Abstract
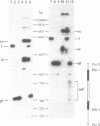
We present characterisation of a hypervariable locus, D8S210, mapped to the telomeric region of the short arm of chromosome 8. The locus is highly polymorphic with alleles varying in size from 1.8 kb to 24 kb. Sequence data from 7 alleles shows that the variable region is entirely polypurine on one strand with a tetranucleotide repeating unit GGAA at the margins and diverged versions of this motif internally. The margins are conserved between alleles; polymorphism occurring in the internal regions of the repeat. Alleles are inherited in a Mendelian manner and one new mutation has been observed in analysis of 51 meioses. Use of single copy flanking sequences to elaborate the polymorphism revealed loss of single copy DNA in 3 unrelated families and in 2 other unrelated individuals. Restriction mapping shows that this loss is similar for different sized alleles in all three families suggesting that it was an early event that may have involved a flanking Alu sequence. We present evidence that the polypurine region can adopt triplex conformations in vitro. Such structures may facilitate loss or gain of unique sequences in the genome, contribute to mutation at conformation transition points and drive the hypervariability (> 99% heterozygosity) of this locus.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armour J. A., Crosier M., Jeffreys A. J. Human minisatellite alleles detectable only after PCR amplification. Genomics. 1992 Jan;12(1):116–124. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90413-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armour J. A., Wong Z., Wilson V., Royle N. J., Jeffreys A. J. Sequences flanking the repeat arrays of human minisatellites: association with tandem and dispersed repeat elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):4925–4935. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.4925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacolla A., Wu F. Y. Mung bean nuclease cleavage pattern at a polypurine.polypyrimidine sequence upstream from the mouse metallothionein-I gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1639–1647. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.7.1639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brereton H. M., Turner D. R., Firgaira F. A., Ruffin R. E. A highly polymorphic polypurine sequence on chromosome 8 (D8S210). Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Dec;1(9):774–774. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.9.774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkholder G. D., Latimer L. J., Lee J. S. Immunofluorescent localization of triplex DNA in polytene chromosomes of Chironomus and Drosophila. Chromosoma. 1991 Oct;101(1):11–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00360681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caddle M. S., Lussier R. H., Heintz N. H. Intramolecular DNA triplexes, bent DNA and DNA unwinding elements in the initiation region of an amplified dihydrofolate reductase replicon. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jan 5;211(1):19–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90008-A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christophe D., Cabrer B., Bacolla A., Targovnik H., Pohl V., Vassart G. An unusually long poly(purine)-poly(pyrimidine) sequence is located upstream from the human thyroglobulin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5127–5144. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collick A., Dunn M. G., Jeffreys A. J. Minisatellite binding protein Msbp-1 is a sequence-specific single-stranded DNA-binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6399–6404. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collick A., Jeffreys A. J. Detection of a novel minisatellite-specific DNA-binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):625–629. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray I. C., Jeffreys A. J. Evolutionary transience of hypervariable minisatellites in man and the primates. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 Mar 22;243(1308):241–253. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampel K. J., Crosson P., Lee J. S. Polyamines favor DNA triplex formation at neutral pH. Biochemistry. 1991 May 7;30(18):4455–4459. doi: 10.1021/bi00232a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanvey J. C., Klysik J., Wells R. D. Influence of DNA sequence on the formation of non-B right-handed helices in oligopurine.oligopyrimidine inserts in plasmids. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7386–7396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman-Liebermann B., Liebermann D., Troutt A., Kedes L. H., Cohen S. N. Human homologs of TU transposon sequences: polypurine/polypyrimidine sequence elements that can alter DNA conformation in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3632–3642. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Htun H., Dahlberg J. E. Single strands, triple strands, and kinks in H-DNA. Science. 1988 Sep 30;241(4874):1791–1796. doi: 10.1126/science.3175620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Htun H., Dahlberg J. E. Topology and formation of triple-stranded H-DNA. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1571–1576. doi: 10.1126/science.2648571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., MacLeod A., Tamaki K., Neil D. L., Monckton D. G. Minisatellite repeat coding as a digital approach to DNA typing. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):204–209. doi: 10.1038/354204a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Neumann R., Wilson V. Repeat unit sequence variation in minisatellites: a novel source of DNA polymorphism for studying variation and mutation by single molecule analysis. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):473–485. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90598-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Royle N. J., Wilson V., Wong Z. Spontaneous mutation rates to new length alleles at tandem-repetitive hypervariable loci in human DNA. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):278–281. doi: 10.1038/332278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Neumann R., Keyte J. Amplification of human minisatellites by the polymerase chain reaction: towards DNA fingerprinting of single cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 9;16(23):10953–10971. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.23.10953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston B. H. The S1-sensitive form of d(C-T)n.d(A-G)n: chemical evidence for a three-stranded structure in plasmids. Science. 1988 Sep 30;241(4874):1800–1804. doi: 10.1126/science.2845572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R., Gibbs M., Collick A., Jeffreys A. J. Spontaneous mutation at the hypervariable mouse minisatellite locus Ms6-hm: flanking DNA sequence and analysis of germline and early somatic mutation events. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 Sep 23;245(1314):235–245. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Burkholder G. D., Latimer L. J., Haug B. L., Braun R. P. A monoclonal antibody to triplex DNA binds to eucaryotic chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1047–1061. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Woodsworth M. L., Latimer L. J., Morgan A. R. Poly(pyrimidine) . poly(purine) synthetic DNAs containing 5-methylcytosine form stable triplexes at neutral pH. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6603–6614. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyamichev V. I., Mirkin S. M., Danilevskaya O. N., Voloshin O. N., Balatskaya S. V., Dobrynin V. N., Filippov S. A., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. An unusual DNA structure detected in a telomeric sequence under superhelical stress and at low pH. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):634–637. doi: 10.1038/339634a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel D., Chatelain G., Herault Y., Brun G. The long repetitive polypurine/polypyrimidine sequence (TTCCC)48 forms DNA triplex with PU-PU-PY base triplets in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 11;20(3):439–443. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.3.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephan W. Tandem-repetitive noncoding DNA: forms and forces. Mol Biol Evol. 1989 Mar;6(2):198–212. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voloshin O. N., Veselkov A. G., Belotserkovskii B. P., Danilevskaya O. N., Pavlova M. N., Dobrynin V. N., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. An eclectic DNA structure adopted by human telomeric sequence under superhelical stress and low pH. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1992 Feb;9(4):643–652. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1992.10507945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. D., Collier D. A., Hanvey J. C., Shimizu M., Wohlrab F. The chemistry and biology of unusual DNA structures adopted by oligopurine.oligopyrimidine sequences. FASEB J. 1988 Nov;2(14):2939–2949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard C., Nguyen H. T., Schmid C. W. Existence of at least three distinct Alu subfamilies. J Mol Evol. 1987;26(3):180–186. doi: 10.1007/BF02099850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff R. K., Nakamura Y., White R. Molecular characterization of a spontaneously generated new allele at a VNTR locus: no exchange of flanking DNA sequence. Genomics. 1988 Nov;3(4):347–351. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff R. K., Plaetke R., Jeffreys A. J., White R. Unequal crossingover between homologous chromosomes is not the major mechanism involved in the generation of new alleles at VNTR loci. Genomics. 1989 Aug;5(2):382–384. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong Z., Wilson V., Jeffreys A. J., Thein S. L. Cloning a selected fragment from a human DNA 'fingerprint': isolation of an extremely polymorphic minisatellite. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4605–4616. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong Z., Wilson V., Patel I., Povey S., Jeffreys A. J. Characterization of a panel of highly variable minisatellites cloned from human DNA. Ann Hum Genet. 1987 Oct;51(Pt 4):269–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1987.tb01062.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]