Abstract
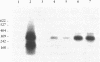
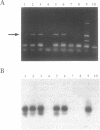
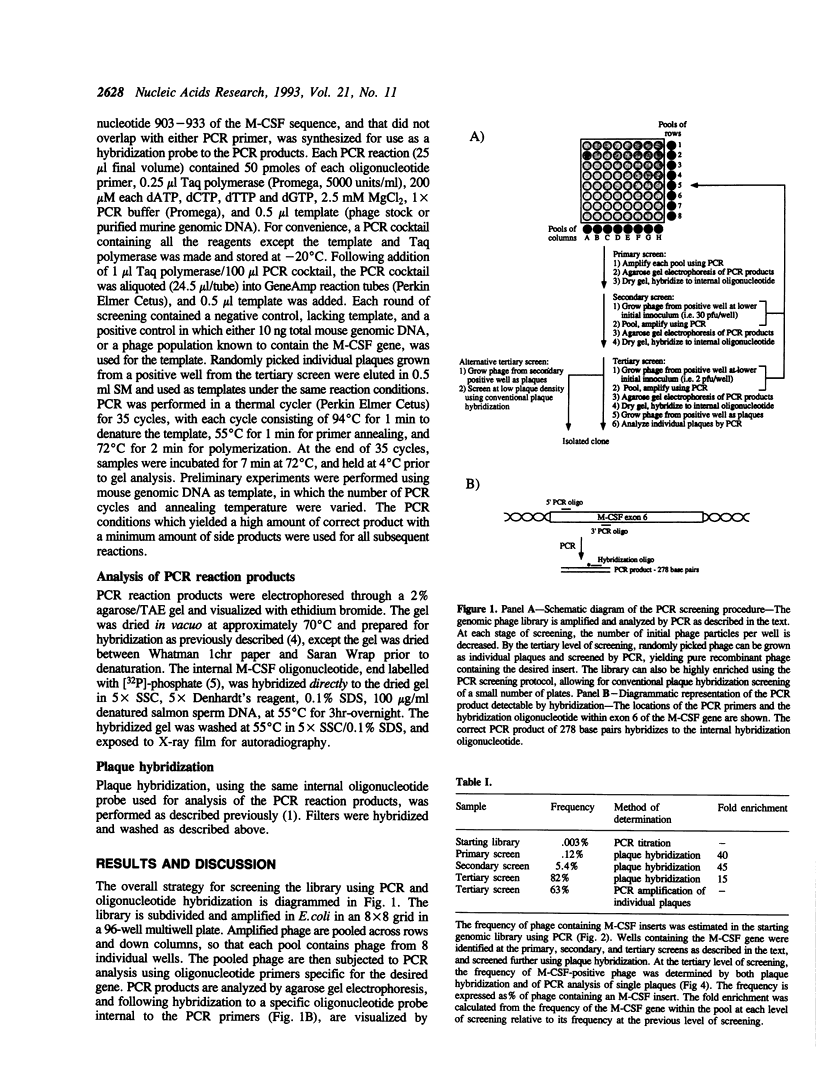
A rapid method for cloning genomic DNA utilizing a PCR-based screening protocol is described. A murine genomic library in lambda phage was subdivided into 64 wells, each containing 1000 clones, and propagated in bacteria. Amplified phage from each of 8 wells across columns, and each of 8 wells down rows, were pooled. The pooled phage were screened for the presence of murine M-CSF DNA by PCR using specific oligonucleotide primers. A single well that contained an M-CSF genomic clone was identified by the synthesis of a PCR product of the correct size that hybridized to an internal M-CSF oligonucleotide probe. This well was subdivided into 64 wells, each containing approximately 30 individual phage, reamplified, and rescreened utilizing the same protocol. A positive well was then subdivided and amplified a third time starting with an average of 2 phage per well, and rescreened for M-CSF DNA by PCR. Phage from a PCR-positive well, now highly enriched for M-CSF DNA, were grown as individual plaques. PCR-screening of randomly picked plaques demonstrated that the majority contained an M-CSF genomic insert. This method obviates the more labor and time intensive method of plaque hybridization screening of DNA libraries, and is more stringent since three oligonucleotides (the two PCR primers, and the hybridization probe) are required to give a true positive signal. Similar methodology has also been used to clone a cDNA gene contained within a plasmid library.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Repetitive and non-repetitive DNA sequences and a speculation on the origins of evolutionary novelty. Q Rev Biol. 1971 Jun;46(2):111–138. doi: 10.1086/406830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green E. D., Olson M. V. Systematic screening of yeast artificial-chromosome libraries by use of the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1213–1217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heard E., Davies B., Feo S., Fried M. An improved method for the screening of YAC libraries. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 25;17(14):5861–5861. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.14.5861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladner M. B., Martin G. A., Noble J. A., Wittman V. P., Warren M. K., McGrogan M., Stanley E. R. cDNA cloning and expression of murine macrophage colony-stimulating factor from L929 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6706–6710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao S. G., Brunk C. F., Pearlman R. E. Hybridization of nucleic acids directly in agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jun;131(2):365–372. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90185-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozney J. M., Rosen V., Celeste A. J., Mitsock L. M., Whitters M. J., Kriz R. W., Hewick R. M., Wang E. A. Novel regulators of bone formation: molecular clones and activities. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1528–1534. doi: 10.1126/science.3201241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]