Abstract
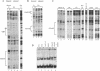
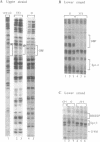
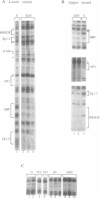
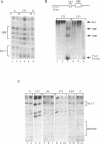
Mammalian housekeeping promoters represent a class of regulatory elements different from those of tissues-specific genes, lacking a TATA box and associated with CG-rich DNA. We have compared the organization of the housekeeping Htf9 promoter in different cell types by genomic footprinting. The sites of in vivo occupancy clearly reflected local combinations of tissue-specific and ubiquitous binding factors. The flexibility of the Htf9 promoter in acting as the target of cell-specific combinations of factors may ensure ubiquitous expression of the Htf9-associated genes.
Full text
PDF
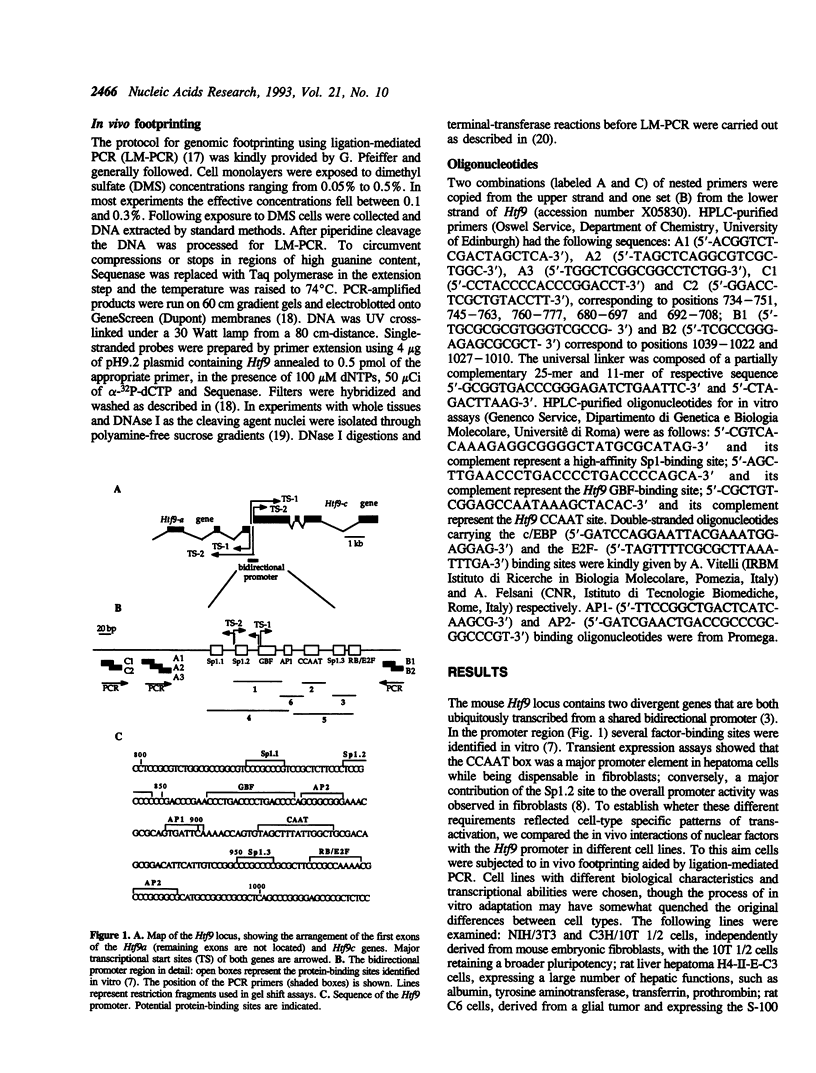
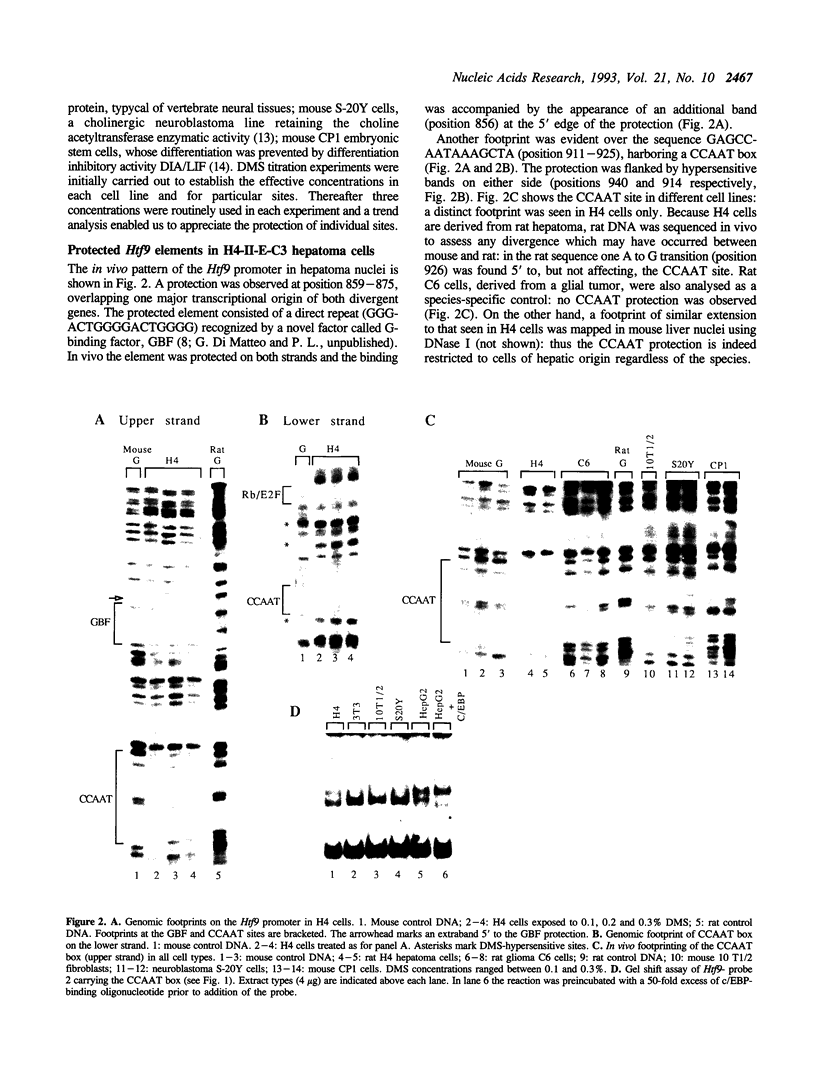
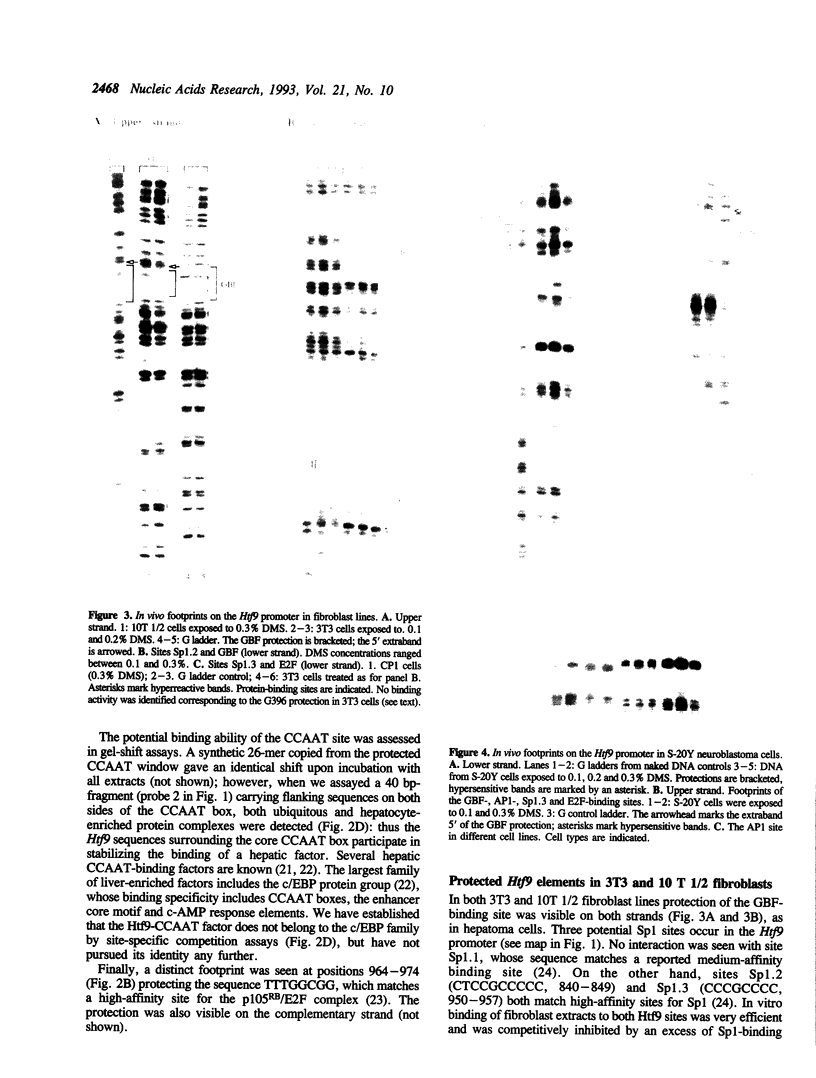
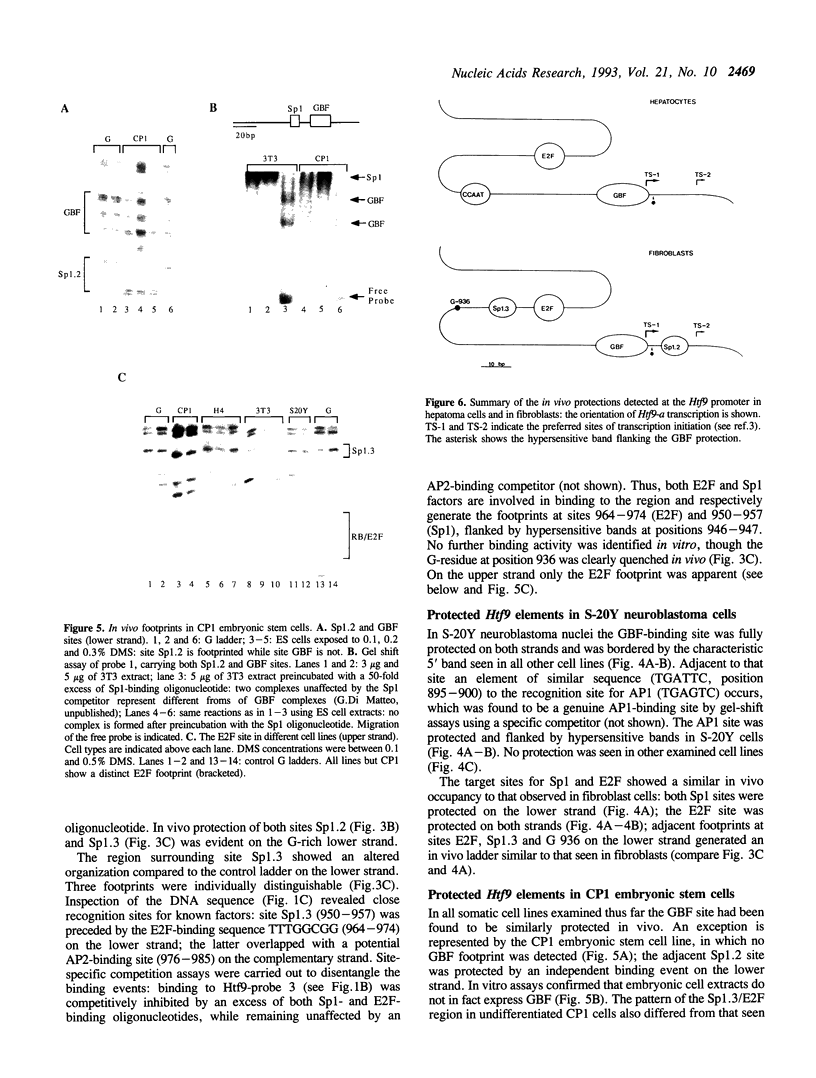


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abravaya K., Phillips B., Morimoto R. I. Heat shock-induced interactions of heat shock transcription factor and the human hsp70 promoter examined by in vivo footprinting. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):586–592. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews N. C., Faller D. V. A rapid micropreparation technique for extraction of DNA-binding proteins from limiting numbers of mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2499–2499. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atchison M. L., Meyuhas O., Perry R. P. Localization of transcriptional regulatory elements and nuclear factor binding sites in mouse ribosomal protein gene rpL32. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2067–2074. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker P. B., Ruppert S., Schütz G. Genomic footprinting reveals cell type-specific DNA binding of ubiquitous factors. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):435–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90639-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bressan A., Somma M. P., Lewis J., Santolamazza C., Copeland N. G., Gilbert D. J., Jenkins N. A., Lavia P. Characterization of the opposite-strand genes from the mouse bidirectionally transcribed HTF9 locus. Gene. 1991 Jul 22;103(2):201–209. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90274-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chittenden T., Livingston D. M., Kaelin W. G., Jr The T/E1A-binding domain of the retinoblastoma product can interact selectively with a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1073–1082. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90559-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Concordet J. P., Maire P., Kahn A., Daegelen D. A ubiquitous enhancer shared by two promoters in the human aldolase A gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4173–4180. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dey A., Nebert D. W., Ozato K. The AP-1 site and the cAMP- and serum response elements of the c-fos gene are constitutively occupied in vivo. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;10(7):537–544. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englander E. W., Wilson S. H. Protein binding elements in the human beta-polymerase promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):919–928. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faisst S., Meyer S. Compilation of vertebrate-encoded transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 11;20(1):3–26. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.1.3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamel P. A., Gill R. M., Phillips R. A., Gallie B. L. Transcriptional repression of the E2-containing promoters EIIaE, c-myc, and RB1 by the product of the RB1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3431–3438. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirshner J. A., Markelonis G. J., Max S. R. Effects of cell division, cell density, and cyclic nucleotides on choline acetyltransferase activity in a cholinergic neuroblastoma cell line (S-20Y). J Neurochem. 1986 Mar;46(3):817–821. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb13045.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Thangue N. B., Thimmappaya B., Rigby P. W. The embryonal carcinoma stem cell Ela-like activity involves a differentiation-regulated transcription factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):2929–2938. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.2929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavia P., Macleod D., Bird A. Coincident start sites for divergent transcripts at a randomly selected CpG-rich island of mouse. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2773–2779. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02572.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennard A. C., Fried M. The bidirectional promoter of the divergently transcribed mouse Surf-1 and Surf-2 genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1281–1294. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton J. P., Yen J. Y., Selby E., Chen Z., Chinsky J. M., Liu K., Kellems R. E., Crouse G. F. Dual bidirectional promoters at the mouse dhfr locus: cloning and characterization of two mRNA classes of the divergently transcribed Rep-1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):3058–3072. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.3058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. L., Farnham P. J. Transcription initiation from the dihydrofolate reductase promoter is positioned by HIP1 binding at the initiation site. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):653–661. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Darnell J. E., Jr Rapid in vivo footprinting technique identifies proteins bound to the TTR gene in the mouse liver. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):83–93. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. R., Salser S. J., Wold B. Constitutive and metal-inducible protein:DNA interactions at the mouse metallothionein I promoter examined by in vivo and in vitro footprinting. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):412–427. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. R., Wold B. In vivo footprinting of a muscle specific enhancer by ligation mediated PCR. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):780–786. doi: 10.1126/science.2814500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. E2F: a link between the Rb tumor suppressor protein and viral oncoproteins. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):424–429. doi: 10.1126/science.1411535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne T. F., Gil G., Brown M. S., Kowal R. C., Goldstein J. L. Identification of promoter elements required for in vitro transcription of hamster 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3614–3618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parvin J. D., Timmers H. T., Sharp P. A. Promoter specificity of basal transcription factors. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1135–1144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90084-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer G. P., Riggs A. D. Chromatin differences between active and inactive X chromosomes revealed by genomic footprinting of permeabilized cells using DNase I and ligation-mediated PCR. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):1102–1113. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.1102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer G. P., Steigerwald S. D., Mueller P. R., Wold B., Riggs A. D. Genomic sequencing and methylation analysis by ligation mediated PCR. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):810–813. doi: 10.1126/science.2814502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer G. P., Tanguay R. L., Steigerwald S. D., Riggs A. D. In vivo footprint and methylation analysis by PCR-aided genomic sequencing: comparison of active and inactive X chromosomal DNA at the CpG island and promoter of human PGK-1. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1277–1287. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce A. J., Jambou R. C., Jensen D. E., Azizkhan J. C. A conserved DNA structural control element modulates transcription of a mammalian gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 25;20(24):6583–6587. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.24.6583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Transcription from a TATA-less promoter requires a multisubunit TFIID complex. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):1935–1945. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.1935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymondjean M., Cereghini S., Yaniv M. Several distinct "CCAAT" box binding proteins coexist in eukaryotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):757–761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigaud G., Roux J., Pictet R., Grange T. In vivo footprinting of rat TAT gene: dynamic interplay between the glucocorticoid receptor and a liver-specific factor. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):977–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90370-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saluz H. P., Feavers I. M., Jiricny J., Jost J. P. Genomic sequencing and in vivo footprinting of an expression-specific DNase I-hypersensitive site of avian vitellogenin II promoter reveal a demethylation of a mCpG and a change in specific interactions of proteins with DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6697–6700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saluz H. P., Wiebauer K., Wallace A. Studying DNA modifications and DNA-protein interactions in vivo. A window onto the native genome. Trends Genet. 1991 Jul;7(7):207–211. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90366-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saluz H., Jost J. P. A simple high-resolution procedure to study DNA methylation and in vivo DNA-protein interactions on a single-copy gene level in higher eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2602–2606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. L., Mitchell P. J., Crouse G. F. Analysis of the mouse Dhfr/Rep-3 major promoter region by using linker-scanning and internal deletion mutations and DNase I footprinting. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):6003–6012. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.6003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somma M. P., Gambino I., Lavia P. Transcription factors binding to the mouse HTF9 housekeeping promoter differ between cell types. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4451–4458. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somma M. P., Pisano C., Lavia P. The housekeeping promoter from the mouse CpG island HTF9 contains multiple protein-binding elements that are functionally redundant. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 11;19(11):2817–2824. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.11.2817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki-Yagawa Y., Kawakami K., Nagano K. Housekeeping Na,K-ATPase alpha 1 subunit gene promoter is composed of multiple cis elements to which common and cell type-specific factors bind. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):4046–4055. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.4046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]