Abstract
Full text
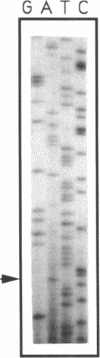
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Murray V. Improved double-stranded DNA sequencing using the linear polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8889–8889. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. L., Ledbetter S. A., Corbo L., Victoria M. F., Ramírez-Solis R., Webster T. D., Ledbetter D. H., Caskey C. T. Alu polymerase chain reaction: a method for rapid isolation of human-specific sequences from complex DNA sources. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6686–6690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks C. L., Chang L. S., Shenk T. A polymerase chain reaction mediated by a single primer: cloning of genomic sequences adjacent to a serotonin receptor protein coding region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec;19(25):7155–7160. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.25.7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver J., Keerikatte V. Novel use of polymerase chain reaction to amplify cellular DNA adjacent to an integrated provirus. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):1924–1928. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.1924-1928.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]