Abstract
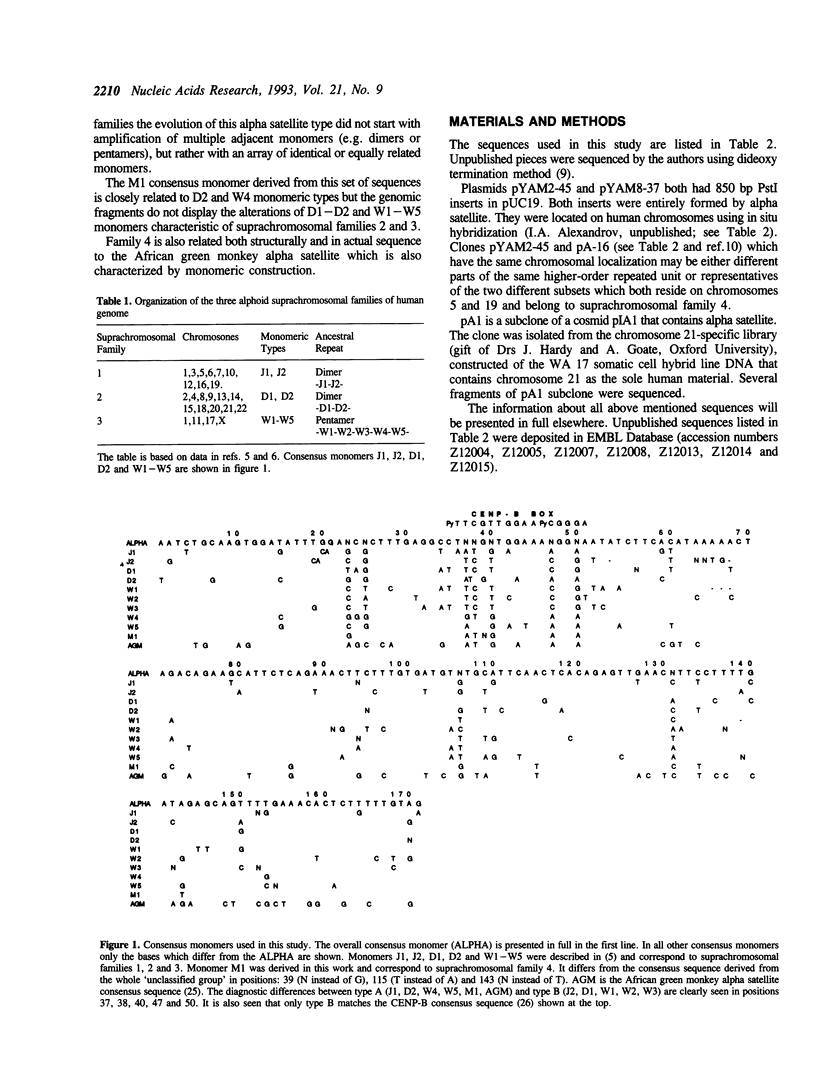
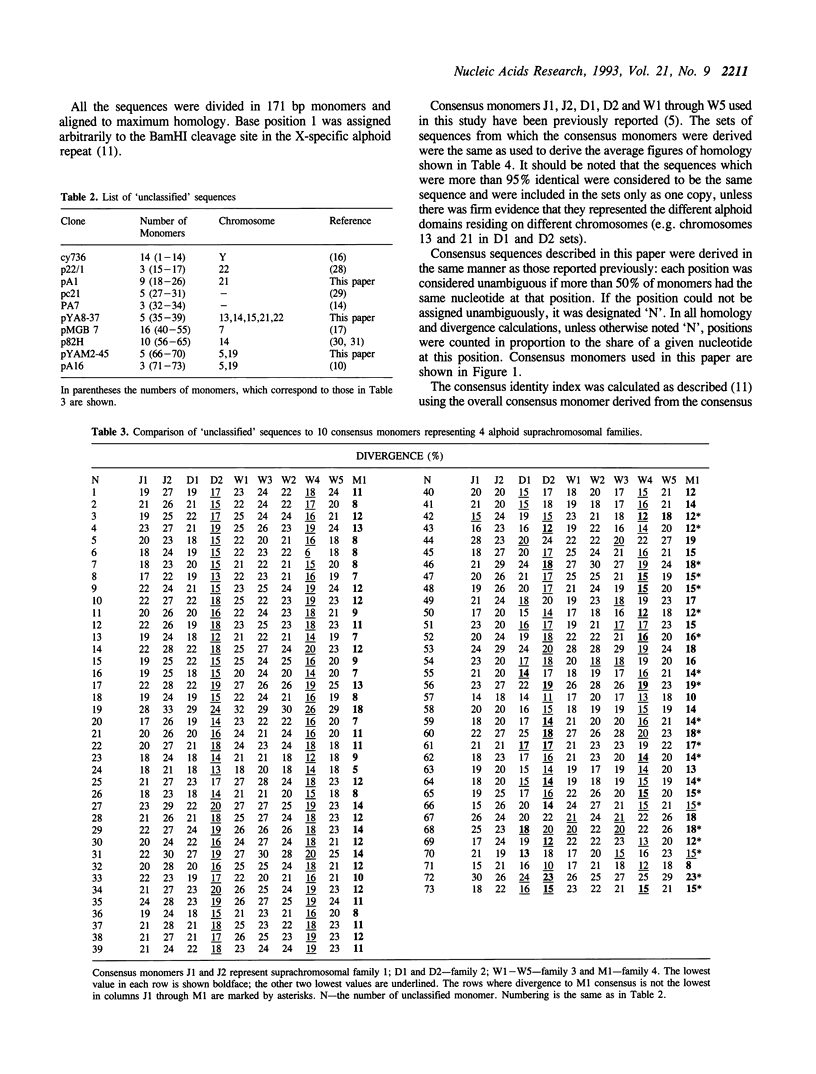
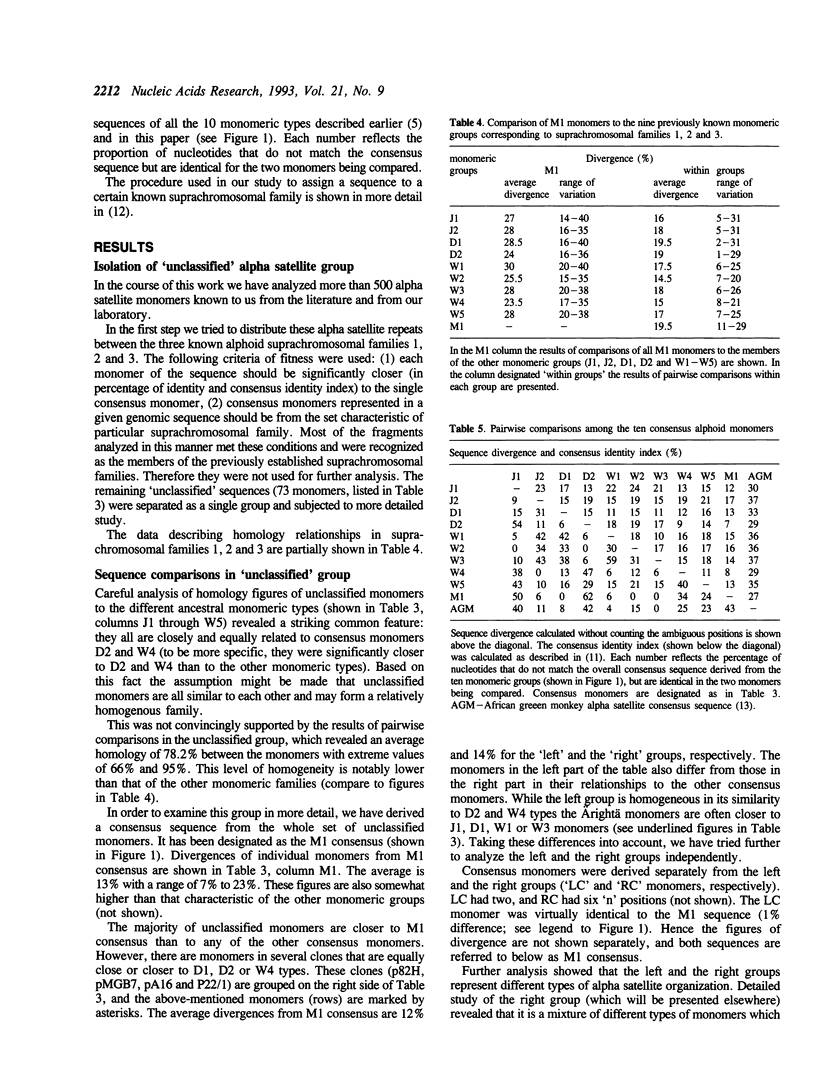
We have analyzed more than 500 alphoid monomers either sequenced in our laboratory or available in the literature. Most of them belonged to the well studied suprachromosomal families 1, 2 and 3 characterized by dimeric (1 and 2) and pentameric (3) ancestral periodicities. The sequences that did not belong to the previously known families were subjected to further analysis. About a half of them formed a relatively homogenous family. Its members were on average 80.5% identical and 89.5% homologous to the M1 consensus sequence derived from this group (39 monomers). In the genome they do not form any ancestral periodicities other than a monomeric one, and are found at least in chromosomes 13, 14, 15, 21, 22 and Y. The newly defined family was termed suprachromosomal family 4. Comparison of all 10 alphoid monomeric groups identified so far showed that the M1 sequence is closely related to the J1-D2-W4-W5 homology grouping. Notably the African Green Monkey alpha satellite, also characterized by monomeric construction, appears to be a member of the same group.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexandrov I. A., Mashkova T. D., Akopian T. A., Medvedev L. I., Kisselev L. L., Mitkevich S. P., Yurov Y. B. Chromosome-specific alpha satellites: two distinct families on human chromosome 18. Genomics. 1991 Sep;11(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90097-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandrov I. A., Mitkevich S. P., Yurov Y. B. The phylogeny of human chromosome specific alpha satellites. Chromosoma. 1988;96(6):443–453. doi: 10.1007/BF00303039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldini A., Archidiacono N., Carbone R., Bolino A., Shridhar V., Miller O. J., Miller D. A., Ward D. C., Rocchi M. Isolation and comparative mapping of a human chromosome 20-specific alpha-satellite DNA clone. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1992;59(1):12–16. doi: 10.1159/000133188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldini A., Miller D. A., Miller O. J., Ryder O. A., Mitchell A. R. A chimpanzee-derived chromosome-specific alpha satellite DNA sequence conserved between chimpanzee and human. Chromosoma. 1991 Mar;100(3):156–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00337244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldini A., Miller D. A., Shridhar V., Rocchi M., Miller O. J., Ward D. C. Comparative mapping of a gorilla-derived alpha satellite DNA clone on great ape and human chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1991 Nov;101(2):109–114. doi: 10.1007/BF00357060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carine K., Jacquemin-Sablon A., Waltzer E., Mascarello J., Scheffler I. E. Molecular characterization of human minichromosomes with centromere from chromosome 1 in human-hamster hybrid cells. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1989 Sep;15(5):445–460. doi: 10.1007/BF01534895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durfy S. J., Willard H. F. Concerted evolution of primate alpha satellite DNA. Evidence for an ancestral sequence shared by gorilla and human X chromosome alpha satellite. J Mol Biol. 1990 Dec 5;216(3):555–566. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90383-W. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulsebos T., Schonk D., van Dalen I., Coerwinkel-Driessen M., Schepens J., Ropers H. H., Wieringa B. Isolation and characterization of alphoid DNA sequences specific for the pericentric regions of chromosomes 4, 5, 9, and 19. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1988;47(3):144–148. doi: 10.1159/000132533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. S., Potter S. S. Characterization of cloned human alphoid satellite with an unusual monomeric construction: evidence for enrichment in HeLa small polydisperse circular DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):1027–1042. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen A. L., Jones C., Bostock C. J., Bak A. L. Different subfamilies of alphoid repetitive DNA are present on the human and chimpanzee homologous chromosomes 21 and 22. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1691–1696. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02419.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen A. L., Laursen H. B., Jones C., Bak A. L. Evolutionarily different alphoid repeat DNA on homologous chromosomes in human and chimpanzee. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3310–3314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laursen H. B., Jørgensen A. L., Jones C., Bak A. L. Higher rate of evolution of X chromosome alpha-repeat DNA in human than in the great apes. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2367–2372. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05300.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masumoto H., Masukata H., Muro Y., Nozaki N., Okazaki T. A human centromere antigen (CENP-B) interacts with a short specific sequence in alphoid DNA, a human centromeric satellite. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):1963–1973. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermid H. E., Duncan A. M., Higgins M. J., Hamerton J. L., Rector E., Brasch K. R., White B. N. Isolation and characterization of an alpha-satellite repeated sequence from human chromosome 22. Chromosoma. 1986;94(3):228–234. doi: 10.1007/BF00288497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell A. R., Gosden J. R., Miller D. A. A cloned sequence, p82H, of the alphoid repeated DNA family found at the centromeres of all human chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1985;92(5):369–377. doi: 10.1007/BF00327469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter S. S., Jones R. S. Unusual domains of human alphoid satellite DNA with contiguous non-satellite sequences: sequence analysis of a junction region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):3137–3153. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.3137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H., Singer M., Rosenberg M. Highly reiterated sequences of SIMIANSIMIANSIMIANSIMIANSIMIAN. Science. 1978 Apr 28;200(4340):394–402. doi: 10.1126/science.205944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P. Evolution of repeated DNA sequences by unequal crossover. Science. 1976 Feb 13;191(4227):528–535. doi: 10.1126/science.1251186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer R. E., Singer M. F., McCutchan T. F. Sequence relationships between single repeat units of highly reiterated African Green monkey DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):169–181. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler-Smith C., Brown W. R. Structure of the major block of alphoid satellite DNA on the human Y chromosome. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 5;195(3):457–470. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vissel B., Choo K. H. Four distinct alpha satellite subfamilies shared by human chromosomes 13, 14 and 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 25;19(2):271–277. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.2.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vissel B., Choo K. H. Four distinct alpha satellite subfamilies shared by human chromosomes 13, 14 and 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 25;19(2):271–277. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.2.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waye J. S., Durfy S. J., Pinkel D., Kenwrick S., Patterson M., Davies K. E., Willard H. F. Chromosome-specific alpha satellite DNA from human chromosome 1: hierarchical structure and genomic organization of a polymorphic domain spanning several hundred kilobase pairs of centromeric DNA. Genomics. 1987 Sep;1(1):43–51. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90103-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waye J. S., England S. B., Willard H. F. Genomic organization of alpha satellite DNA on human chromosome 7: evidence for two distinct alphoid domains on a single chromosome. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):349–356. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waye J. S., Mitchell A. R., Willard H. F. Organization and genomic distribution of "82H" alpha satellite DNA. Evidence for a low-copy or single-copy alphoid domain located on human chromosome 14. Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;78(1):27–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00291229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waye J. S., Willard H. F. Chromosome-specific alpha satellite DNA: nucleotide sequence analysis of the 2.0 kilobasepair repeat from the human X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 25;13(8):2731–2743. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.8.2731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waye J. S., Willard H. F. Nucleotide sequence heterogeneity of alpha satellite repetitive DNA: a survey of alphoid sequences from different human chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7549–7569. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard H. F. Evolution of alpha satellite. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1991 Dec;1(4):509–514. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80200-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



