B. S., Bakic M., Acton E. M., Newman R. A. Effects of 3'-deamino-3'-(3-cyano-4-morpholinyl)doxorubicin and doxorubicin on the survival, DNA integrity, and nucleolar morphology of human leukemia cells in vitro. Cancer Res. 1986 Aug;46(8):4041–4046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westendorf J., Aydin M., Groth G., Weller O., Marquardt H. Mechanistic aspects of DNA damage by morpholinyl and cyanomorpholinyl anthracyclines. Cancer Res. 1989 Oct 1;49(19):5262–5266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. J., Phillips D. R. Transcriptional analysis of multisite drug-DNA dissociation kinetics: delayed termination of transcription by actinomycin D. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 27;27(26):9122–9132. doi: 10.1021/bi00426a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. C., Ozols R. F., Myers C. E. The anthracycline antineoplastic drugs. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jul 16;305(3):139–153. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198107163050305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]