Abstract
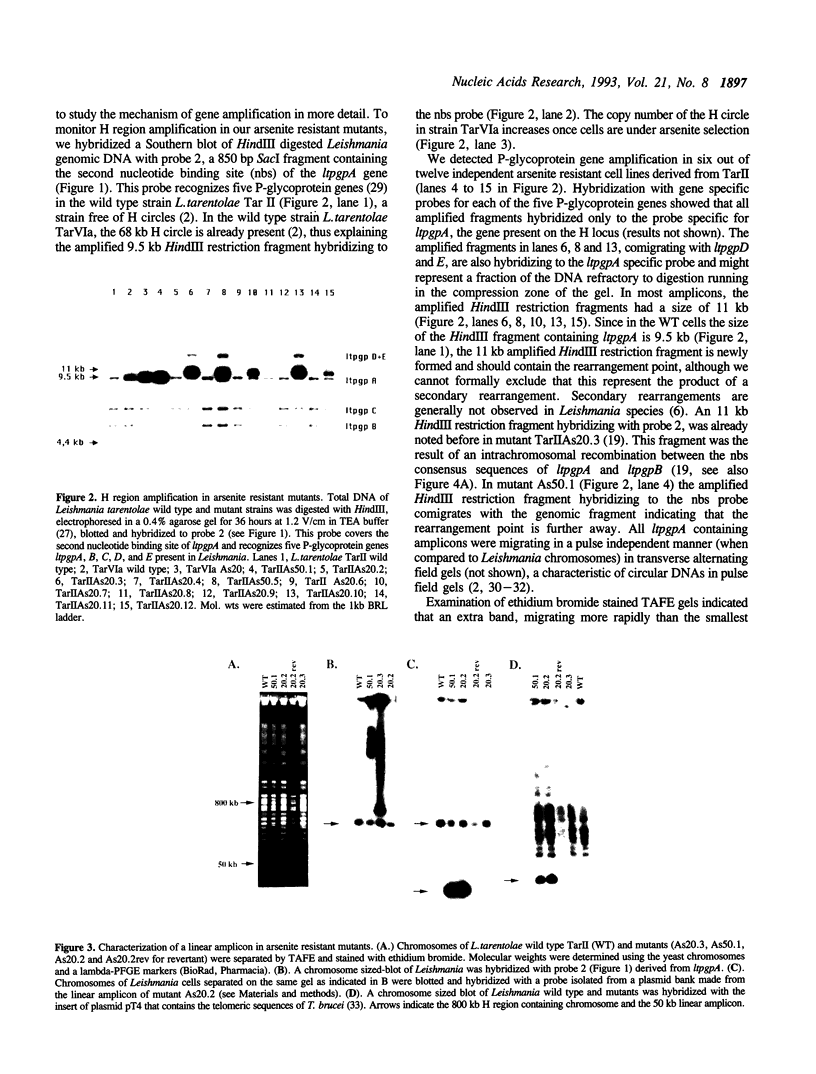
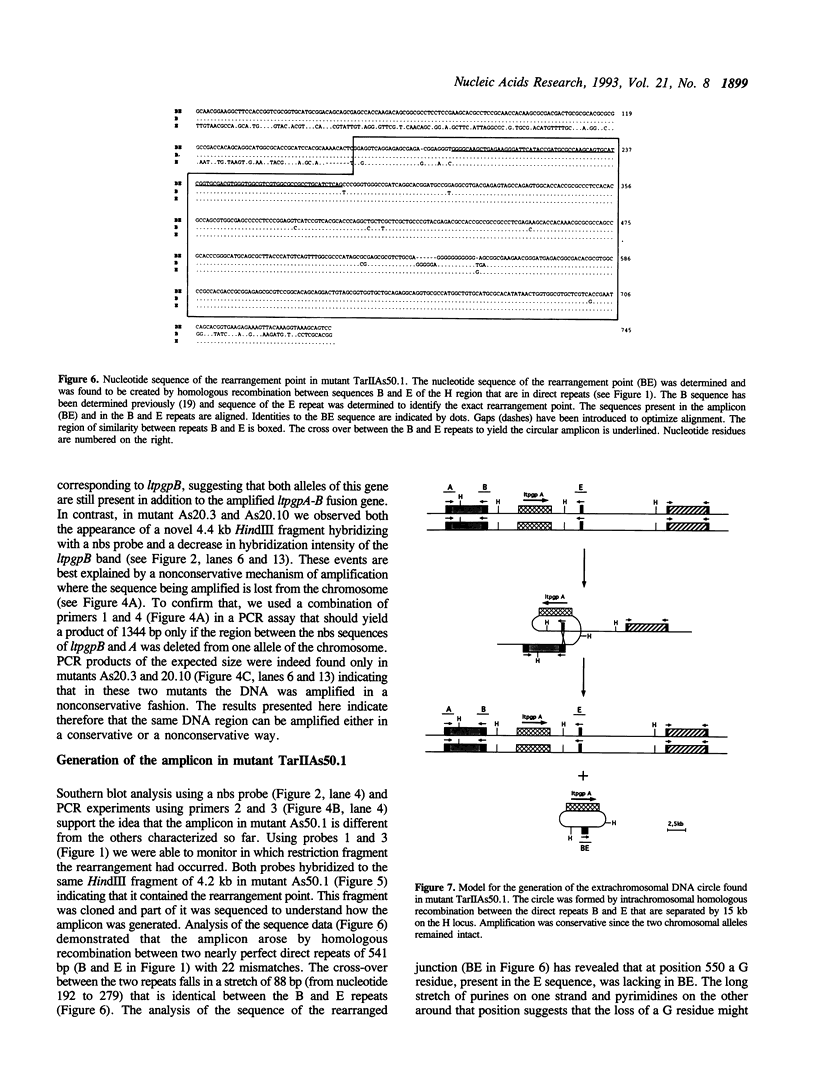
The protozoan parasite Leishmania often responds to drug pressure by amplifying part of its genome. At least two loci derived from the same 800 kb chromosome were amplified either as extrachromosomal circles or linear fragments after sodium arsenite selection. A 50 kb linear amplicon was detected in six independent arsenite mutants and revertants grown in absence of arsenite rapidly lost the amplicon and part of their resistance. The circular extrachromosomal amplicons, all derived from the H locus of Leishmania, were characterized more extensively. In all cases, direct repeated sequences appeared to be involved in the formation of circular amplicons. Most amplicons were generated after homologous recombination between two linked P-glycoprotein genes. This recombination event was, in two cases, associated with the loss of one allele of the chromosomal copy. A novel rearrangement point was found in a mutant where the amplicon was created by recombination between two 541 bp direct repeats surrounding the P-glycoprotein gene present at the H locus. It is also at one of these repeats that an H circle with large inverted duplications was formed. We propose that the presence of repeated sequences in the H locus facilitates the amplification of the drug resistance genes concentrated in this locus.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beverley S. M. Characterization of the 'unusual' mobility of large circular DNAs in pulsed field-gradient electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):925–939. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beverley S. M., Coburn C. M. Recurrent de novo appearance of small linear DNAs in Leishmania major and relationship to extra-chromosomal DNAs in other species. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Aug;42(1):133–141. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90121-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beverley S. M., Coderre J. A., Santi D. V., Schimke R. T. Unstable DNA amplifications in methotrexate-resistant Leishmania consist of extrachromosomal circles which relocalize during stabilization. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):431–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90498-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beverley S. M. Gene amplification in Leishmania. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:417–444. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.002221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan H. L., Beverley S. M. A member of the aldoketo reductase family confers methotrexate resistance in Leishmania. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24165–24168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan H. L., Beverley S. M. Heavy metal resistance: a new role for P-glycoproteins in Leishmania. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18427–18430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. M., DeRose M. L., Gaudray P., Moore C. M., Needham-Vandevanter D. R., Von Hoff D. D., Wahl G. M. Double minute chromosomes can be produced from precursors derived from a chromosomal deletion. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1525–1533. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coderre J. A., Beverley S. M., Schimke R. T., Santi D. V. Overproduction of a bifunctional thymidylate synthetase-dihydrofolate reductase and DNA amplification in methotrexate-resistant Leishmania tropica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2132–2136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz A., Beverley S. M. Gene replacement in parasitic protozoa. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):171–173. doi: 10.1038/348171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detke S., Chaudhuri G., Kink J. A., Chang K. P. DNA amplification in tunicamycin-resistant Leishmania mexicana. Multicopies of a single 63-kilobase supercoiled molecule and their expression. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3418–3424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detke S., Katakura K., Chang K. P. DNA amplification in arsenite-resistant Leishmania. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Jan;180(1):161–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90220-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberger T. E., Beverley S. M. Multiple drug resistance and conservative amplification of the H region in Leishmania major. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):15094–15103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey E. P., Santi D. V. Stable amplified DNA in drug-resistant Leishmania exists as extrachromosomal circles. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):535–540. doi: 10.1126/science.3726545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesdiener K. M., Goriparthi L., Masucci J. P., Van der Ploeg L. H. A proposed mechanism for promoter-associated DNA rearrangement events at a variant surface glycoprotein gene expression site. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4784–4795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson S., Beverley S. M., Wagner W., Ullman B. Unstable amplification of two extrachromosomal elements in alpha-difluoromethylornithine-resistant Leishmania donovani. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5499–5507. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson D. M., Sifri C. D., Rodgers M., Wirth D. F., Hendrickson N., Ullman B. Multidrug resistance in Leishmania donovani is conferred by amplification of a gene homologous to the mammalian mdr1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2855–2865. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hightower R. C., Metge D. W., Santi D. V. Plasmid migration using orthogonal-field-alternation gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8387–8398. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hightower R. C., Ruiz-Perez L. M., Wong M. L., Santi D. V. Extrachromosomal elements in the lower eukaryote Leishmania. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16970–16976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katakura K., Chang K. P. H DNA amplification in Leishmania resistant to both arsenite and methotrexate. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 May 1;34(2):189–191. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur P., Rosen B. P. Plasmid-encoded resistance to arsenic and antimony. Plasmid. 1992 Jan;27(1):29–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(92)90004-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Van der Ploeg L. H. Homologous recombination and stable transfection in the parasitic protozoan Trypanosoma brucei. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1583–1587. doi: 10.1126/science.2177225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. C., Tanaka N., Lamb P. W., Gilmer T. M., Barrett J. C. Induction of gene amplification by arsenic. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):79–81. doi: 10.1126/science.3388020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Salinas G., Gajendran N., Muthui D., Muyldermans S., Hamers R. DNA recombination associated with short direct repeats in Leishmania mexicana M379. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Feb;50(2):351–353. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90233-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. F., Gibbs C. P., Haas R. Variation and control of protein expression in Neisseria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:451–477. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.002315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette M., Borst P. Drug resistance and P-glycoprotein gene amplification in the protozoan parasite Leishmania. Res Microbiol. 1991 Jul-Aug;142(6):737–746. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90089-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette M., Fase-Fowler F., Borst P. The amplified H circle of methotrexate-resistant leishmania tarentolae contains a novel P-glycoprotein gene. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1027–1033. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08206.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette M., Hettema E., Wüst D., Fase-Fowler F., Borst P. Direct and inverted DNA repeats associated with P-glycoprotein gene amplification in drug resistant Leishmania. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):1009–1016. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08035.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulou B., Roy G., Ouellette M. A novel antifolate resistance gene on the amplified H circle of Leishmania. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3601–3608. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauletti G., Lai E., Attardi G. Early appearance and long-term persistence of the submicroscopic extrachromosomal elements (amplisomes) containing the amplified DHFR genes in human cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2955–2959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrillo-Peixoto M. L., Beverley S. M. Amplified DNAs in laboratory stocks of Leishmania tarentolae: extrachromosomal circles structurally and functionally similar to the inverted-H-region amplification of methotrexate-resistant Leishmania major. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5188–5199. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovai L., Tripp C., Stuart K., Simpson L. Recurrent polymorphisms in small chromosomes of Leishmania tarentolae after nutrient stress or subcloning. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Jan;50(1):115–125. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90249-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R., Debatisse M., Giulotto E., Wahl G. M. Recent progress in understanding mechanisms of mammalian DNA amplification. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):901–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90328-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart K. D. Circular and linear multicopy DNAs in Leishmania. Parasitol Today. 1991 Jul;7(7):158–159. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(91)90119-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripp C. A., Wisdom W. A., Myler P. J., Stuart K. D. A multicopy, extrachromosomal DNA in Leishmania infantum contains two inverted repeats of the 27.5-kilobase LD1 sequence and encodes numerous transcripts. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Oct;55(1-2):39–50. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90125-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Liu A. Y., Borst P. Structure of the growing telomeres of Trypanosomes. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):459–468. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90239-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R., Borst P. Antigenic variation in Trypanosoma brucei analyzed by electrophoretic separation of chromosome-sized DNA molecules. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90302-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M. The importance of circular DNA in mammalian gene amplification. Cancer Res. 1989 Mar 15;49(6):1333–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White T. C., Fase-Fowler F., van Luenen H., Calafat J., Borst P. The H circles of Leishmania tarentolae are a unique amplifiable system of oligomeric DNAs associated with drug resistance. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16977–16983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K., Beverley S. M., Ullman B. Stable amplification of a linear extrachromosomal DNA in mycophenolic acid-resistant Leishmania donovani. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Oct;55(1-2):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90140-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windle B., Draper B. W., Yin Y. X., O'Gorman S., Wahl G. M. A central role for chromosome breakage in gene amplification, deletion formation, and amplicon integration. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):160–174. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Asbroek A. L., Ouellette M., Borst P. Targeted insertion of the neomycin phosphotransferase gene into the tubulin gene cluster of Trypanosoma brucei. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):174–175. doi: 10.1038/348174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]