Abstract
Protein synthesis in cytosolic and rough endoplasmic reticulum associated ribosomes is directed by factors, many of which have been well characterized. Although these factors have been the subject of intense study, most of the corresponding factors regulating protein synthesis in the mitochondrial ribosomes remain unknown. In this report we present the cloning and initial characterization of the gene encoding the rat mitochondrial elongation factor-G (rEF-Gmt). The rat gene encoding EF-Gmt (rMef-g) maps to rat chromosome 2 and it is expressed in all tissues with highest levels in liver, thymus and brain. Its DNA sequence predicts a 752 amino acid protein exhibiting 72% homology to the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondrial elongation factor-G (YMEF-G), 62% and 61% homology to the Thermus thermophilus and E. coli elongation factor-G (EF-G) respectively and 52% homology to the rat elongation factor-2 (EF-2). The deduced amino acid sequence of EF-G contains characteristic motifs shared by all GTP binding proteins. Therefore, similarly to other elongation factors, the enzymatic function of EF-Gmt is predicted to depend on GTP binding and hydrolysis. EF-Gmt differs from its cytoplasmic homolog, EF-2, in that it contains an aspartic acid residue at amino acid position 621 which corresponds to the EF-2 histidine residue at position 715. Since this histidine residue, following posttranslational modification into diphthamide, appears to be the sole cellular target of diphtheria toxin and Pseudomonas aeruginosa endotoxin A, we conclude that EF-Gmt will not be inactivated by these toxins. The severe effects of these toxins on protein elongation in tissues expressing EF-Gmt suggest that EF-Gmt and EF-2 exhibit nonoverlapping functions. The cloning and characterization of the mammalian mitochondrial elongation factor G will permit us to address its role in the regulation of normal mitochondrial function and in disease states attributed to mitochondrial dysfunction.
Full text
PDF

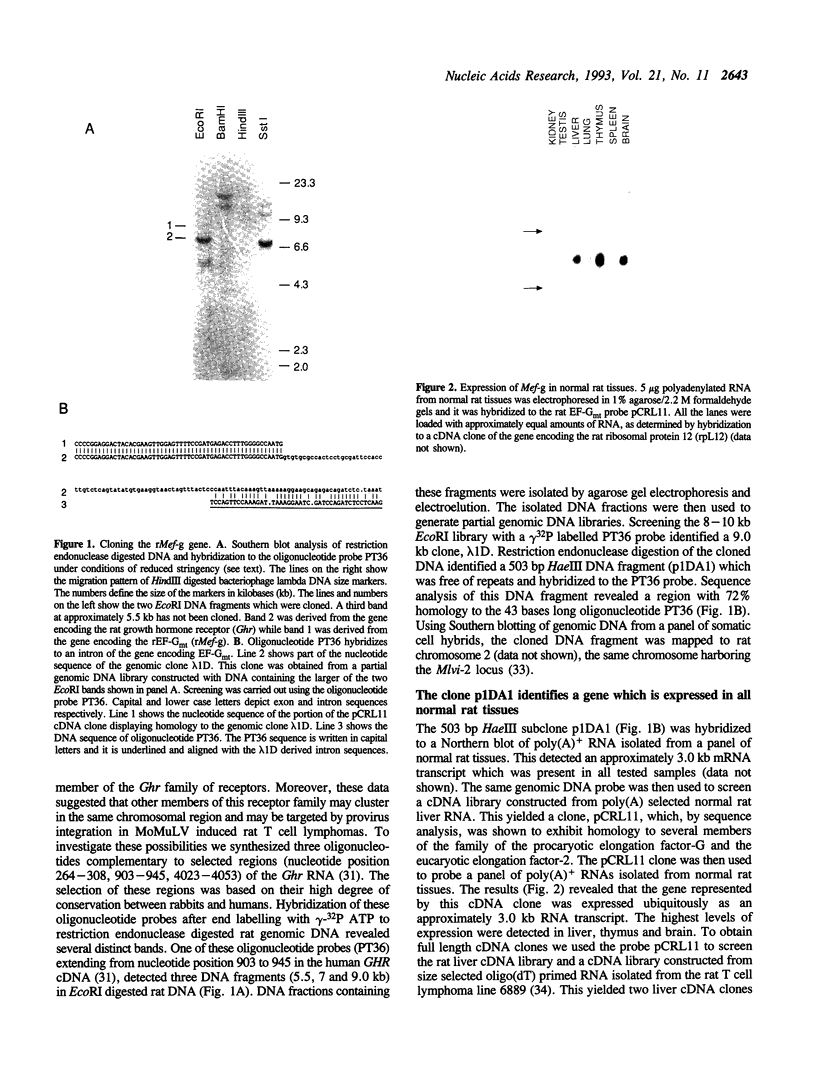

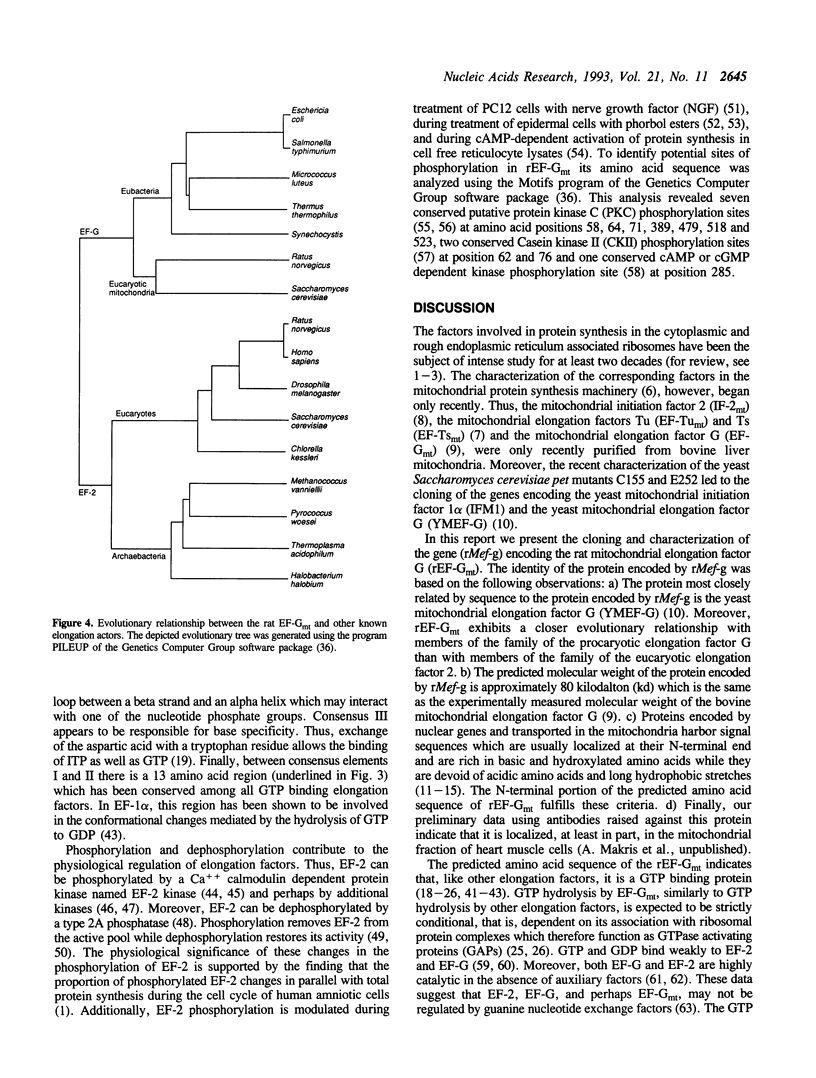


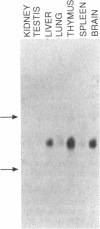
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker C. S., Bear S. E., Keler T., Copeland N. G., Gilbert D. J., Jenkins N. A., Yeung R. S., Tsichlis P. N. Activation of the prolactin receptor gene by promoter insertion in a Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced rat thymoma. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6763–6768. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6763-6768.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellacosa A., Lazo P. A., Bear S. E., Tsichlis P. N. The rat leukocyte antigen MRC OX-44 is a member of a new family of cell surface proteins which appear to be involved in growth regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2864–2872. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellacosa A., Testa J. R., Staal S. P., Tsichlis P. N. A retroviral oncogene, akt, encoding a serine-threonine kinase containing an SH2-like region. Science. 1991 Oct 11;254(5029):274–277. doi: 10.1126/science.254.5029.274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Poritz M. A., Strub K., Hoben P. J., Brenner S., Walter P. Model for signal sequence recognition from amino-acid sequence of 54K subunit of signal recognition particle. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):482–486. doi: 10.1038/340482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Stryer L. G proteins. The target sets the tempo. Nature. 1992 Aug 13;358(6387):541–543. doi: 10.1038/358541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boutin J. M., Jolicoeur C., Okamura H., Gagnon J., Edery M., Shirota M., Banville D., Dusanter-Fourt I., Djiane J., Kelly P. A. Cloning and expression of the rat prolactin receptor, a member of the growth hormone/prolactin receptor gene family. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90488-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung H. K., Spremulli L. L. Purification and characterization of elongation factor G from bovine liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21000–21004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyr D. M., Douglas M. G. Early events in the transport of proteins into mitochondria. Import competition by a mitochondrial presequence. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21700–21708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dever T. E., Glynias M. J., Merrick W. C. GTP-binding domain: three consensus sequence elements with distinct spacing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1814–1818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D. B., el-Maghrabi M. R., Pilkis S. J. Synthetic peptides corresponding to the site phosphorylated in 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase as substrates of cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2987–2993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb D. S. Are the cytosolic components of the nuclear, ER, and mitochondrial import apparatus functionally related? Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):185–188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90094-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinblat Y., Brown N. H., Kafatos F. C. Isolation and characterization of the Drosophila translational elongation factor 2 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7303–7314. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gschwendt M., Kittstein W., Marks F. Effect of tumor promoting phorbol ester TPA on epidermal protein synthesis: stimulation of an elongation factor 2 phosphatase activity by TPA in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 30;153(3):1129–1135. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81345-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gschwendt M., Kittstein W., Mieskes G., Marks F. A type 2A protein phosphatase dephosphorylates the elongation factor 2 and is stimulated by the phorbol ester TPA in mouse epidermis in vivo. FEBS Lett. 1989 Nov 6;257(2):357–360. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81571-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gschwendt M., Kittstein W., Mieskes G., Marks F. A type 2A protein phosphatase dephosphorylates the elongation factor 2 and is stimulated by the phorbol ester TPA in mouse epidermis in vivo. FEBS Lett. 1989 Nov 6;257(2):357–360. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81571-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen O., Robinson E. A., Maxwell E. S. Interaction of guanosine nucleotides with elongation factor 2. I. Equilibrium dialysis studies. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):720–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraoka K., Kaibuchi K., Ando S., Musha T., Takaishi K., Mizuno T., Asada M., Ménard L., Tomhave E., Didsbury J. Both stimulatory and inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange proteins, smg GDS and rho GDI, are active on multiple small GTP-binding proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jan 31;182(2):921–930. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91820-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwabe N., Kuma K., Hasegawa M., Osawa S., Miyata T. Evolutionary relationship of archaebacteria, eubacteria, and eukaryotes inferred from phylogenetic trees of duplicated genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9355–9359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. W., Kim C. W., Kang K. R., Byun S. M., Kang Y. S. Elongation factor-2 in chick embryo is phosphorylated on tyrosine as well as serine and threonine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 15;175(2):400–406. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91578-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto A., Nishiyama K., Nakanishi H., Uratsuji Y., Nomura H., Takeyama Y., Nishizuka Y. Studies on the phosphorylation of myelin basic protein by protein kinase C and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12492–12499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno K., Uchida T. Highly frequent single amino acid substitution in mammalian elongation factor 2 (EF-2) results in expression of resistance to EF-2-ADP-ribosylating toxins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12298–12305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno K., Uchida T., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S., Nakanishi T., Fukui T., Ohtsuka E., Ikehara M., Okada Y. Amino acid sequence of mammalian elongation factor 2 deduced from the cDNA sequence: homology with GTP-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):4978–4982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.4978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi S., Ryazanov A., Hama T., Chen H. C., Guroff G. Identification of Nsp100 as elongation factor 2 (EF-2). FEBS Lett. 1989 Aug 14;253(1-2):55–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80928-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriki Y., Inoue N., Kaziro Y. Formation of a complex between GTP, G factor, and ribosomes as an intermediate of ribosome-dependent GTPase reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 14;224(2):487–497. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90581-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. W., Spencer S. A., Cachianes G., Hammonds R. G., Collins C., Henzel W. J., Barnard R., Waters M. J., Wood W. I. Growth hormone receptor and serum binding protein: purification, cloning and expression. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):537–543. doi: 10.1038/330537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao H. X., Spremulli L. L. Initiation of protein synthesis in animal mitochondria. Purification and characterization of translational initiation factor 2. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):20714–20719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahlke K., Pfanner N., Martin J., Horwich A. L., Hartl F. U., Neupert W. Sorting pathways of mitochondrial inner membrane proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Sep 11;192(2):551–555. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick W. C., Kemper W. M., Kantor J. A., Anderson W. F. Purification and properties of rabbit reticulocyte protein synthesis elongation factor 2. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 10;250(7):2620–2625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick W. C. Mechanism and regulation of eukaryotic protein synthesis. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Jun;56(2):291–315. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.2.291-315.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizumoto K., Iwasaki K., Tanaka M., Kaziro Y. Studies on polypeptide elongation factor 2 from pig liver. I. Purification and properties. J Biochem. 1974 May;75(5):1047–1056. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller W., Schipper A., Amons R. A conserved amino acid sequence around Arg-68 of Artemia elongation factor 1 alpha is involved in the binding of guanine nucleotides and aminoacyl transfer RNAs. Biochimie. 1987 Sep;69(9):983–989. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90232-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn A. C., Palfrey H. C. Identification of the major Mr 100,000 substrate for calmodulin-dependent protein kinase III in mammalian cells as elongation factor-2. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17299–17303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson L., Nygård O. Localization of the sites of ADP-ribosylation and GTP binding in the eukaryotic elongation factor EF-2. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Apr 15;148(2):299–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08839.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien T. W., Denslow N. D., Anders J. C., Courtney B. C. The translation system of mammalian mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):174–178. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90162-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofulue E. N., Candido E. P. Molecular cloning and characterization of the Caenorhabditis elegans elongation factor 2 gene (eft-2). DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;10(8):603–611. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA, Alakhov YuB, Bundulis YuP, Bundule M. A., Dovgas N. V., Kozlov V. P., Motuz L. P., Vinokurov L. M. The primary structure of elongation factor G from Escherichia coli. A complete amino acid sequence. FEBS Lett. 1982 Mar 8;139(1):130–135. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80503-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfanner N., Rassow J., van der Klei I. J., Neupert W. A dynamic model of the mitochondrial protein import machinery. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):999–1002. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90069-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinna L. A. Casein kinase 2: an 'eminence grise' in cellular regulation? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Sep 24;1054(3):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riis B., Rattan S. I., Clark B. F., Merrick W. C. Eukaryotic protein elongation factors. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Nov;15(11):420–424. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90279-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson E. A., Henriksen O., Maxwell E. S. Elongation factor 2. Amino acid sequence at the site of adenosine diphosphate ribosylation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5088–5093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roise D., Schatz G. Mitochondrial presequences. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4509–4511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryazanov A. G. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent phosphorylation of elongation factor 2. FEBS Lett. 1987 Apr 20;214(2):331–334. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80081-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryazanov A. G., Davydova E. K. Mechanism of elongation factor 2 (EF-2) inactivation upon phosphorylation. Phosphorylated EF-2 is unable to catalyze translocation. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 17;251(1-2):187–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81452-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryazanov A. G., Rudkin B. B., Spirin A. S. Regulation of protein synthesis at the elongation stage. New insights into the control of gene expression in eukaryotes. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jul 22;285(2):170–175. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80798-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryazanov A. G., Shestakova E. A., Natapov P. G. Phosphorylation of elongation factor 2 by EF-2 kinase affects rate of translation. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):170–173. doi: 10.1038/334170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste M., Sibbald P. R., Wittinghofer A. The P-loop--a common motif in ATP- and GTP-binding proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Nov;15(11):430–434. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90281-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz G. 17th Sir Hans Krebs lecture. Signals guiding proteins to their correct locations in mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1987 May 15;165(1):1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11186.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzbach C. J., Spremulli L. L. Bovine mitochondrial protein synthesis elongation factors. Identification and initial characterization of an elongation factor Tu-elongation factor Ts complex. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19125–19131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitikov A. S., Simonenko P. N., Shestakova E. A., Ryazanov A. G., Ovchinnikov L. P. cAMP-dependent activation of protein synthesis correlates with dephosphorylation of elongation factor 2. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 15;228(2):327–331. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Strauss P. G., Hu L. F. A common region for proviral DNA integration in MoMuLV-induced rat thymic lymphomas. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):445–449. doi: 10.1038/302445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Strauss P. G., Lohse M. A. Concerted DNA rearrangements in Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced thymomas: a potential synergistic relationship in oncogenesis. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):258–267. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.258-267.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuazon P. T., Merrick W. C., Traugh J. A. Comparative analysis of phosphorylation of translational initiation and elongation factors by seven protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2773–2777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vambutas A., Ackerman S. H., Tzagoloff A. Mitochondrial translational-initiation and elongation factors in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Nov 1;201(3):643–652. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16325.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ness B. G., Howard J. B., Bodley J. W. Isolation and properties of the trypsin-derived ADP-ribosyl peptide from diphtheria toxin-modified yeast elongation factor 2. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8687–8690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verner K., Schatz G. Protein translocation across membranes. Science. 1988 Sep 9;241(4871):1307–1313. doi: 10.1126/science.2842866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittinghofer A., Pai E. F. The structure of Ras protein: a model for a universal molecular switch. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Oct;16(10):382–387. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90156-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodgett J. R., Gould K. L., Hunter T. Substrate specificity of protein kinase C. Use of synthetic peptides corresponding to physiological sites as probes for substrate recognition requirements. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 17;161(1):177–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakhnin A. V., Vorozheykina D. P., Matvienko N. I. Nucleotide sequence of the Thermus thermophilus HB8 gene coding for elongation factor G. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8863–8863. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- la Cour T. F., Nyborg J., Thirup S., Clark B. F. Structural details of the binding of guanosine diphosphate to elongation factor Tu from E. coli as studied by X-ray crystallography. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2385–2388. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03943.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]