Abstract
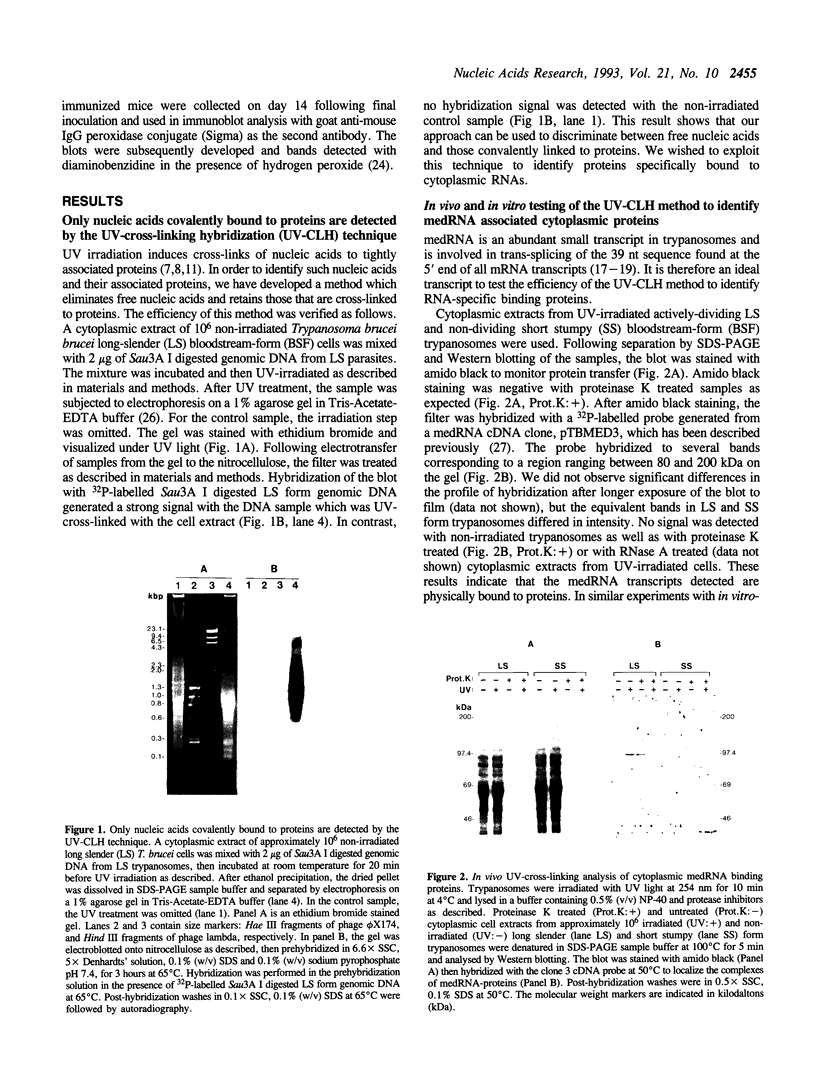
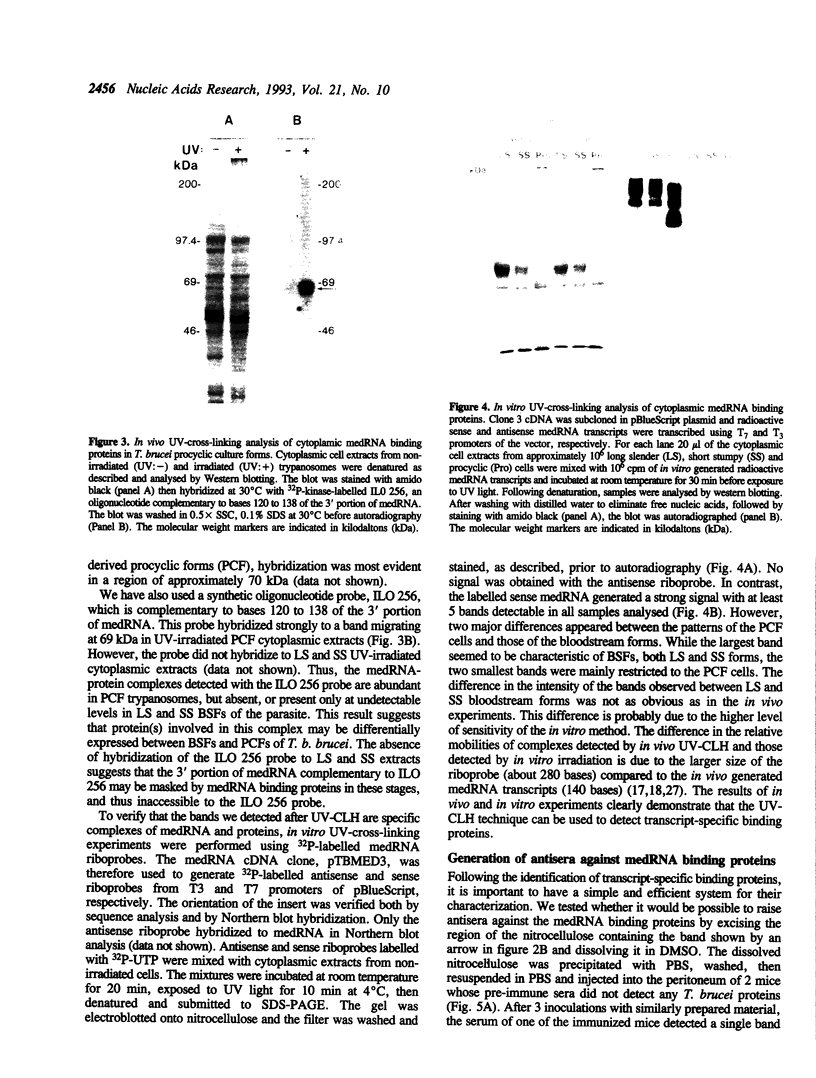
Differential gene expression in cells achieved, in part, through direct RNA-protein interactions. Methods for the identification of RNA binding proteins require cross-linking of proteins to RNA by chemicals or ultraviolet (UV) light followed by chromatography or density-gradient centrifugation (7,11,16). We have developed a simplified method for the rapid and efficient identification of potential regulatory RNA binding proteins. In this method, irradiation of cells with UV light induces cross-links between RNA and proteins in close contact (7,11). Boiling of extracts from irradiated cells in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate dissociates any non-specific RNA-protein interactions (11). After analysis of the cell extracts by SDS-PAGE, followed by Western blotting onto a nitrocellulose membrane and washing of the filter, we have found that only RNA molecules that are covalently bound to proteins are retained on the filter. Hybridization of this Western blot with an appropriate nucleic acid probe allows detection of bands of RNA-protein complexes. Antisera against the binding proteins are raised by immunizing mice with a region of the nitrocellulose membrane containing the bands of RNA-protein complexes. Using this approach we have found that in African trypanosomes, mini-exon derived RNA transcripts form complexes with cytoplasmic binding proteins in different life cycle stages of the parasite. Evidence for the specificity of mini-exon derived RNA-protein interactions is shown using in vitro UV-cross-linking analysis in which only in vitro generated sense (but not antisense) mini-exon derived RNA transcripts form complexes with cytoplasmic proteins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam S. A., Nakagawa T., Swanson M. S., Woodruff T. K., Dreyfuss G. mRNA polyadenylate-binding protein: gene isolation and sequencing and identification of a ribonucleoprotein consensus sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2932–2943. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun R., Schönenberger Cultivation and in vitro cloning or procyclic culture forms of Trypanosoma brucei in a semi-defined medium. Short communication. Acta Trop. 1979 Sep;36(3):289–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross M., Günzl A., Palfi Z., Bindereif A. Analysis of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (RNPs) in Trypanosoma brucei: structural organization and protein components of the spliced leader RNP. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5516–5526. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Adam S. A., Choi Y. D. Physical change in cytoplasmic messenger ribonucleoproteins in cells treated with inhibitors of mRNA transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):415–423. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferies D., Tebabi P., Pays E. Transient activity assays of the Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein gene promoter: control of gene expression at the posttranscriptional level. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):338–343. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kooter J. M., De Lange T., Borst P. Discontinuous synthesis of mRNA in trypanosomes. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2387–2392. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02144.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse B., Narasimhan N., Attardi G. Termination of transcription in human mitochondria: identification and purification of a DNA binding protein factor that promotes termination. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):391–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90853-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanham S. M. Separation of trypanosomes from the blood of infected rats and mice by anion-exchangers. Nature. 1968 Jun 29;218(5148):1273–1274. doi: 10.1038/2181273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau P. P., Chen S. H., Wang J. C., Chan L. A 40 kilodalton rat liver nuclear protein binds specifically to apolipoprotein B mRNA around the RNA editing site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5817–5821. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Commitment and activation at pol II promoters: a tail of protein-protein interactions. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1161–1164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90675-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrand S., Setyono B., Greenberg J. R., Pederson T. Structure of nuclear ribonucleoprotein: identification of proteins in contact with poly(A)+ heterogeneous nuclear RNA in living HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;90(2):380–384. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.2.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaeli S., Roberts T. G., Watkins K. P., Agabian N. Isolation of distinct small ribonucleoprotein particles containing the spliced leader and U2 RNAs of Trypanosoma brucei. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10582–10588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy W. J., Watkins K. P., Agabian N. Identification of a novel Y branch structure as an intermediate in trypanosome mRNA processing: evidence for trans splicing. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):517–525. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90616-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neupert B., Thompson N. A., Meyer C., Kühn L. C. A high yield affinity purification method for specific RNA-binding proteins: isolation of the iron regulatory factor from human placenta. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 11;18(1):51–55. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osswald M., Greuer B., Brimacombe R. Localization of a series of RNA-protein cross-link sites in the 23S and 5S ribosomal RNA from Escherichia coli, induced by treatment of 50S subunits with three different bifunctional reagents. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6755–6760. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pashev I. G., Dimitrov S. I., Angelov D. Crosslinking proteins to nucleic acids by ultraviolet laser irradiation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Sep;16(9):323–326. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90133-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberger S., Müllner E. W., Kühn L. C. The mRNA-binding protein which controls ferritin and transferrin receptor expression is conserved during evolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1175–1179. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommerville J. RNA-binding proteins: masking proteins revealed. Bioessays. 1992 May;14(5):337–339. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickerman K. Developmental cycles and biology of pathogenic trypanosomes. Br Med Bull. 1985 Apr;41(2):105–114. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickerman K., Tetley L., Hendry K. A., Turner C. M. Biology of African trypanosomes in the tsetse fly. Biol Cell. 1988;64(2):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0248-4900(88)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwierzynski T. A., Buck G. A. RNA-protein complexes mediate in vitro capping of the spliced-leader primary transcript and U-RNAs in Trypanosoma cruzi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5626–5630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









